Check the below NCERT Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry MCQ Questions with Answers available with PDF free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers were prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Our teachers have provided below Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry MCQs Questions with answers which will help students to revise and get more marks in exams
Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry MCQ Questions with Answers
Refer below for Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry MCQ Questions with solutions. Solve questions and compare with the answers provided below
Chemistry Biomolecules Class 12 MCQ Questions have been gathered for students to rehearse. Students can prepare these Chemistry Biomolecules MCQs Class 12 Question. Each question has four choices with answers. Firstly, Solve all these Questions and check your answer with the given answer. If your answers do not match with the right answer, Don’t worry try again because You need to prepare daily to score higher marks in the Class 12 Chemistry Exam.
Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry MCQ Questions
Question. The function of enzymes in the living system is to
(a) catalyse biochemical reactions
(b) provide energy
(c) transport oxygen
(d) provide immunity.
Answer
A
Question. Deficiency of vitamin B1 causes the disease
(a) convulsions
(b) beri-beri
(c) cheilosis
(d) sterility.
Answer
B
Question. The difference between amylose and amylopectin is
(a) amylopectin have 1 → 4 a-linkage and 1 → 6 a-linkage
(b) amylose have 1 → 4 a-linkage and 1 → 6 b-linkage
(c) amylopectin have 1 → 4 a-linkage and 1 → 6 b-linkage
(d) amylose is made up of glucose and galactose.
Answer
A
Question. Which one given below is a non-reducing sugar?
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Maltose
(d) Lactose
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following statements is not true regarding (+)–lactose?
(a) On hydrolysis (+)–lactose gives equal amount of D(+)–glucose and D(+)–galactose.
(b) (+)–Lactose is a b-glucoside formed by the union of a molecule of D(+)–glucose and a molecule of D(+)–galactose.
(c) (+)–Lactose is a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation.
(d) (+)–Lactose, C12H22O11 contains 8 –OH groups.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following hormones contains iodine?
(a) Testosterone
(b) Adrenaline
(c) Thyroxine
(d) Insulin
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is a peptide hormone?
(a) Adrenaline
(b) Glucagon
(c) Testosterone
(d) Thyroxine
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation?
(a) (+)–Sucrose
(b) (+)–Lactose
(c) (+)–Maltose
(d) (–)–Fructose
Answer
A
Question. Fructose reduces Tollens’ reagent due to
(a) asymmetric carbons
(b) primary alcoholic group
(c) secondary alcoholic group
(d) enolisation of fructose followed by conversion to aldehyde by base.
Answer
D
Question. Number of chiral carbons in b-D-(+) glucose is
(a) five
(b) six
(c) three
(d) four.
Answer
D
Question. Glycolysis is
(a) oxidation of glucose to glutamate
(b) conversion of pyruvate to citrate
(c) oxidation of glucose to pyruvate
(d) conversion of glucose to haem.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements about enzymes is true?
(a) Enzymes catalyse chemical reactions by increasing the activation energy.
(b) Enzymes are highly specific both in binding chiral substrates and in catalysing their reactions.
(c) Enzymes lack in nucleophilic groups.
(d) Pepsin is proteolytic enzyme.
Answer
B
Question. Enzymes take part in a reaction and
(a) decrease the rate of a chemical reaction
(b) increase the rate of a chemical reaction
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
Question. Cellulose is polymer of
(a) glucose
(b) fructose
(c) ribose
(d) sucrose.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following gives positive Fehling solution test?
(a) Sucrose
(b) Glucose
(c) Fats (d) Protein
Answer
B
Question. RNA and DNA are chiral molecules, their chirality is due to
(a) chiral bases
(b) chiral phosphate ester units
(c) D-sugar component
(d) L-sugar component.
Answer
C
Question. Chargaff’s rule states that in an organism
(a) amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of thymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G) is equal to that of cytosine (C)
(b) amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of guanine (G) and the amount of thymine (T) is equal to that of cytosine (C)
(c) amount of adenine (A) is equal to that of cytosine (C) and the amount of thymine (T) is equal to that of guanine (G)
(d) amounts of all bases are equal.
Answer
A
Question. Lipids are
(a) nucleic acids occurring in plants
(b) proteins occurring in animals
(c) carbohydrates occurring in plants
(d) fats of natural origin
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statements is true?
(a) Saponification of oil yields a diol
(b) Drying ofoil involves hydrolysis
(c) Addition of antioxidant to oil minimises rancidity
(d) Refining of oil involves hydrogenation
Answer
C
Question. Which base is present in RNA but not in DNA ?
(a) Uracil
(b) Cytosine
(c) Guanine
(d) Thymine
Answer
A
Question. The pyrimidine bases present in DNA are
(a) cytosine and adenine
(b) cytosine and guanine
(c) cytosine and thymine
(d) cytosine and uracil
Answer
C
Question. There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids.The maximum number of tripeptides that can be obtained is
(a) 8000
(b) 6470
(c) 7465
(d) 5360
Answer
A
Question. Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
(a) Thiolacetone
(b) Thiol
(c) Thioether
(d) Thioester
Answer
B
Question. The purine base present in RNA is
(a) guanine
(b) thymine
(c) cytosine
(d) uracil
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is not present in RNA?
(a) Uracil
(b) Thymine
(c) Ribose
(d) Phosphate
Answer
B
Question. In both DNA and RNA, heterocylic base and phosphate ester linkages are at
(a) C’5 and C’1 respectively of the sugar molecule
(b) C’1 and C’5 respectively of the sugar molecule
(c) C’2 and C’5 respectively of the sugar molecule
(d) C’5 and C’2 respectively of the sugar molecule
Answer
A
Question. How many hydrogen bonds are present between pair of thymine and adenine in DNA ?
(a) 1-hydrogen bond
(b) 2-hydrogen bonds
(c) 3-hydrogen bonds
(d) No bonds occur
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not present in a nucleotide?
(a) Cytosine
(b) Guanine
(c) Adenine
(d) Tyrosine
Answer
D
Question. A substance forms Zwitter ion. It can have functional groups
(a) —NH2 , —COOH
(b) —NH2, —SO3H
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following bases is not present in DNA?
(a) Quinoline
(b) Adenine
(c) Cytosine
(d) Thymine
Answer
A
Question. In biological systems, the RNA molecules direct the synthesis of specific proteins which are characteristics of each kinds of organism. This process is known as
(a) transcription
(b) mutation
(c) replication
(d) translation
(e) flocculation
Answer
D
Question. Night-blindness may be caused by the deficiency of vitamin
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer
A
Question. Sanger’s method is used to identify
(a) C-terminal amino acid
(b) N-terminal amino acid
(c) side chain
(d) molecular weight protein
Answer
D
Question. Helical structure of protein is stablilised by
(a) peptide bond
(b) hydrogen bond
(c) van der Waals’ force
(d) dipole association
Answer
B
Question. Match the following Columns.
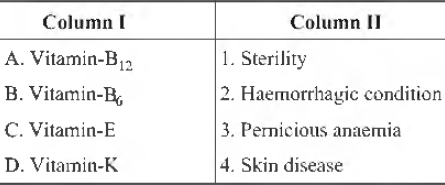
Codes
A B C D
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 3 4 1 2
(d) 3 4 2 1
Answer
C
Question. The chemical name of vitamin B1 is
(a) ascorbic acid
(b) riboflavin
(c) pyridoxine
(d) thiamine
Answer
D
Question. Match the following Columns.

Codes
A B C D E
(a) 3 4 5 2 1
(b) 3 4 5 1 2
(c) 4 5 1 3 2
(d) 3 5 4 2 2
(e) 4 5 3 1 2
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds is not of the lipid series ?
(a) Fat
(c) Oil
(b) Soap
(d) Lard
Answer
B
Question. a-D-glucose and b-D-glucose are
(a) epimers
(b) anomers
(c) enantiomers
(d) diastereomers.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the sweetest sugar?
(a) Fructose
(b) Glucose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Maltose
Answer
A
Question. Glucose molecule reacts with X number of molecules of phenyl hydrazine to yield osazone. The value of X is
(a) two
(b) one
(c) four
(d) three.
Answer
D
Question. The oxidation of glucose is one of the most important reactions in a living cell. What is the number of ATP molecules generated in cells from one molecule of glucose?
(a) 28
(b) 38
(c) 12
(d) 18
Answer
B
Question. The a-D-glucose and b-D-glucose differ from each other due to difference in carbon atom with respect to its
(a) number of OH groups
(b) size of hemiacetal ring
(c) conformation
(d) configuration.
Answer
D
Question. The correct statement regarding RNA and DNA, respectively is
(a) the sugar component in RNA is a arabinose and the sugar component in DNA is ribose
(b) the sugar component in RNA is 2′-deoxyribose and the sugar component in DNA is arabinose
(c) the sugar component in RNA is arabinose and the sugar component in DNA is 2′-deoxyribose
(d) the sugar component in RNA is ribose and the sugar component in DNA is 2′-deoxyribose.
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following sets of monosaccharides forms sucrose?
(a) a-D-galactopyranose and a-D-glucopyranose
(b) a-D-glucopyranose and b-D-fructofuranose
(c) b-D-glucopyranose and a-D-fructofuranose
(d) a-D-glucopyranose and b-D-fructopyranose
Answer
B
Question. In DNA, the linkages between different nitrogenous bases are
(a) phosphate linkage
(b) H-bonding
(c) glycosidic linkage
(d) peptide linkage.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is an amine hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Progesterone
(c) Thyroxine
(d) Oxypurin
Answer
C
Question. The segment of DNA which acts as the instrumental manual for the synthesis of the protein is
(a) ribose
(b) gene
(c) nucleoside
(d) nucleotide.
Answer
B
Question. Chemically considering digestion is basically
(a) anabolism
(b) hydrogenation
(c) hydrolysis
(d) dehydrogenation.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a basic amino acid?
(a) Serine
(b) Alanine
(c) Tyrosine
(d) Lysine
Answer
D
Question. The non-essential amino acid among the following is
(a) lysine
(b) valine
(c) leucine
(d) alanine.
Answer
D
Question. Which structure(s) of proteins remain(s) intact during denaturation process?
(a) Both secondary and tertiary structures
(b) Primary structure only
(c) Secondary structure only
(d) Tertiary structure only
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds can form a zwitter ion?
(a) Aniline
(b) Acetanilide
(c) Benzoic acid
(d) Glycine
Answer
D
Question. The hormone that helps in the conversion of glucose to glycogen is
(a) cortisone
(b) bile acids
(c) adrenaline
(d) insulin.
Answer
D
Question. The cell membranes are mainly composed of
(a) fats
(b) proteins
(c) phospholipids
(d) carbohydrates.
Answer
C
Question. In a protein molecule various amino acids are linked together by
(a) peptide bond
(b) dative bond
(c) a-glycosidic bond
(d) b-glycosidic bond.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the statements about “Denaturation” given below are correct?
(1) Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
(2) Denaturation leads to the conversion of double strand of DNA into single strand.
(3) Denaturation affects primary structure which gets distorted.
(a) (2) and (3)
(b) (1) and (3)
(c) (1) and (2)
(d) (1), (2) and (3)
Answer
C
Question. On hydrolysis of starch, we finally get
(a) glucose
(b) fructose
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) sucrose.
Answer
A
Question. Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
(a) Thioester
(b) Thioether
(c) Thio
l (d) Thiolactone
Answer
C

We hope you liked Biomolecules MCQs Class 12 Questions with answers provided above. In case you have any questions please post them in the comments section below and our Chemistry teachers will provide a response.
We hope this Biomolecules Class 12 MCQ Pdf Download shared with you will help you to get good marks in your exam. We have also other study material like NCERT Solutions, NCERT Book, Exam Question, and simpler paper of Class 12. If You want to score higher in your exam, So practice all this study material and if you have any problem in regard to the Biomolecules MCQs Class 12 then, write it in the comment box and we will guide you as much as possible.
