Please refer to Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Case/Passage – 1
Metallic Character The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ion (cation) is known as electropositivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to rightelectropositivity decreases due to decreasein atomic size. Non-Metallic Character The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity
decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electronegativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
Question: Hydrogen is placed along with Alkali metals in the modern periodic table though it shows non-metallic character
(a) as Hydrogen has one electron & readily loses electron to form negative ion
(b) as Hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion
(c) as Hydrogen can gain one electron easily like Halogens to form negative ion
(d) as Hydrogen shows the properties of non-metals
Answer
B
Question: Which of the following has highest electronegativity?
(a) F
(b) Cl
(c) Br
(d) I
Answer
A
Question: Which of the following correctly represents the decreasing order of metallic character of Alkali metals plotted in the graph?
(a) Cs > Rb > Li > Na > K
(b) K > Rb > Li > Na > Cs
(c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li
(d) Cs > K > Rb > Na > Li
Answer
C
Question: Which of the following reason correctly justifies that “Fluorine (72pm) has smaller atomic radius than Lithium (152pm)”?
(a) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size increases down the group
(b) F and Li are in the same period. Atomic size increases across the period due to increase in number of shells
(c) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size decreases down the group
(d) F and Li are in the same period and across the period atomic size/radius decreases from left to right.
Answer
D
Question: Identify the reason for the gradual change in electronegativity in halogens down the group.
(a) Electronegativity increases down the group due to decrease in atomic size
(b) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to decrease in tendency to lose electrons
(c) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/ tendency to gain electron decreases
(d) Electronegativity increases down the group due to increase in forces of attractions between nucleus & valence electrons
Answer
C
Case/Passage – 2
The table given below refers to the elements of the periodic table with atomic number from 3 to 18. These elements are shown by letters. (not by the usual symbols of the elements).
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
A B C D E F G H
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
I J K L M N O P
Question: Which of the following are noble gases?
(a) H and P
(b) G and O
(c) D and L
(d) A and I
Answer
A
Question: Which of the following elements have valency 4?
(a) F and N
(b) C and K
(c) D and L
(d) H and P
Answer
C
Question: Which are halogens?
(a) H and L
(b) C and M
(c) G and O
(d) E and P
Answer
C
Case/Passage – 3
Group VII A elements are strong non-metals because they can easily accept an electron to form an anion whereas group 1 A element are strong metals because they can very easily lose one electron to form cation. Metals have the tendency to lose their valence electrons and form positive ions, so metallic character is related to the ionisation potential. Elements having low ionisation potential, lose electrons easily. Thus, metallic character generally decreases across a period and increases down a group.
Question: Group 1 and group 2 elements are considered as strong metals because
(a) they have incomplete octet.
(b) they can easily gain electrons.
(c) they can easily lose electrons.
(d) they form anions.
Answer
C
Question: Which of the following is the correct decreasing order of metallic character?
(a) Ca > Sc > Ti > K
(b) K > Ca > Sc > Ti
(c) K > Sc > Ca > Ti
(d) Ti > Sc > Ca > K
Answer
B
Question: The non metallic character on moving along a period –
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) depends on the period
(d) remains the same
Answer
A
Case/Passage – 4
Question: numbers 1 – 3 are based on the periodic table. Study the part of the modern periodic table presented below in which the alphabets represent the symbols of elements and answer the following questions.

Question: Consult the above part of the periodic table to predict which of the given combination is a covalent compound:
RQ2, AT, JQ, JX2.
Answer
R and Q are members of group 16th having elements,O, S, Se, Te etc. RQ2 is characterised by showing the formation of covalent bond.
Question: Which of the given element is the most electronegative element?
Answer
Element ‘V’ is the most electronegative element
Question: Considering the above part of the periodic table, which of the given element is the most electropositive element?
Answer
Element ‘G’ is the most electropositive element.
Question: Study the data of the following three categories A, B and C.

(i) From the given three categories A, B and C, Pick the one which forms Dobereiner’s Triads.
(ii) Why did Mendeleev placed elements of category A, B and C in three different groups?
(iii) Is Newland law of octaves applicable to all the three categories?
Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer
(i) Dobereiner’s Triads is A.
(ii) Mendeleev placed elements of category A,B and C
in three different groups because they have different physical and chemical properties.
(iii) No, Newland’s Law of octaves is not applicable for all three categories.
Because the law of octaves states that every eighth element has similar properties when the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses.
Case/Passage – 5
Around the year 1800, only 30 elements were known. Dobereiner in 1817 and Newlands in 1866 tried to arrange the then known elements and framed laws which were rejected by the scientists. Even after the rejection of the proposed laws, many scientists continued to search for a pattern that correlated the properties of elements with their atomic masses.
The main credit for classifying elements goes to Mendeleev for his most important contribution to the early development of a Periodic table of elements wherein he arranged the elements on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties. The formulae of their hydrides and oxides were treated as basic criteria for the classification of the elements.
However, Mendeleev’s classification also had some limitations as it could not assign the position to isotopes. He also left some gaps in the periodic table.
Question. If the letter ‘R’ was used to represent any of the elements in the group, then the hydride and oxide of carbon would respectively be represented as
(a) RH4, RO
(b) RH4, RO2
(c) RH2, RO2
(d) RH2, RO
Answer
B
Question. Isotopes are:
(a) Atoms of an element with similar chemical properties but different atomic masses.
(b) Atoms of different elements with similar chemical properties but different atomic masses.
(c) Atoms of an element with different chemical properties but same atomic masses.
(d) Atoms of different elements with different chemical properties but same atomic masses.
Answer
A
Question. How many groups and periods are there in Mandeleev’s periodic table?
(a) 6 group, 8 period
(b) 18 group, 7 period
(c) 7 group, 18 period
(d) 8 group, 6 period
Answer
D
Question. According to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law properties of elements are periodic function of
(a) atomic mass
(b) atomic number
(c) number of protons
(d) number of electrons
Answer
A
Question. Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in the Periodic table?
(a) For elements to be discovered
(b) For isotopes
(c) For isobars
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Case/Passage – 6
Modern periodic table has 18 vertical columns known as groups and 7 horizontal rows known as periods. First period contains 2 elements second and third period contain 8 elements. 4th and 5th period contains 18 elements and 6th and 7th period contains 32 elements. The graph is plotted between atomic number and atomic radius of group 17 and group 1 elements.
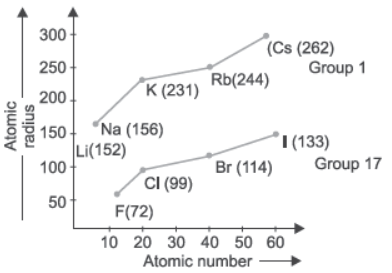
Question. What happens to atomic radii in a group from top to bottom?
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) First decreases then increases
(d) Number of shells remains the same
Answer
A
Question. Atomic size decreases from left to right in a period because
(a) Effective nuclear charge increases
(b) Number of shells remains the same
(c) Force of attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons increases
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which group elements will have largest atomic size?
(a) Group 1
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 3
(d) Group 18
Answer
A
Question. Which group elements will gain electrons to form negative ions?
(a) Group 1
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 17
(d) Group 18
Answer
C
Question. Which element in group 17 has smallest size?
(a) Flourine
(b) Bromine
(c) Chlorine
(d) Iodine
Answer
A
Case/Passage – 7

Question. How electronegativity varies in a period?
(a) Increases from left to right
(b) Decreases from left to right
(c) First increases then decreases
(d) Vary independently
Answer
A
Question. What happens to tendency to gain electron in a period?
(a) Increases,
(b) Decreases,
(c) Remaining same,
(d) First increases then decreases.
Answer
A
Question. How electronegativity varies in a period?
(a) Increases down the group
(b) Decreasing down the group
(c) First increases then decreases down the group
(d) Vary independently
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following has least electronegativity?
(a) Li,
(b) Be,
(c) O,
(d) N
Answer
A
Question. Which element has highest electronegativity?
(a) C
(b) N
(c) O
(d) F
Answer
D
Class 10 Science Periodic Classification of Elements Exam Questions
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. State Mendeleev’s periodic law. Write two achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Answer : Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic mass.
Achievements:
a. It could arrange all the elements discovered at that time.
b. It left some gaps for the elements to be discovered and helped in their discovery by predicting their properties.
Question. The elements of the second period of the periodic table are given below:
Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F
a. Give reason to explain why atomic radii decreases from Li to F.
b. Identify the most (i) metallic and (ii) non-metallic element.
Answer :
a. It is because effective nuclear increases due to increase in forces of attraction between more electrons with more protons, even though number of shells remain the same.
b. (i) Li is the most metallic element, (ii) F is the most non-metallic element.
Question. Give reasons for the following:
a. Lithium atom is smaller than sodium atom.
b. Chlorine (Atomic number 17) is more electronegative than Sulphur (Atomic number 16)
Answer :
a. Li(3): 2, 1; Na(11): (2, 8, 1).
Li has two shells, therefore it is smaller than Na which has 3 shells.
b. Chlorine (17) is smaller than sulphur (16),therefore it is more electronegative than sulphur.
Question. a. State the main characteristic of elements on which modern periodic table is based.
b. No fixed position is assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table, why?
Answer :
a. Modem periodic table is based on the trend of increasing order of atomic number. Elements of same group have same number of valence electrons.
b. Hydrogen resembles with both group 1 and group 17 elements, therefore it does not have a fixed position.
Question. An element X has mass number 35 and the number of its neutrons is 18. Identify the group number, period and valency of element X’.
Answer : X has mass number 35, number of neutrons = 18
Atomic Number = 35 – 18 = 17
a. Electronic configuration: X = 2, 8, 7 It has 7 valence electrons. It belongs to group 17.
b. It has 3 shells, therefore it belongs to 3rd period.
c. It can gain 1 electron to become stable, so its valency is equal to 1.
Question. Why is lithium with atomic number 3 and potassium with atomic number 19 are placed in group one? What will be atomic number of the first two elements in the second group?
Answer : Group 1 Group 2
Li(3): 2,1 Be(4): 2, 2
K(19):2,8,8,1 Mg (12): 2, 8, 2
Li and K are placed in group 1 due to same number ofvalence electrons. In second group the atomic number of first two elements will be 4 and 12 respectively.
Question. Two elements M and N belong to group 1 and 2 respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of M and N vary?
a. Sizes of their atoms.
b. Their metallic character.
c. Their valencies in forming oxides.
d. Formulae of their chlorides.
Answer :
a. M has bigger size than N.
b. M has more metallic character than N.
c. M has valency equal to 1, N has valency equal to 2.
d. MCl and MCl2 are formula of their chlorides.
Question. The following table shows the elements represented by the letters A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H. (Table 81)
a. Which of the elements has the atomic size (i) biggest and (ii) smallest?
b. Which element has valency equal to (i) 3 and (ii) zero?
Answer :
a. (i) A has the biggest size. (ii) G has the smallest size.
b. (i) C has valency equal to 3. (ii) H has valency equal to zero.
Question. a. State Modern Periodic Law
b. Elements A, B, C and D have atomic number 1, 8, 11, 19 respectively. Choose the odd element and give reason for your answer.
Answer : [
a. Modern Periodic Law: It states ‘properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number’.
b. B(8): 2, 6 is an odd element because it has 6 valence electrons whereas others have 1 valence electron.
Question. Arrange the following elements in descending order of their atomic size and give reason for your answer.
Mg(12), P(15), Cl(17), Ar(18)
Answer :
Mg > P > Ar > Cl
As we move from left to right, atomic size decreases due to increase in effective nuclear charge. Ar is bigger than Cl due repulsion between 8 valence electrons.
Question. Na, Mg, A1 are the elements having one, two and three valence electrons respectively. Which of these elements (a) has longest atomic radius, (b) is least reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each.
Answer : a. Na has the largest atomic radius due to least effective nuclear charge due to less forces of attraction between 11 protons and 11 electrons.
b. A1 is the least reactive element due to small its size and least tendency to lose electrons.
Question. The atomic number of these elements are given below: (table 85)
Arrange this elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers. Give reason for your answer.
Answer : =
B(5), C(6), N(7), 0(8) is the increasing order of their atomic numbers.
It is because when we move along a period,atomic radii decreases due to increase in effective nuclear charge due to increase in number of protons and electrons continuously.
Question. Would you place the two isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37 in different slots because of their different atomic masses or in the same slot because their chemical properties
are same? Justify your answer.
Answer : They will be placed in the same slot because they have similar chemical properties due to same number of valence electrons.
Question. The electronic configuration of an element X is 2, 8, 8, 2. To which period and group of periodic table does the element X belong to? State the valency and justify your answer in each case.
Answer :
It belongs to 4th period because it has four shells.
It belongs to group 2 because it has 2 valence
electrons. X has a valency equal to 2 because it can lose 2 electrons to become stable.
Question. Study the variation in atomic radii of first group elements given below and arrange them in an increasing order:
a. Name the element which have the smallest and the largest atoms (Table 91)
b. How does the atomic size vary as you go down the group?
Answer :
Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs
a. Li is the smallest, Cs is the largest atom.
b. Atomic size increases down the group.
Question. Atomic radii of the elements of second period are given below: (table 92)
b. Are the elements now arranged in the pattern of a period in periodic table?
c. Which elements have the largest and the smallest atoms?
d. How does the atomic radius change as you go from left to right in a period.
Answer :
a. Li > Be > B > C > N > O
b. Yes, They belong to the second period.
c. Li is the largest, oxygen is the smallest.
d. Atomic size decreases along a period from left to right.
Question. Li, Be, B, C are the elements of same period of Modem Periodic table.
a. Arrange them in increasing order of their atomic size.
b. In which shell (number) would last electron enter for all of them.
c. Calculate the valence electrons in each.
d. Which element amongst them is most electropositive?
Answer :
a. C < B < Be < Li
b. Second shell
c.

Question. Give reasons:
a. Elements in a group have similar chemical properties.
b. Elements of Group 1 form ions with a charge of +1.
Answer :
a. It is due to the same number of valence electrons.
b. Group-1 elements can lose one electron to form positive ions with charge equal to +1.
Question. What is meant by periodicity of properties of elements? Why are the properties of elements placed on the same group of the periodic table similar?
Answer :The repetition of similar properties after a definite interval is called periodicity of properties. It is due to the same number of valence electrons.
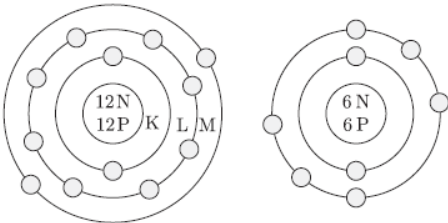
Question. Elements Mg and O respectively belong to group 2 and group 16 of the modem periodic table. If the atomic number of Mg and O are 12 and 8 respectively,draw their electronic structures and show the process of formation of the compound by transfer of electrons between them.
Answer : Mg(12): 2,8,2
O(8): 2,6
Question. Calcium is an element with atomic number 20.
a. Will it be a metal/non-metal?
b. What will be its valency?
c. What would be the formula of its chloride?
d. Will it be smaller / larger than K?
Answer : Ca(20): 2, 8, 8, 2
a. It will be a metal.
b. Its valency is equal to 2.
c. CaCl2 is the formula of its chloride.
d. It will be smaller than K.
Question. List the anomalies of Mendeleev’s periodic table which were removed in Modem Periodic Table.
Answer :Co with higher atomic mass proceeds Ni with lower atomic mass. It was solved because Co has lower atomic number than Ni.
Isotopes should have been given different slots due to different atomic mass, but it is not possible due to same chemical properties. The problem was solved because isotopes have same atomic numbers.
Question. Choose from the following:
6C, 8O, 10Ne, 11Na, 14S1
a. Elements that should be in the same period.
b. Elements that should be in the same group.
State the reason for your selection in each case.
Answer :
a. 6C(2, 4), 8O(2, 6), 10Ne(2, 8) belong to the same period i.e., 2nd period and 11Na(2, 8, 1), 14Si(2, 8, 4) belongs to the same period i.e., 3rd period.
b. 6C(2,4) and 14Si(2,8,4) belongs to the same group -14 due to same number of valence electrons,which is equal to 4.
Question. a. Amongst the following elements identify the ones that would form anions:
K, O, Na, F, Ca, Cl, Mg
b. Write the electronic configuration of the anions identified above.
Answer :
O, F, Cl will form anions.
O2- (18): 2, 8
F-(10): 2, 8
Cl-(18): 2, 8, 8
Question. An element belongs to third period and second group of the periodic table:
a. State the number of valence electrons in it.
b. Is it a metal or a non-metal?
c. Name the element.
d. Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer :
a. It has 2 valence electrons.
b. It is a metal
c. Magnesium.
d. MgO is the formula of its oxide.
Question. Write the trend of atomic size and metallic character along a group and a period in modern periodic table.
Answer : Atomic size increases down the group and decreases along a period from left to right in the periodic table.
Metallic character increases down the group and it decreases along a period from left to right.
Question. Elements in Periodic table show periodicity in properties. List any four such properties.
Answer : Valence electrons, Valency, Atomic size, Metallic character.
Question. An element ‘X’ has atomic number 13.
a. Write its electronic configuration.
b. State the group to which ‘X’ belongs to.
c. Is ‘X’ a metal or a non-metal?
d. Write the formula of its bromide.
Answer :
a. X(13) : 2, 8, 3
b. It belongs to group 13.
c. It is a metal.
d. XBr3 is the formula of its bromide.
Question. The elements of the third period of the Periodic Table are given below: (Table 76)
a. Which atom is bigger, Na or Mg? Why?
b. Identify the most (i) metallic and (ii) non-metallic element in Period 3.
Answer :
a. Na is bigger because it has 11p and 11e i.e., less forces of attraction than in Mg which has 12 protons and 12 electrons and has more forces of attraction, due to more effective nuclear charge.
b. (i) Na is the most metallic element, (ii) Cl is the most non-metallic element.
Question. Given below are four elements with their atomic numbers:
A(16), B(11), C(3), D(14)
a. Identify the elements which belong to the same group of the Modem periodic table.
b. Arrange the elements in decreasing order of the atomic size.
c. Write the formula of oxide of B.
d. Which of these elements is a metalloid?
Answer :
a. C(3) and B( 11) belongs to the same group.
b. A<D<B<C is the decreasing order of atomic size.
c. B2O is the formula of oxide.
d. D is a metalloid.
Question. An element M has atomic number 12.
a. Write its electronic configuration.
b. State the group to which M belongs to.
c. Is M a metal or a non-metal?
d. Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer :
a. 2, 8, 2,
b. Group 2,
c. Metal,
d. MO is formula of its oxide.
Question. How can the valency of an element be determined if its electronic configuration is known? What will be valency of an element with atomic number 9?
Answer : Valency=Number of valence electrons in case of metals and metalloids. It is also equal to 8 — Number of valence electrons in case of non-metals.
F(9) has electronic configuration of 2, 7. It is a nonmetal.
Its valency is equal to 1.
Question. An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 17 of the periodic table. State its (a) electronic configuration,
(b) valency. Justify your answer with a reason.
Answer :
a. 2, 8, 7; because it has 3 shells as it belongs to 3rd period. Group 17 means 7 valence electrons.
b. Valency = 1
It can gain 1 electron to become stable i.e. to complete its octet.
Question. Choose from the following:
20Ca, 3Li, 11Na, 10Ne
a. An element having two shells completely filled with electrons.
b. Two elements belonging to same group of the periodic table.
Answer :
a. 10Ne (2, 8)
b. 3Li(2, 1) and 11Na(2, 9, 1) belong to the same group.
Question. In the modern periodic table, the element Calcium (atomic number = 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21 and 38. Which ofthese elements has physical and chemical properties resembling those of Calcium and why?
Answer :
Ca(20): 2, 8, 8, 2
Mg(12): 2,8, 2
Sr(38): 2, 8, 18, 8, 2
Mg and Sr has similar properties to Ca because each of them have 2 valence electrons.
Question. How does metallic character of the elements change along a period in the periodic table from left to right and why?
Answer : Metallic character of elements decreases along a period from left to right because atomic size decreases, tendency to lose electrons decreases.
Question. Why do all elements of the
a. same group have similar properties?
b. same period have different properties?
Answer :
a. It is due to same number of valence electrons which will decide the chemical properties.
b. They differ in number of valence electrons,therefore they differ in chemical properties. They have the same number of shells.
Question. An element ‘E’ has the following electronic configuration:
| K | L | M |
| 2 | 8 | 6 |
a. To which group of the periodic table does element E belong to?
b. To which period of the periodic table does element E belong to?
c. State the number of valence electrons present in element E.
d. State the valency of the element E.
Answer :
a. E (2, 8, 6) belongs to group 16,
b. It belongs to 3rd period.
c. It has 6 valence electrons.
d. The valency of E is 2.
Question. Choose from the following: 4Be, 9F, 19K, 20Ca
a. The element having one electron in the outermost shell.
b. Two elements of the same group.
Answer :
a. 19K(2,8,8,1) has one valence electron,
b. 4Be(2, 2) and 20Ca(2, 8, 8, 2) belongs to the same group.
Question. The elements X, Y and Z having atomic numbers 11,7 and 6 respectively react with oxygen to form their oxides.
a. Arrange these oxides in increasing order of their basic nature.
b. Give reason for your answer.
Answer :
X(11) is sodium and it will form Na2O, Y(7) is Nitrogen that will form N2O5, Z(6) is carbon which will form CO2.
a. N2O5 < CO2 < Na2O
b. It is because non-metallic character increases along a period, therefore basic character of oxides decreases, and acidic nature increases from left to right across the period.
Short Answer Questions
Question. An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 16 of the Modern Periodic table.
a. Determine the number of valence electrons and the valency of X.
b. Molecular formula of the compound of X when it reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot diagram.
c. Name the element X and state whether it is metallic or non-metallic.
Answer :
a. X has 6 valence electrons and its valency is equal to 2.
b. H2X is its formula,
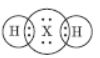
c. X is sulphur. It is a non-metallic element.
Question. Two elements X and Y have atomic number 11 and 16 respectively.
a. Write the electronic configuration of both.
b. Write the formula of the compound formed by their combination (in terms of X and Y).
Answer :
a. X(11): 2, 8, 1; Y(16): 2, 8, 6
b. X2Y is the formula of compound formed.
Question. Differentiate between the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table and Modern Periodic Table.
Answer :
| Mandeleev’s Periodic Table | Modern Periodic Table |
| It is based on increasing order of atomic mass. | It is based on increasing order of atomic number. |
| It has 8 groups and 6 periods. | It has 18 groups and 7 periods. |
| Increasing order of atomic mass could not be maintained. | Increasing order of atomic number can be maintained. |
Question. Write the names given to the vertical columns and horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving down a vertical column? How does the size of atomic radius vary on moving from left to right in a horizontal row? Give reason in support of your answer in the above two cases.
Answer : Vertical columns are called groups. Horizontal rows are called periods. Metallic character of elements increases down the group because tendency to lose electrons increases down the group due to increase in atomic size. Atomic size goes on decreasing along the period due to increase in effective nuclear charge due to increase in number of protons and electrons.
Question. An element ‘P’ (atomic number 20) reacts with an element ‘Q’ (atomic number 17) to form a compound.
Answer the following questions giving reason: Write the position of ‘P’ and ‘Q’ in the Modem Periodic Table and the molecular formula of the compound formed when ‘P* reacts with ‘Q’.
Answer :
P(20): 2, 9, 9, 2; Q(17): 2, 8, 7
‘P’ belongs to group 2 and 4th period.
‘Q’ belongs to group 17 and 3rd period.
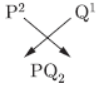
PQ2 is the molecular formula of the compound formed.
Question. Write the electronic configuration of two elements X’ and ‘Y’ whose atomic numbers are 20 and 17 respectively. Write the molecular formula of the compound formed when element X’ reacts with element ‘Y’. Draw electron-dot structure of the product and also state the nature of the bond formed between both the elements.
Answer : X(20): 2, 8, 8, 2; Y(17): 2, 8, 7
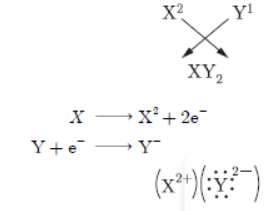
Y This bond is ionic bond.
Question. What is periodicity in properties of elements with reference to the Modern Periodic Table? Why do all the elements of the same group have similar properties?
How does the tendency of elements to gain electrons change as we move from left in a period? State the reason of this change.
Answer :
The repetition of similar properties after a definite interval is called periodicity of properties.
Tendency to gain electrons increases along a period from left to right because atomic size decreases.
Question. The atomic number of an element is 19.
a. Write the electronic configuration of this element and determine (i) the valency of this element,and (ii) whether this element is a metal or a nonmetal?
b. Write the formula of the oxide of this element.
c. Is this element more reactive or less reactive than Na (atomic number 11)? Justify your answer, giving example.
Answer :
a. 2, 8, 8, 1
i. Valency = 1
ii. It is a metal.
a. X2O
b. It is more reactive than Na(11) because it is large in size and it can lose electrons easily due to less effective nuclear charge.
K reacts more vigorously with H2O than Na.
Question. Why is atomic number considered to be a more appropriate parameter than atomic mass for the classification of elements in a periodic table? How does the metallic character of elements vary as we move (a) from left to right in a period, and (b) top to bottom in a group of the modem periodic table? Give reasons to justify your answer.
Answer :
It is because chemical properties depend upon the number of valence electrons which is determined with the help of atomic number.
a. Metallic character decreases from left to right because atomic size decreases, tendency to lose electrons decreases, b. Metallic character increases from top to bottom
in a group because atomic size increases due to which effective nuclear charge decreases.
Question. a. Identify the elements among the following which will belong to the same group: H, He, Li, B, C.
b. State the group number of the recognised elements.
c. Name another one element belonging to the same group.
Answer :
a. H and Li belong to the same group.
b. They belong to group 1.
c. Na (sodium) also belong to this group.
Question. Justify the following with suitable reasons:
a. Cations are smaller than the corresponding atoms.
b. Size of atom increases as we move down the group.
c. Atomic size decreases as we move across a period.
Answer :
a. Cations are formed by loss of electrons, therefore effective nuclear charge increases, size of atom decreases.
b. It is because number of shells goes on increasing down the group.
c. It is because effective nuclear charge increases along a period.
Question. Name the element with atomic number 19.
a. In which group it is placed?
b. To which period does it belong to?
c. Write its electronic configuration.
Answer : The name of element is Potassium, K(19): 2, 8, 8, 1.
a. It belongs to group 1.
b. It belongs to 4th period.
c. Its electronic configuration is 2,8 8,1.
Question. The atomic number of an element is 20.
a. Write its electronic configuration and determine its valency.
b. Is it a metal or a non-metal?
c. Write formula of its chloride.
d. Is it more or less reactive than Mg(12)? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer :
a. Ca(20): 2, 8 8, 2. Its valency is equal to 2.
b. It is a metal.
c. CaCl2.
d. It is more reactive than Mg due to larger atomic size. It can lose electrons easily due to less effective nuclear charge.
Question. The atomic number of an element is 12.
a. Write its electronic configuration and determine its valency.
b. Is it more reactive or less reactive than Ca(20)?
c. Is it a metal or a non-metal?
d. Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer :
a. Mg(12): 2, 8, 2. Its valency is equal to 2.
b. It is less reactive than Ca.
c. It is a metal.
d. MgO
Question. Out of the elements H(1), Be(4), Na(11) and Mg(12).
a. Write the pair of elements having similar chemical properties.
b. State the group number of each pair,
c. Name one another element belonging to each of these groups.
Answer :
a. Be(4) and Mg(12) have similar chemical properties.
H( 1) and Na(ll) have similar chemical properties.
b. Be and Mg belong to group 2, H and Na belong to group 1.
c. K belongs to group 1 and Ca belongs to group 2.
Question. Calcium is an element with atomic number 20. Stating the reason, answer each of the following questions:
a. Is calcium a metal or a non-metal?
b. Will its atomic radius be larger or smaller than that of potassium with atomic number 19?
c. Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer :
a. Calcium is a metal because it can lose electrons to form cations.
b. Its atomic radius will be smaller due to more number of protons and electrons, more forces of attraction.
c. CaO
Question. An element M with electronic configuration (2,8,2) combines separately with NO3 , (SO4)-2and (PO4)2-
radicals. Write the formula of the three compounds so formed. To which group and period of the Modern Periodic Table does the element M belong to? Will M form covalent or ionic compounds? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer : M(2, 8, 2). It has valency equal to 2.
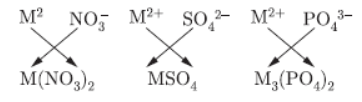
M belongs to group 2.
It belongs to 3rd period.
M will form ionic compound because M can easily lose electrons.
Bond will be formed by transfer of electrons.
Question. An element X’(Atomic number 20) burns in the presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
a. Identify the element and write its electronic configuration.
b. State its group number and period number in the Modern Periodic Table.
c. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction when this oxide is dissolved in water.
Answer : a. X is calcium because it forms CaO (basic oxide).
Its electronic configuration is 2, 8 8, 2.
b. It belongs to group 2 and 4th period.
c. CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Question. An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 16 of the Modern Periodic Table.
a. Determine the number of valence electrons and the valency of X.
b. Molecular formula of the compound when X reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot structure.
c. Name the element X and state whether it is metallic or non-metallic.
Answer :
a. X is sulphur, S(16): 2, 8, 6. It has 6 valence electrons. Its valency is equal to 2.
b. H2X,
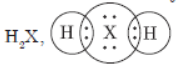
c. X is a non-metal.
Question. How does tendency to lose electrons change in the Modern Periodic Table in (a) a group, (b) a period and why?
Answer :
a. In a group, tendency to lose electrons increases down the group because atomic size increases,forces of attraction between the valence electronand nucleus decreases.
b. In a period, tendency to lose electrons decreases due to decrease in atomic size due to more effective nuclear charge.
Question. Three elements ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ have atomic numbers 7, 8 and 9 respectively.
a. State their positions (Group number and period number both) in the Modern Periodic Table.
b. Arrange these elements in decreasing order of their atomic radii.
c. Write the formula of the compound formed when
X’ combines with ‘Z’.
Answer :
X(7): 2, 5,
Y(8): 2, 6
Z(9): 2, 7
a. X belong to Group 15 and 2nd period.
Y belong to Group 16 and 2nd period.
Z belong to Group 17 and 2nd period.
b. X > Y > Z
C.
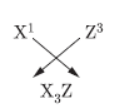
Question. The atomic number of Na and Mg are 11 and 12 respectively and they belong to the same period
a. Which one should have smaller atomic size?
b. Which would be more electropositive?
c. To which group would each one belong?
Answer :
Na(11): 2, 8, 1; Mg(12): 2, 8, 2
a. Mg will have smaller size.
b. Na is more electropositive.
c. Na(11) belongs to group 1 whereas Mg(12) belongs to group 2.
Question. Explain the basic character of oxides of elements down the group and across the period.
Answer : Basic character of oxides increases down the group because metallic character increases.
Basic character of oxides decreases along the period from left to right because non¬metallic character increases, metallic character decreases.
Question. Describe the basic character of oxides of third period elements across the period from left to right.
Answer :
Na2O, MgO are basic oxides.
SiO2, Al2O3 are amphoteric oxides.
P2O5, SO2, Cl2O7 are acidic oxides.
Basic character of oxides decreases across the period.
Question. Write the number of periods in the modern periodic table. State the changes in valency and metallic character of elements as we move from left to right in a period. Also state the changes, if any, in the valency and atomic size of elements as we move down the group.
Answer : There are 7 periods in Modern Periodic Table.
Valency first increases and then decreases. Metallic character decreases along a period from left to right.
There is no change in valency down the group.
Atomic size increases down the group.
Question. How many groups and periods are there in the Modern Periodic Table? How do the atomic size and metallic character of elements vary as we move
a. down a group and
b. from left to right in a period?
Answer :
There are 7 periods in Modern Periodic Table.
Valency first increases and then decreases. Metallic character decreases along a period from left to right.
There is no change in valency down the group.
Atomic size increases down the group.
Question. Two elements P and Q belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form:
a. The number of electrons in their atoms.
b. The size of their atoms.
c. Their metallic character.
d. Their tendency to lose electrons.
e. The formula of their oxides.
f. The formula of their chlorides.
Answer :
a. P has 1 valence electron, Q has 2 valence electrons.
b. P is bigger than Q.
c. P is more metallic than Q.
d. P can lose electrons more easily than Q.
e. P2O and QO
f. PCl and QCl2
Question. Taking example of an element of atomic number 16,explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the Modern Periodic Table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number?
Answer :
S(16) has electronic configuration of 2,8, 6,Group number = valence electrons + 10= 6 + 10 = 16
Period number = Number of shells = 3 Valency = 8 – valence electrons =8-6=2
Question. The atomic number of an element X’is 20.
a. Determine the position of the element “X’ in the periodic table.
b. Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ reacts/combines with another element *Y’(atomic number 8).
c. What would be the nature (acidic or basic) of the compound formed? Justify your answer.
Answer :
X(20): 2, 8, 8, 2; Y(8): 2, 6
a. It belongs to group 2, 4th period because its valence electrons are 2 and no. of shells = 4
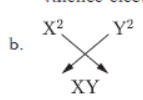
c. Compound formed will be basic because “X’ is a metal.
Question. An element X’ is placed in 13th group and 3rd period of Modern Periodic Table. Answer the following stating reason for your answer.
a. Write the electronic configuration of the element X’.
b. Write the formula of the compound formed when element X’ reacts with another element ‘Y’,having atomic number 17.
c. Will oxide of this element be acidic or basic?
Answer :
X is Aluminium (13); Y(17) 2, 8, 7
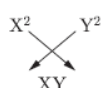
c. It will be amphoteric i.e., it is acidic as well as basic.
Question. Given below are some elements of the Modern Periodic Table. Atomic number of the element is given in the parentheses:
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
a. Select the element that has only one electron in the outermost shell. Also write the electronic configuration of this element.
b. Which two elements amongst these belong to the same group? Give reason for your answer.
c. Which two elements amongst these belong to the same period? Which among the two has bigger atomic radius?
Answer :
a. D(19): 2,8,8,1 has 1 valence electron.
b. A(4): 2, 2 and E(20): 2, 8, 8, 2 belong to same group because they have the same number of valence electrons.
c. A(2, 2), B(2, 7) belong to the same period. A has bigger atomic radius than B.
Question. Write the main aim of classifying elements. Name the basic property of elements which is used in the development of Modern Periodic Table. State the Modern Periodic Law. On which side (part) of the Modern Periodic Table do you find metals, metalloids and non- metals?
Answer :
Classification is done so as to study the properties of 118 elements easily. Modern periodic table is based on atomic number of the atom an element. ‘Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers.’ Metals are placed on the left and middle, non-metals are placed on the right and Metalloids are placed on the border line between metals and nonmetals in a zig-zag manner.



