Please refer to Carbon And Its Compound Class 10 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 10. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 10 Science Carbon And Its Compound Notes and Questions
i) Catenation: The self-linking property of an element mainly carbon atom through covalent bonds to form long straight, branched and rings of different sizes are called Catenation.
This property is due to
* The small size of the carbon atom.
* The great strength of the carbon-carbon bond.
Versatile Nature of Carbon: The existence of such a large number of organic compounds is due to the following nature of carbon,
* Catenation Tetravalent nature
Hydrocarbons: Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons.
For example; Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Ethene (C2H4), Ethyne (C2H2) etc.

Isomerism: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formula and properties are known as Isomers and this phenomenon is known as Isomerism.
Structural Isomerism: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are called Structural isomers.Example: Isomers of butane (C4H10)

Homologous Series: Series of organic compounds having the same functional group and chemical properties and successive members differ by a CH2 unit or 14 mass units are known as Homologous series.
Homologous series of Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes

Functional Group: An atom or group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemical properties are called Functional Group.


Important Questions Carbon And Its Compound Class 10 Science
Very Short answer Type Questions :
Question. Write the name and formula of second member of homologous series with general formula CnH2n+2
Answer: C2H6, Ethane
Question. Write the name and formula of second member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n–2.
Answer: C3H4, Propyne
Question. Draw electron dot structure of NH3 molecule. Predict the total no. of bonds around N-atom. OR
A molecule of ammonia has the formula NH3. Predict the total number of bonds present around nitrogen atom.
Answer:

Question. Write the next homologue of each of the following: (i) C2H4, (ii) C4H6
Answer: (i) C3H6, (ii) C5H8
Question. Write the structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in the molecule.
Answer:

Question. Write the molecular formula of alcohol derived from butane.
Answer: C4H9OH or CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (Butan-1-ol)
Question. Write the molecular formula of an alkyne containing 10 atoms of hydrogen.
Answer: C6H10
Question. Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Answer: C4H10, Butane (CH3CH2CH2CH3)
Question. Which of the following organic compounds belong to the same homologous series:
C2H6, C2H6O, C2H6O2, CH4O
Answer: C2H6O (C2H5OH) and CH4O (CH3OH)
Question. The formula of citric acid is shown below:

State the name of —COOH functional group in citric acid.
Answer: Carboxylic acid
Question. Why covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity?
Answer: It is because covalent compounds do not form ions.
Question. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula, CO2?
Answer:

Question. Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
Answer: Carbon since it forms strong covalent bond, due to smaller atomic size.
Question. Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group Cl.
Answer: The general formula of the compounds having – Cl functional group is CnH2n + 1Cl. Its two members are:
(i) CH3Cl (ii) CH3 – CH2 – Cl
Question. Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and the 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is methane (CH4).
Answer: (i) CH3CH3 (Ethane); where n is 2
(ii) CH3CH2CH3 (Propane); where n is 3
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane (C4H10).
Answer: There are 13 covalent bonds.

Question. State the valency of the carbon atom in (i) an alkane (ii) an alkyne.
Answer: (i) Four, (ii) Four
Question. Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
Answer: Benzene is cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.

Question. The molecular formula of ‘A’ is C10H18 and ‘B’ is C18H36. Name the homologous series to which they belong.
Answer: ‘A’ belongs to Alkynes, ‘B’ belongs to Alkenes.
Question. Write the next homologous of CH3CH2OH and HCOOH.
Answer: CH3 – CH2 – CH2OH. Propanol and, CH3COOH ethanoic acid
Short answer Type Questions :
Question. How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of ethane, C2H6?
Ans. There are seven covalent bonds in a molecule of ethane:
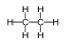
Question. Write the electron dot structure of ethane molecule, C2H4
Ans.
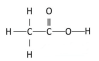
Question. Draw the structure of ethanoic acid molecule, CH3COOH
Ans. Structure of ethanoic acid molecule:
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds.
(i) C2H5Cl (ii) C2H5OH
Ans. Functional group present in:
(i) C2H5Cl – chloro(halide) (ii) C2H5OH —- Alcohol
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compound:
(i) CH3COCH3 (ii) C2H5COOH
Ans. (i) CH3COCH3 —- >C=O ketonic group (ii) C2H5COOH — (-COOH) Carboxylic acid
Question. Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general
Formula CnH2n.
Ans. CnH2n: alkene Name: propene(2nd member) formula: C3H6
Question. Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following:
C3H6, C5H10, C4H10, C6H14, C2H4
Ans. Saturated hydrocarbons:
General formula= CnH2n+2
C4H10, C6H14
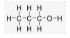
Question. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule.
Ans. Name of an alcohol: Propanol
Structure of propanol: H2C – CH2 – CH2 – OH
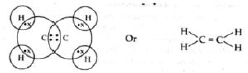
Question. What are isomers? Draw the structure of two isomers of butane C4H10.
Ans. The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as isomers. Isomers of butane C4H10.
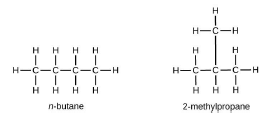
Question. What are homologous series of carbon compounds? Write the molecular formula of two Consecutive members of homologous series of aldehydes.
Ans. A series of carbon compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for Hydrogen on a carbon chain is called homologous series. There is difference of –CH2 in nThe molecular formula of two nearest compounds of a homologous series. Each such Series has same general molecular formula and has a general scientific name. There Is a difference of 14u in the molecular mass of two nearest compound of a series?
Members of homologous series of aldehydes:
H – CHO
CH3 – CHO
C2H5 – CHO
Long answer Type Questions :
Question. List two reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Name the type of Bonding found in most of its compounds. Why does carbon form compounds mainly by this kind of bonding?
Ans. Carbon forms a large number of compounds.
The two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds are:
-catenation: it’s a unique property of carbon atoms to form bonds with other atoms of Carbon giving rise to large molecules.
-Tetravalency: Since carbon has four valencies, it is capable of bonding with four other atoms Of carbon or atoms of some other monovalent elements.
Carbon compounds are formed mainly by sharing of electron with covalent bond because carbon atoms have 4 electrons in their outermost shell. So, needs to gain or lose Electrons to achieve inert gas electronic configuration. It could gain four electron forming C4-anion. But it is difficult due to energy consideration. It could lose 4 electrons to form C4+cation. But it is difficult due to energy consideration.
Because of this reason carbon Share their electron to form covalent bond only.
Question. What are covalent compounds? Why are they different from ionic compound? List any Three characteristics properties.
Ans. (i) The chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms is known as a covalent bond. The molecules formed by sharing of electrons between two or more same atoms or between two or more non-metals are called covalent compound.
(ii)Covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds as ionic compounds are Formed by transfer of electrons.
Characteristics of covalent compound:
(i) Covalent compounds usually have low melting and boiling point because force Of attraction between molecules is very weak.
(ii) Covalent compounds are usually insoluble in water but they are soluble in organic compound.
(iii) Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity as they do not contain ions.

We hope the above Carbon And Its Compound Class 10 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science

