Please refer to Introduction to Computers Class 9 Computer Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Computer Science books for Class 9. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 9 Computer Science Introduction to Computers Notes and Questions
Question: Describe Charles Babbage work in the history of computers.
Answer: Charles Babbage Work: Charles Babbage a mathematical professor
- He began to design an automatic mechanical calculating machine which he called as difference engine
- By 1822 he developed a model to demonstrate the difference engine which he developed. It was powered by steam and it had the ability to print the results
- After 10 years he had a better idea to work on fully functional automatic digital computer called as analytic engine. One person was required to operate this machine and required steam power to run.
Question: What is Von Neumann theory?
Answer: Von Neumann Theory: according to von Neumann theory data and program can be stored in the same memory, thus the machine can itself alter its program or internal data.
Question: Who gave the idea of modern stored-program computers?
Answer: Von Neumann gave the idea of modern stored program computer, which is universally adopted and become essential for future generations of computers.
Question: What are the goals of fifth generation of computing?
Answer: The goal of fifth generation computer is to develop devices that respond the natural language input and are capable of learning and self organization.
Question. What are the advantages of transistors?
Answer:
- Very small in size than vacuum tubes
- Less expensive than vacuum tubes
- Much faster than vacuum tubes about 40 times
- Do not become hot and burn like vacuum tubes
Question. What is computer terminal?
Answer: A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that is used for entering data into, and displaying data from, a computer or a computing system.
Question. What is computer simulation?
Answer: A computer simulation or a computer model is a computer program that used to replicate an abstract model of a particular system.
Question: What are the language translators?
Answer: Language translators are the programs that are used to translate a high level language into machine into machine code.
Question: What is compiler?
Answer: A compiler is a program that translates a source program into machine language.
Question: What is assembler?
Answer: A compiler is a program that translates an assembly language into machine code.
Question: Differentiate between compiler and interpreter?
Answer:

Question: What is the difference between digital and analogue computers?
Answer: Digital Computers: Digital computers process data in numerical form using digital circuits. The digital computers perform arithmetic and logic operations with discrete values. In early 1940‟s Aiken built the first general purpose digital computer called MARK-1. Digital computers are used in business, educational institute, hospitals etc. Examples of digital computers are IBM PC, Apple‟s Macintosh etc.
Analogue Computers:
Analogue computers use electronic or mechanical phenomenon to solve the problem by using one kind of physical quantity to represent another.
Early special purpose analogue computers were the slide rule, the curvimeter, plainmeter and the harmonic analyzer. General purpose analogue computers were first built in 1930‟s. Speed meter in the car is best example of analogue computer.
Difference between Digital and Analogue Computers:
The difference between an analog and digital computer is the type of data they process. Analog computers process measured data. A speedometer in your car is a common type of analog device. A digital computer processed discrete data (digits). In this case 0 and 1.
Question: Define computer. Briefly describe classification of computers.
Answer: Computers:
An electronic device which processes the data and gives output in the form of information,
Classification of Computers:
Computers are classified into following four classes
1. Super computers
2. Mainframe computer
3. Mini Computers
4. Microcomputers
Supercomputer: The fastest type of computer. Supercomputers are very powerful and are employed for specialized applications that require huge amounts of mathematical calculations.
- Super computer can perform more than trillion of calculations per second.
- Super computer can have thousands of processors.
- Super computer can help in global weather forecasting.
- CRAY T90 is an example of super computers. Cray, IBM and Hp are the manufacturer of the supercomputers.
Mainframe computer:
Mainframes are powerful computers used primarily by corporate and governmental organizations for critical applications, bulk data processing enterprise resource planning, and financial transaction processing.
Mini computers:
A mini computer is a computer that sits in-between the range of a mainframe and a personal computer, or microcomputer. The mini computer is still a multi-user system like a mainframe, but more compact.
Most of the mini computers were able to run proprietary operating systems and specialized hardware.
Microcomputers:
Microcomputers are the small computers that are found frequently in homes and businesses. The term microcomputer is now rarely used in the market because all desktop computers qualify as microcomputers.
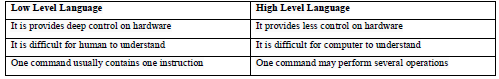
Question: What is difference between low level and high level languages?
Answer:
Question: What is the difference between Digital and Analogue computers?
Answer: Digital Computers:
Digital computers process data in numerical form using digital circuits. The digital computers perform arithmetic and logic operations with discrete values. In early 1940‟s Aiken built the first general purpose digital computer called MARK-1. Digital computers are used in business, educational institute, hospitals etc. Examples of digital computers are IBM PC, Apple‟s Macintosh etc.
Analogue Computers:
Analogue computers use electronic or mechanical phenomenon to solve the problem by using one kind of physical quantity to represent another. Early special purpose analogue computers were the slide rule, the curvimeter, plainmeter and the harmonic analyzer. General purpose analogue computers were first built in 1930‟s. Speed meter in the car is best example of analogue computer.
Question: For what purpose JAVA was developed?
Answer: JAVA was developed by the Sun Microsystems with the basic purpose to control microprocessors which are used in the consumer items such as VCR Toasters and for PDA. Java has the powerful capabilities of network programming.
Question: Modern computers are based on stored program concept. Who introduces this concept and discuss his contribution in history.
Answer: VON Neumann introduced this concept. He gave the idea which states that “data and program can be stored in the same memory, thus the machine can itself alter its program or internal data.”
Question: Which language is used for scientific purposes?
Answer: FORTRAN (Formula Translation) is designed at IBM for scientific computing. It was mainly used for scientific purposes.
Question: Which language is used for artificial intelligence?
LISP is used in artificial intelligence.
Question: What are different computer applications? Briefly explain
Answer: Various types of computer applications are developed , computer hardware and computer application is very advanced. Computer Application could be define in the some categories. Research in computer science is decided into basic research and applied research in computer science. Some of the computer application used are as detailed as under.
NETWORK APPLICATIONS Computer Networking is the coordination of communication within a particular system between central (server) and some of its members. Network Topology is the pattern of relationships between a terminal in a computer network, there are various types of network topology.
GRAPH APPLICATIONS Many types of computers with difference graph applications. Computer graphics applications beginning of its development began in the late 1950s and early 1960s. It is a computer program used to draw a picture that gives a new dimension in the field of computer time. There are two obvious ways to enter information into the computer graphics into an application, namely: 1. Direct Graphics Programming, by writing into the programming language. 2. Digitizing (or Graphics) Tablets, by using the mouse.
ANIMATION Each computer may be having difference specification, so the choosing computer components must be carefully. It is a form of art that appear spontaneously generate life movement on an object. To achieve these effects, animators have to construct a series of frames / images of a subject, that each of the next frames is slightly different from the previous frame. Animation is one of computer applications which intended to give more interesting when using computer.
Computer with a lot of animation is run slowly than poor of animation, so it must increase computer performance for which use many animation. There are actually several different functions to produce computer-based animation and one thereof is an animated three-dimensional (3D). One rather than the technique is to create an object which is then adjusted and moved, in which ultimately will produce a complete 3D animation. Another function is to create computer animations using a standard computer paint tools to paint the frames a single prior to the merger. This is then stored as an image file.
WEB APPLICATIONS
Web applications are a part of computer applications.WWW is the most exciting applications on the Internet and applications such as email is very important and widely used. Every computer have a CPU as main brain, one of main components of a CPU is for support the web applications and computer development.
In this application a lot of convenience that can be done such as:
• ordered or purchased an item online
• register online
• reached multimedia, etc
Network technology both cabling and wireless issues bought us connects everywhere. Notices are placed on the WWW called “HomePage” and every home page has the address of each. In order to attract users’ attention so that the homepage can be visited, then we have them shape it interesting and there are many clear edicts. In this field of art is necessary, so that the world of advertising and commerce world, the better. The computer applications especially web application most commonly used browser today is Netscape Navigator in the world other than Internet Explorer. Web application be the largest used application because the role of internet history. Without internet web application could not interact with people.
APPLICATION OF EDUCATION
Computer Assisted Instruction (CAI).
- Computers are directly used in the learning process, as a substitute teacher or a book. Some CAI applications are: Drill and Practice, Tutorials, Simulation.
- Computer Managed Instruction (CMI). The teachers use computers to plan for college, the students adapted to the conditions, which consisted of computer-assisted learning programs, reading, and exams.
- Computer Assisted Testing (CAT). Computers are used as test media. Many forms, ranging from simple where the computer (usually through the display) is used as a substitute for examination questions in paper form, to the more advanced form, where the ability of computers used to explore students’ abilities in ways actively questioning.
APPLICATION OF BUSINESS / OFFICE
Another computer applications is office application, this applications is used for business purpose. Every business, large or small, to process large amounts of data in daily operations. Data obtained from the payroll, customer invoicing and financial accounts, inventory management, and account customers that all fees must be calculated, stored, classified, sorted, directive, processed again, reported, communicated and disseminated at a time. Processing of such data is known as Business Data Processing or Data Processing (DP). If the processing is done by computer, this is known as Electronic Data Processing (EDP). Now every office’s employee must could operate computer, so they must know how to use computer to make their job easy.
DBMS (Data Base Management System) Computers also can be used as Effective in business management. Through a computerized database management system (DBMS) and the SIM, a manager or company executive can be assisted in making decisions about the entire business operation and to provide guidance and instructions to subordinates. DBMS types which common used nowadays is relational database and RDBMS concept.
Application for a Certain Class
• Air Traffic Control System
• Airline Reservation Systems
There are so many computer applications; every application has a unique function and specification. Everyone could use computer or explore CPU architecture easily by learning computer tutorial.
Computer
A Computer is an automatic electronic, calculating device which can process a given input in a prescribed manner to produce a desired output, at a very high speed with remarkable accuracy. It can also perform all arithmetic and logical functions according to instructions given in a systematic order to solve any problem and produce processed information.
Advantages of Computers
Speed
Since Computer is an electronic machine and electrical pulses travel at the rate of passage of electric current. This speed enables the computer to perform millions of calculations per second.
Storage
A computer has too much storage capacity. Once recorded, a piece of information can never be forgotten.
High Accuracy
A computer can be considered as 100% accurate. Checking circuits are built directly into the computer, that computer errors that undetected are extremely rare.
Versatility
Computer can perform any task, provided it can be reduced to a series of logical steps.
Diligence
Computer never gets tired. It performs most boring, repetitive and monotnous task.
Automatic Operation
Once a program is fed into computer the individual instructions are processed on after the other. Thus computer works automatically without manual intervention.
Obedience
The ability to take in and store a sequence of instructions for the computer to obey. Such a sequence of instruction is called a PROGRAM and it must be written in the Computer Language.
Decision Making Capability
Computer can take simple decisions, such as less than, greater than or equal to. It also determines whether a statement is true or false.
Hardware
the physical components and other attached input and output devices of computers are called Hardware. All Hardware components may be connected mechanically, electrically or electronically with each other. Hardware includes input/output devices, CPU, backing storage devices and electronic circuit.
Software
Computer required a number of instructions to do any job. The set of these instructions forms programs. Numbers of programs are combined for some purposes are called software.
They are designed by manufactures and programmers.
Types of Software
- System Software
- Application Software
Ages of Computer
At the early age people used pebbles, stones, sticks, scratches, symbols and finger tips to count, which were later replaced by numbers.
The history of computing is divided into three ages during which man invented and improved different types of calculating machines. These ages are,
Dark age – 300 BC to 1890
Middle age – 1890 AD to 1944
Modern age – since 1944 AD
Dark Age (3000 BC to 1890 AD
ABACUS
About 3000 years BC, Chinese developed the first calculating machine named Abacus or Soroban.
Abacus consists of a rectangular wooden frame having rods which carry round beads. Counting is done by shifting the beads from one side to another.
OUGHTRED’S SLIDE RULES
In 1632 AD William Oughtred, an English mathematician developed a slide rule. This device consists of two movable rules placed side by side on which number were marked.
PASCAL’S CALCULATOR
Blasé Pascal (1623-1662), a French developed the first mechanical calculating machine in 1642. This machine consists of gears, wheels and dials. It was capable of adding and subtracting operations.
GOTTEFRIED WILHOLM LEIBNITZ
In 1671, a German, Gottfried Von Leibnitz (1646-1716) improved Pascal‟s calculator to make it capable of performing all maths operations.
JACQUARD’S LOOM
In 1801, a French, Joseph Marie Jacquard developed the first punch card machine.
BABBAGE DIFFERENCE ENGINE
Charles Babbage (1792-1871) an English mathematician also called Father of modern computer. As he gave the true con cept of computer at Cambridge University, he developed Babbage Difference Engine in 1823 and Babbage Analytical Engine in 1833. Lady Ada Augusta an assistant of Babbage is called the first programmer.
Middle Age (1890 AD TO 1944 AD)
DOCTOR HERMAN HOLLERITH
In 1880s Herman Hollerith an American developed a machine which used punch card system. The machine could sense and punch holes, recognize the number and make required calculations. This machine was first used in 1890s by American Census Bureau.
HOWARD AIKEN- MARK-1 COMPUTER
In 1937, Professor Howard Aiken build the first electro-mechanical computer Mark-1, by trying to combine Babbage‟s theory and Hollerith‟s punching technologies. He completed his project in 1944 with the help of IBM Engineers.
Mark 1 could multiply two, twenty digit numbers in 5 seconds and made a lot of noise. It had a shape like a monster about 50 feet long, 8 feet high, having wiring of length equal to distance from Lahore to Gilgit or Karachi to Bahawalpur (800km) and had thousand ends of electro-magnetic relays.
ABC (ATANASOFF BERRY COMPUTER)
ABC a special purpose computer was developed in 1938 by Dr. John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State College, USA.
Modern Ages (Since 1944 AD)
JOHN VON NEUMAN
In 1945, Dr. John Von Neumann suggested the concept of Automatic Data Processing (ADP) according to the stored program and data. ENIAC
(FIRST ELECTRONIC COMPUTER)
Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator (ENIAC) was the first electronic computer made in 1946 by John Presper Eckert and John Williams Mauchly, at the University of Pennsylvania, USA. This was based on decimal number system and it has no memory.
It could perform 5000 additions or 350 multiplications in one second. It contained 18000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 resistors, 10,000 capacitors and 60,000 switches and occupied a two room car garage. It consumed 150 kW of power. It weighed 27 tons.
EDSAC (FIRST STORED PROGRAM COMPUTER)
Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer (EDSAC) was first computer based on stored program concept. It was completed by Mourice Wilkes at Cambridge University in 1949.
EDVAC
Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer (EDVAC) was built by John Williams Mauchly, John Presper Eckert at Moore School, Pennsylvania in 1951.
UNIVAC (FIRST COMMERCIAL COMPUTER)
UNIVersal Automatic Computer (UNIVAC) was the first commercially used computer made by John Presper Eckert and John Williams Mauchly in June 14, 1951.
Classification of Computers According to Purpose
- General Purpose Computers
General purpose computers are designed to solve a large variety of problems. The different programs can be used to solve many problems. Most digital computers are general purpose computers and used in business and commercial data processing.
- Special Purpose Computers
A computer designed for machine control or process control would be different than a general purpose computer. The special purpose computers are designed to solve specific problems. The computer program for solving a specific problem is built right into the computer. Most analog computers are special purpose computers. These special purpose computers are widely used in industrial robotics.
Types of Computers
- Analog Computers
Analog computers are used to process continuous data. Analog computers represent variables by physical quantities. Thus any computer which solve problem by translating physical conditions such as flow, temperature, pressure, angular position or volt age into related mechanical or electrical related circuits as an analog for the physical phenomenon being investigated in general it is a computer which uses an analog quantity and produces analog values as output. Thus an analog computer measures continuously. Analog computers are very much speedy. They produce their results very fast. But their results are approximately correct. All the analog computers are special purpose computers.
- Digital Computers
Digital computer represents physical quantities with the help of digits or numbers. These numbers are used to perform Arithmetic calculations and also make logical decision to reach a conclusion, depending on, the data they receive from the user.
- Hybrid Computers
Various specifically designed computers are with both digital and analog characteristics combining the advantages of analog and digital computers when working as a system. Hybrid computers are being used extensively in process control system where it is necessary to have a close representation with the physical world.
The hybrid system provides the good precision that can be attained with analog computers and the greater control that is possible with digital computers, plus the ability to accept the input data in either form.
Classification of Computers According to Size
- Super Computers
Large scientific and research laboratories as well as the government organizations have extra ordinary demand for processing data which required tremendous processing speed, memory and other services which may not be provided with any other category to meet their needs. Therefore very large computers used are called Super Computers. These computers are extremely expensive and the speed is measured in billions of instructions per seconds.
- Main Frame Computers
The most expensive, largest and the most quickest or speedy computer are called mainframe computers. These computers are used in large companies, factories, organizations etc. the mainframe computers are the most expensive computers, they cost more th an 20 million rupees. In these computers 150 users are able to work on one C.P.U. The mainframes are able to process 1 to 8 bits at a time. They have several hundreds of megabytes of primary storage and operate at a speed measured in nano second.
- Mini Computers
Mini computers are smaller than mainframes, both in size and other facilities such as speed, storage capacity and other servi ces. They are versatile that they can be fitted where ever they are needed. Their speeds are rated between one and fifty million instructions per second (MIPS). They have primary storage in hundred to three hundred megabytes range with direct access storage device.
- Micro Computers
These are the smallest range of computers. They were introduced in the early 70‟s having less storing space and processing speed.
Micro computers of today‟s are equivalent to the mini computers of yesterday in terms of performing and processing. They are also called “computer of a chip” because its entire circuitry is contained in one tiny chip. The micro computers have a wide range of applications including uses as portable computer that can be plugged into any wall.
- Laptop Computers
The smallest computer in size has been developed. This type of small computers look like an office brief case and called “LAPTOP” computer. The laptops are also termed as “PORTABLE COMPUTERS.” Due to the small size and light weight, they become popular among the computer users. The businessmen found laptop very useful, during traveling and when they are far away from their desktop computers. A typical laptop computer has all the facilities available in microcomputer. The smallest laptops are called “PALMTOP”.
Generations of Computer
First Generation of Computer (1946-1959)
Main Features
Major Innovation – Vacuum Tubes
Main Memory – Punched Cards
Input Output Devices – Punched cards and papers
Languages – Low level machine language
Operating System – No operating system, human operators to set switches
Size – Main frame for example ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC
The duration lasted from 1946-1959 was based on vacuum tubes. These vacuum tubes were about the size of 100 watt light bulb and used as the internal computer component. However because thousands of such bulbs were used, the computers were very large and generate a large amount of heat, causing many problems in temperature regulation and climate control.
In this generation input and output device (punched card) that was used fro data storing purpose were very slow. The computer s were operating manually and the language used was a low level machine language (symbolic language) with binary code that required a high programming skill. ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC and Mark-1 were some of the major inventions of this generation.
Advantages of First Generation
- Vacuum tubes were used as electronic component.
- Electronic digital computers were developed for the first time.
- These computers were the fastest calculating devices of their time.
- Computations were performed in millisecond.
Disadvantages of First Generation
- Too large in size.
- They were unreliable.
- Induce a large amount of heat due to the vacuum tubes.
- Not portable.
- Limited commercial use.
Second Generation of Computers (1959-1964)
Main Features
Major Innovation – Transistors as main component.
Main Memory – RAM and ROM.
External Storage – Magnetic tapes and Magnetic Disk. Input Output Devices – Magnetic tapes and Magnetic Disk.
Languages – Assembly language, some high level languages for Example BASIC, COBOL, FORTRAN. Operating System – Human handles punched card.
Size – Main frame for example IBM-1401, NCR-300, IBM-600 etc.
The period of this generation is from 1959 to 1964. During this period transistor were used for internal logic circuits of computers. These computers could execute 200000 instructions per second. The input/output devices became much faster by the use of magnetic table. During this period the low level programing language were used however the high level programming languages such as FORTRAN and COBOL were also used. The problem of heat maintenance was solved and size of computer reduced, while speed and reliability were increased. Many companies manufactured second generation computers and many of those for business applications. The most popular second generation computer was IBM-1401, introduced in 1960, while the following computers were used by many business organizations. IBM-1400 series, IBM-1600 series, UNIVAC-III, NCR-300 etc.
Advantages of Second Generation
- Smaller in size as compares to 1st generation.
- Much more reliable.
- Less heat generated.
- Computation was performing in micro second.
- Less hardware and maintenance problem.
- Could be used for commercial use.
Disadvantages of Second Generation
- Very costly for commercial use.
- It still required frequent maintenance.
- Frequent cooling also required.
Third Generation of Computers (1965-1970) Main Features
Major Innovation – Integrated circuit (ICs) as basic electronic component.
Main Memory – PROM and DRAM.
External Storage – Improve disk (Floppy Disk)
Input and Output Devices – Keyboard for input, monitor for output. Languages – More high level languages.
Operating System – Complete operating systems were introduced.
Size – Mini, for example: IBM SYSTEM / 360, ICH-360, HONEY WELL-316 etc.
In this generation the integrated circuits (IC) were used. Integrated circuits contain many electronic components on a single chip. The disk oriented systems were made at the end of this generation. The size of computer became very small with better performance and reliability. High level programming languages were extensively used. In 1969 the first microprocessor chip INTEL 4004 was developed but it was used only in calculators. The faster input/output devices made possible multi-processing and multi programming. Where by a number of input terminals could be run virtually at the same time on a single centrally located computer. The famous computer were IBM-360, IBM-370, UNIVAC 9000 series etc.
Advantages of Third Generation
- Smaller in size as compared to second generation.
- More reliable.
- Portable
- Less electricity consumption.
- Heat generation was rare.
- General purpose computer.
Disadvantages of Third Generation
- Air conditioning was required in many cases due to ICs.
- Very advance technology was required to make the ICs.
Fourth Generation of Computers (1971-1981)
Main Features
Major Innovation – LSIC and VLSIC (Micro Processor)
Main Memory – EPROM and SRAM.
External Storage – Floppy Disk and Hard Disk. Input and Output Devices – Monitor for output. Languages – Languages and application software. Operating System – MS-DOS and PC-DOS
Size – Micro computer e.g. IBM-PC, Apple Macintosh etc.
The Integrated circuits were more developed and called Small scale integration (SSI), after some time the SSI were more developed and termed as Large scale integration (LSI). There was a great versatility of input/output devices. In 1971, a powerful microprocessor chip INTEL 8008 was introduced. The first microprocessor which is used in personal computers (PC) was INTEL The 8 inch floppy disk was also introduced in 1971, while hard disk was introduced in 1973. The 5.25 floppy disk was fi rst time used in 1978. The optical disk was developed in 1980. First portable computer “Osborne I” was marketed in 1981. IBM-3033, IBM-370, IBM system 34, IBM system 36, Cray-I, CP/M etc were introduced in this generation.
Advantages of Fourth Generation
- Smaller in size and much reliable.
- No cooling system required in many cases.
- Much faster computation.
- Portable and cheap.
- The heat generated was negligible.
- Totally general purpose computer.
Disadvantages of Fourth Generation
- Very advanced technology was required to fabricate to the ICs.
Fifth Generation (1981-Onward) Main Features
Major Innovations – ULSIC (Ultra large scale integrated circuit)
Main Memory – EEPROM, SIMM and DIMM.
External Storage – Modified magnetic and Optical disks.
Input/output Devices – Keyboard, Pointing Device, Scanner as input and Monitor as main output. Languages – AI (Artificial Intelligence) Expert systems.
Operating System – GUI based e.g. Windows 95, Windows NT.
Size – Very small in size example: Laptop, Note book, Digital Diary, Palm top and Pocket PC.
This generation is started from 1981 and still continued, new technologies are adopted to fabricate IC chips, such as electron beam, X-rays or laser rays. The Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) was developed, so the computer became much smaller than ever before. New memory storage device like bubble memory, optical or memory are being designed. the new computer will be controlled by using human voice and will work by giving command in our own language. Future computer will in some way to be intelligent and capable of making decision.
Advantages of Fifth Generation
- Very large storage capacity.
- Long bit processor builds.
- Artificial Intelligence Language developed.
Short Notes
- Super Computer
These are the largest and fastest machines today where numerical computations are carried out speeds of up to 50 million operation per second. Super computers are very sophisticated machines designed to perform complex calculations at fastest speeds. Super computers are used to model very large dynamic systems, such as weather patterns national or global weather forecasting, satellite tracking, cold-testing of atomic and nuclear weapon etc. Carry research and Intel are well known producers of Super Computers.
- Main Frames
A main frame originally meant the cabinet containing the central processor unit of a very large computer. After mini computer became available, the word main-frame comes to refers to the large computer itself.
Mainframes, the biggest and the most productive general purpose systems, that are made to model large dynamic computing need of a big organizations that serve hundreds of terminals all at the same time. A terminal consists of a monitor and keyboard that allow a person to enter information and retrieve it from the computer. These computers are the ultimate in sophistication, flexibility and speed.
- Mini-Computer
Mini computer are increasingly powerful and do almost anything that large computers do, only more slowly and at much lower cost than mainframes. This makes it ideal for small companies where capacity and speed of operations in not highly critical. These computers are smaller than mainframe and larger than micro computer in size. A mini computer is a multiprocessing system having terminals attached to it and is capable of supporting 4 to 200 users simultaneously. DEC VAX and IBM AS/400 are commonly used mini-computers.
- Micro-Computer
Micro-Computers are computers that are powered by microprocessors. Sometimes they are referred as SINGLE CHIP PROCESSOR a SYSTEM-ON-A-CHIP. Micro-computers or personal computers are the smallest computers, designed to be used by individuals for writing, illustrating, budgeting, playing games and communicating with other computers.

