Please refer to Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology Important Questions given below. These solved questions for Biotechnology Principles and Processes have been prepared based on the latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. We have provided important examination questions for Class 12 Biology all chapters.
Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Important Questions
Diagram Type Question
Question. The given figure shows the E.Coli cloning vector PBR322 showing restriction sites. Some parts are labelled as A, B, C & D. Choose the option showing the correct labelling.
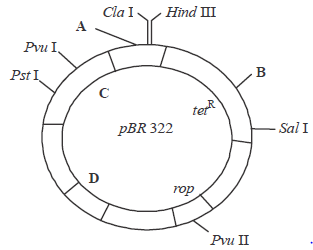
| A | B | C | D |
| (a) Hind I | EcoR I | ampR | ori |
| (b) Hind I | BamH I | kanR | ampR |
| (c) BamH I | Pst I | ori | ampR |
| (d) EcoR I | BamH I | ampR | ori |
Answer
D
Question. The given figure shows a simple stirred tank bioreactor with their parts labelled as A, B, C and D. Identify A, B, C and D.

(a) A-Motor; B-pH control; C-Foam braker; D-Sterile air
(b) A-pH control; B-Motor; C-Foam braker; D-Sterile air
(c) A-pH control; B-Sterile air; C-Motor; D-Foam braker
(d) A-Motor; B-Sterile air; C-pH control; D-Foam braker
Answer
A
Question. Identify the correct match of the technique with their role shown in the given figure.

(a) Electrophoresis – Differential migration of DNA fragments
(b) Column – Separation of chlorophyll chromatography pigments
(c) Gene cloning – Technique of obtaining identical copies of a particular DNA or a gene segment
(d) Microinjection – Technique of introducing foreign genes into a host cell
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Questions
Question. Restriction endonucleases
(a) are enzymes that process pre-RNA’s.
(b) are enzymes that degrade DNA.
(c) protect bacterial cells from viral infection.
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. A gene is said to be cloned if
(a) the DNA sequence of the gene is known.
(b) the function of the gene is known.
(c) there is a DNA probe for the gene.
(d) the gene has been isolated and copied.
Answer
D
Question. DNA fragments are separated using gel electrophoresis
(a) because DNA is pulled through the gel towards the negative end of the field.
(b) because larger DNA fragments move faster through the gel than smaller DNA fragments.
(c) to identify and isolate DNA fragments.
(d) to synthesize DNA for cloning.
Answer
C
Question. Imagine a gel through which DNA fragments have moved in response to an applied electrical current. The band on this gel that is farthest from the top (that is, from the place where the DNA fragments were added to the “well”) represents the
(a) shortest fragments of DNA.
(b) longest fragments of DNA.
(c) restriction enzyme used to cut the DNA into fragments.
(d) ligase used to bind the DNA fragments together.
Answer
A
Question. In genetic engineering, where genes can be inserted from one organism into another or back into the original organism uses which of the following techniques?
(a) Polymerase chain reaction
(b) Gene gun
(c) DNA hybridization
(d) Gel electrophoresis
Answer
B
Question. Biolistics (gene-gun) is suitable for
(a) DNA finger printing.
(b) Disarming pathogen vectors.
(c) Transformation of plant cells.
(d) Constructing recombinant DNA molecules.
Answer
D
Question. Plasmid present in bacterial cells are
(a) circular double helical DNA molecules.
(b) linear double helical DNA molecules.
(c) circular double helical RNA molecules.
(d) linear double helical RNA molecules.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following has the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells in animals ?
(a) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(b) Retroviruses
(c) DNA-viruses
(d) Plasmids
Answer
B
Question. A kind of biotechnology involving manipulation of DNA is called
(a) DNA replication
(b) genetic engineering
(c) denaturation
(d) renaturation
Answer
B
Question. Restriction-modification systems of bacteria exist to
(a) protect bacteria from invading foreign DNA.
(b) promote conjugation.
(c) help the bacterial chromosome to replicate.
(d) encourage recombination of new genetic material.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following process require energy?
(a) Ligation
(b) Transformation
(c) Restriction digestion
(d) Hybridization
Answer
A
Question. Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which
(a) make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule.
(b) recognize a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase.
(c) restrict the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
(d) remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule.
Answer
A
Question. The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of
(a) insertional inactivation of alphaga-lactosidase in nonrecombinant bacteria.
(b) insertional inactivation of alpha-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria.
(c) inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria.
(d) non-recombinant bacteria containing betagalactosidase.
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Mention the role of Restriction Enzymes in Recombinant DNA technology.
Answer : To cut DNA at specific sites / Molecular scissors (DNA).
Question. Name two enzymes that are essential for constructing a recombinant DNA.
Answer : Restriction enzymes / polymerase enzymes / ligase.
Question. What is the name of the process given to separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing?
Answer : After completion of the biosynthetic stage, the product has to be subjected to a series of processes before it is ready for marketing as a finished product.
The processes include separation & purification,which are collectively referred to as downstream processing.
Question. Mention the use of gel electrophoresis in biotechnology experiments.
Answer : Cut fragments of DNA can be segregated / separated.
Question. Write the function of a bioreactor.
Answer : Bioreactors are required to produce large volumes (100 – 1000 litres) of recombinant proteins / desired protein / enzymes.
Question. Write the two components of the first artificial recombinant DNA molecule constructed by Cohen and Boyer.
Ans. The two components were—antibiotic resistance gene and plasmid vector of Salmonella typhimurium.
Question. Why is it not possible for an alien DNA to become part of a chromosome anywhere along its length and replicate normally?
Ans. Alien DNA must be linked to ori or origin of replication site to start replication.
Question. What is the host called that produces a foreign gene product? What is this product called?
Ans. The host that produces a foreign gene product is called competent host. The product is called recombinant protein.
Question. Which main technique and instrument is used to isolate DNA from any plant cell?
Ans. Centrifugation and centrifuge
Question. Mention the uses of cloning vector in biotechnology.
Ans. Cloning vectors are used for transferring fragments of foreign DNA into a suitable host. They are also used to select recombinants from non-recombinants.
Question. How does an alien DNA gain entry into a plant cell by ‘biolistics’ method?
Ans. In biolistics method, cells are bombarded with high velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA.
Question. Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Ans. A recombinant DNA is made during pachytene stage of meiosis-I by crossing over.
Question. What is the function of restriction enzyme?
Ans. To cut DNA at specific site.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Collect 5 examples of palindromic DNA sequences by consulting your teacher. Better try to create a palindromic sequence by following base-pair rules.
Ans. (i) 5′ G A A ′ T T C 3 (ii) 5′ G G A T C C 3′
3′ C T T A A G 5′ 3′ C C T A G G 5′
(iii) 5′ A C T A G′ T 3 (iv) 5′ A A G C T T 3′
3′ T G A T C A 5′ 3′ T T C G A A 5′
(v) 5′ A G G C′ C T 3
3 ′ T C C G ′ G A
Question. How are recombinant vectors created? Why is only one type of restriction endonuclease required for creating one recombinant vector?
Ans. The construction of recombinant DNA is done by linking a gene encoding antibiotic resistance with a native plasmid. These plasmid DNA act as vectors to transfer the piece of DNA attached to it.
Only one type of restriction endonuclease is required for creating recombinant vector because when cut by the same enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have the same sticky ends, which can be joined together using DNA ligases.
Question. (a) A recombinant vector with a gene of interest inserted within the gene of α-galactosidase enzyme, is introduced into a bacterium. Explain the method that would help in selection of recombinant colonies from non-recombinant ones.
(b) Why is this method of selection referred to as “insertional inactivation”?
Ans. (a) Bacteria is grown in a medium with chromogenic substrate, blue coloured colonies show no recombinations and colonies with no blue colour show presence of recombinants.
(b) Gene for the enzyme is inactivated by insertion of foreign DNA.
Question. Discuss with your teacher and find out how to distinguish between (a) Plasmid DNA and chromosomal DNA (b) RNA and DNA
(c) Exonuclease and endonuclease
Ans. (a) Table 11.1: Differences between Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA
| S.No. | Plasmid DNA | Chromosomal DNA |
| (i) | This is present in prokaryotic cells (bacteria). | This is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. |
| (ii) | This is the circular extra-chromosomal DNA not associated with histone proteins. | It is linear and associated with histones proteins in eukaryotes but is double stranded and circular in prokaryotes. |
| (iii) | It gives the cell extra characters like antibiotic resistance. | It contains genes for characters essential for life of organism. |
(b) RNA and DNA
| S. No. | DNA | RNA |
| (i) | It has deoxyribose sugar. | It has ribose sugar. |
| (ii) | It is the genetic material in almost all organisms. | It is the genetic material in only some viruses. |
| (iii) | It is double stranded. | It is single stranded. |
| (iv) | It has A, G, C, T bases. | It has A, G, C, U bases. |
(c) Exonuclease and endonuclease
| S. No. | Exonuclease | Endonuclease |
| (i) | These cut the end regions of the DNA. | These cut at specific regions within the DNA. |
| (ii) | These act on single strand of DNA. | These act on both strands as well as on DNA strand. |
Question. Name the type of bioreactor shown. Write the purpose for which it is used.

Ans. The given bioreactor is the simple stirred tank bioreactor.
Its purpose is large scale production of recombinant protein or enzymes, using microbial plants/animals/human cells.
Question. Describe the role of CaCl2 in preparation of competent cells.
Ans. CaCl2 is known to increase the efficiency of DNA uptake to produce transformed bacterial cells.
The divalent Ca2+ ions supposedly create transient pores in the bacterial cell wall, by which the entry of foreign DNA is facilitated into the bacterial cells.
Question. How can the following be made possible for biotechnology experiments?
(a) Isolation of DNA from bacterial cell.
(b) Reintroduction of the recombinant DNA into a bacterial cell.
Ans. (a) By treating cell with lysozyme
(b) Microinjection/gene gun
Question. Write the role of ‘ori’ and ‘restriction’ site in a cloning vector pBR322.
Ans. ori is the site where replication starts. This site is responsible for controlling the copy number of linked DNA. If we want to produce many copies of target DNA, we should clone in a vector whose ori supports high copy number.
Restriction site is the site of ligation of alien/foreign DNA in the vector, in one of the two antibiotic resistance site or coding sequence of α-galactosidase.
Question. Name the source organism from which Ti plasmid is isolated. Explain the use of this plasmid in biotechnology.
Ans. Ti plasmid is isolated from Agrobacterium tumifaciens.
Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens has been modified into a cloning vector, which is not pathogenic to plants but still is able to use the mechanisms to deliver genes of interest into plants.
Question. While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Ans. If denaturation of double-stranded DNA does not take place, then primers will not be able to anneal to the template, no extension will take place, hence no amplification will occur.
Question. What would happen when one grows a recombinant bacterium in a bioreactor forget to add antibiotic to the medium in which the recombinant is growing bacterium?
Ans. In the absence of antibiotic, there will be no pressure on recombinants to retain the plasmid (containing the gene of your interest). Since, maintaining a high copy number of plasmids is a metabolic burden to the microbial cells, it will thus tend to lose the plasmid.
Question. Describe briefly the following:
(a) Origin of replication (b) Bioreactors (c) Downstream processing
Ans. (a) Origin of replication is a DNA sequence that initiates any piece of linked DNA to replicate and is also called ori site. It controls the copy numbers of the linked DNA.
(b) Bioreactors
• Bioreactors are vessels of large volumes (100–1000 litres) in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products.
• It provides all the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimal growth conditions like temperature, pH, substrates, salts, vitamins and oxygen.
• Stirred-tank bioreactors are commonly used bioreactors.
(c) Process of Recombinant DNA Technology
• Recombinant DNA technology involves the following steps:
(i) Isolation of DNA
(ii) Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonucleases
(iii) Isolation of a desired DNA fragment
(iv) Amplification of the gene of interest
(v) Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector
(vi) Insertio n of recombinant DNA into the host
(vii) Culturing the host cells on a suitable medium at a large scale
(viii) Extraction of the desired gene product
(ix) Downstream processing of the products as finished product
Question. Name the source of the DNA polymerase used in PCR technique. Mention why it is used.
Ans. The source is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus. It is used because it is thermostable and do not denature at high temperatures.
Question. Where and why do we use Taq polymerase enzyme when it works exactly as DNA polymerase?
Ans. In PCR, because it is a thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme, is isolated from bacteria Thermus aquaticus from hot water springs, and it does not get denatured at high temperature which is required during PCR and works as normal DNA polymerase enzyme (whereas the normal DNA polymerase gets denatured at high temperature).
Long Answer Questions
Question. (a) List the three steps involved in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
(b) Name the source organism of Taq polymerase. Explain the specific role of this enzyme in PCR.
Ans. (a) The three steps involved in polymerase chain reaction (PCR):
(i) Denaturation of double stranded DdNsDAN A( ) at high temperature.
(ii) Annealing of two sets of primers.
(iii) Extension of primers to form dsDNA by Taq polymerase and deoxynucleotides.
(b) Source organism of Taq polymerase is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus. This enzyme is heat tolerant and can repeatedly amplify DNA at high temperatures.
Question. Explain the action of the restriction endonuclease EcoRI.
Ans. (i) The recognition sequence shows palindrome character in which the sequence of base pairs read the same on both the DNA strands,i .e., same in 5′ → 3′ or 3′ → 5′ directions, e.g.,
5′ — G A A T T C — 3′
3′ — C T T A A G — 5′
(ii) The restriction endonuclease acts on specified length of a DNA and binds to the DNA at the recognition sequence.
(iii) It cuts the opposite double helix of DNA in the sugar-phosphate backbones, a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites.
(iv) There are overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand, which form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness of the ends facilitates the
action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. (a) Why must a cell be made ‘competent’ in biotechnology experiments? How does calcium ion help in doing so?
(b) State the role of ‘biolistic gun’ in biotechnology experiments.
Ans. (a) A cell must be made competent so that it can take up the hydrophilic DNA from the external medium. Divalent calcium ions increases the efficiency, of DNA entering the cell through pores in the cell wall.
(b) Biolistic gun is used to introduce alien DNA into the plant cell by bombarding them with high velocity microparticles (gold or tungsten coated with DNA).
Question. Draw a labelled sketch of sparged stirred-tank bioreactor. Write its application.
Ans.

bubbles are sparged.
Application: Produces larger biomass leading to higher yields of desired protein.
Question. “A very small sample of tissue or even a drop of blood can help determine paternity”. Provide a scientific explanation to substantiate the statement.
Ans. (i) DNA from all cells of an individual shows the same degree of polymorphism and therefore becomes a useful identification tool.
(ii) Polymorphs are heritable and the child inherits 50% of the chromosome from each parent.
(iii) With the help of PCR, the small amount of DNA from blood can be amplified and be used in DNA finger printing to identify the paternity.
Question. (a) With the help of diagrams show the different steps in the formation of recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoRI.
(b) Name the technique that is used for separating the fragments of DNA cut by restriction endonucleases.
Ans.
(b) Gel electrophoresis is used for separating the fragments of DNA cut by restriction endonucleases.
Question. If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some experiments, explain the process of the following:
(i) Cutting this desired gene at specific location.
(ii) Synthesis of multiple copies of this desired gene.
Ans. (i) The desired gene is cut using the enzymes restriction endonucleases. Firstly, the restriction endonucleases that recognise the palindromic nucleotide sequence of the desired gene is identified. The endonuclease inspects the entire DNA sequences to find and recognise the site. It cuts each of the double helix at a specific point which is a little away from the centre of the palindromic site. The cutting site is between the same two bases on the opposite strands.
This results in over-hanging single stranded stretches which act as sticky ends.
(ii) Multiple copies of the desired gene is synthesised by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. In this method, the desired gene is synthesised in vitro. The double stranded DNA is denatured using high temperature of 95°C and the strands are separated. Each separated strand acts as template.
Two sets of oligonucleotide primers are annealed to the denatured DNA strands. The thermostable Taq polymerase extends the primers, using nucleotides provided in the reaction
mixture. Finally the amplified fragments are ligated into recipient cells.
Question. (a) Mention the role of vectors in recombinant DNA technology. Give any two examples.
(b) With the help of diagrammatic representation only, show the steps of recombinant DNA technology.
Ans. (a) Role of vectors: The vectors have the ability to replicate within the bacterial cells independent of the control of chromosomal DNA. If an alien piece of DNA is linked to the vector like bacteriophage or plasmid DNA, it can be made to multiply, its number being equal to the copy number of the vector. Vectors are also used in the selection of recombinants from nonrecombinants. Plasmids and bacteriophages are the most commonly used vectors.
(b) Refer to Fig. 11.4. (Imge 397)
Question. A schematic representation of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) up to the extension stage is given below. Answer the questions that follow:
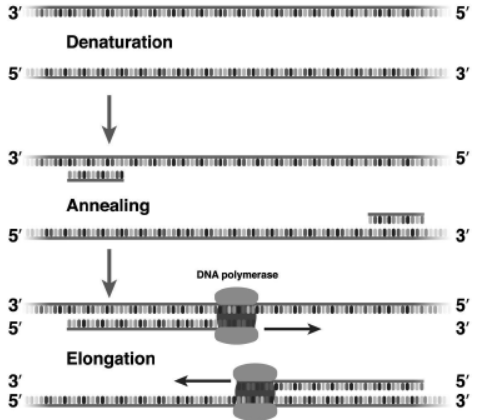
(i) Name the process ‘a’. (ii) Identify ‘b’
(iii) Identify ‘c’ and mention its importance in PCR.
Ans. (i) a—Denaturation process
(ii) b—Primers
(iii) c—Taq DNA polymerase. Taq polymerase is a thermostable enzyme which remains active
during the high temperature required for extension of DNA.
Question. Which methodology is used while sequencing the total DNA from a cell? Explain it in detail.
Ans. Methodology used:
• Sequence Annotation – total DNA from a cell is isolated, converted into random fragments of relatively smaller sizes, and cloned in suitable host using specialized vectors.
• The cloning resulted into amplification of each piece of DNA fragment.
• The fragments were sequenced using automated DNA sequencers, these sequences are then arranged based on some overlapping regions (present in them).
• This requires generation of overlapping fragments (for sequencing).
• Specialised computer based programmes were developed, and these sequences were subsequently annotated and assigned to each chromosome.
Question. (a) Explain how recombinants and non-recombinants are differentiated on the basis of colour production in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. Name that procedure.
(b) Describe the temperature treatment that enhances the bacteria to take up the rDNA.
Ans. (a) The procedure is called insertional inactivation.
In this method recombinants and non-recombinants are differentiated on the basis of the ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromosomic substrate. In this method, a rDNA is inserted in an enzyme – b-galactosidase which leads to inactivation of the enzyme which does not produce colour due to insertion.
(b) (i) Host cells are incubated rwDiNthA on ice.
(ii) Followed by placing them briefly at 42°C.
(iii) Then transfer them back on ice.
This enables the host cells (bacteria) to take up the rDNA.


