Please refer to Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Term 1 With Solutions Set C provided below. The Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared based on the latest pattern issued by CBSE. Students should practice these guess papers for Class 12 Chemistry to gain more practice and get better marks in examinations. The Term 1 Sample Papers for Chemistry Standard 12 will help you to understand the type of questions which can be asked in upcoming examinations.
Term 1 Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry With Solutions Set C
Section ‘A’
1. Which of the following is the characteristic of polar solid molecules:
(A) They have strong dipole-dipole interaction.
(B) The molecules are held by weak dispersion forces.
(C) They have low melting point comparatively.
(D) Argon and Helium are its examples.
Answer
A
2. Which of the following is a photo voltaic material ?
(A) Glass
(B) Amorphous silicon
(C) Crystalline copper
(D) Amorphous copper
Answer
B
3. Many wet gases are dried by passing through sulphuric acid, this shows sulphuric acid is:
(A) a strong oxidizing agent
(B) a strong reducing agent
(C) a strong dehydrating agent
(D) a strong dehydrogenation agent
Answer
C
4. Which of the following is not an example of denaturation of proteins ?
(A) boiled eggs become hard
(B) boiled corns
(C) cooked meat becomes firm
(D) curdling of milk
Answer
B
5. Which of the following is incorrectly paired:
(A) chloramphenicol – dengue fever
(B) chloroquine – malaria
(C) halothane – surgery
(D) thyroxine – goiter
Answer
A
6. 1/8th of an atom actually belongs to a particular unit cell in:
(A) Primitive cubic unit cell
(B) Body centred cubic unit cell
(C) Face centred cubic unit cell
(D) End centred cubic unit cell
Answer
A
7. Which of the following is not a correct statement ?
(A) A racemic mixture is a mixture containing two enantiomers in equal proportion with zero optical rotation.
(B) a racemic mixture is represented by “dl”.
(C) chiral molecules are optically active.
(D) If the compound rotates the plane of plane polarised light to the right, i.e., clockwise direction, it is called laevo-rotatory
Answer
D
8. A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of:
(A) [Fe(H2O)5(NO)]2+
(B) FeSO4.NO2
(C) [Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
(D) FeSO4.HNO3
Answer
A
9. The correct order for increase in density is:
(A) n-C3H7I < n-C3H7Cl < n- C3H7Br
(B) n-C3H7I < n-C3H7Br < n-C3H7Cl
(C) n-C3H7Cl < n- C3H7Br < n-C3H7I
(D) n- C3H7Br < n-C3H7I < n-C3H7Cl
Answer
A
10. Which reagent will you use for the following reaction ?
CH3CH2CH2CH3 → CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl+ CH3CH2CHClCH3
(A) Cl2/UV light
(B) NaCl + H2SO4
(C) Cl2 gas in dark
(D) Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
Answer
A
11. What is not true for Frenkel defect ?
(A) It is shown by ionic solids.
(B) It decreases the density of substance.
(C) it is also called as dislocation defect.
(D) It does not change the density of solids.
Answer
B
12. Choose the correct sequence of the examples of the reactions given:
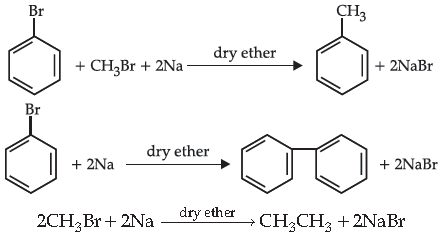
(A) Wurtz-Fittig reaction, Wurtz reaction, Fittig reaction
(B) Wurtz reaction, Fittig reaction, Wurtz-Fittig reaction
(C) Wurtz-Fittig reaction, Fittig reaction, Wurtz reaction
(D) Wurtz reaction, Fittig reaction, Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Answer
C
13. Which of the following statements are true ?
(A) Only types of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(B) Hydrolysis of XeF6 is a redox reaction.
(C) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
(D) None of the above.
Answer
A
14. Based on the given reaction, which is the incorrect statement:
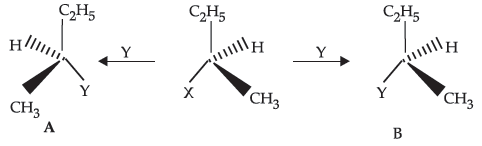
(i) When A is the product, the process is called as inversion of configuration.
(ii) When B is the product, the process is called as retention of configuration.
(iii) If both A and B are formed , the process is racemisation.
(A) (i)
(B) (i), (ii)
(C) all three are incorrect
(D) all three are correct.
Answer
B
15. Elements A and B form a compound. Atoms of the element B(as anions) make CCP and the elements of A (as cations) occupy all the octahedral voids. Based on the given information , the formula of the compound is:
(A) A2B
(B) A4B
(C) AB
(D) BA2
Answer
C
16. Which of the following orders are correct as per the properties mentioned against each ?

Answer
D
17. Which of the following statements are correct ?
(A) S–S bond is present in H2S2O6.
(B) In peroxosulphuric acid (H2SO5) sulphur is in +6 oxidation state.
(C) Iron powder along with Al2O3 and K2O is used as a catalyst in the preparation of NH3 by Haber’s process.
(D) Change in enthalpy is positive for the preparation of SO3 by catalytic oxidation of SO2.
Answer
B
18. Complete the following reaction:
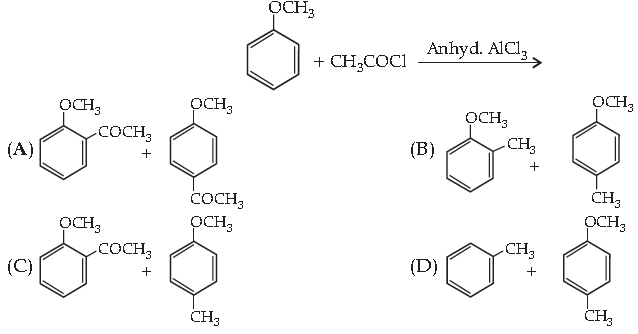
Answer
A
19. The laboratory method used for the preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
(A) Kolbe’s reduction
(B) Williamson synthesis
(C) Dehydration
(D) Esterification
Answer
B
20. Choose the correct naming:
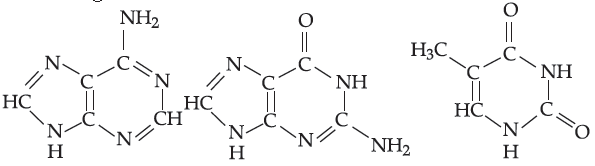
(A) Adenine, Guanine, Thymine
(B) Thymine, Guanine, Adenine
(C) Thymine, Adenine, Guanine
(D) Adenine, Thymine, Guanine
Answer
A
21. What is not true for the structure of nucleic acid ?
(A) When a nitrogenous base is attached to 1’ position of sugar a nucleoside is formed.
(B) A nucleotide is formed when nucleoside is linked to phosphoric acid at 5´ position of sugar molecule.
(C) Nucleosides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of the pentose sugar.
(D) DNA has double helix strand structure.
Answer
C
22. A black compound of manganese reacts with a halogen acid to give greenish yellow gas. When excess of this gas reacts with NH3, an unstable tri-halide is formed. In this process, the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from:
(A) – 3 to +3
(B) – 3 to 0
(C) – 3 to +5
(D) 0 to – 3
Answer
A
23. The number of atoms per unit cell in bcc arrangement is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer
B
24. Osmotic pressure is same for:
(A) isotonic solution
(B) hypertonic solutions
(C) hypotonic solutions
(D) saturated solutions
Answer
A
25. Which of the following elements can form oxides in oxidation states varying from +1 to +5 ?
(A) N
(B) P
(C) As
(D) Sb
Answer
A
Section ‘B’
26. Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reaction with _____
(A) Br2/water
(B) Na
(C) Glycerol
(D) All of the above
Answer
A
27. IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________.
(A) 3-methylphenol
(B) 3-chlorophenol
(C) 3-methoxyphenol
(D) benzene-1,3-diol
Answer
A
28. Mark the correct statements about amorphous solids :
(A) They are isotopic
(B) They melt over a range of temperature
(C) They are rigid and incompressible
(D) All of the above
Answer
D
29. Which of the followings statements is TRUE about a crystalline solid ?
(A) It has an irregular three-dimensional arrangement.
(B) It has no definite meeting point.
(C) It changes abruptly from solid to liquid when heated.
(D) It undergoes deformation of its geometry easily.
Answer
C
30. Which of the followings crystals does not show Frenkel defect ?
(A) AgCl
(B) NaCl
(C) AgBr
(D) ZnS
Answer
B
31. The depression of concentration of a solution is related to its vapour pressure. It is:
(A) Molality
(B) Mass percentage
(C) Normality
(D) Mole fraction
Answer
D
32. The elevation in boilng point of 0.01 M BaCl2 Solution is about __________________than that of 0.01 M Solution of glucose.
(A) same
(B) two times
(C) three times
(D) four times
Answer
C
33. At a given temperature, osmotic pressure of a concentrated solution of a substance is ______________ than that of a dilute solution.
(A) same
(B) higher
(C) lower
(D) infinite
Answer
B
34. Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is liquid ?
(A) NO2
(B) N2O
(C) N2O3
(D) N2O5
Answer
B
35. Which of the following oxides is basic in nature ?
(A) N2O3
(B) As2O3
(C) Sb2O3
(D) Bi2O3
Answer
D
36. When XeF6 reacts with water under complete hydrolysis, it forms:
(A) Only Xe
(B) XeO2F2 and HI
(C) Both Xe and XeO3
(D) Both XeO3 and XeOF4
Answer
B
37. Which of the following halide ions posses highest nucleophilicity ?
(A) F–
(B) Cl–
(C) Br–
(D) I–
Answer
D
38. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point ?

Answer
C
39. Which of the following compounds exhibit gem-dihalide ?
(A) CH3 CH2X
(B) CH3CH (X) CH2(X)
(C) CH3C(X2) CH3
(D) CH2X−CH2X
Answer
C
40. Which of the following compounds is least acidic ?
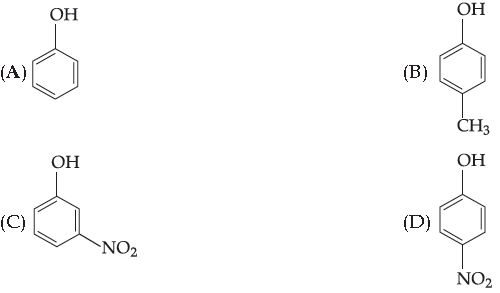
Answer
B
41. Give the product:
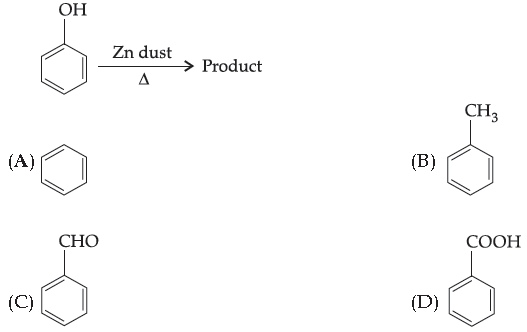
Answer
A
42. An ether is more volatile than an alcohol having the same molecular formula. This is due to:
(A) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in ethers
(B) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in alcohols
(C) Dipolar character of ethers
(D) Resonance in alcohols
Answer
B
43. The helical structure of protein is stabilised by
(A) Van Der Waal’s forces
(B) Dipole-dipole interaction
(C) Dipeptide bond
(D) Hydrogen bond
Answer
D
44. DNA differs from RNA in reference to nitrogenous bases DNA does not contains:
(A) Thymine
(B) Adenine
(C) Uracil
(D) Guanine
Answer
C
From Q.45 to Q.49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
45. Assertion (A): HI cannot be prepared by reacting KI with conc.H2SO4.
Reason (R): HI is the weakest bond among all halogen -hydrogen bonding.
Answer
B
46. Assertion (A): Amorphous solids possess a long-range order in the arrangement of their particles.
Reason (R): The formation of amorphous solids involves very rapid cooling.
Answer
D
47. Assertion (A): The packing efficiency is maximum for the fcc structure.
Reason (R): The coordination number is 12 in fcc structure.
Answer
B
48. Assertion (A): Chromium do not dissolve in conc. nitric acid.
Reason (R): Chromium gives a mirror finish to stainless steel.
Answer
B
49. Assertion (A): Protein loses its biological activity and is known as denaturation of proteins.
Reason (R): Protein in its native form is unaffected by any physical changes.
Answer
C
Section ‘C’
50. Match the following:
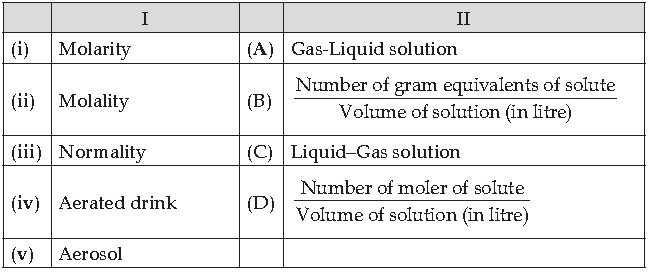
Which of the following is the best matched options ?
(A) i- B, ii-A, iii-D, v-C
(B) i-D, ii- B, iii-A, v-C
(C) i-D, iii-B, iv- A, v-C
(D) i-D, iii-B, iv-C, v-A
Answer
C
51. Which of the following analogies is correct:
(A) Finkelstein reaction: Haloalkanes:: Swarts reaction: Alcohol
(B) SN1 reaction: Two steps: SN2 reaction: one step
(C) Enantiomer: Optically active:: Diastereomer: optically inactive
(D) Iodoform: Analgesic:: DDT: insecticide
Answer
B
52. Complete the following analogy:
95.5% ethyl alcohol + 45% water: A: 20% alcohol + 80% petrol
(A) A: Wood spirit ; B: Rectified spirit
(B) A:Power alcohol: B:Rectified spirit
(C) A: methylated Spirit; B:Power alcohol
(D) A: Rectified spirit; B: Power alcohol
Answer
D
CASE 1: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
53. Phenol is less acidic than_________.
(A) ethanol
(B) o-nitrophenol
(C) o-methylphenol
(D) o-methoxy phenol
Answer
B
54. Which of the following is most acidic ?
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) Cyclohexanol
(C) Phenol
(D) m-Chlorophenol
Answer
D
55. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.
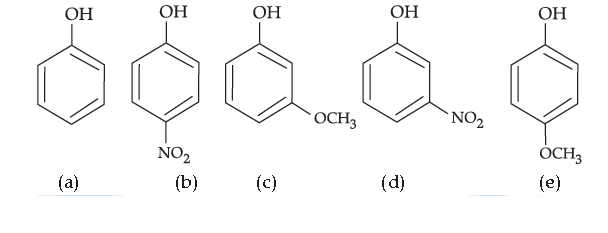
(A) e > d > b > a > c
(B) b > d > a > c > e
(C) d > e > c > b > a
(D) e > d > c > b > a
Answer
B

