Students can read the important questions given below for Oscillations Class 11 Physics. All Oscillations Class 11 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 11 Physics Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Physics Question Bank Class 11 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Oscillations Class 11
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. The figure shows circular motion of a reference particle to represent simple harmonic motion. What is the amplitude of simple harmonic motion?
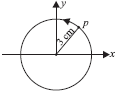
Answer : The amplitude in simple harmonic motion is equal to the radius of the circle of reference. Hence, the amplitude of simple harmonic motion is 3 cm.
Question. What will be the time period of a second pendulum inside an artificial satellite?
Answer : Time period of a second pendulum inside an artificial satellite will be infinity due to the absence of gravitation force.
Question. Glass window panes are sometimes broken by a explosion several miles away. Explain why?
Answer : The disturbance set by the explosion reaches the glass panes and sets them into vibration. Sometimes, the frequency of vibration of these panes becomes equal to their natural frequency and resonance occurs. At resonance, the amplitude of vibration becomes large to such an extent that the glass panes break.
Question. x(t) = Acos(ωt + Φ) is the equation of simple harmonic motion. What do we call Φ in this equation?
Answer : The equation of simple harmonic motion is x(t) = Acos(ωt + f )
Here, Φ = Phase constant and ωt + Φ = Phase
Question. What are the basic properties required by a system to oscillate?
Answer : Inertia and elasticity are the properties which are required by a system to oscillate.
Question. Two simple pendulums of unequal length meet each other at mean position while oscillating. What is their phase difference?
Answer : If both pendulums are moving in the same direction,
then Φ = 0° and if they are moving in opposite directions,
then Φ = 180° or p radian.
Question. On what factors does the energy of a simple harmonically vibrating particle depends?
Answer : The energy (E) of a simple harmonically vibrating particle depends upon its : (i) mass, m (ii) frequency, u and (iii) amplitude A. In fact, (i) E ∝ m (ii) E ∝ ν2 and (iii) E ∝ A2.
Question. What is the :
(a) distance moved
(b) displacement of a particle executing SHM in one vibration?
Answer : (a) 4 times the amplitude
(b) zero.
Question. A simple harmonic motion is described by a = –16x where a is acceleration and x is displacement in meter. What is the time-period ?
Answer : Given equation for S.H.M.,
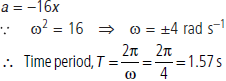
Question. How is the frequency of oscillation related with the frequency of change in the of K.E and P.E of the body in S.H.M.?
Answer : P.E. or K.E. completes two vibrations in a time during which S.H.M completes one vibration or the frequency of PE. or K.E. is double than that of S.H.M
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Three springs of spring factor k, 2k, k, respectively are connected in parallel to a mass m. If the mass = 0.08 kg and k = 2 N/m, then find the new time period?
Answer : Given that, mass m = 0.08 kg. Spring factor, k = 2 N/m. Effective spring constant for the given parallel combination of springs can be calculated as

K = k + 2k + k = 4k = 8 N/m Hence, new time period is
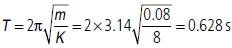
Question. Define S.H.M. What are its chracteristics? At what distance from the mean position in S.H.M of amplitude r, the energy is half kinetic and half potential ?
Answer : A particular type of periodic motion in which a particle moves to and fro repeatedly about a mean position under the influence of a restoring force is termed as simple harmonic motion (SHM).
A body is undergoing simple harmonic motion if it has an acceleration which is
– directed towards a fixed point, and
– proportional to the displacement of the body from that point.
acceleration a ∝ – x ⇒ a = – kx

Question. Show the time period for vertical harmonic oscillations of the three system shown in figure (a), (b) and (c) in the ratio of 1 : √2 : 1/√2. Spring constant of each spring of k.
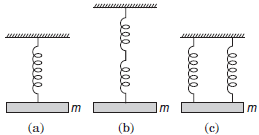
Answer : In the given figures,

Question. Three springs of constants k1, k2 and k3 are connected end to end and are used to hang a mass M from the roof. Determine the elastic potential energy stored in the array.
Answer :
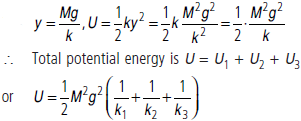
Question. How is the time period of the pendulum effected when pendulum is taken to hills or in mines?
Answer : On the top of a mountain or below the earth, the values of g is less than that on the surface of Earth. With a decrease in the value of g, time period of the simple pendulum increases and accordingly the pendulum loses time.
Question. A particle set to be in SHM having two types of energies potential and kinetic. The potential energy is on account of displacement of particle from mean position and kinetic energy is an account of velocity of the particle. At any instant of time t, these are
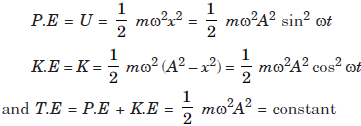
where, m = mass of particle.
(a) At what distance from the mean position
(a fixed point) will K.E of particle would be twice of its P.E?
(b) What are the applications of this study in our day to day life ?
Answer : (a) As conditions is KE = 2PE
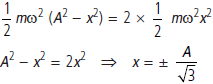
The ± signs represent the distance of particle on either side.
(b) This study shows that sum total of P.E and K.E of a particle in SHM stays constant at all positions and at all times. However, P.E and K.E both keep on changing with position or time. The same is true in day to day life. We can acquire one form of energy by spending some other form of energy and vice-versa.
Question. Figure shows the acceleration-displacement graph of a particle in SHM. Find the time period (in second).

Answer : The slope of given graph is
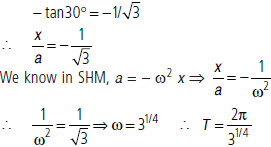
Question. Draw (a) displacement time graph of a particle executing SHM with phase angle Φ equal to zero (b) velocity-time graph and (c) acceleration-time graph of the particle.
Answer :
Question. The maximum velocity of a body undergoing simple harmonic motion is 0.04 m s–1 and its acceleration at 0.02 m from the mean position is 0.06 m s–2. Determine its amplitude and time period.
Answer :
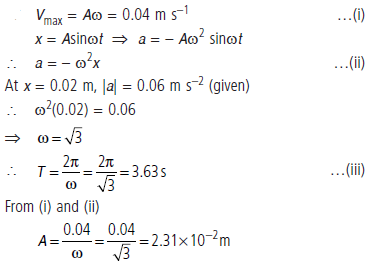
Question. Two particles P1 and P2 are executing SHM along the same straight line, whose equations are given x1 = Asin(ωt + δ1) and x2 = Asin(ωt + δ2). An observer on the ground, at t = 0, observes particle P1 at distance A/√2 moving the right from mean position O and particle P2 at − √3/2 A moving to the left from mean position O, as shown in figure. Find the value of δ2 – δ1.
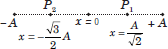
Answer :

Question. A simple pendulum is hung in a stationary lift and its periodic time is T. What will be the effect on its periodic time T if
(i) the lift goes up with uniform velocity v,
(ii) the lift goes up with uniform acceleration a, and
(iii) the lift comes down with uniform acceleration a?
Answer : (i) When the lift goes up figure (a) with uniform velocity v, tension in the string, T ′ = mg.
The value of g remains unaffected.

The period T remains same as that in stationary lift, i.e.,
T = 2π√l/g
(ii) When the lift goes up with acceleration a as shown in figure (b), the net upward force on the bob is T′ – mg = ma ⇒ T′ = m(g + a)
The effective value of g is (g + a) and the time period is
T1 = 2π√l/g+a
Clearly, T1 < T, i.e., time period decreases.
(iii) When lift comes down with acceleration a figure (c), the net downward force on the bob is
mg – T′ = ma ⇒ T′ = m(g – a)
The effective value of g becomes (g – a) and the time period is
T2 = 2π√l/g-a
Clearly, T2 > T, i.e., time period increases.
Question. A body is executing a simple harmonic motion such that its potential energy is U1 at x and U2 at y. When the displacement is x + y, calculate the potential energy.
Answer :
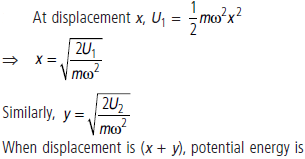

Question. Two particles are executing SHM with same amplitudes A and time period T. When one of the particles is located at extreme right, the other particle is located at mean position and moving towards left. From this instant, find the time after which both the particles will have same displacement from the equilibrium position.
Answer : If this instant is taken as t = 0. Then, initial phase for particle (1) is δ1 = π/2
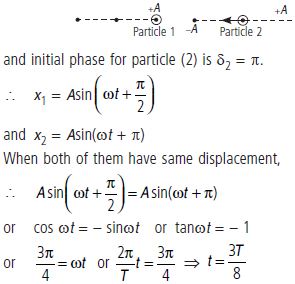
Question. The formula for time period T for a loaded spring, T = 2π √displacement/acceleration Does the time period depend on the length of the spring?
Answer : Although length of the spring does not appear in the expression for the time period, yet the time period depends on the length of the spring. It is because, force constant of the spring depends on the length of the spring.
Question. Two exactly identical pendulums are executing (approximiate) SHMs with amplitudes a and na respectively. Calculate the ratio of their energies of oscillation.
Answer : According to question, for two identical pendulums
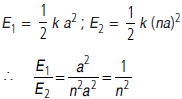
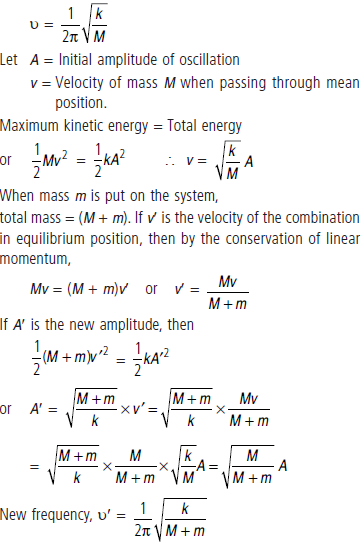
Question. A horizontal spring block system of mass M executes simple harmonic motion. When the block is passing through its equilibrium position, an object of mass m is put on it and the two move together. Find the new amplitude and frequency of vibration.
Answer : Original frequency,
Question. A 10 kg collar is attached to a spring (spring constant 600 N/m), it slides without friction over a horizontal rod. The collar is displaced from its equilibrium position by 20 cm and released. What is the speed of the oscillation?
Answer : Angular frequency of spring – block system is given by

Question. A 2 kg particle undergoes SHM according to x = 1.5 sin {π/4 t + π/6}, when x is in metre and t in second. What is the total mechanical energy of the particle ?
Answer :
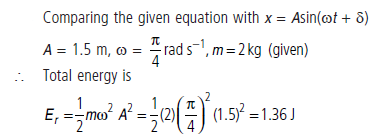
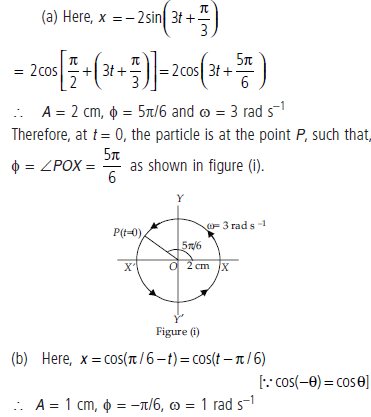
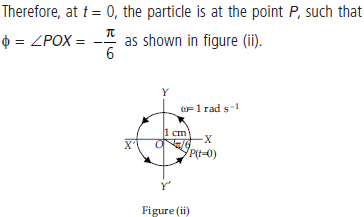
Question. Plot the corresponding reference circle for each of the following simple harmonic motions. Indicate the initial (t = 0) position of the particle, the radius of the circle, and the angular speed of the rotating particle. For simplicity, the sense of rotation may be fixed to be anticlockwise in every case: (x is in cm and t is in s)
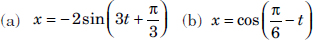
Answer :
Question. Find the displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator at which its P.E. is half of the maximum energy of the oscillator.
Answer : PE of the oscillator at displacement y,

Question. Show that the acceleration of a particle in SHM is proportional to its displacement from the mean position.
Answer : A particular type of periodic motion in which a particle moves to and fro repeatedly about a mean position under the influence of a restoring force is termed as simple harmonic motion (SHM).
A body is undergoing simple harmonic motion if it has an acceleration which is
(i) directed towards a fixed point, and
(ii) proportional to the displacement of the body from that point.
acceleration a ∝ – x or, a = – kx (where k is any constant) or d2x/dt2 = – kx = , where x = displacement at any instant t Simple harmonic motion can also be represented as the projection of uniform circular motion on a diameter of the circle in which the circular motion occurs.
Question. If the ratio of the mechanical energy of a mass m whose oscillations are damped to that of its free oscillations is e–3t/m, then determine the ratio of the amplitudes of the damped oscillations to that of free oscillations.
Answer : If E and E0 represent the mechanical energy of the damped and free oscillations respectively, then as per question E/E = e−3t/2m
As mechanical energy ∝ (amplitude)2
∴ The ratio of the amplitudes of the damped oscillations to that of free oscillations is
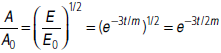
Question. A particle is moving in a straight line with SHM of amplitude r. At a distance s from the mean position of motion, the particle receives a blow in the direction of motion which instantaneously doubles the velocity. Find the new amplitude.
Answer :
Question. A block weighing 40 N is suspended from a spring that has a force constant of 200 Nm–1. The system is undamped and is subjected to a harmonic driving force of frequency 10 Hz, resulting a forced-motion amplitude of 2 cm. What is the maximum value of driving force ?
Answer :

Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. (a) Draw a graph showing the variation of kinetic energy and potential energy of a particle executing SHM with its displacement from mean position.
(b) Show that total mechanical energy of a particle executing simple harmonic motion remains conserved with time, when dissipative forces are neglected.
Answer : (a) The variations of kinetic energy K, potential energy U and total energy E with displacement x. The graphs for K and U are parabolic while that for E is a straight line parallel to the displacement axis. At x = 0, the energy is all kinetic and for x = ± A, the energy is all potential.
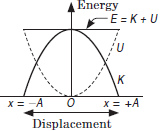
(b) The energy of a harmonic oscillator is partly kinetic and partly potential. When a body is displaced from its equilibrium position by doing work upon it, it acquires potential energy. When the body is released, it begins to move back to equilibrium position, thus acquires kinetic energy.
At any instant, the displacement of a particle executing SHM is given by

Thus the total mechanical energy of a harmonic oscillator is independent of time or displacement.
Hence in the absence of any frictional force, the total energy of a harmonic oscillator is conserved.
Question. You are riding an automobile of mass 3000 kg. Assuming that you are examining the oscillation characteristics of its suspension system. The suspension sags 15 cm when the entire automobile is placed on it. Also, the amplitude of oscillation decreases by 50% during one complete oscillation. Estimate the values of
(a) the spring constant k and
(b) the damping constant b for the spring and shock absorber system of one wheel, assuming that each wheel supports 750 kg.
Answer : (a) Here mass supported by each wheel, M = 750 kg and x =15 cm = 0.15 m
If k is spring constant of the spring, then restoring force developed on being compressed through a distance x
F = – kx
If M is mass supported by each wheel, then

Question. A body oscillates with SHM along the X-axis. Its displacement varies with time according to the equation : x = (4.00 m) cos (πt + π/4). Calculate
(a) displacement
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration at t = 1.00 s
(d) the maximum speed and maximum acceleration and
(e) phase at t = 2.00 s.
Answer : By comparing the given equation with the general equation for SHM along X-axis, i.e.,


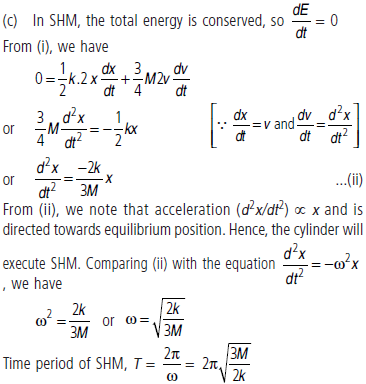
Question. A solid cylinder of mass M is attached to a horizontal massless spring so that it can roll without slipping along a horizontal surface as shown in figure. The spring constant k is 3 N m–1. If the system is released from rest t a point in which the spring is stretched by 0.25 m, find
(a) the translational kinetic energy and
(b) the rotational kinetic energy of the cylinder as it passes the equilibrium position.
(c) Show that under these conditions, the centre of mass of cylinder executes SHM with time period,
T = 2π √(3M / 2k).
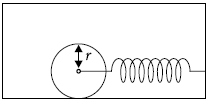
Answer : Let at any position, x be the extension in the spring and v be the velocity of centre of mass of the cylinder. Then,