Please refer to the Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper below. These CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared based on the latest guidelines and examination patterns issued for the current academic year. We have provided Term 1 and Term 2 sample papers with solutions. You can click on the links below and access the free latest CBSE Sample Papers for Social Science for Standard 10. All guess papers for Social Science Class 10 have been prepared by expert teachers. You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected to come in the examinations and get better marks.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science
Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper Term 1 With Solutions Set A
Choose and write the correct option in the following questions.
1. What major issue was criticised against by the liberal nationalists?
(a) Censorship laws to control the press
(b) Preservation of the Church
(c) A modern army
(d) Efficient bureaucracy
Answer
A
2. Under which of the following is power shared in the ‘Community Government’ of Belgium?
(a) Different social groups
(b) Different organs of government
(c) Central and State government
(d) State government and Community government
Answer
D
3. Which one of the following is not true for pulses?
(a) Pulses are grown in both rabi and kharif seasons.
(b) Pulses are leguminous crops.
(c) They are grown in rotation with other crops.
(d) Pulses require intensive irrigation facilities.
Answer
D
4. Which of the following is not the form of power sharing?
(a) Vertical division of power
(b) Horizontal division of power
(c) Division of power between people
(d) Division of power among social groups
Answer
C
5. What did ‘Das Volk’ stand for?
(a) Democracy
(b) Factory workers
(c) Slum dwellers
(d) common people
Answer
D
6. Which one of the following statements about power sharing arrangement is correct?
(a) Power sharing is necessary only in societies which have religious, linguistic or ethnic divisions.
(b) Power sharing is suitable only for big countries that have regional divisions.
(c) Every society needs some form of power sharing even if it is small or does not have social divisions.
(d) Power sharing is not necessary at all.
Answer
C
7. Development is sustained by the _.
(a) conservation of resources and the environment
(b) conservation of the factors of production
(c) continuous increase in per capita income
(d) continuous increase in gross domestic product
Answer
D
8. The term ‘Universal Suffrage’ means:
(a) the right to vote and get elected, granted only to men.
(b) the right to vote for all adults.
(c) the right to vote and get elected, granted exclusively to property owning men.
(d) the right to vote and get elected, granted only to educated men and women.
Answer
B
9. The task of measuring GDP is undertaken by the
(a) central government
(b) state government
(c) provincial government
(d) all of the above
Answer
A
10. Which among the following is more likely to be the developmental goal of a landless labour?
(a) To be able to visit abroad frequently
(b) More days of work with better wages
(c) To send his children in one of the best school in a nearby city
(d) To be able to buy expensive clothes from the nearby market
Answer
B
11. Which is the right condition for the growth of maize?
(a) Temperature between 21 to 27 degrees Celsius and old alluvial soil
(b) Temperature below 17 degree Celsius and shallow black soil
(c) Temperature of 25 degrees Celsius and 200 cm of rainfall
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
12. The belief that the majority community should be able to rule a country in whichever way it wants, by disregarding the wishes and needs of the minority is
(a) Power sharing
(b) Absolutism
(c) Majoritarianism
(d) Community government
Answer
C
13. Which of the following is not a feature or belief of ‘Conservatism’?
(a) Conservatives believe in established, traditional institutions of state and policy.
(b) Conservatives stressed the importance of tradition and preferred gradual development to quick change.
(c) Conservatives proposed to return to the society of pre-revolutionary days and were against the ideas of modernisation to strengthen monarchy.
(d) Conservatives believed in the monarchy, church, and other social hierarchies.
Answer
B
14. How do big private companies contribute in the development of a nation?
(a) By increasing the demands for their products through advertisements.
(b) By increasing their profits.
(c) By increasing productivity of the country in the manufacturing of industrial goods.
(d) By providing private hospital facilities for the rich.
Answer
C
Case-based Question–I :
Read the source given below and answer the questions (15-18) that follow:
The most serious source of nationalist tension in Europe after 1871 was the area called the Balkans. The Balkans was a region of geographical and ethnic variation comprising modern-day Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, Greece, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Slovenia, Serbia and Montenegro whose inhabitants were broadly known as the Slavs. A large part of the Balkans was under the control of the Ottoman Empire. The spread of the ideas of romantic nationalism in the Balkans together with the disintegration of the Ottoman Empire made this region very explosive. All through the nineteenth century the Ottoman Empire had sought to strengthen itself through modernisation and internal reforms but with very little success. One by one, its European subject nationalities broke away from its control and declared independence. The Balkan peoples based their claims for independence or political rights on nationality and used history to prove that they had once been independent but had subsequently been subjugated by foreign powers. Hence the rebellious nationalities in the Balkans thought of their struggles as attempts to win back their long-lost independence.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
15. The Ottoman Empire sought to strengthen itself through:
(a) Modernisation
(b) internal reforms
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of the above
Answer
C
16. The Balkan peoples based their claims for __________ or on nationality.
(a) independence, political rights
(b) power sharing, federalism
(c) secularism, political rights
(d) modernisation, strength
Answer
A
17. The most serious source of nationalist tension in Europe after 1871 was the area of _.
(a) Ottoman Empire
(b) Balkans
(c) Greece
(d) Albania
Answer
B
18. The spread of the ideas of romantic nationalism was responsible for:
(a) disintegration of Greece
(b) Balkans disintegration from the Ottoman Empire
(c) integration of Macedonia
(d) none of the above
Answer
B
Case-based Question–II :
Read the source given below and answer the questions (19-22) that follow:
Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue.
In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless.
Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals.
Community owned resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there.
National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals.
Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land.
All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
19. The resources which are owned by the community are:
(a) plantation
(b) pasture land
(c) ponds
(d) all the above
Answer
D
20. Which one of the following is an example of Biotic Resources?
(a) Rock
(b) Mountain
(c) Mineral
(d) Flora
Answer
D
21. On the basis of ownership, plantations can be better considered as which of the following types of resources?
(a) Individual resource
(b) Community owned resource
(c) National resource
(d) International resource
Answer
A
22. The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone can be termed as which of the following types of resource?
(a) Individual resources
(b) Community owned resources
(c) National resources
(d) International resources
Answer
D
Case-based Question–III :
Read the source given below and answer the questions (23-26) that follow:
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need. Whatever people like, and should have, they will be able to get with greater income. So, greater income itself is considered to be one important goal. Now, what is the income of a country? Intuitively, the income of the country is the income of all the residents of the country. This gives us the total income of the country. However, for comparison between countries, total income is not such an useful measure. Since, countries have different populations, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn. Are people in one country better off than others in a different country? Hence, we compare the average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
23. Per capita income is:
(a) Income per person
(b) Income per family
(c) Income per earning person
(d) Income per month
Answer
A
24. In World Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, which criterion is used in Classifying countries?
(a) Total income
(b) Gross income
(c) per capita income
(d) Net income
Answer
C
25. The average income is also called:
(a) Per capita profit
(b) Per capita income
(c) Limited income
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
26. What is the most important attribute while comparing countries?
(a) Their population
(b) Their political status
(c) Their income
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Case-based Question–IV :
Read the source given below and answer the questions (27-30) that follow:
Power is shared among different organs of government, such as the legislature, executive and judiciary. Let us call this horizontal distribution of power because it allows different organs of government placed at the same level to exercise different powers. Such a separation ensures that none of the organs can exercise unlimited power. Each organ checks the others. This results in a balance of power among various institutions. We studied that in a democracy, even though ministers and government officials exercise power, they are responsible to the Parliament or State Assemblies. Similarly, although judges are appointed by the executive, they can check the functioning of executive or laws made by the legislatures. This arrangement is called a system of checks and balances.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
27. Power sharing is between –
(a) legislature, executive and parliament
(b) legislature, executive and judiciary
(c) legislature, high court and judiciary
(d) none of the above
Answer
B
28. It allows different organs of government placed at the same level to exercise different powers is known as _.
(a) circular distribution of power
(b) vertical distribution of power
(c) horizontal distribution of power
(d) all the above
Answer
C
29. Judges are appointed by the executive, they can check the functioning of executive or laws made by the legislatures, known as _.
(a) horizontal distribution of power
(b) checks and balances
(c) vertical distribution of power
(d) all the above
Answer
B
30. Power sharing means –
(a) system of political arrangements in which power is shared between ministers of the government
(b) system of political arrangements in which power is shared between different organs of the government
(c) system of political arrangements in which power is shared between different levels of government
(d) all the above
Answer
B
The following questions (31-38) consist of two statements — Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
31. Assertion (A) : The development of nationalism did not come about only through wars and territorial expansion.
Reason (R) : Culture played an important role in creating the idea of the nation: art and poetry, stories and music helped express and shape nationalist feelings.
Answer
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
32. Assertion (A) : Arid soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau.
Reason (R) : Yellow and red soils are also found in parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, southern parts of the middle Ganga plain and along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
Answer
(d) A is false but R is true.
33. Assertion (A) : In Belgium, the Dutch community could take advantage of its numeric majority and force its will on the French and German-speaking population.
Reason (R) : In Sri Lanka, the Sinhala community enjoyed an even bigger majority and could impose its will on the entire country.
Answer
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
34. Assertion (A) : Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends.
Reason (R) : But the quality of our life does not depend on non-material things.
Answer
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
35. Assertion (A) : Although judges are appointed by the executive, they can check the functioning of executive or laws made by the legislatures.
Reason (R) : This arrangement is called a system of chess and balances.
Answer
(c) A is true but R is false.
36. Assertion (A) : The developmental goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
Reason (R) : A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Answer
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
37. Assertion (A) : The 1830s were years of great economic hardship in Europe.
Reason (R) : National Assembly proclaimed a Republic, granted suffrage to all adult males above 21, and guaranteed the right to work.
Answer
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
38. Assertion (A) : Laterite has been derived from the Latin word ‘later’ which means brick.
Reason (R) : The Forest soil develops under tropical and subtropical climate with alternate wet and dry season.
Answer
(c) A is true but R is false.
The following questions (39 – 40) are based on map. Answer the questions by selecting the correct option marked on the map.
39. Select the correct name of the dam that is marked on the map.

(a) Rana Pratap Sagar
(b) Bhakar Nagal
(c) Tehri
(d) Salal
Answer
B
40. Select the correct name of the dam that is marked on the map.
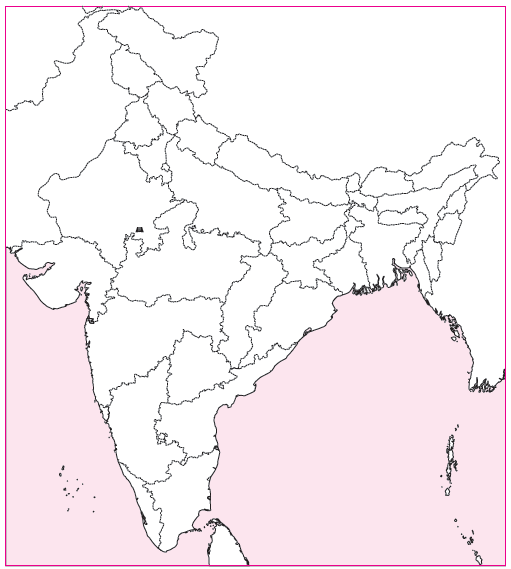
(a) Rana Pratap Sagar
(b) Sardar Sarovar
(c) Tungabhadra
(d) Tehri
Answer
A

