Please refer to Constant, Variables and Data Types Class 11 Computer Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Computer Science books for Class 11. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 11 Computer Science Constant, Variables and Data Types Notes and Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1 Which of the following is not the correct data type of C language?
a. Char b. float c. long d. double
Answer
float
Question 2 Which of the following is not an arithmetic operator?
a. + b. & c. % d. *
Answer
&
Question 3 The operator % can only be applied on which type of values?
a. float values b. double values c. int values d. All of these
Answer
int values
Question 4 Which of the the following is not a correct value for the type int?
a. 3750 b. 32800 c. -32767 d. 0
Answer
32800
Question 5 What is the value range of data type int in C language?
a. 0 to 32767 b. 0 to 65535 c. -32768 to 32767 d. -32767 to 32768
Answer
-32768 to 32767
Question 6.Which of the following is a reserve word?
a. for b. goto c. doo d. switch
Answer
doo
Question 7 What will be the value of the expression 5/6/3/+8/3?
a. 4 b. 2 c. 2.333(appr.) d. None of these
Answer
2
Question 8 Which of the following is not a C Token?
a. keywords b. constants c. operators d. all of these
Answer
all of these
Question 9 Which of the following is not a keyword in C Language?
a. const b. main c. size of d. void
Answer
main
Question 10 There are __ no of arithmetic operators in C Language.
a. 5 b. 4 c. 6 d. 7
Answer
5
Question 11 Which name of the variable is wrong?
a. roll-no b. interest _ paid c. SUM d. none of these
Answer
roll-no
Write True or False
Question 1 Variables are those quantities which allow change in their value during program implementation.
Answer
True
Question 2 Delimeter is a symbol which has statement structure and importance.
Answer
True
Question 3 One char data type always occupies one byte.
Answer
True
Question 4 Size of operand is its data type.
Answer
True
Question 5 Semicolon is a declaration delimiter.
Answer
True
Marks Questions
Question 1 if x=12.4565, then printf(“%3f”,x); will print _?
Answer
12.457
Question 2 What will be printed by the statement printf(“%d”,‘B’);
Answer
66
Question 3 What will be the value of float x=1/2.0 – 1/2?
Answer
0.50
Question 4 A computer program can be extracted into a number of _____
Amswer
Tokens
Question 5 Which keyword is used to declare a variable as a constant?
Answer
const
Question 6 if a=-11 and b=-3, then what will be the value of a%b?
Answer
-2
Question 7 How many relational operators are there in C Language?
Answer
6
Question 8 If we have operators *, /, ( ), % in an expression, then which of these has highest precedence?
Answer
( )
Marks Questions
Q:1 What are delimiters?
Ans: Delimiters are also called separator’s. Delimiters are those symbols which defines the fundamental limits of
program elements. Some of the commonly used delimiters are given below:
Hash – # – It is used for pre-processor directives. For example: #define PI 3.14
Comma – , – It is used as separator during variable declarations. For example: int a,b,c;
Curly Brckets – { } – It is used to define the block of statements
square brackets – [ ] – it is used for arrays. For example: int a[5];
Paarenthesis – ( ) – It is used for functions. For examples: printf( )
Colon – : – It is used for defining labels. For example- my label:
Q:2 What are Identifiers?
Ans: Identifier’s are the names given to different elements in the C program. A Program element can be a variable,
constant, function, array, structure, union etc. An identifier consists by the combination of alphabets and numbers.
When we define the name of identifier, we have to follow some naming rules. These naming rules are given below:
1. An identifier must not begin with a digit.
2. No special character except under scorer is allowed in the identifier.
3. We can not use two consecutive underscores.
4. Maximum 31 characters are allowed in the identifier.
5. We can not use blank space in the identifier.
6. A keyword can not be used as the identifier.
7. Identifier’s are case sensitive.
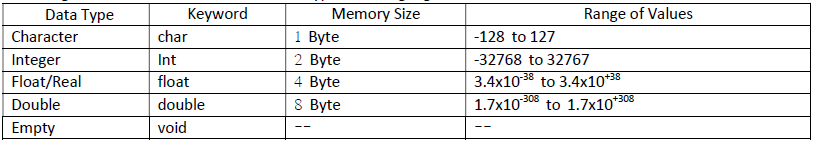
Q:3 What are Data Types?
Ans: In programming languages, data types are the set of defined values. A data type points out the type of data.
There are many data types already built into the C Compiler. We can also define our own data types also in C
language. Therefore, we can say that there are two categories of data types:
• Built In data types
• User defined data types
Following table shows the list of buil-in data types in C language:
Marks – Extra Questions
Q: 1 What are Tokens?
Ans: Tokens are the fundamental and smallest elements of the C program. These are like the words and punctuation
marks in the C Language. A C program can be extracted into a number of tokens. There are 6 types of tokens in C
language which are given below:
1. Keywords: These are the predefine words in the c language. For example: int, float, char, if, else, void etc.
2. Identifiers: These are the name of elements in the program. For example: main, printf, scanf etc.
3. Constants: These are the fixed values in the program. For example: 5, -25, 3.14, ’A’ etc.
4. Strings: These are the set of characters written in double quotes. For example: “Hello”, “H.No.196” etc.
5. Operators: These are the symbols to perform operations. For example: +, -, *, /, >, <, = etc.
6. Special Characters: These are the special symbols in the program. For example: #, &, { }, ( ), [ ], :, ; etc.
We hope the above Constant, Variables and Data Types Class 11 Computer Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 11 Computer Science


