Please go through Introduction to International Trade MCQ Questions with Answers provided below. Students should have strong knowledge about Introduction to International Trade as in various competition exams, MCQ questions are asked from this topic. We have provided below the biggest collection of Introduction to International Trade MCQ with Answers. These International Business MCQ Questions and objective questions will improve your performance in exams and help you to get good scores.
Multiple Choice Questions for The Introduction to International Trade with Answers
Question. The first phase of globalization started around 1870 and ended with …..
(a) World War I
(b) World War II
(c) The Establishment of GATT
(d) In 1913 when GDP was High
Answer
A
Question. In the 2-factor, 2 good Heckscher-Ohlin model, the two countries differ in
(a) Military capabilities
(b) labor productivities
(c) relative availabilities of factors of production
(d) tastes
Answer
C
Question. Nations conduct international trade because:
(a) Some nations prefer to produce one thing while others produce other things.
(b) Resources are not equally distributed among all trading nations.
(c) Trade enhances opportunities to accumulate profits.
(d) Interest rates are not identical in all trading nations
Answer
B
Question. According to this theory, the holdings of a country’s treasure primarily in the form of gold constituted its wealth.
(a) Gold Theory
(b) Ricardo Theory
(c) Mercantilism
(d) Hecksher Theory
Answer
C
Question. The Heckscher- Ohlin model is principally focused on what aspect of economics?
(a) International trade
(b) Supply and demand
(c) Normative economics
(d) Production possibility frontier
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following trade policies limits specified quantity of goods to be imported at one tariff rate?
(a) Quota
(b) Import tariff
(c) Specific tariff
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. International Trade is most likely to generate short-term unemployment in:
(a) Industries in which there are neither imports nor exports
(b) Import-competing industries
(c) Industries that sell to domestic and foreign buyers.
(d) Industries that sell to only foreign buyers
Answer
B
Question. What was the first economic theory of international trade to be developed?
(a) The theory of mercantilism
(b) The theory of comparative advantage
(c) The theory of absolute advantage
(d) The Heckscher-Ohlin theory
Answer
A
Question. The Theory of Relative Factor Endowments is given by
(a) David Ricardo
(b) Adam Smith
(c) c. F W Taussig
(d) Ohlin and Hecksher
Answer
D
Question. The theory of comparative cost advantage is given by
(a) David Ricardo
(b) Adam Smith
(c) F W Taussig
(d) Ohlin and Heckscher
Answer
A
Question. Mercantilists believed that a country could increase the amount of wealth it had by _____.
(a) Promoting exports and discouraging imports
(b) Discouraging exports and promoting imports
(c) Controlling imports and exports
(d) Increasing both imports and exports
Answer
A
Question. International trade forces domestic firms to become more competitive in terms of
(a) The introduction of new products
(b) Product design and quality
(c) Product price
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. How is comparative advantage defined?
(a) You produce the things you are especially good at, and buy from others, the goods you are less efficient in producing.
(b) To produce and consume all goods without trade.
(c) How the world actually works.
(d) Globalization, growing economic linkages among countries.
Answer
A
Question. What are the four factor endowments?
(a) National resources, labor, physical capital and human capital
(b) Types of technology
(c) Material inputs used up in the process of production
(d) International differences in climate
Answer
A
Question. The movement to free international trade is most likely to generate short-term unemployment in which industries
(a) Industries in which there are neither imports nor exports
(b) Import-competing industries.
(c) Industries that sell to domestic and foreign buyers
(d) Industries that sell to only foreign buyers
Answer
B
Question. Increased foreign competition tend to
(a) Intensify inflationary pressure at home
(b) Induce falling output per worker-hour for domestic workers
(c) Place constraints on the wages of domestic workers
(d) Increase profits of domestic import-competing industries
Answer
C
Question. ………………is the payment method most often used in International Trade which offers the exporter best assurance of being paid for the products sold internationally.
(a) Bill of Lading
(b) Letter of Credit
(c) Open Account
(d) Drafts
Answer
B
Question. Key controllable factors in global marketing are:
(a) Government policy and legislation
(b) social and technical changes
(c) marketing activities and plans
(d) all of the above.
Answer
C
Question. The Theory of Absolute Cost Advantage is given by
(a) David Ricardo
(b) Adam Smith
(c) F W Taylor
(d) Ohlin and Heckscher
Answer
B
Question. Globalization refers to:
(a) Lower incomes worldwide
(b) Less foreign trade and investment
(c) Global warming and their effects
(d) A more integrated and interdependent world
Answer
D
Question. A no-trade world will have which of the following characteristics:
(a) Countries will have same relative endowments of production factors
(b) Consumers across countries will have identical and homogenous tastes
(c) There will be no distortions or externalities
(d) all of the above
Answer
D
Question. Transportation cost of trade affects:
(a) pattern of trade
(b) boundaries between tradable and non-tradable goods
(c) Global supply chains
(d) all of the above
Answer
D
Question. Comparative Cost Trade Theory is given by
(a) Adam Smith
(b) David Ricardo
(c) Gottfried Haberle
(d) Heckscher Ohlin
Answer
B
Question. According to Adam Smith, the trade between countries should happen _____.
(a) Naturally according to the market forces
(b) Under government regulation
(c) Using factors that are available
(d) Only when a country has an absolute advantage
Answer
D
Question. If a nation has an open economy it means that the nation:
(a) Allows private ownership of capital.
(b) Has flexible exchange rates
(c) Has fixed exchange rates
(d) Conducts trade with other countries
Answer
D
Answer the following questions based on the production table below:
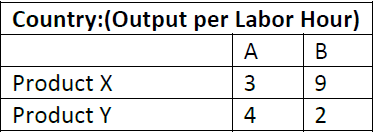
Question. If the countries were to trade along the lines of absolute advantage:
(a) A would export X to B
(b) B would import Y from A
(c) Neither country would want to trade
Answer
B
Question. Country A has an absolute advantage in
(a) Product X
(b) Product Y
(c) Neither X nor Y
(d) Both X and Y
Answer
B
Question. If countries were to trade along the lines of comparative advantage:
(a) A would export X to B
(b) A would export Y to B
(c) Neither country would want to trade
Answer
B
Question. Country B has an absolute advantage in
(a) Product X
(b) Product Y
(c) Neither X nor Y
(d) Both X and Y
Answer
A
Use the information in the table below to answer the following questions:
| Country | Tons of steel | DVDs |
| South Korea | 80 | 40 |
| Japan | 20 | 20 |
Question. According to the principle of comparative advantage:
(a) South Korea should export steel
(b) South Korea should export steel and DVDs
(c) Japan should export steel
(d) Japan should export steel and DVDs
Answer
A
Question. The opportunity cost of one DVD in Japan:
(a) One ton of steel
(b) Two tons of steel
(c) Three tons of steel
(d) Four tons of steel
Answer
A
Question. The opportunity cost of one DVD in South Korea is:
(a) One-half ton of steel
(b) One ton of steel
(c) One and one-half tons of steel
(d) Two tons of steel
Answer
D



