Please refer to Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound
Case/Passage – 1
A carbon atom attached to one, two, three and four other carbon atoms is called primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon respectively. Now consider following compound and answer the following questions.
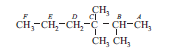
Question: In above compound how many carbon atom are primary?
(a) 7
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question: In above compound which carbon atom is quaternary?
(a) B
(b) D
(c) F
(d) C
Answer
D
Question: In above compound how many carbon atoms are secondary?
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 0
Answer
A
Case/Passage – 2
Reactions in which an atom or a group of atoms is replaced by some other atom or another group of atoms without causing any change in the structure of the remaining part of the molecule, are called substitution reactions.
All organic compounds containing double or triple bonds give addition reactions, i.e., alkenes, alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons give addition reactions.Reactions in which the compounds react with oxygen and form carbon dioxide and water is known as combustion reaction. This process occurs with release of great amount of heat.
Question: The reaction CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl is :
(a) substitution reaction
(b) addition reaction
(c) rearrangement reaction
(d) elimination reaction
Answer
A
Question: The reaction C2H6 + O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O is :
(a) substitution reaction
(b) rearrangement reaction
(c) addition reaction
(d) combustion reaction
Answer
D
Question: The reaction CH2 = CH2 + H2 → CH3 – CH3 is :
(a) substitution reaction
(b) addition reaction
(c) rearrangement reaction
(d) elimination reaction
Answer
B
Case/Passage – 3
The given diagram represent an experiment in which a test tube contains 1 mL of ethanol (absolute alcohol) and 1 mL glacial acetic acid along with a few drops of concentrated H2SO4. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
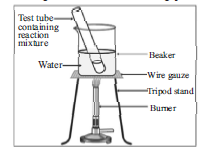
Question: Name the type of reaction taking place in this experiment.
Answer
Esterification reaction
Question: Why reverse of this reaction is known as saponification reaction?
Answer
Reverse reaction is known as saponification reaction because it is used in the prepration of soap.
Question: Give two uses of the resulting product.
Answer
Esters are used in making perfumes and as a flavouring agent
Question: Write the chemical equation.
Answer
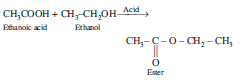
Case/Passage – 4
Study the table related to three hydrocarbons X, Y and Z carefully and answer the following questions from.

Question. X, Y and Z are classified as hydrocarbons because these contain:
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Carbon
(d) Both carbon and hydrogen
Answer
D
Question. To which series C5H10 belongs?
(a) CnH2n + 2
(b) CnH2n
(c) CnH2n – 2
(d) CnHn+2
Answer
B
Question. Choose the incorrect statement regarding above three hydrocarbons
(a) All have different general formula
(b) X and Y differ by –CH2 unit
(c) Z is an alkyne
(d) Y is an alkene
Answer
B
Study the table given below carefully and answer any four questions from :


Question. What is the molecular formula of K?
(a) C12H26
(b) C12H24
(c) C12H22
(d) C12H28
Answer
A
Question. Choose the correct statements regarding compounds H, J and K
(a) All have the same chemical properties
(b) All have different general formula
(c) All differ by –CH2 unit
(d) All have same melting and boiling points
Answer
A
Question. What is the molecular formula of J?
(a) C12H26
(b) C8H16
(c) C8H18
(d) C8H14
Answer
C
Question. Compounds H, J, K belong to which homologous series?
(a) CnH2n
(b) CnH2n–2
(b) CnH2n+2
(d) CnH2n+1
Answer
C
Case/Passage – 5
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions from The phenomenon of the existence of an element in two or more physical forms within the same physical state is known as allotropy. Allotropes have similar chemical properties but they differ in chemical properties. In crystalline form, Carbon occurs as graphite, diamond, and fullerenes. Diamond is the hardest natural substance known and is used in cutting marbles, granite, and glass. Graphite is a greyish black and opaque substance, lighter than a diamond with comparative low density. Graphite has a sheet-like structure having hexagonal layers. One layer slides over the other layer due to weak forces and hence it is soft to touch and breaks easily. Graphite is also used as a lubricant.
Question. Which three allotropes of carbon do the given figures represent?
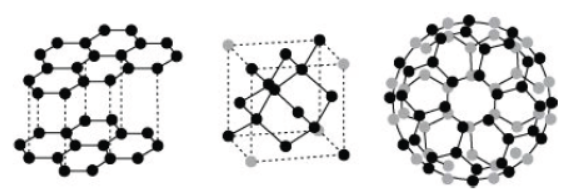
(a) I-Graphite II-Diamond III-Fullerene
(b) I-Diamond II-Fullerene III-Graphite
(b) I-Graphite II-Fullerene III-Diamond
(d) I-Fullerene II-Graphite III-Diamond
Answer
A
Question. Identify the incorrect statement(s):
I. Diamond is the hardest substance known while graphite breaks easily.
II. Each carbon atom in diamond is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms in a tetrahaderal manner to form a giant lattice. All carbon atoms are bonded by strong covalent bonds.
III. Graphite is poor conductor of electricity unlike other non metals.
IV. In each layer of graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms foming hexagonal rings of carbon atoms.
(a) I and III
(b) Only III
(b) II and IV
(d) I, II and IV
Answer
B
Question. The number of carbon atoms surrounding each carbon atom in a diamond are:
(a) 3
(b) 4
(b) 2
(d) 5
Answer
B
Question. Substance A is a moderate conductor of electricity. Observe the structure of substance A given below.
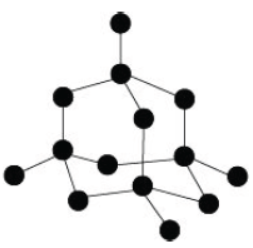
Choose the correct statements regrading substance A.
Statement I – It is a covalent compound.
Statement II – It has a giant molecular structure.
Statement III – It has the same structure as graphite.
Statement IV – It has the same structure as diamond.
(a) I and III
(b) II and III
(c) II and IV
(d) I, II and IV
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is correct about the structure of diamond?
(a) Carbon atoms are held together by single covalent bonds.
(b) Electrons move freely through the structure.
(b) Layers of atoms slide easily over each other.
(d) Carbon atoms conduct electricity in the molten state.
Answer
A
Case/Passage – 6
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions from As a versatile element, carbon can form large compounds because of its tetravalency and the property of catenation that it exhibits. Here, catenation refers to the combination of carbon atoms with itself to form large molecules. Carbon forms stronger covalent bonds with itself and other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur, nitrogen and chlorine. This is because its nucleus has a strong force of attraction and holds these bonds tightly together.
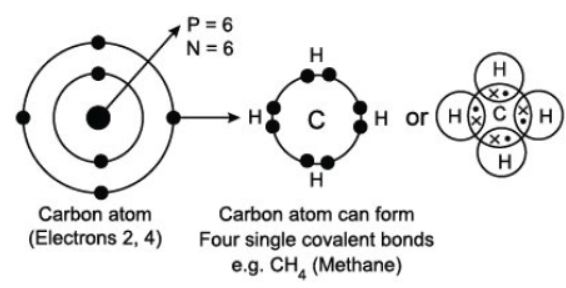
Question. Put the elements in the right order in terms of their valency, starting with the element of lowest valency?
(a) O, C, N, H
(b) C, O, N, H
(c) H, C, O, N
(d) H, O, N, C
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following does not represent the molecular formula C6H14?
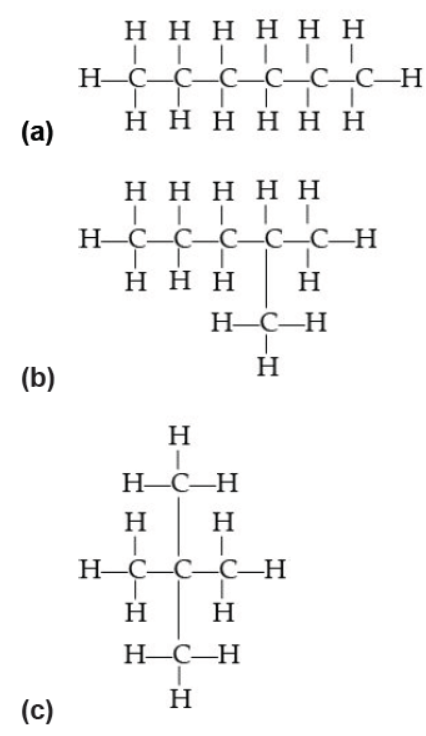
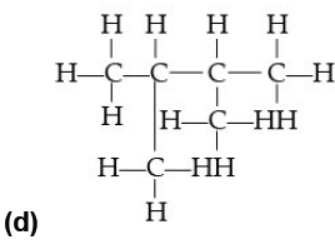
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns:
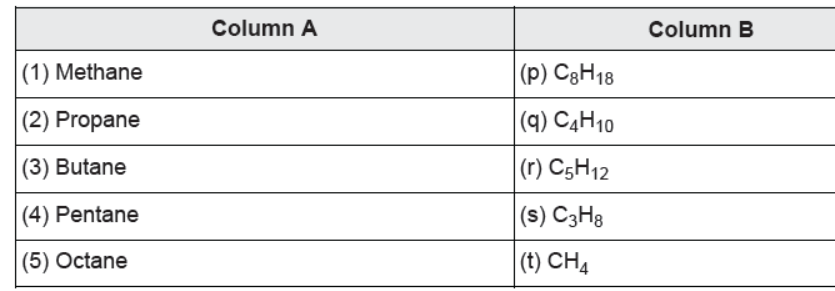
(a) (1)-(q), (2)-(s), (3)-(t), (4)-(p), (5)-(r)
(b) (1)-(p), (2)-(r), (3)-(s), (4)-(q), (5)-(t)
(c) (1)-(t), (2)-(s), (3)-(q), (4)-(r), (5)-(p)
(d) (1)-(t), (2)-(q), (3)-(s), (4)-(r), (5)-(p)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements regarding carbon is incorrect?
(a) A single atom of carbon can participate in two double bonds
(b) A single atom of carbon can participate in three single bonds and one double bond
(c) A single atom of carbon can participate in four single bonds
(d) A single atom of carbon can participate in two single bonds and one double bond
Answer
B
Case/Passage – 7
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions from The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are called isomers and this phenomenon is known as isomerism. Structural isomerism is when isomers have difference in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space. We can say that compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structural formula show structural isomerism. Compounds of carbon show this phenomenon as the atoms can be linked together in the form of straight chains, banched chains or even rings.
Question. The number of isomers of pentane is:
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 5
Answer
B
Question. Among the following sets of compounds, choose the set having the same molecular formulae:
(a) Butane and iso-butane
(b) Cyclohexane and hexene
(b) Propanal and propanone
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. The minimum number of carbon atoms required in an organic compound, in order to form branching:
(a) 3
(b) 4
(b) 5
(d) 2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following pairs show isomerism?
(a) Ethane and ethene
(b) Propane and butane
(b) Ethane and propane
(d) Butane and 2-methyl propane
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following has the longest chain?
(a) Iso-pentane
(b) 2-methylpentane
(c) 2,2-dimethylbutane
(d) neopentane
Answer
B
Case/Passage – 8
Food, clothes, medicines, books, or many of the things are all based on this versatile element carbon. In addition, all living structures are carbon based. The earth’s crust has only 0.02% carbon in the form of minerals. The element carbon occurs in different forms in nature with widely varying physical properties. Both diamond and graphite are formed by carbon atoms, the difference lies in the manner in which the carbon atoms are bonded to one another. Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
Question: Which of the following are isomers?
(a) Butane and isobutene
(b) Ethane and ethene
(c) Propane and propyne
(d) Butane and isobutane
Answer
D
Question: From the given alternatives, whose chemical and physical properties are not same?
(a) Graphite and Diamond
(b) Phosphorous and Sulphur
(c) Carbon and Hydrogen
(d) Methyl alcohol and Acetic acid
Answer
D
Question: Which one of the following is not an allotrope of carbon?
(a) Soot
(b) Graphite
(c) Diamond
(d) Carborundum
Answer
D
Question: Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Graphite is much less dense than diamond
(b) Graphite is black and soft
(c) Graphite has low melting point
(d) Graphite feels smooth and slippery
Answer
C
Question: Pentane has the molecular formula C5H12. It has
(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Answer
C
Case/Passage – 9
Water is a simple molecule consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to two different hydrogen atoms. Because of the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the bonds are polar covalent (polar bonds). The oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons of the covalent bonds to a significantly greater extent than the hydrogen atoms. The molecule has a bent structure, the H—O—H bond angle is about 105°.
Question. Select the correct type of bonding in a water molecule
(a) Ionic Bonding
(b) Covalent Bonding
(c) Hydrogen Bonding
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is
(a) H ..O O
(b) H ..O O
(c) H : O:H
(d) H :O:O
Answer
C
Question. The H—O—H bond angle in water molecule is
(a) 109.5°
(b) 180°
(c) 90°
(d) 105.0°
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is true regarding the electronegativity of atoms in water molecule?
(a) Hydrogen is more electronegative than oxygen
(b) Hydrogen is less electronegative than oxygen
(c) Electronegativity is same in Hydrogen and oxygen
(d) Hydrogen and oxygen do no show significant electronegativity in water
Answer
B
Question. What is the shape of water molecule?
(a) Linear
(b) Trigonal planar
(c) Bent
(d) Octahedral
Answer
C



