Please refer to Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Term 1 With Solutions Set B provided below. The Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared based on the latest pattern issued by CBSE. Students should practice these guess papers for Class 12 Chemistry to gain more practice and get better marks in examinations. The Term 1 Sample Papers for Chemistry Standard 12 will help you to understand the type of questions which can be asked in upcoming examinations.
Term 1 Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry With Solutions Set B
Section ‘A’
1. Which of the statements is incorrect for haloalkanes:
(i) Haloalkanes are extremely soluble in water.
(ii) Alkyl halides are colourless when pure.
(iii) Haloalkanes tend to dissolve in organic solvents.
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) only (i)
(D) (i), (ii), (iii)
Answer
C
2. How does the branching in haloalkanes affect its boiling point ?
(A) Increases with branching
(B) decreases with branching
(C) does not affect the branching
(D) initially increases then decreases
Answer
B
3. IUPAC name of the following compound is:

(A) 2-ethoxy-1-1-dimethylcyclohexane
(B) 2,6 -dimethyl phenol
(C) 2 -ethoxy propane
(D) 1-ethoxy-2-methylcyclohexanev
Answer
A
4. Which of the following is not the requirement while preparing ammonia by Haber’s process:
(A) A high pressure of 200 atm.
(B) A temp of nearly 700 K
(C) Catalyst iron oxide
(D) Reactants in solid state
Answer
D
5. Which is the correct sequence to be followed in Ostwald’s process:
(i) Formation of nitrogen dioxide (ii) Formation of nitric acid
(iii) Catalytic oxidation of ammonia
(A) (i),(ii),(iii)
(B) (i),(iii),(ii)
(C) (iii),(ii),(i)
(D) (iii),(i),(ii)
Answer
D
6. The general formula for carbohydrate is:
(A) Cx-1 (H2O)2y
(B) Cx (H2O)x
(C) C2x (H2O)y
(D) Cx+1 (H2O)y
Answer
B
7. Conc. nitric acid oxidises non -metals. Based on it, which of the following is wrongly paired ?
(A) Phosphorus –phosphoric acid
(B) Carbon -carbonic acid
(C) Sulphur – sulphuric acid
(D) Iodine – iodic acid
Answer
B
8. In preparation of phenol, benzene is sulphonated with oleum. Benzene sulphonic acid so formed is converted to sodium phenoxide on heating with:
(A) molten sodium chloride
(B) molten sodium hydroxide
(C) solid sodium hydroxide
(D) sodium nitrate with HCl
Answer
B
9. During preparation of alcohol, the addition of borane to the double bond involves addition of boron to:
(A) sp2 carbon carrying higher number of hydrogen atoms
(B) sp3 carbon carrying higher number of hydrogen atoms
(C) sp2 carbon carrying lower number of hydrogen atoms
(D) sp3 carbon carrying lower number of hydrogen atoms
Answer
A
10. Which of the following is not the correct statement in relation to vapour pressure:
(A) The lowering of vapour pressure depends only on the concentration of the solute particles.
(B) The lowering of vapour pressure is independent of the identity of solute particles.
(C) In non- volatile solutes, the lowering of the vapour pressure depends on the sum of the mole fraction of different solutes.
(D) vapour pressure of the solvent decreases in the presence of non-volatile solute.
Answer
D
11. Peptide linkage:
(i) is a bond formed between COOH and -NH2 group
(ii) is a bond between two amino acids
(iii) it’s a connection between two proteins
What is untrue about peptide linkage:
(A) only (i)
(B) only (ii)
(C) (i) and (iii)
(D) (i) and (ii)
Answer
B
12. What happens when glucose reacts with bromine water:
(A) glucose gets reduced to gluconic acid
(B) it form oxime.
(C) glucose gets oxidised to gluconic acid.
(D) it forms oxalic acid
Answer
C
13. Which of the following is not the right pair as per the uses of various nitrogen compounds:
(A) Pickling of stainless steel-nitric acid
(B) Refrigerant-liquid nitrogen
(C) In the manufacture of ammonia-dinitrogen
(D) Preparing nitrates used in explosives-dinitrogen
Answer
D
14. Formation of ortho hydroxy benzoic acid from phenol using sodium hydroxide is:
(A) Kolbe’s reaction
(B) Reimer Tiemann reaction
(C) Esterification
(D) Williamson synthesis
Answer
A
15. Helium is used in filling balloons for meteorological observation because:
(A) it is non – inflammable and light gas.
(B) it is a good oxidising agent
(C) it is a good reducing agent.
(D) all of the above
Answer
A
16. Which of the following colligative property is directly proportional to molarity:
(A) Lowering of vapour pressure
(B) Elevation of boiling point
(C) Osmotic pressure
(D) Depression of freezing point
Answer
C
17. The concentration of pollutants in water is expressed in:
(A) μ g / mL
(B) w /v
(C) v/v
(D) w/w
Answer
A
18. Deacon’s process is used for the manufacture of:
(A) dinitrogen
(B) dioxygen
(C) sulphuric acid
(D) chlorine
Answer
D
19. Choose the correct relation:

Answer
C
20. Primary alkyl groups form ____________ on dehydration while __________ is formed on dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohol.
(A) ethers, alkenes
(B) alkenes, ethers
(C) ethers, phenols
(D) alkenes, phenols
Answer
A
21. Among halogens, which is a radioactive element:
(A) Bromine
(B) Iodine
(C) Astatine
(D) fluorine
Answer
C
22. What is the half life of radon?
(A) 10 days
(B) 4.56 days
(C) 3.82 days
(D) 5.46 days
Answer
D
23. Which of the following compounds of hydrogen does not from hydrogen bonding ?
(A) NH3
(B) H2O
(C) HCl
(D) HF
Answer
C
24. Alkali metal halide do not represent Frenkel defect. It is due to:
(A) Large difference in size of atoms and anions
(B) Almost same size of atoms and anions
(C) low coordination number of atoms and anions
(D) None of these
Answer
B
25. Glycosidic linkage belongs to which functional group ?
(A) Amide
(B) Ether
(C) Ester
(D) Alcohol
Answer
B
Section ‘B’
26. A unit cell is characterised by ___________parametres:
(A) two
(B) four
(C) Six
(D) One
Answer
C
27. The correct axial angle for tetragonal crystal system is:
(A) α = β = γ = 90°
(B) α = β≠γ = 90°
(C) α = β = γ ≠ 90°
(D) α≠β = γ≠ 90°
Answer
A
28. When crystallisation occurs at fast rate:
(A) Single crystals are formed
(B) Crystals with no defects are formed.
(C) Small crystals with defects are formed.
(D) Huge size crystals with no defects are formed.
Answer
C
29. Close packed structures have:
(A) Tetrahedral and octahedral voids
(B) Only tetrahedral voids
(C) Only octahedral voids
(D) None of octahedral or tetrahedral voids.
Answer
A
30. When there are deviations from ideal arrangement around a point or an atom in a crystalline substance ,it is known as:
(A) point defect
(B) vacancy defect
(C) line defect
(D) interstitial defect
Answer
A
31. Complete the reaction:
H3C-Br + AgF →
(A) H3C-Br + AgF → H3C-F + AgBr
(B) H3C-Br + AgF → Br-CH2-F + AgH
(C) H3C-Br + AgF → [Ag(CH3)]F + Br
(D) None of the above
Answer
A
32. Name the major monohalo product of the following reaction:
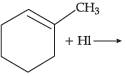
(A) 1-Iodo-1-methyl cyclohexane
(B) 1-Iodomethyl cyclohexane
(C) 1-Chloro cyclohexane
(D) None of the above
Answer
B
33. 2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction:
(A) 2-Bromopentane
(B) 1- Bromopentane
(C) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(D) None of the above
Answer
C
34. Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction ?

Answer
A
35. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.

(A) (ii) < (iii) < (i)
(B) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(C) (iii) < (i) < (ii)
(D) (iii) < (ii) < (i)
Answer
C
36. Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows _______.
(A) SN1 mechanism
(B) SN2 mechanism
(C) Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction
(D) Saytzeff rule.
Answer
A
37. What is the correct order of dissociation energy of C-X bond:
(A) C-Cl > C-Br > C-I
(B) C– Br > C-I > C-Cl
(C) C–Cl > C-I > C-Br
(D) C-I > C-Br > C-Cl
Answer
A
38. Glucose forms glucose penta acetate when reacts with acetyl chloride. This reaction represents:
(A) Cyclic structure of glucose
(B) Open chain structure of glucose
(C) Presence of five –OH groups in glucose
(D) Presence of –CHO group in glucose
Answer
C
39. In carbohydrates, the Letter ‘D’ represents:
(A) Configuration
(B) dextrorotating
(C) Conformation
(D) Laevorotating
Answer
A
40. An element having bcc structure has unit cell edge 500 pm. The density of element is:
(atomic mass of element = 100 g/mol)
(A) 2.657 g/cm3
(B) 5.189 g/cm3
(C) 7.971 g/cm3
(D) 3.985 g/cm3
Answer
A
41. Which of the following solutions has the highest boiling point at one atmospheric pressure ?
(A) 0.1 M NaCl
(B) 0.1 M Sucrose
(C) 0.1 M CaCl2
(D) 0.1 M Glucose
Answer
C
42. The anhydride of nitrous acid is:
(A) NO
(B) NO2
(C) N2O3
(D) N2O4
Answer
C
43. Identify the products X and Y in the following sequence:

(A) X =C2H4, Y=C2H6
(B) X=C2H5CN, Y=C2H5NH2
(C) X=C2H5CN, Y=C3H7NH2
(D) X=C2H5NH2, Y=C2H6
Answer
C
44. Which one of the following alcohol does not react with Lucas reagent ?
(A) 2-methyle propom-2-ol
(B) Propanol
(C) Propan-2-ol
(D) Sec. butyl alcohol
Answer
B
From Q. 45 to Q. 49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
45. Assertion (A): Ionization enthalpy in group 15 elements decreases down the group.
Reason (R): Atomic size of group 15 elements gradually increases down the group.
Answer
A
46. Assertion (A): The vapour pressure of some solutions is higher and show positive deviation.
Reason (R): The intermolecular attractive forces between the solute-solvent molecules are weaker than those between the solute-solute and solvent-solvent molecules.
Answer
A
47. Assertion (A): Osmosis is the process used in desalination of sea water.
Reason (R): The direction of osmosis can be reversed if a pressure smaller than the osmotic pressure is applied to the solution side.
Answer
D
48. Assertion (A): Pressure does not have any significant effect on solubility of solids in liquids.
Reason (R): Dinitrogen is a toxic gas.
Answer
C
49. Assertion (A): Formation of sulphuric acid is exothermic and reversible process.
Reason (R): Low temperature and high pressure are the favourable conditions for the maximum yield.
Answer
A
Section ‘C’
50. Match the following:

Which of the following is the best matched options ?
(A) i-B, v-C, iii-A, iv-D
(B) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
(C) i-D, v- C, iii-B, iv-A
(D) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
Answer
C
51. Which of the following analogies is correct:
(A) Group 15: Carfon family:: Group 16: Oxygen family
(B) Rhomfic sulphur: α-sulpher:: Monoclinic sulpher: β-sulpher
(C) Caro’s acid: H2SO3:: Oleum: H2S2O7
(D) Halide ion: Cl-:: Pseudohalide ion: OH-
Answer
B
52. Complete the following analogy:
Glucose: A:: Fructose: B
(A) A: -NH2; B: -CHO
(B) A: ñC=O ; B: -CHO
(C) A: -CHO; B: ñC=O
(D) A: -CONH2;B: -OH
Answer
C
CASE 1: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions due to the following reasons:
(i) In haloarenes, the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring.
(ii) In haloalkane, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp3 hybridised while in case of haloarene, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp2 -hybridised.
(iii) In case of haloarenes, the phenyl cation formed as a result of self-ionisation will not be stabilised by resonance.
The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
53. A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ________.
(A) SN1 reaction
(B) SN2 reaction
(C) α-Elimination
(D) Racemisation
Answer
B
54. Which of the following alkyl halides will undergoes SN1 reaction most readily ?
(A) (CH3)3C—F
(B) (CH3)3C—Cl
(C) (CH3)3C—Br
(D) (CH3)3C—I
Answer
D
55. What is ‘A’ in the following reaction ?


Answer
C

