Please refer to Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology Important Questions given below. These solved questions for Human Reproduction have been prepared based on the latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. We have provided important examination questions for Class 12 Biology all chapters.
Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question. Spermatogenesis starts at the age of
(a) 1–5 years
(b) 12–18 years
(c) 30–35 years
(d) 40–50 years
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following hormone is a gonadotropin?
(a) Luteinising hormone and thyroid hormone
(b) Luteinising and adrenaline hormone
(c) Luteinising and follicle stimulating hormone
(d) Thyroid and adrenaline hormone
Answer
C
Question. In male reproductive system luteinising hormone acts on which cell and stimulates the secretion of
(a) Sertoli cells, androgens
(b) Leydig cells, progesterone
(c) Sertoli cells, androgens
(d) Leydig cells, androgens
Answer
D
Question. Follicle stimulating hormone acts on
(a) Leydig cells
(b) Sertoli cells
(c) Spermatogonia
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The sperm structure doesn’t consist of
(a) Head
(b) Neck
(c) Polar body
(d) Middle piece
Answer
C
Question. Sperm nucleus is present in which region
(a) Head
(b) Neck
(c) Middle piece
(d) Tail
Answer
A
Question. Acrosome contains
(a) Fat
(b) Enzymes helpful in fertilisation
(c) Basophils
(d) Lipid
Answer
B
Question. The role of mitochondria in sperm is to
(a) Provide energy for sperm motility
(b) Provide energy for movement of tail
(c) Provide energy for fat formation
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Female gamete mother cells are known as
(a) Primary oocyte
(b) Secondary oocyte
(c) Oogonia
(d) Ovum
Answer
C
Question. Primary oocyte is formed by
(a) Ovum
(b) Secondary oocyte
(c) Oogonia
(d) Spermatids
Answer
B
Question. Primary follicle surrounds /encloses which of the following cell?
(a) Ovum
(b) Primary oocyte
(c) Oogonia
(d) Spermatids
Answer
B
Question. How many primary follicles are left in both the ovaries at puberty?
(a) 1,20,000 – 1.60,000
(b) 60,000 – 80,000
(c) 10,000 – 20,000
(d) 6,000 – 8,000
Answer
A
Question. Secondary follicle is surrounded by
(a) Theca only
(b) More granulosa cells layer and new theca
(c) Only one granulosa layer
(d) Zona pellucida
Answer
B
Question. Primary oocyte grows in size and completes its first meiotic division in which stage
(a) Primary follicle
(b) Secondary follicle
(c) Tertiary follicle
(d) Graffin follicle
Answer
C
Question. The ploidy of oogonia and secondary oocyte respectively is
(a) Both n
(b) Both 2n
(c) n, 2n
(d) 2n, n
Answer
D
Question. Bulk of the nutrient rich cytoplasm that secondary oocyte contains comes from
(a) Graffian follicle
(b) Primary oocyte
(c) Ovum
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Zona pellucida is a layer formed around
(a) Acrosome
(b) Primary oocyte
(c) Secondary oocyte
(d) Graffian follicle
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following menstrual cycle does not take place?
(a) Monkey
(b) Sheep
(c) Apes
(d) Human beings
Answer
B
Question. Semen consists of
(a) Sperms
(b) Seminal plasma
(c) Primary spermatocytes
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Oogenesis is
(a) Formation of spermnogonia
(b) Formation of spermnid
(c) Formation of immature female gamete
(d) Formation of mature female gamete
Answer
D
Question. The innermost layer if uterine lining is known as
(a) Myometrium
(b) Ectometrium
(c) Perimetrium
(d) Endometrium
Answer
D
Question. Which layer of uterine lining exhibits cyclic changes during mei cycle?
(a) Myometrium
(b) Endometrium
(c) Perimetrium
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. In female reproductive system a cushion of fatty tissue covered by skin and pubic hairs is known as
(a) Labia majora
(b) Mons Pubis
(c) Hymen
(d) Clitoris
Answer
B
Question. Labia minora is a part of
(a) Female accessory duct
(b) Female external genetalia
(c) Primary sex organ of female
(d) Male external genita
Answer
B
Question. The opening of vagina is often covered by a membrane called
(a) Scrotum
(b) Hymen
(c) Penis
(d) Labia majora
Answer
B
Question. Clitoris is present at the opening of
(a) Vagina
(b) Penis
(c) Urethra
(d) Cervix
Answer
A
Question. The mammary glands of female contains
(a) Glandular tissue
(b) Fat
(c) Zinc
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. The correct sequence of ducts from inside to outside the mammy gland is
(a) Alveoli, mammary duct, mammary tubules. mammary ampulla lactiferous ducts
(b) Alveoli, mammary tubules, mammary ampulla. mammary duct lactiferous ducts
(c) Alveoli, mammary tubules. mammary duct. mammary ampulla lactiferous ducts
(d) Alveoli, mammary duct, mammary ampulla. mammary tubules lactiferous ducts
Answer
C
Question. Gametogenesis in humans is the process in which?
(a) Male produces sperms
(b) Female produces ovum
(c) Male produces pollen
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. The Ploidy of spermatogonium is
(a) 2n
(b) n
(c) Initial n and afterwards 2n
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The ploidy of primary spermatocytes is
(a) n
(b) 2n
(c) Initial n and afterwards 2n
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The ploidy of secondary spermatocytes is
(a) n
(b) 2n
(c) Initial n and afterwards 2n
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes which type of cell division and gives rise to how many cells
(a) Mitotic. Four
(b) First meiotic. Four
(c) Mitotic. Two
(d) Second meiotic two
Answer
D
Question. Spermiogenesis is the process in which
(a) Primary spermatocytes are formed by spermatogonia
(b) Secondary spermatocytes are formed by spermatids
(c) Spermatids are formed by secondary spermatocytes
(d) Spermatozoa are formed by spermatids
Answer
D
Question. Spermiation is the process in which
(a) Primary spermatocytes are formed by spermatogonia
(b) Secondary spermatocytes are formed by spermatids
(c) Spermands are formed from secondary spermatocytes
(d) Sperms are released from seminiferous tubules
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Mention the function of trophoblast in human embryo.
Ans. Trophoblast is the outer layer of blastocyst which helps in the attachment of blastocyst to the endometrium of the uterus.
Question. Explain the function of umbilical cord.
Ans. Umbilical cord transports nutrients and respiratory gases and metabolic wastes to and from mother and foetus.
Question. The path of sperm transport is given below. Provide the missing steps in blank boxes. (Image 96 P)
Ans. Vasa efferentia, Vas deferens.
Question. What is corona radiata?
Ans. The follicle cells that envelope the egg outside zona pellucida are called corona radiata.
Question. Which part of the blastula is destined to form the germ layers of the developing embryo in humans?
Ans. Inner cell mass.
Question. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Ans. It is not correct to blame women for giving birth to daughters. The male sperm contains either X or Y chromosome whereas the female egg contains only X chromosomes. At the time of fertilisation when sperm carrying X chromosome combines with egg carrying X chromosome of female, XXzygote is formed which would be a female and when sperm with Y chromosome combines with egg containing X chromosome, XY-zygote is formed which would be a male. Thus, scientifically sex of the baby is determined by the father and not by the mother as blamed in our society.
Question. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Ans. Seminal plasma is the mixture of secretions of male accessory glands which include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate gland and a pair of bulbourethral glands.
Question. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Ans. The process of delivery of the foetus (child birth) at the end of the pregnancy is called parturition.
The signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta, which trigger the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary. Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscles and induces stronger uterine contractions leading to expulsion of the baby. Relaxin hormone released by the ovary widens the vagina to facilitate birth.
Question. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Ans. Six eggs are released by the ovary of a female dog if it gave birth to six puppies.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Ans.

Short Answer Questions
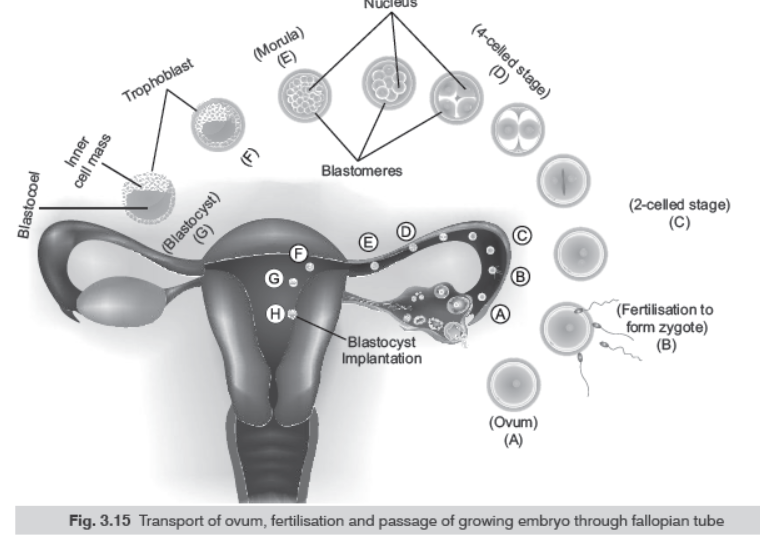
Question. Differentiate with the help of diagrams only between morula and blastocyst of a human.
Ans.
Question. Write the function of each one of the following:
(i) (Oviducal) Fimbriae (ii) Oxytocin
Ans. (i) Collection of ovum released by ovary.
(ii) Cause uterine contraction for parturition; promotes milk ejection.
Question. State the fate of trophoblast of a human blastocyst at the time of implantation and that of the inner cell mass immediately after implantation.
Ans. The trophoblast layer gets attached to the endometrium, and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo.
Question. Placenta acts as an endocrine tissue. Justify.
Ans. Placenta produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogens, progesterones that are essential to maintain pregnancy. This way placenta acts as an endocrine tissue.
Question. What stimulates pituitary to release the hormone responsible for parturition? Name the hormone.
Ans. The signal from the fully developed foetus and placenta or the foetal ejection reflex induces mild uterine contraction. The hormone released is oxytocin.
Question What is the number of chromosomes in the following cells of a human male?
(i) Spermatogonial cells (ii) Spermatids
(iii) Primary spermatocytes (iv) Sertoli cells
Ans. (i) 46 (ii) 23
(iii) 46 (iv) 46.
Question. What are the events taking place in the ovary and uterus during follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
Ans. (i) The primarfyo llicles grow and become mfualtluy re Graafia n follicles.
(ii) Secretion of estrogen hormone.
(iii) Endometrium of uterus regenerates through proliferation.
Question. (i) Where do the signals for parturition originate from in humans?
(ii) Why is it important to feed the newborn babies on colostrum?
Ans. (i) Signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus the placenta which induce uterine contractions. This is called as foetal ejection reflex. (Any one)
(ii) Colostrum contains antibodies (IgA), to (passively) immunise the baby.
Question. Why is breast-feeding recommended during the initial period of an infant’s growth? Give reasons.
OR
Medically it is advised to all young mothers that breast feeding is the best for their newborn babies. Do you agree? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Ans. The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called colostrum. It contains several antibodies (IgA) absolutely essential, to develop passive immunity in the new-born babies. It also contains nutrients such as calcium, fats, lactose. Breast feeding also develops a bond between mother and child.
Question. Name the functions of the following:
(a) Corpus luteum (b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome (d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae
Ans. (a) Corpus luteum: It acts as an endocrine gland and secretes progesterone which is essential for maintenance of the endometrium.
(b) Endometrium: It is the innermost layer of uterus responsible for nutrition and development of the foetus. It undergoes cyclic changes during menstrual cycle. Implantation of blastocyst takes place on the endometrium.
(c) Acrosome: It contains hydrolytic enzymes that help in dissolving membranes of the ovum for fertilisation.
(d) Sperm tail: It helps in the sperm movement in the female genital tract for fertilisation.
(e) Fimbriae: It is present at the opening of oviduct which helps in the collection of the eggs after ovulation.
Long Answer Questions
Questions. When and where do chorionic villi appear in humans? State their function.
Ans. Chorionic villi appear after implantation on the trophoblast.
It becomes interdigitated with uterine tissue to form the placenta and increases the surface area for exchange of materials between the mother and the embryo.
Questions. (i) How is placenta formed in the human female?
(ii) Name any two hormones which are secreted by it and are also present in a non-pregnant woman.
Ans. (i) The chorionic villi and uterine tissue become interdigitated with each other and jointly form a structural and functional unit called placenta.
(ii) Estrogen and progestogens.
Questions.

Read the graph given above showing the levels of ovarian hormones during menstruation and correlate the uterine events that take place according to the hormonal levels on:
(i) 6–15 days
(ii) 16–25 days
(iii) 26–28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised)
Ans. (i) Regeneration of endometrium.
(ii) Uterus gets highly vascularised, ready for embryo implantation.
(iii) Disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation.
Questions. Study the graph given below and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the hormones ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
(b) Explain the ovarian events (i), (ii) and (iii) under the influence of hormones ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
Ans. (a) Hormone ‘X’: Luteinising hormone.
Hormone ‘Y’: Follicle stimulating hormone.
(b) (i) FSH is secreted by the anterior pituitary which stimulates the ovarian follicle to secrete estrogen, which in turn stimulates the proliferation of the endometrium of the uterine wall.
(ii) Both LH and FSH attain a peak level in the middle of cycle (about 14th day). Rapid secretion of LH leading to its maximum level during the mid-cycle called LH surge induces rupture of Graafian follicle and thereby the release of ovum (ovulation).
(iii) The remaining cells of ovarian follicles are stimulated by the LH to transform into corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for maintenance of the endometrium.
Questions. Explain the hormonal control of spermatogenesis in humans.
Ans. Refer to Basic concept 3 (i) Hormonal control of spermatogenesis.
Questions. (i) Draw a sectional view of human ovary and label
(a) Primary follicle (b) Graafian follicle (c) Corpus luteum
(ii) Mention the effect of pituitary hormones on the parts labelled.
Ans. (i)

(ii) The pituitary hormones FSH and LH effect the growth and development of primary follicle, Graafian follicle and corpus luteum.
Questions. (a) Write the specific location and the functions of the following cells in human males:
(i) Leydig cells (ii) Sertoli cells
(iii) Primary spermatocyte.
(ii) Explain the role of any two accessory glands in human male reproductive system.
Ans. (a) (Table 106)
Questions. (a) Where does spermatogenesis occur in human testes? Describe the process of spermatogenesis upto the formation of spermatozoa.
(b) Trace the path of spermatozoa from the testes upto the ejaculatory duct only.
OR
Schematically represent and explain the events of spermatogenesis in humans.
Ans. (a) Spermatogenesis occur in seminiferous tubules.

(b) The path of spermatozoa is as follows:
Seminiferous tubules Rete testis Vasa efferentia Epididymis
Vas deferens Ejaculatory duct
OR
Questions. What role does pituitary gonadotropins play during follicular and ovulatory phases of menstrual cycle and also explain the shift in steroidal secretions.
Ans. Menstrual cycle is regulated by hypothalamus through the pituitary gland. At the end of menstrual phase, the pituitary FSH gradually increases resulting in follicular development within the ovaries. As the follicles mature, estrogen secretion increases resulting in a surge in FSH and LH. The surge of LH is responsible for ovulation and formation of corpus luteum that secretes progesterone which helps in maintaining the endometrium for implantation.
Questions. Give the term/reason:
(a) Mechanism responsible for parturition.
(b) Role of oxytocin during expulsion of the baby out of uterus
(c) Why does zona pellucida layer block the entry of additional sperms?
(d) Sperm cannot reach ovum without seminal plasma.
(e) All copulations do not lead to fertilisation and pregnancy.
Ans. (a) The complete neuro-endocrine mechanism.
(b) Oxytocin acts on uterine muscle for stronger contraction.
(c) To ensure the fusion of only one sperm with the ovum nucleus.
(d) Seminal plasma is a liquid medium which helps the sperm to move and nourishes it.
(e) All copulations do not lead to fertilization and pregnancy because fertilisation can only occur of the ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary-isthmic junction.
Questions. (a) When and where does spermatogenesis occur in a human male?
(b) Draw a diagram of a mature human male gamete. Label the following parts: Acrosome, nucleus, middle piece and tail.
(c) Mention the functions of acrosome and middle piece.
Ans. (a) Spermatogenesis occurs at puberty in testes.
(c) Acrosome: Acrosome contains hydrolytic enzymes that help in dissolving membranes of the ovum for sperm entry, ensuring fertilisation.
Middle piece: It contains a number of mitochondria that provide energy for the movement of the tail and thus provides motility to sperm.
Questions. (i) Draw a diagrammatic sectional view of the female reproductive system of human and label the parts
(a) where the secondary oocytes develop
(b) which helps in collection of ovum after ovulation
(c) where fertilisation occurs
(d) where implantation of embryo occurs.
(ii) Explain the role of pituitary and the ovarian hormones in menstrual cycle in human females.
Ans. (i) Fig
(ii) Pituitary hormone:
(a) FSH stimulates maturation of follicle.
(b) Rapid secretion of LH (LH surge) induces rupture of Graafian follicle, thereby leading to ovulation (release of ovum).
Ovarian hormone:
(a) Estrogen stimulates follicular development.
(b) Progesterone produced by corpus luteum helps to maintain endometrium.
In the absence of fertilisation corpus luteum degenerates and the endometrium disintegrates leading to menstruation.



