Check the below Structure Of The Atom Class 9 MCQ for Science Chapter 4 with Answers available with PDF free download. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Our teachers have provided below Structure Of The Atom Class 9 Science MCQs Questions with answers which will help students to revise and get more marks in exams
Structure Of The Atom Class 9 Science MCQ Questions with Answers
Refer below for Structure Of The Atom Class 9 MCQ with solutions. Solve MCQ questions and compare them with the answers provided below
Question. Cathode rays have :
a. Charge only
b. Mass only
c. Charge as well as mass
d. Neither charge nor mass
Answer
A
Question. The number of valence electrons determines:
a. Physical properties of elements
b. Chemical properties of elements
c. Both physical and chemical properties of elements
d. Neither physical nor chemical properties of elements
Answer
B
Question. Na+ has 12 neutrons and 10 electrons. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Na+ has atomic number 10 and mass number 22.
b. Na+ has atomic number 11 and mass number 23.
c. Na+ has atomic number 10 and mass number 23.
d. Na+ has atomic number 11 and mass number 22.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is correct about proton?
a. It is the nucleus of deuterium
b. It is an ionized hydrogen molecule
c. It is an ionized Hydrogen atom
d. It is an α particle with unit positive charge
Answer
C
Question. The highest value of e/m ratio for anode rays is observed when the discharge tube is filled with:
a. N2
b. H2
c. He
d. Ar
Answer
B
Question. When a gold foil is bombarded by a beam of α particle, only a few of them get deflected whereas most go straight undeflected. This is because
a. The force of attraction exerted on α particles by the electrons is insufficient
b. The volume of nucleus is much smaller than that of the atom
c. The force of repulsion acting on the fast moving α particles is very small
d. The neutrons have no effect on α particles
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements does not belong to Bohr’s model?
a. Energy of the electrons in the orbit is quantized
b. The electrons in the orbit nearest to the nucleus is the lowest energy
c. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in different orbits having fixed energies
d. The electrons radiate energy during revolution due to force of attraction between nucleus and electrons
Answer
B
Question. How many electrons, protons and neutrons are present in X+, if atomic number of X is 19 and its mass number is 39
a. E=19, P=19, N= 20
b. E=18, P=19, N= 20
c. E=18, P=19, N= 19
d. E=19, P=20, N= 20
Answer
A
Question. A student weighs 30kg. Suppose his body is entirely made of electrons. How any electrons are there in his body? Mass of an electron= 9.1X10-31kg
a. 3.29 X1031
b. 3.29 X1030
c. 3.29 X1023
d. 3.29 X1032
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following does not have 8 valence electrons:
a. He
b. Ne
c. Ar
d. Cl-
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following does not have one electron in its valance shell
a. Na
b. Li
c. H
d. Ca
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following are isobars:18 Ar40,19K39 ,20Ca40, 19[K+]39
a. 19 K39 , 19+[K+]39
b. 18 Ar40,19 K39
c. 18Ar40,20 Ca40,
d. 18 Ar40,19 K39 ,20Ca40
Answer
C
Question. The electronic configuration of Cl- ion is:
a. 2,8,7
b. 2,8,8
c. 2,8,6
d. 2,8,8,1
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are isotopes:1
a. E=19, P=19, N= 20
b. E=18, P=19, N= 20
c. E=18, P=19, N= 19
d. E=19, P=20, N= 20
Answer
A
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
The mass of an atom is due to the masses of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The relative masses of protons and neutrons are almost equal to one. Therefore, the atomic mass of an element should be nearly a whole number. But in many cases the atomic masses are fractional. The main reason for these fractional atomic masses is that these elements occur in nature as a mixture of several isotopes. The atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of these isotopes in the ratio of their proportion of occurrence.
Question: An element occurs in two isotopic forms with atomic masses 10 and 11. What is the percentage abundance of two isotopes in the sample having atomic mass 10.80?
(a) 20, 80
(b) 50, 50
(c) 25, 70
(d) 60, 40
Answer:
A
Question: The fractional atomic masses of elements are due to the existence of
(a) isotopes having different masses
(b) diagonal relationship
(c) equal number of electrons and protons
(d) none of these.
Answer:
A
Question: Chlorine occurs in nature in the form of two isotopes with atomic masses 35 u and 37 u in the ratio of 3 : 1 respectively. Atomic mass of chlorine is
(a) 35.5 u
(b) 34.5 u
(c) 35 u
(d) 36 u
Answer:
A
a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question: Assertion : Thomson’s atomic model is known as ‘raisin pudding’ model.
Reason : The atom is visualized as a pudding of positive charge with electrons (raisins) embedded in it.
Answer:
A
Question: Assertion : Anions are larger in size than the parent atom.
Reason : In an anion, the number of protons in the nucleus is less than the number of electrons moving around it.
Answer:
A
Question: Assertion : The number of electrons gained,lost or shared by the atom of an element so as to complete its octet is called the valency of the element.
Reason : Elements having the same number of valence electrons in their atoms possess different chemical properties.
Answer:
C
Question: Assertion : Cathode rays get deflected towards the positive plate of electric field.
Reason : Cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles known as electrons.
Answer:
A
Question: Assertion : For noble gases, valency is zero.
Reason : Noble gases have 8 valence electrons.
Answer:
A
Question: Assertion : Electrons moving in the same orbit will not lose or gain energy.
Reason : On jumping from higher to lower energy level, the electron will gain energy.
Answer:
C
Question: Assertion : The distribution of electrons in different orbits or shells is governed by a scheme known as Bohr-Bury scheme.
Reason : Electrons are filled in the shells in a stepwise manner in increasing order of energy of the energy shell.
Answer:
B
Question: Assertion : Bohr’s orbits are called stationary orbits.
Reason : Electrons remain stationary in these orbits for sometime.
Answer:
C
Question: Assertion : The size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom.
Reason : The electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom.
Answer:
B
Question: Assertion : In Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, very few a-particles are deflected back.
Reason : The size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom
Answer:
B
Case Based MCQs
The maximum number of the electrons which are permitted to be assigned to an energy shell of an atom is called the electron capacity of that shell. The distribution of electrons in different orbits or shell is governed by a scheme known as Bohr-Bury scheme. According to this scheme :
(i) The maximum number of the electrons that can be present in any shell is given by the formula 2n2 where, n is the number of energy level.
(ii) The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the outermost shell is 8.
Electrons are filled in the shells in a stepwise manner in increasing order of energy of the energy shell.
Question: Which of the following configuration represent sodium?
(a) 2, 8, 4
(b) 2, 8, 5
(c) 2, 3
(d) 2, 8, 1
Answer:
D
Question: Identify the element with the configuration K-2, L-8, M-3.
(a) Aluminium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Sodium
(d) Beryllium
Answer:
A
Question: What is the maximum electrons capacity of N shell?
(a) 24
(b) 8
(c) 18
(d) 32
Answer:
D
The table shows the number of sub-atomic particles in arbitrary elements, A to H.
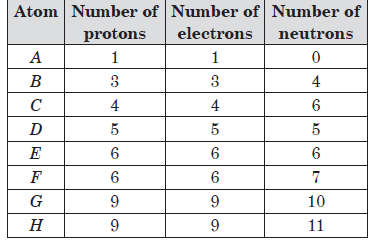
Question: Which of the given elements attains noble gas configuration by gaining an electron?
(i) A (ii) E
(iii) C (iv) H
(a) (iii) only
(b) (iv) only
(c) (i) and (iv) only
(d) (i) only C
Answer:
C
Question: The pair of isotopes from the table is/are
(i) C and D (ii) E and F
(iii) B and C (iv) G and H
(a) (ii) only
(b) (iv) only
(c) (ii) and (iv) only
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
C
Question: The atom _____ has nucleon number 13 and atom _____ has valency 3.
(a) G and F
(b) F and D
(c) C and E
(d) F and B
Answer:
B
Question: Identify pair of isobars from the table.
(a) C and D
(b) B and E
(c) G and H
(d) E and F
Answer:
A
The given diagrams show the atomic structures of elements X and Y.
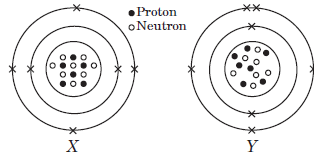
Question: Valency of elements X and Y are respectively,
(a) 4 and 3
(b) 2 and 5
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 3 and 4 A
Answer:
A
Question: Element X and Y could be _____ and _____respectively.
(a) Be and B
(b) C and O
(c) F and N
(d) C and N
Answer:
D
Question: Elements X and Y are
(a) isotopes
(b) isoelectronic
(c) isobars
(d) isomers.
Answer:
C

