Please refer to MCQ Questions Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques for Chapter 2 Class 11 Chemistry given below. All MCQ questions are provided with answers. These MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry are designed based on the chapters given in your CBSE NCERT Textbook for Class 11 Chemistry. These MCQ Questions are expected to come in your class 11 Board exams.
Question. Which of the following organic compound was synthesised by F. Wohler from an inorganic compound?
(a) Methane
(b) Urea
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Chloroform
Answer
B
Question. The discovery that shook the belief in the vital force theory was
(a) Stereoisomerism
(b) Synthesis of indigo
(c) Wholer’s synthesis of urea from ammonium cyanate
(d) Fermentation of sugars
Answer
C
Question. The absolute configuration of the following

(a) 2S, 3R
(b) 2S, 3S
(c) 2R, 3S
(d) 2R, 3R
Answer
B
Question. In laboratory, first organic compound was synthesised by
(a) Kekule
(b) Hennel
(c) Wohler
(d) Liebig
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following scientist proposed that a ‘vital force’ was responsible for the formation of organic compounds ?
(a) Berzilius
(b) Wohler
(c) Berthelot
(d) Kolbe
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following molecules is expected to rotate the plane of plane polarised light?

Question. First organic compound to be synthesised was
(a) methane
(b) cane sugar
(c) acetic acid
(d) urea
Answer
A
Question. Who is known as the “Father of Chemistry”?
(a) Faraday
(b) Priestley
(c) Rutherford
(d) Lavoisier
Answer
D
Question. The percentage of s- character of the hybrid orbitals in ethane, ethene and ethyne are respectively.
(a) 50, 75, 100
(b) 10, 20, 40
(c) 25, 33, 50
(d) 25, 50, 75
Answer
C
Question. Tautomerism is exhibited by
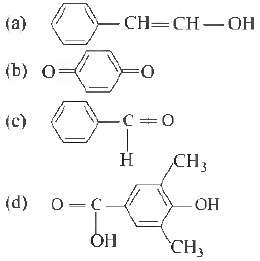
Answer
A
Question. Select the molecule which has only one π-bond
(a) CH ≡ CH
(b) CH2 = CHCHO
(c) CH3CH = CH2
(d) CH3CH=CHCOOH
Answer
C
Question. 2- Pentene contains
(a) 15 σ- and one π- bond
(b) 14 σ-and one π- bond
(c) 15 σ- and two π- bonds
(d) 14 σ- and two π- bonds
Answer
B
Question. The successive members in a homologues series differ from each other by ________
(a) – CH2CH2 – unit
(b) – CH2 unit
(c) – OCH3 unit
(d) – CH3 unit
Answer
B
Question. Among the following four structures I to IV

it is true that
(a) all fow- are chiral compounds
(b) I and II are chiral compounds
(c) only ill is a chiral compound
(d) IT and IV are chiral compounds
Answer
B
Question. The hybridisation of carbon atom in C — C single bond of H2C = CH — CH = CH2 is
(a) sp3 — sp
(b) sp2 — sp
(c) sp2 — sp2
(b) sp3 — sp3
Answer
C
Question. In the hydrocarbon CH3 – CH = CH – CH2 – C ≡ CH
6 5 4 3 2 1
The state of hybrization of carbons 1, 3 and 5 are in the following sequence
(a) sp2, sp, sp3
(b) sp, sp3, sp2
(c) sp, sp2, sp3
(d) sp3, sp2, sp
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is incorrectly matched –
(a) vinegar →carboxylic acid
(b) C2H6 →alkane
(c) ethanol →alcohol
(d) methanol →ketone
Answer
D
Question. Amongst the following compounds, the optically active alkane having lowest molecular mass is

Answer
C
Question. The functional group present in organic, acid is –
(a) – OH
(b) – CHO
(c) –COOH
(d) > C = O
Answer
C
Question. Which of these contains the carbonyl group?
(a) ketones
(b) aldehydes
(c) esters
(d) all of these
Answer
D
Question. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group –
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde.
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol.
Answer
C
Question. The compound, whose stereo-chemical fommla is written below, exhibits x geometrical isomers and y optical isomers The values of x and y are
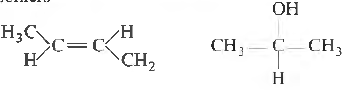
(a) 4 and 4
(b) 2 and 2
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 4 and 2
Answer
B
Question. The functional group present in CH3COOC2H5 is –
(a) ketonic
(b) aldehydic
(c) ester
(d) carboxylic
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following have incorrect molecular formula?
A. Icosane – C10H22
B. Triacontane – C30H62
C. Nonane – C9H20
D. Heptane – C7H14
(a) (A) and (D)
(b) Only (D)
(c) (B) and (D)
(d) Only (B)
Answer
A
Question. The compound which has one isopropyl group is
(a) 2, 2, 3, 3 – Tetramethylpentane
(b) 2, 2 – Dimethylpentane
(c) 2, 2, 3- Trimethylpentane
(d) 2- Methypentane
Answer
D
Question.

Compound can exhibit
(a) geometrical isomerism
(b) tautomerism
(c) optical isomerism
(d) geometrical and optical isomerism
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is false for isopentane ?
(a) It has three CH3 groups
(b) It has one CH2 group
(c) It has one CH group
(d) It has a carbon which is not bonded to hydrogen
Answer
D
Question. Geometrical isomerism is possible in
(a) acetone oxime
(b) isobutene
(c) acetophenone oxime
(d) benzophenone oxime
Answer
C
Question. Ethers are isomeric with
(a) aldehydes
(b) ketones
(c) both aldehydes and ketones
(d) alcohols
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following will have a meso-isomer also?
(a) 2-chlorobutane
(b) 2, 3-dichlorobutane
(c) 2, 3-dichloropentane
(d) 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
Answer
B
Question. In this reaction,
CH3CHO+HCN → CH3CH(OH)CN
→H·OH CH3CH(OH)COOH
an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be
(a) 50% D + 50% L-isomer
(b) 20% D + 80% L-isomer
(c) D-isomer
(d) L-isomer
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following shows functional isomerism?
(a) C2H4
(b) C3H6
(c) C2H5OH
(d) CH2Cl2
Answer
C
Question. The name of the compound

is
(a) (2Z, 4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
(b) (2Z, 4E)-2, 4-hexadiene
(c) (2E, 4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
(d) (4E, 4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
(e) (2E, 4E)-2, 4-hexadiene
Answer
A
Question. Geometrical isomerism is shown by
(a) —C—C—
(b) C=C
(c) — C- C—
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds is optically active ?
(a) (CH3 )2CHCH2OH
(b) CH3CH2OH
(c) CCI2F2
(d) CH3CHOHC2H5
Answer
D
Question. Isomers of prop ionic acid are
(a) HCOOC2H5 and CH3COOCH3
(b) HCOOCC2H5 and C3H7COOH
(c) CH3COOCH3 and C3H7OH
(d) C3H7OH and CH3COOCH3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following Fischer’s projection fommla is identical to D-glyceraldehyde?

Answer
B
Question. Metamers of ethyl propionate are
(a) C4H9COOH and HCOOC4H9
(b) C4H9COOH and CH3COOC3H7
(c) CH3COOCH3 and CH3COOC3H7
(d) CH3COOC3H7 and C3H7COOCH3
Answer
D
Question. n-pentane, iso-pentane and neo-pentane are examples for isomers of the type
(a) geometrical
(b) optical
(c) chain
(d) positional
Answer
C
Question. Different structures generated due to rotation about, C—C axis, of an organic molecule, are examples of
(a) geometrical isomerism
(b) conformational isomerism
(c) optical isomerism
(d) structural isomerism
Answer
B
Question. For which of the following parameters the structural isomers C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 would be expected to have the same values? (Assume ideal behaviour)
(a) Heat of vaporisation
(b) Vapour pressure at the same temperature
(c) Boiling points
(d) Gaseous densities at the same temperature and pressure
Answer
D
Question. Maximun1 enol content is in

Answer
B
Question. Increasing order of stability among the three main conformations, (i.e. Eclipse, Anti, Gauche) of 2-fluoroethanol is
(a) Eclipse, Gauche, Anti
(b) Gauche, Eclipse, Anti
(c) Eclipse, Anti, Gauche
(d) Anti, Gauche, Eclipse
Answer
C
Question. How many asymmetric carbon atoms are present in
I. 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane
II. 3-methylcyclopentane and
III. 3-methylcyclohexene ?
(a) Two, one, one
(b) One, one, one
(c) Two, none, two
(d) Two, none, one
Answer
D
Question. Geometrical isomerism is possible in case of
(a) pentene-2
(b) propane
(c) pentane
(d) ethene
Answer
A
Question. The number of isomers of the compound with molecular fommla C2H2Br2 is
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 2
Answer
D
Question. C6H5C = N and C6H5N = C exhibit which type of isomerism?
(a) Position
(b) Functional
(c) Metamerism
(d) Dextro-isomerism
Answer
B
Question. How many isomers are possible for the alkane C4H10 ?
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer
C
Question. The number of meso-forms in the following compound is
HOOC- CH(CH3 )· CH(OH)· CH(Cl)
· CH(OH)CH(CH3 )· COOH
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 16
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds is optically active ?
(a) 1-butanol
(b) Isopropyl alcohol
(c) Acetaldehyde
(d) 2-butanol
Answer
D
Question. The number of primary, secondary and tertiary carbons in 3, 4-dimethylheptane are respectively
(a) 4, 3 and 2
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 4, 2 and 3
(d) 3, 4 and 2
Answer
A
Question. The number of primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbons in neopentane are respectively
(a) 4, 3, 2 and 1
(b) 5, 0, 0 and 1
(c) 4, 0, 0 and 1
(d) 4, 0, 1 and 1
Answer
C
Question. What is the IUPAC name of t-butyl alcohol.
(a) Butanol–2
(b) 2–Methyl-propan–2-ol
(c) Butanol–1
(d) Propanol-2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds contains 1°, 2°, 3° as well as 4° carbon atoms ?
(a) Neopentane
(b) 2-methyl pentane
(c) 2,3-dimethyl butane
(d) 2,2,3-trimethyl pentane
Answer
D
Question. The number of secondary hydrogens in 2, 2-dimethylbutane is
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 2
Answer
D
Question. The IUPAC name of CH3COCH (CH3)2 is –
(a) isopropyl methyl ketone
(b) 2-methyl-3-butanone
(c) 4-methylisopropyl ketone
(d) 3-methyl-2-butanone
Answer
D
Question. IUPAC name of (CH3)3 CCl is
(a) 1-butyl chloride
(b) 3-chloro butane
(c) 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
(d) 2-butyl chloride
Answer
C
Question. The IUPAC name of neopentane is
(a) 2, 2-dimethylpropane
(b) 2-methylpropane
(c) 2, 2-dimethylbutane
(d) 2-methylbutane
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of the compound CH3 — CH(CH3) — CO – CH3, is
(a) 3-methyl 2-butanone
(b) 2-methyl 3-butanone
(c) isopropyl methyl ketone
(d) methyl isopropyl ketone
Answer
A
Question. Total number of structural isomers possible for C3H6 are :
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is false for isopentane–
(a) It has three CH3 groups
(b) It has one CH2 group
(c) It has one CH group
(d) It has a carbon which is not bonded to hydrogen
Answer
D
Question. The IUPAC name of the compound CH3OCH2CH2CH2OCH2CH3 is
(a) 3-ethoxy-1-methoxypropane
(b) 1-ethoxy-3-methoxypropane
(c) 2, 5-dioxyhexane
(d) ethoxypropane oxymethane
Answer
A
Question. Which organic structure among the following is not an isomer of the compound CH3–CO–CH2CH2CH2CH3 ?
(a) CH3CH2OCH =CHCH2CH3
(b) CH3CH = CHCH2CH2CHO
(c) (CH3)2CH–CO–CH2CH3
(d) CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3
Answer
B
Question. The least number of carbon atoms in alkane showing isomerism is
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer
D
Question. The number of possible alkynes with molecular formula C5H8 is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
B
Question. The total number of isomers for C4H8 is
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer
B
Question. An aromatic compound of formula C7H7Cl has in all ….. isomers :
(a) 5
(d) 2
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer
C
Question. CH3CH2OH and CH3OCH3 are the examples of
(a) chain isomerism
(b) functional isomerism
(c) position isomerism
(d) metamerism
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds is isomeric with 2, 2, 4, 4- tetramethylhexane?
(a) 3-ethyl -2, 2- dimethylpentane
(b) 4-isopropylheptane
(c) 4-ethyl-3-methyl-4-n propyloctane
(d) 4, 4-diethyl-3-methylheptane
Answer
B
Question. Isomers of propionic acid are
(a) HCOOC2H5 and CH3COOCH3
(b) HCOOC2H5 and C3H7COOH
(c) CH3COOCH3 and C3H7OH
(d) C3H7OH and CH3COCH3
Answer
A
Question. C6H5C ≡ N and C6H5N ≡ C are which type of isomers?
(a) Position
(b) Functional
(c) Tautomerism
(d) Linkage
Answer
B
Question. A functional isomer of 1-butyne is
(a) 2-butyne
(b) 1-butene
(c) 2-butene
(d) 1, 3-butadiene
Answer
D
Question. In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?
(a) Alcohols
(b) Aldehydes
(c) Alkyl halides
(d) Cyanides
Answer
C
Question. Which are isomers ?
(a) ethyl alcohol and dimethyl ether
(b) acetone and acetaldehyde
(c) propionic acid and propanone
(d) methyl alcohol and dimethyl ether
Answer
A
Question. Methoxyethane and propanol are the examples of isomerism of the type
(a) structural
(b) position
(c) functional
(d) tautomerism
Answer
C
Question. The compounds CH3CH == CHCH3 and CH3CH2CH == CH2
(a) are tautomers
(b) are position isomers
(c) contain same number of sp3– sp3, sp3– sp2 and sp2– sp2 carbon-carbon bonds
(d) exist together in dynamic equilibrium
Answer
B
Question. Heterolytic fission of C – Br bond results in the formation of
(a) free radical
(b) carbanion
(c) carbocation
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following carbocations is least stable?
(a) tert-Alkyl
(b) sec-Alkyl
(c) pri-Alkyl
(d) Methyl
Answer
D
Question. The organic reaction which proceed through heterolytic bond cleavage are called ________
(a) ionic
(b) polar
(c) nonpolar
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. The shape of methyl carbanion is similar to that of –
(a) BF3
(b) NH3
(c) methyl free radical
(d) methyl carbocation
Answer
B

Organic Chemistry Class 11 MCQ Chapter 12 has been gathered for students to rehearse. Students can prepare this Class 11 Organic Chemistry MCQ. Each question has four choices with answers. Firstly, Solve all these Questions and check your answer with the right answer. If your answers do not match with the right answer, Don’t worry try again because You need to prepare daily to score higher marks in the Class 11 Chemistry Exam.
We hope this Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 MCQ shared with you will help you to get good marks in your exam. We have also other study materials like NCERT Solutions, NCERT Book, Exam Question, and sampler paper of Class 11. If You want to score higher in your exam, So practice all this study material and if you have any problem in regard to the MCQ of Organic Chemistry Class 11 then, write it in the comment box and we will guide you as much as possible.


