Students can read the important questions given below for Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry. All Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions provid ed for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Chemistry Question Bank Class 12 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the given compound :
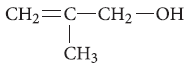
Answer. 2-Methylprop-2-en-1-ol
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:

Answer. 3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following compound :
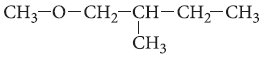
Answer. 1-methoxy-2-methylbutane
Question. The C — O bond is much shorter in phenol than in ethanol. Give reason.
Answer. Due to resonance C—O bond acquires some partial double bond character.
So, in phenol C—O bond length is smaller than ethanol.
Question. Which of the following isomers is more volatile :
o-nitrophenol or p-nitrophenol?
Answer. o-Nitrophenol is more steam volatile than p-Nitrophenol due to the presence of intramolecular H-bonding. p-nitrophenol shows intermolecular H–bonding.
Question. Write the equation involved in the following reaction :
Reimer –Tiemann reaction
Answer.
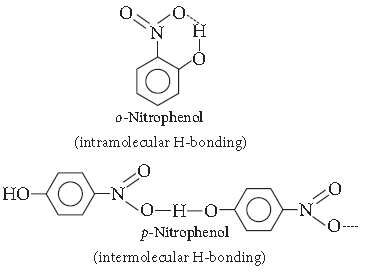
That’s why o-nitrophenol has lower boiling point than p-nitrophenol.
Question. Name the following according to IUPAC system :
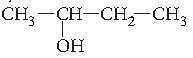
Answer. Butan-2-ol
Question. Write the structure of the molecule of compound whose IUPAC name is 1-Phenylpropan-2-o1
Answer.
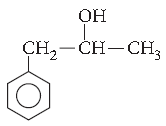
Question. Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
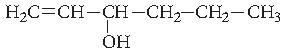
Answer. Hex-1-en-3-ol
Question. Write the structure of the following compound :
2-Methyl-2-ethoxypentane.
Answer.
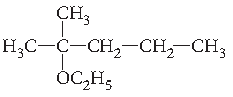
Question. Write the equation involved in the following reaction :
Kolbe’s reaction
Answer. Reimer–Tiemann reaction
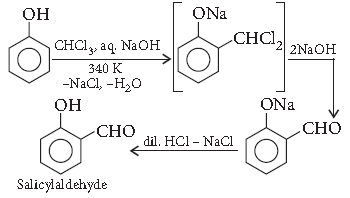
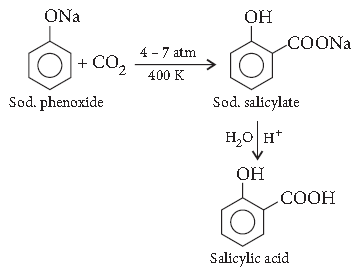
Question. How is toluene obtained from phenol?
Answer. Kolbe’s reaction : When sodium phenoxide is heated with carbon dioxide under pressure, it gives salicylic acid.
Question. Give a chemical test to distinguish between 2-propanol and 2-methyl-2-propanol.
Answer. 2-propanol will give yellow precipitate of iodoform on addition of I2 and NaOH while 2-methyl-2-propanol will not.
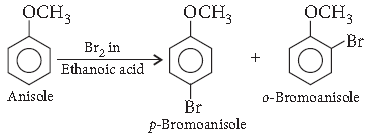
Question. How is the following conversion carried out?
Anisole to p-bromoanisole
Answer.
Question. Write the equations involved in the following reaction :
Williamson synthesis
Answer. Williamson ether synthesis : Alkyl halide when treated with sodium alkoxide gives dialkyl ether.
C2H5ONa + C2H5Cl → C2H5 — O — C2H5 + NaCl
Question. How would you convert ethanol to ethene?
Answer.
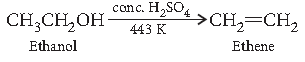
Question. Write IUPAC name of the following compound :
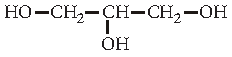
Answer. Propane-1,2,3-triol
Question. Write IUPAC name of the following :
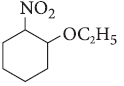
Answer. 1-Ethoxy-2-nitrocyclohexane.
Question. Account for the following :
The boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols.
Answer. The boiling points of ethers are much lower than, those of alcohol of comparable molar masses because like alcohols they cannot form intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
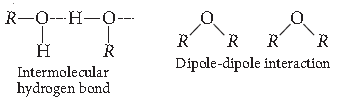
Question. Phenylmethyl ether reacts with HI to give phenol and methyl iodide and not iodobenzene and methyl alcohol. Why?
Answer. Protonation of anisole (Phenyl methyl ether) gives methyl phenyl oxonium ion.
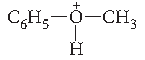
In this ion, the stronger bond is O—C6H5. Therefore, attack by I– ion exclusively breaks the weaker O—CH3 bond forming methyl iodide and phenol. The phenol formed does not react further to give aryl halides.
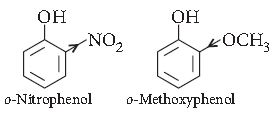
Question. Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than orthomethoxyphenol. Why?
Answer. As we know that the electron withdrawing groups enhance the acidic character of phenols because they help in the stabilisation of phenoxide ion be dispersing negative charge. Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group whereas methoxy group destabiliser the phenoxide ion by intensifying the negative charge. Thus, o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol.
Question. Draw the structural formula of 2-Methylpropan-2-ol molecule.
Answer.
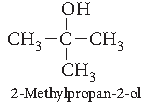
Short Answer Questions
Question. Explain the mechanism of dehydration steps of ethanol :
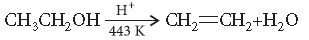
Answer. Acid catalysed dehydration of alcohols at high temperature takes place with formation of an alkene.
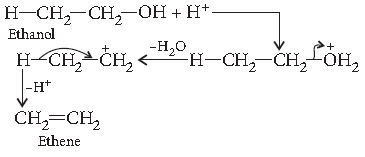
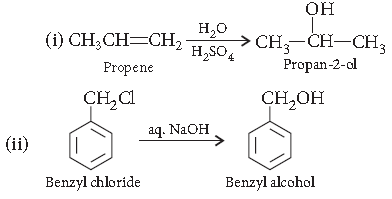
Question. How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Propene to propane-2-ol
(ii) Benzyl chloride to Benzyl alcohol
Answer.
Question. Give the names of the reagents of bringing about the following transformations :
(i) Hexan-1-ol to hexanal
(ii) But-2-ene to ethanol
Answer.
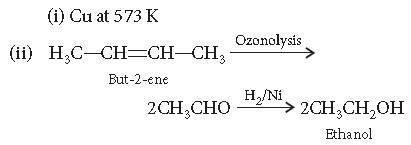
Question. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Boiling point of ethanol is higher in comparison to methoxymethane.
(ii) (CH3)3C—O—CH3 on reaction with HI gives CH3OH and (CH3)3C—I as the main products and not (CH3)3C—OH and CH3I.
Answer. (i) Ethanol has higher boiling point because of strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding whereas in methoxymethane, molecules are held by dipoledipole interaction.
(ii) When one alkyl group is a tertiary group the halide formed is tertiary halide.
In step II the departure of leaving group (CH3—OH) creates a more stable carbocation (3°) and the reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
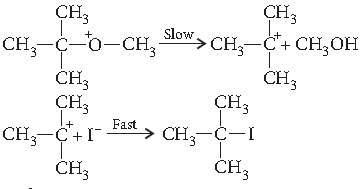
Question. Write the mechanism of the following reaction :
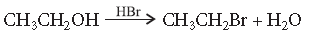
Answer. The reaction proceeds through nucleophilic substitution bimolecular (SN2) mechanism, as shown below :
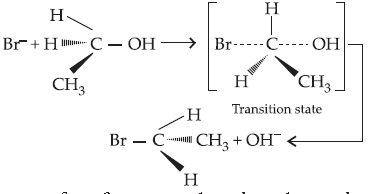
Inversion of configuration takes place during the reaction.
Question. Write the mechanism of the following reaction :
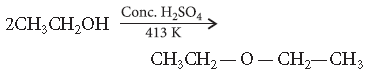
Answer. Mechanism : The formation of ether is nucleophilic bimolecular reaction.
Question. Name the reagents which are used in the following conversions :
(i) A primary alcohol to an aldehyde
(ii) Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol
(iii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
Answer. (i) Copper at 573 K
(ii) Sodium borohydride (NaBH4)
(iii) Bromine water (Br2(aq))
Long Answer Questions
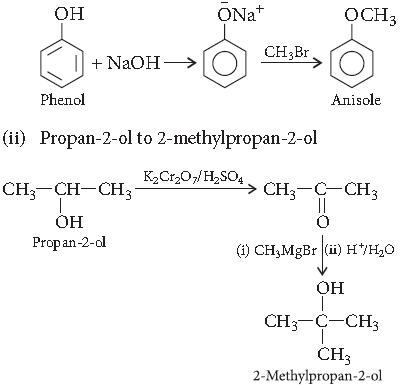
Question. How do you convert the following?
(i) Phenol to anisole
(ii) Propan-2-ol to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Aniline to phenol
Answer. (i) Phenol to anisole

Question. Predict the products of the following reactions :
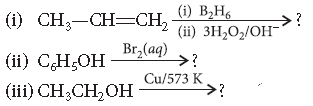
Answer.


