Students can read the important questions given below for Popular Struggles and Movements Class 10 Social Science. All Popular Struggles and Movements Class 10 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 10 Social Science Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Social Science Question Bank Class 10 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Popular Struggles and Movements Class 10
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Which agency in Bolivia pressurised the government to give its control of municipal water supply?
Answer : World Bank.
Question. Who was the ruler of Nepal when the movement for the restoration of democracy took place ?
Answer : King Gyanendra.
Question. The ‘Third Wave’ country that had won democracy in 1990.
Answer : Nepal.
Question. State the main aim of Backward and Minority Communities Employees Federation.
Answer : Its main aim is with social justice and social equality for the entire society.
Question. How are issue specific movements different from generic movements ?
Answer : Issue specific movements seek to achieve a single objective within a limited time frame, while generic movements seek to achieve a broad goal in the long term.
Question. Give an example of a public interest group.
Answer : BAMCEF.
Question. Which feature distinguishes a pressure group from a political party ?
Answer : The pressure groups do not aim to directly control or share political power while political parties do.
Question. Of whom the Human Rights Organizations are an example ?
Answer : Public interest group.
Question. Write any one aim of the pressure groups.
Answer : To influence government policies.
Question. Which type of group are trade unions ?
Answer : Sectional interest group.
Question. Differentiate between ‘Sectional Interest Groups’ and ‘Public Interest Groups‘.
Answer : Sectional interest groups seek to promote the interest of a particular section while public interest groups promotes collective rather than selective good.
Question. What is the relationship between political parties and pressure groups ?
Answer : The pressure groups are either formed or led by the leaders of political parties.
Question. Which agency is not helpful in making the effective participation of the people at the time of conflicts and mobilisation ?
Answer : The Trade Unions
Question. Which organization led the protest against water privatisation in Bolivia ?
Answer : FEDECOR.
Question. What was the main aim to start movement in April 2006, in Nepal ?
Answer : To restore democracy in Nepal.
Question. What does SPA stand for ?
Answer : Seven Party Alliance.
Question. What is the main feature of public interest groups ?
Answer : They promote collective goods.
Question. Name any two sectional interest groups.
Answer : The two sectional interest groups are :
(a) Trade Unions
(b) Business associations
(c) Professional bodies–lawyers, doctors, teachers etc.
Question. What is common among FEDECOR, BAMCEF, and Human Rights Organizations ?
Answer : They are examples of public interest groups.
Question. Write any one characteristic of groups. social interest
Answer : They seek to promote the interests of a particular section or a group of society.
Question. Regarding the demands for democracy in Nepal, what was not demanded by the ? Seven Party Alliance ?
Answer : Absolute monarchy.
Question. To which continent does Bolivia belong ?
Answer : South America.
Question. Who was not involved in the protest against water privatisation in Bolivia ?
Answer : Political parties
Question. Which political party is a result of social reform movements ?
Answer : Asom Gana Parishad.
Question. What was the main role of ‘FEDECOR’ organization in Bolivia?
Answer : The protest against water privatisation in Bolivia was led by FEDECOR and it made the government concede to all the demands of the protesters.
Question. What action of MNC had agitated the people in Bolivia?
Answer : Enhancement of the price of water
Question. Who dissolved the popularly elected Parliament in February 2005, in Nepal ?
Answer : King Gyanendra dissolved the popularly elected Parliament in February 2005, in Nepal.
Question. What was the result of Bolivia’s Water War ?
Answer : Cancellation of MNC contract and restoration of water supply to the municipality.
Question. Distinguish between pressure groups and political parties by stating any one point of distinction.
Answer : Pressure groups do not aim to directly control or share political power but political parties directly control and share political power.
Question. What is FEDECOR ?
Answer : Organisation that led Bolivian mass protest.
Question. In which two ways, the public interest groups achieve their aims ?
Answer : They raise slogans against the government and disrupt public.
Question. What do you understand by “A group fighting against bonded labour” ?
Answer : It is an example of sectional interest group.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How are popular struggles integral to the working democracy ? Explain with an example of Bolivia’s struggle against privatisation of water.
Answer : The popular struggles are integral to the development of democracy :
(a) Popular struggles are a part of working democracy.
(b) Struggles are essential to save democracy. For example, Nepal’s struggle for restoration of democracy and Bolivia’s Water War.
(c) It is only in democracy that different individual groups can express their feelings.
(d) The people do not agree with policies of the government, they can oppose it with all their might and constant popular struggle to achieve their goal.
(e) Democracy evolves through popular struggle.
Question. State the issue of struggle in Bolivia. Which groups participated in it?
Answer : The World Bank pressurised Bolivian government to privatise municipal water supply (Privatisation of Water).
The government sold the rights to an MNC which increased the price of water by four times. Groups- FEDECOR consisting of professionals like engineers and environmentalists, federation of farmers, confederation of factory workers’ union, students of university of Cochabamba and city’s homeless street children.
Question. What do you understand by sectional interest groups ? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Usually interest groups seek to promote the interests of a particular section or group of society.
(ii) They are sectional interest groups as they represent a section of society—workers, employees, business persons etc.
(iii) BAMCEF—Backward and Minority Community Employees Federation—It is an organization largely made of government employees and it addresses the problems of its members who suffer discrimination in trade unions and business organizations.
Question. Describe any three features of sectional interest groups.
Answer : Features of sectional interest groups :
(a) Interest groups seek to promote the interests of a particular section or group of society.
(b) Trade unions, business associations, professional etc. are the examples.
(c) They are sectional because they represent a section of society.
(d) Their principal concern is the betterment and well- being of their members, not society in general.
Question. What are sectional interest groups ? Describe their functioning.
Answer : Sectional interest groups :
The groups that seek to promote the interests of a particular section or a group of society is called sectional interest groups.
Functioning :
(i) They perform a meaningful role in countering the undue influence of other groups.
(ii) They create awareness about the needs and concerns of their own society.
(iii) Their principal concern is the betterment and well- being of their members not society in general.
Question. What is the full form of SPA ? Explain any two demands of the SPA.
Answer : Seven Party Alliance is the full form of SPA.
Their demands are :
(a) Restoration of Parliament.
(b) Power to all-party government.
(c) A new Constituent Assembly.
Question. “The struggle of the Nepali people is a source of inspiration to democrats all over the world.“ Support the statement.
Answer : The struggle of the Nepali people is a source of inspiration to democrats all over the world :
The autocratic decision of King Gyanendra in February 2005 resulted in protest by the political parties and people of Nepal. Political parties having diverse ideology joined together and defied the curfew. The leaders rejected the half hearted concessions by the king, ultimately the king was compelled to concede all the three demands made by the protesters. Hence, this struggle of Nepalis known as the Second Movement for Democracy became a source of inspiration to democrats all over the world.
Question. What was the Green Belt Movement ? What was the attitude of the government towards this movement ?
Answer : (i) The Green Belt Movement was the tree plantation movement in Kenya.
(ii) 30 million trees had been planted across Kenya.
(iii) The leader of this movement was Wangari Maathai.
(iv) The government officials and politicians did not show any response towards this movement.
Question. In what two ways do organizations influence the decisions in a democracy ?
Answer : The different organizations influence the decisions in a democracy in two ways :
(a) Direct ways : Participation in competitive politics. This is done by creating parties, contesting election and forming governments.
(b) Indirect ways : They could do so by forming an organization and undertaking activities to promote citizens interest or view point through interest groups or pressure groups.
Question. Explain any three common features of the popular mass struggle in Nepal and Bolivia.
Answer : (a) Both these are instances of political conflict that led to popular struggles.
(b) In both cases, the struggle involves mass mobilizations and public demonstration of mass support clinched the dispute.
(c) Both instances involved the critical role of political organization.
Question. Who led the Protest against water privatisation in Bolivia ? Describe the ways of protest adopted by that organization.
Answer : Protest against water privatisation in Bolivia :
FEDECOR (comprised local professionals, including engineers and environmentalists), human rights and community leaders.
Ways of their Protest :
(i) Organized a successful four-day general strike in the city.
(ii) Influenced the decision through direct participation in competitive politics.
(iii) Created parties and formed governments.
(iv) Formed pressure groups for the protest.
Question. What are pressure groups ? How are they formed? Explain.
Answer : Pressure groups are organizations that attempt to influence government policies. These organizations are formed when people with common occupation, interest, aspirations or opinions come together in order to achieve a common objective.
Question. What are public interest pressure groups ? Describe their functioning.
Answer : Public interest groups are those that promote collective rather than selective interests.
Their functioning is as follows :
(i) It aims to help groups other than their own members.
(ii) They represent some common interest that needs to be defended.
(iii) The members of the organization may not benefit from the cause that the organization represents. e.g., a group fighting against bonded labour fights not for itself but for those who are suffering under such bondage.
Question. What is the objective of movement groups ? Give the name of one such movement group. Mention how do these movements exert influence on politics.
Answer : (i) The main objective of movement groups is to influence politics without directly taking part in electoral competitions and achieving the desired goals.
(ii) Most of the movement groups are issue-specific movements that seek to achieve a single objective within a limited time frame. Others are more general or generic movements that seek to achieve a broad goal.
(iii) The struggle in Nepal was called a movement for democracy or the Narmada Bachao Andolan is an example of one such movement group.
(iv) These movements try to gain public support and sympathy for their goals and their activities by carrying out information campaigns, organizing meetings, filing petitions, etc.
Question. What are interest groups ? Give two features of promotional pressure groups in India.
Answer : (a) Interest groups or pressure groups are organizations that attempt to influence government policies. They do not aim to directly share political power. These are formed when people with common occupation, interest, aspirations or opinions come together for common objective.
(b) Two features of promotional groups are :
(i) They promote collective rather than selective good.
(ii) They aim to help groups other than their own members.
Question. Mention any three indirect ways in which people can force the government to listen to their demands.
Answer : Indirect ways to force the government :
(a) By forming organization.
(b) By undertaking activities.
(c) By deciding to act together without forming organization.
Question. Describe the three major demands put forward by the Seven Party Alliance in Nepal.
Answer : Demands put forward by the Seven Party Alliance in Nepal are :
(a) Restoration of Parliament.
(b) Power to an all-party government.
(c) A new Constituent Assembly.
Question. How would you differentiate between sectional interest groups and public interest groups ?
Answer :
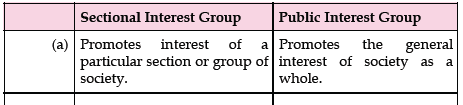
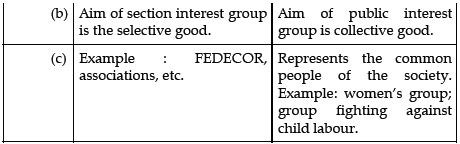
Question. Explain any three types of pressure groups.
Answer : (1) Social/Identity Group-have a special identity.
(a) Community based-Ram Krishna Mission.
(b) Sectional-Vishva Hindu Parishad.
(2) Associational/Identity based group–promote vocational or professional interest.
(a) Business group-FICCI
(b) Trade Union-INTUC, CITU
(c) Farmers and peasants.
(3) Institutional Group—
Groups within the government e.g.,-IAS Officers’ Association, IPS Officers’ Association, Ad hoc group formed for temporary cause, e.g., to open a college or hospital.

