Please refer to the Class 11 Accountancy Sample Paper below. These CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Accountancy have been prepared based on the latest guidelines and examination patterns issued for the current academic year. We have provided Term 1 and Term 2 sample papers with solutions. You can click on the links below and access the free latest CBSE Sample Papers for Accountancy for Standard 11. All guess papers for Accountancy Class 11 have been prepared by expert teachers. You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected to come in the examinations and get better marks.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Accountancy
| Term 2 Sample Papers |
| Class 11 Accountancy Sample Paper Term 2 with Solutions Set A |
Class 11 Accountancy Sample Paper Term 2 with Solutions Set A
Part – A
1. State any three features of trial balance.
Answer : The features of a trial balance are as follows (any three)
(i) Trial balance contains a list of all ledger accounts including cash account.
(ii) It is a statement, not an account.
(iii) It can be prepared at any time during the accounting period i.e., at the end of any chosen period which may be monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annually depending upon the requirements.
(iv) It is not an absolute proof of the accuracy of accounting records.
(v) It is prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts.
Or
From the following information, draw up a trial balance in the books of Shri Manmohan as on 31st March,
2021. Capital ₹ 1,12,000; purchases ₹ 28,800; discount allowed ₹ 960; carriage inwards ₹ 6,960; carriage outwards ₹ 1,840; sales ₹ 48,000; return inwards ₹ 240; return outwards ₹ 560; rent and taxes ₹ 960; plant and machinery ₹ 64,560; stock on 1st April, 2020 ₹ 12,400; sundry debtors ₹ 16,160; sundry creditors ₹ 9,600; investments ₹ 2,880; commission received ₹ 1,440; cash in hand ₹ 80; cash at bank ₹ 8,080; motor cycle ₹ 27,680 and stock on 31st March, 2021 (not adjusted) ₹ 16,400.
Answer :


Note Closing stock will not be taken in the trial balance because it represents a part of the goods purchased but not yet sold. As the total purchases have been included in the trial balance, there is no need of including closing stock again.
If closing stock is adjusted against purchases, then only closing stock is shown in the trial balance.
2. Who is a notary public? Enumerate the facts which are noted by notary public when a bill is dishonoured.
Answer : Notary public is an officer appointed by the central government or state government to exercise the power and functions relating to noting and protesting negotiable instrument for dishonour.
The following facts are generally noted by the notary public
(i) Date, facts and reasons of dishonour.
(ii) If the bill is not expressly dishonoured, the reasons why it is being treated as dishonoured.
(iii) The amount of noting charges.
Or
On 1st January, 2020, Rao sold goods worth ₹ 20,000 to Reddy. Half of the payment was made immediately and for the remaining half, Rao drew a bill of exchange upon Reddy payable after 30 days. Reddy accepted the bill and returned it to Rao. On the due date, Rao presented the bill to Reddy and received the payment. Journalise the above transactions in the books of Rao and prepare Rao’s account in the books of Reddy.
Answer :

3. Name the errors, which affect the trial balance.
Answer : Errors which affect the trial balance are one sided errors and are disclosed by trial balance. Thus, trial balance does not tally if these errors are made.
Following are the errors which affect the agreement of trial balance
(i) Error of casting
(ii) Error in carrying forward
(iii) Error of posting to the wrong side but in correct account
(iv) Posting twice in an account
(v) Error in posting with wrong amount
(vi) Error of partial omission
(vii) Error in totalling or balancing of an account
4. Give journal entries to rectify the following errors.
(i) ₹ 65,000 paid for furniture purchased has been debited to purchases account.
(ii) ₹ 10,000 paid to Golu for salary were debited to his personal account.
(iii) An amount of ₹ 64,000 spent on annual white-washing was debited to building account.
Shubhangi Jain, PGT commerce at Jain Public School gave assignment on financial statements (without adjustments) to all weak students during remedial class.
All the students were able to correctly solve all questions except Mohak Bansal.
She decided to observe Mohak’s behaviour during the class and analysed his assignment carefully Following errors were done by Mohak
(i) He has wrongly shown items in debit and credit side of trading account and profit and loss account.
(ii) He has copied wrong formulae of adjusted purchases from the book.
(iii) He don’t know about the items to be shown in balance sheet
(iv) He has done mistakes in totalling.
Shubhangi, after analysing his assignment again, discovered that he has visual dyslexia.
Answer :

Part – B
5. Which of the following is correct formula of adjusted purchases?
(a) Adjusted Purchases = Purchases + Opening Stock + Direct Expenses − Closing Stock
(b) Adjusted Purchases = Net Purchases + Opening Stock − Closing Stock
(c) Adjusted Purchases = Net Purchases + Closing Stock − Opening Stock
(d) Adjusted Purchases = Net Purchases + Closing Stock + Direct Expenses − Opening Stock
Answer
B
6. Can you identify where contingent liabilities are shown while preparing financial statements.
(a) They are shown on liabilities side of balance sheet
(b) They are shown as a footnote below the balance sheet
(c) They are shown on debit side of profit and loss account
(d) They are added to capital in balance sheet
Answer
B
7. Which of the following item(s) is/are not shown in profit and loss account?
(i) Royalty
(ii) Export duties
(iii) Warehousing expenses
(iv) Consumable stores
Alternatives
(a) Only (i)
(b) Only (ii) and (iii)
(c) Only (ii)
(d) Only (i) and (iv)
Answer
D
8. Sales during the year 2021 ₹ 2,85,000 and Gross profit is 25% on sales. Cost of goods sold in given question is
(a) ₹ 2,13,750
(b) ₹ 3,56,250
(c) ₹ 2,22,750
(d) ₹ 3,57,250
Answer
A
9. Identify the correct arrangement of assets listed in order of liquidity in a balance sheet.
(a) Land and Building, Plant and Machinery, Bills Receivable, Cash in Hand.
(b) Bills Receivable, Cash in Hand, Land and Building, Plant and Machinery.
(c) Cash in Hand, Bills Receivable, Plant and Machinery, Land and Building.
(d) Cash in Hand, Bills Receivable, Plant and Machinery, Land and Building.
Answer
C
10. Mention main components/parts of a computer and draw a block diagram depicting the same.
Answer : Main components of computer are as follows
(i) Input Unit
(ii) Output Unit
(iii) Central Processing Unit (CPU) It has two main unit
(a) Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
(b) Control Unit
(iv) Memory Unit

Or
Explain any three types of software.
Answer : Types of software are as follows
(i) Language Processors It translate or interpret the program written in a programming language into machine language.
(ii) System Software It controls internal functions such as reading data from input devices and checking the system to ensure that its components are functioning properly.
(iii) Application Software It is designed and developed for performing certain specified tasks such as payroll accounting, inventory accounting , etc.
11. State whether the following expenditures are capital or revenue in nature.
(i) Payment of rent ₹ 50,000
(ii) Custom duty ₹ 10,000 paid on import of a machinery.
(iii) Air conditioning of the office of director ₹ 1,00,000.
(iv) Annual Insurance premium paid on car ₹ 1,000.
(v) Electricity bill of office ₹ 50,000
Answer : (i) Payment of rent ₹ 50,000 is revenue expenditure because it is incurred for day to day conduct of the business.
(ii) Custom duty ₹ 10,000 paid on import of a machinery is capital expenditure because it is incurred for the acquisition of a new asset.
(iii) It is a capital expenditure because the benefit of this expenditure will be available for number of years.
(iv) It is a revenue expenditure because it will not increase the value of the car and its benefit will be exhausted within the year.
(v) It is a revenue expenditure because it is a part of operating cost.
Or
From the following trial balance and additional information of Mr Rajesh Ahuja, a proprietor, prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2020 and balance sheet as at that date.

Closing stock at cost ₹ 2,00,000 but at market price ₹ 1,77,000
Answer :
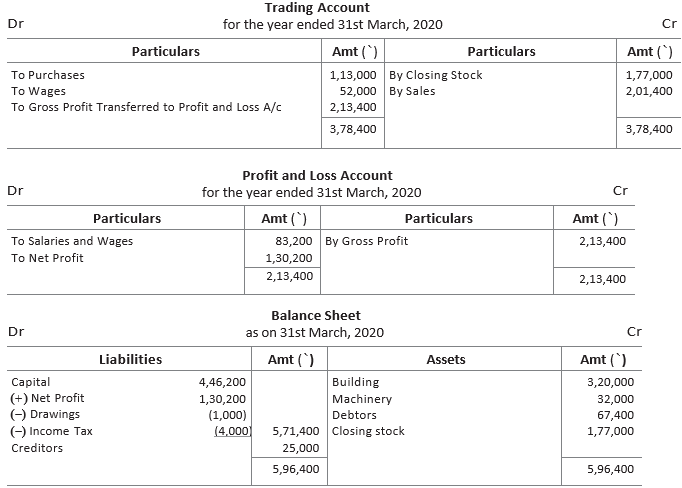
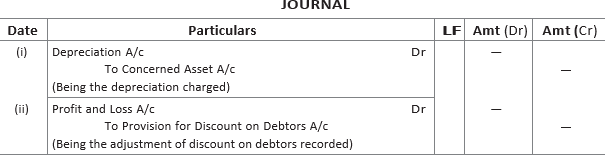
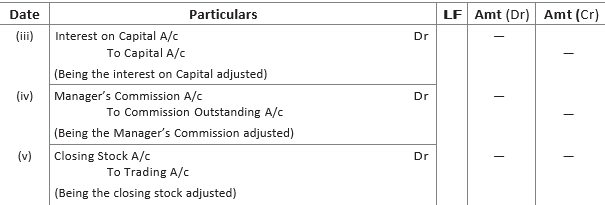
12. What adjusting entries would you record for the following?
(i) Depreciation
(ii) Discount on debtors
(iii) Interest on capital
(iv) Manager’s commission
(v) Closing stock
Answer :
Or
From the following trial balance, prepare the trading and profit and loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2020 and the balance sheet as at that date.

Additional Information
(i) Closing stock ₹ 40,000.
(ii) Goods costing ₹ 4,000 were taken by the proprietor for personal use.
(iii) A credit sale of ₹ 16,000 was not recorded in the sales book.
(iv) Maintain provision for doubtful debts @ 5%.
Answer :


13. Balance sheet is not prepared under single entry system. Is it true? If not, identify the statement of financial position produced from incomplete accounting record.
Enumerate few points about it and show its format?
Answer : Yes, Balance sheet is not prepared under single entry system.
Statement of affairs is prepared at the beginning of year and at the end of the accounting period. It is a statement of all assets and liabilities. Assets are shown on one side and the liabilities on the other, just as in case of a Balance sheet. It is also based on accounting equation, viz.
Capital = Assets − Liabilities.
Format of statement of affairs is given below

Or
M/s Shyama Sports Equipment does not keep proper records. From the following information, find out profit or loss for the year ended 31st December, 2020.

Drawings ₹ 10,000 per month for personal use and fresh capital introduced during the year ₹ 2,00,000.
A bad debts of ₹ 2,000 and a provision of 5% to be made on debtors. Outstanding salary ₹ 2,400, prepaid insurance ₹ 700 and depreciation on furniture and machinery @ 10% p.a.
Answer :



14. ‘‘Accounting software is an integral part of the computerised accounting system’’, explain. Briefly list the generic considerations before sourcing accounting software.
Answer : The following factors are usually taken into consideration before sourcing an accounting software
(i) Flexibility The choice of accounting software depends on the degree of flexibility it offers, in respect of data entry and the availability and design of various reports expected from it. The user should be able to run the software on variety of computer environments and machines.
(ii) Cost of Installation and Maintenance The cost of installation and maintenance are important considerations in the choice of software. Sometimes, certain software which are cheap involve heavy maintenance and alteration costs, e.g., cost of addition of modules, training of staff, etc. Conversely, the accounting software which are expensive may require least maintenance and free upgrading and negligible alteration costs.
(iii) Size of Organisation The choice of software also depends on the size of organisation and volume of business. The single user operated software may be useful for small organisations having less number of transactions. Whereas sophisticated software may be best suited for large organisations, to meet the multi-user requirements.
(iv) Ease of Adaptation and Training Needs The software must be capable of attracting users and be able to motivate its potential users. Some accounting softwares are user friendly and require simple training. However, some other complex softwares packages require intensive training on a continuous basis.
(v) Utilities/MIS Reports The choice of software also depends on the MIS report and the degree to which they are used in the organisation.
(vi) Expected Level of Secrecy The choice of accounting software also depends on the level of security features offered by it. Software should be able to prevent unauthorised access and manipulation of data.
(vii) Exporting/Importing Data Facility The accounting software should allow easy data transfer to other systems or software for flexible reporting such as organisations may transfer information directly from the ledger into spreadsheet software such as lotus or excel.
(viii) Vendors Reputation and Capability Another important consideration in the choice of accounting software is the capability and reputation of the vendor. This depends upon how long the vendor has been in the business of software development, whether there are other users of the software and extent of support available from people other than the vendor.



