Check the below NCERT MCQ on Electrochemistry Class 12 with Answers available with PDF free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers were prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination pattern issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Our teachers have provided below MCQ on Electrochemistry Class 12 with Answers which will help students to revise and get more marks in exams
MCQ on Electrochemistry Class 12 with Answers with Answers
Refer below for MCQ on Electrochemistry Class 12 with Answers. Solve questions and compare with the answers provided below
MCQ on Electrochemistry Class 12 with Answers
Question. The standard electrode potential (E°) values of Al3+/Al, Ag+/Ag, K+/K and Cr3+/Cr are –1.66 V, 0.80 V, –2.93 V and –0.74 V, respectively. The correct decreasing order of reducing power of the metal is
(a) Ag > Cr > Al > K
(b) K > Al > Cr > Ag
(c) K > Al > Ag > Cr
(d) Al > K > Ag > Cr
Answer
B
Question. A button cell used in watches function as following :
Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ 2Ag(s) + Zn2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq)
If half cell potentials are
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s); E° = – 0.76 V
Ag2O(s) + H2O(l) + 2e– → 2Ag(s) + 2OH–(aq); E° = 0.34 V
The cell potential will be
(a) 0.84 V
(b) 1.34 V
(c) 1.10 V
(d) 0.42 V
Answer
C
Question. Standard reduction potentials of the half reactions are given below :
F2(g) + 2e– → 2F–(aq) ; E° = + 2.85 V
Cl2(g) + 2e– → 2Cl–(aq) ; E° = + 1.36 V
Br2(l) + 2e– → 2Br–(aq) ; E° = + 1.06 V
I2(s) + 2e– → 2I–(aq) ; E° = + 0.53 V
The strongest oxidising and reducing agents respectively are
(a) F2 and I–
(b) Br2 and Cl–
(c) Cl2 and Br–
(d) Cl2 and I2
Answer
A
Question. Standard electrode potentials of three metals X, Y and Z are –1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V respectively.
The reducing power of these metals will be
(a) Y > Z > X
(b) Y > X > Z
(c) Z > X > Y
(d) X > Y > Z
Answer
C
Question. Standard electrode potential for Sn4+/Sn2+ couple is +0.15 V and that for the Cr3+/Cr couple is –0.74 V. These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be
(a) + 1.19 V
(b) + 0.89 V
(c) + 0.18 V
(d) + 1.83 V
Answer
B
Question. A solution contains Fe2+, Fe3+ and I– ions. This solution was treated with iodine at 35°C. E° for Fe3+/Fe2+ is + 0.77 V and E° for I2/2I– = 0.536 V. The favourable redox reaction is
(a) I2 will be reduced to I–
(b) there will be no redox reaction
(c) I– will be oxidised to I2
(d) Fe2+ will be oxidised to Fe3+.
Answer
C
Question. Consider the following relations for emf of an electrochemical cell
(i) EMF of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) –(Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) EMF of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iii) EMF of cell = (Reductional potential of anode)+ (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iv) EMF of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?
(a) (iii) and (i)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing agent is
[Fe(CN)6]4– → [Fe(CN)6]3– + e– ; E° = –0.35 V
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– ; E° = –0.77 V
(a) Fe3+
(b) [Fe(CN)6]3–
(c) [Fe(CN)6]4–
(d) Fe2+
Answer
A
Question. A hypothetical electrochemical cell is shown below : A/ A+ (x M)||B+(y M)|B
The emf measured is + 0.20 V. The cell reaction is
(a) A + B+ → A+ + B
(b) A+ + B → A + B+
(c) A+ + e– → A; B+ + e– → B
(d) the cell reaction cannot be predicted.
Answer
A
Question. E°Fe2+/Fe = – 0.441 V and E°Fe3+/Fe2+ = 0.771 V, the standard EMF of the reaction Fe + 2Fe3+ → 3Fe2+ will be
(a) 0.111 V
(b) 0.330 V
(c) 1.653 V
(d) 1.212 V
Answer
D
Question. Standard electrode potentials are Fe2+/Fe;
E° = –0.44 and Fe3+/Fe2+; E° = 0.77. Fe2+, Fe3+ and Fe blocks are kept together, then
(a) Fe3+ increases
(b) Fe3+ decreases
(c) Fe2+/Fe3+ remains unchanged
(d) Fe2+ decreases.
Answer
B
Question. Electrode potential for the following half-cell reactions are
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e–; E° = + 0.76 V;
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–; E° = + 0.44 V.
The EMF for the cell reaction
Fe2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Fe will be
(a) – 0.32 V
(b) + 1.20 V
(c) – 1.20 V
(d) + 0.32 V
Answer
D
Question. An electrochemical cell is set up as :
Pt; H2 (1 atm)|HCl(0.1 M) || CH3COOH (0.1 M) |H2 (1 atm); Pt. The e.m.f. of this cell will not be zero, because
(a) acids used in two compartments are different
(b) e.m.f. depends on molarities of acids used
(c) the temperature is constant
(d) pH of 0.1 M HCl and 0.1 M CH3COOH is not same.
Answer
D
Question. Standard reduction potentials at 25°C of Li+|Li, Ba2+|Ba, Na+|Na and Mg2+|Mg are –3.05, –2.90,–2.71 and –2.37 volt respectively. Which one of the following is the strongest oxidising agent?
(a) Ba2+
(b) Mg2+
(c) Na+
(d) Li+
Answer
B
Question. A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine?
(a) Hydrogen iodide
(b) Sulphur dioxide
(c) Chlorine
(d) Iodine
Answer
C
Question. For the cell reaction :
2Fe3+(aq) + 2I–(aq) 2Fe2+(aq) + I2(aq)
E°cell = 0.24 V at 298 K. The standard Gibbs’ energy (ΔrG°)of the cell reaction is
[Given that Faraday constant, F = 96500 C mol–1]
(a) 23.16 kJ mol–1
(b) –46.32 kJ mol–1
(c) –23.16 kJ mol–1
(d) 46.32 kJ mol–1
Answer
B
Question. In the electrochemical cell :
Zn|ZnSO4(0.01 M)||CuSO4(1.0 M)|Cu, the emf of this Daniell cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that of CuSO4 changed to 0.01 M, the emf changes to E2.
From the followings, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2? (Given, RT/F = 0.059)
(a) E1 < E2
(b) E1 > E2
(c) E2 = 0 ≠ E1
(d) E1 = E2
Answer
B
Question. If the E°cell for a given reaction has a negative value,which of the following gives the correct relationships for the values of ΔG° and Keq ?
(a) ΔG° > 0; Keq < 1
(b) ΔG° > 0; Keq > 1
(c) ΔG° < 0; Keq > 1
(d) ΔG° < 0; Keq < 1
Answer
A
Question. The pressure of H2 required to make the potential of H2 electrode zero in pure water at 298 K is
(a) 10–10 atm
(b) 10–4 atm
(c) 10–14 atm
(d) 10–12 atm.
Answer
C
Question. A hydrogen gas electrode is made by dipping platinum wire in a solution of HCl of pH = 10 and by passing hydrogen gas around the platinum wire at one atm pressure. The oxidation potential of electrode would be
(a) 0.118 V
(b) 1.18 V
(c) 0.059 V
(d) 0.59 V
Answer
D
Question. Consider the half-cell reduction reaction
Mn2+ + 2e– → Mn, E° = – 1.18 V
Mn2+ → Mn3+ + e–, E° = – 1.51 V
The E° for the reaction, 3Mn2+ → Mn0 + 2Mn3+, and possibility of the forward reaction are respectively
(a) – 4.18 V and yes
(b) + 0.33 V and yes
(c) + 2.69 V and no
(d) – 2.69 V and no.
Answer
D
Question. For the reduction of silver ions with copper metal, the standard cell potential was found to be + 0.46 V at 25 °C. The value of standard Gibbs energy, DG°
will be (F = 96500 C mol–1)
(a) – 89.0 kJ
(b) – 89.0 J
(c) – 44.5 kJ
(d) – 98.0 kJ
Answer
A
Question. Given :
(i) Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu, E° = 0.337 V
(ii) Cu2+ + e– → Cu+, E° = 0.153 V
Electrode potential, E° for the reaction,
Cu+ + e– → Cu, will be
(a) 0.90 V
(b) 0.30 V
(c) 0.38 V
(d) 0.52 V
Answer
D
Question. Standard free energies of formation (in kJ/mol) at 298 K are –237.2, –394.4 and –8.2 for H2O(l), CO2(g) and pentane(g) respectively. The value of E°cell for the pentane-oxygen fuel cell is
(a) 1.0968 V
(b) 0.0968 V
(c) 1.968 V
(d) 2.0968 V
Answer
A
Question. The equilibrium constant of the reaction :
Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s);
E° = 0.46 V at 298 K is
(a) 2.0 × 1010
(b) 4.0 × 1010
(c) 4.0 × 1015
(d) 2.4 × 1010
Answer
C
Question. The standard e.m.f. of a galvanic cell involving cell reaction with n = 2 is found to be 0.295 V at 25°C.
The equilibrium constant of the reaction would be (Given F = 96500 C mol–1, R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1)
(a) 2.0 × 1011
(b) 4.0 × 1012
(c) 1.0 × 102
(d) 1.0 × 1010
Answer
D
Question. On the basis of the information available from the reaction, 4/3Al + O2 → 2/3Al2O3, ΔG = –827 kJ mol–1 of O2, the minimum e.m.f. required to carry out an electrolysis of Al2O3 is (F = 96500 C mol–1)
(a) 2.14 V
(b) 4.28 V
(c) 6.42 V
(d) 8.56 V
Answer
A
Question. For the disproportionation of copper
2Cu+ → Cu2+ + Cu, E° is (Given : E° for Cu2+/Cu is 0.34 V and E° for Cu2+/Cu+ is 0.15 V)
(a) 0.49 V
(b) –0.19 V
(c) 0.38 V
(d) –0.38 V
Answer
C
Question. E° for the cell, Zn | Zn2+(aq) ||Cu2+(aq) | Cu is 1.10 V at 25°C, the equilibrium constant for the reaction
Zn + Cu2+ (aq) → Cu + Zn2+
(aq) is of the order
(a) 10+18
(b) 10+17
(c) 10–28
(d) 10+37
Answer
D
Question. The molar conductivity of a 0.5 mol/dm3 solution of AgNO3 with electrolytic conductivity of 5.76 × 10–3 S cm–1 at 298 K is
(a) 2.88 S cm2/mol
(b) 11.52 S cm2/mol
(c) 0.086 S cm2/mol
(d) 28.8 S cm2/mol
Answer
B
Question. At 25 °C molar conductance of 0.1 molar aqueous solution of ammonium hydroxide is 9.54 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1 and at infinite dilution its molar conductance is 238 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1. The degree of ionisation of ammonium hydroxide at the same concentration and temperature is
(a) 4.008%
(b) 40.800%
(c) 2.080%
(d) 20.800%
Answer
A
Question. Limiting molar conductivity of NH4OH [i.e., L°m(NH4OH)] is equal to
(a) L°m(NH4Cl) + L°m(NaCl) – L°m(NaOH)
(b) L°m(NaOH) + L°m(NaCl) – L°m(NH4Cl)
(c) L°m(NH4OH) + L°m(NH4Cl) – L°m(HCl)
(d) L°m(NH4Cl) + L°m(NaOH) – L°m(NaCl)
Answer
D
Question. The oxidation potential values of A, B, C and D are – 0.03, + 0.108 V, – 0.07 Vand + 0.1 V respectively. The non-spontaneous cell reaction takes place between
(a) A and B
(b) B and D
(c) D and A
(d) B and C
Answer
A
Question. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction, at 25°C
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s)
at 25°C, E°cell = 0.47V, R = 8.314 JK-1 F = 96500 C is
(a) 1.8 x1015
(b) 8.5 x1015
(c) 1.8 x 1010
(d) 85 x 1015
Answer
B
Question. The metal used to recover copper from a solution of CuSO4 is
(a) Fe
(b) He
(c) Na
(d) Ag
Answer
A
Question. The standard electrode potential is measured by
(a) electrometer
(b) voltmeter
(c) pyrometer
(d) galvanometer
Answer
B
Question. The standard electrode potentials of Ag+/ Ag is + 0. 80V and Cu+ /Cu is + 0. 34 V. These electrodes are connected through a salt bridge and if
(a) copper electrode acts as a cathode, then E°cell is + 0.46V.
(b) silver electrode acts as anode, then E°cell is – 0.34 V
(c) copper electrode acts as anode, then E°cell is + 0.46V
(d) silver electrode acts as a cathode, then E°cell is – 0.34 V
(e) silver electrode acts as anode and E°cell is + 1.14 V
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following expression is correct?
(a) ΔG0 = – nFE°cell
(b) ΔGo = + nFE°cell
(c) ΔG0 = – 2.303RT nFE°cell
(d) ΔG0 = – nF log Kc
Answer
A
Question. The standard reduction potential of Zn and Ag in water at 298 K are, Zn2+ + 2e– ⇌ Zn; E° = – 0.76 V and Ag+ + e– ⇌ Ag; E° = + 0.80V. Which of the following reactions take place?
(a) Zn2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) → 2Ag+ (aq) + Zn(s)
(b) Zn(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s)
(c) Zn2+ (aq) + Ag+ (aq) → Zn(s) + Ag(s)
(d) Zn(s) + Ag(s) → Zn2+ (aq) + Ag+ (aq)
Answer
B
Question. For cell reaction, Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu cell representation is
(a) Zn l Zn2+ ll Cu2+ l Cu
(b) Cu l Cu2+ ll Zn2+ l Zn
(c) Cu l Zn2+ ll Zn l Cu2+
(d) Cu2+ I Zn ll Zn2+ l Cu
Answer
A
Question. For the following cell with hydrogen electrodes at two different pressures p1 and p2
Pt(H2 ) l H+ (aq) l Pt (H2 ) emf is given by
Pt 1M P2
(a) RT/F loge P1/P2
(b) RT/2F loge P1/P2
(c) RT/F loge P2/P1
(d) RT/2F loge P2/P1
Answer
B
Question. For a cell given below,
Ag l Ag+ ll Cu2+ l Cu
Ag+ +e– → Ag,E° = x
Cu 2+ + 2e– → Cu, E° = y E°cell is
(a) x + 2y
(b) 2x + y
(c) y – x
(d) y – 2x
Answer
C
Question. A standard hydrogen electrode has zero electrode potential because
(a) hydrogen is easier to oxidise
(b) this electrode potential is assumed to be zero
(c) hydrogen atom has only one electron
(d) hydrogen is the lightest element
Answer
B
Question. For hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell at 1 atm and 298 K
H2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) → H2O(l), ΔG = – 240 kJ
E° for the cell is approximately (Given, F = 96500 C)
(a) 2.48 V
(b) 1.25 V
(c) 2.5 V
(d) 1.24 V
Answer
D
Question. The rusting of iron takes place as follows
2H+ + 2e– + 1/2 O2 →H2O(/);E° = + 1.23 V
Fe2+ + 2e– → Fe (s);E° = – 0.44 V
Calculate ΔG° for the net process.
(a) – 322 kJ mol-1
(b) – 161 kJ mol-1
(c) – 152 kJ mol-1
(d) – 76 kJ mol-1
Answer
A
Question. The hydrogen electrode is dipped in a solution of pH 3 at 25°C. The potential would be (the value of 2.303 RT/F is 0.059 V)
(a) 0.177 V
(b) 0.087 V
(c) 0.059 V
(d) – 0.177 V
Answer
D
Question. The standard reduction potential of the reaction,
H2O + e – → 1/2 H2 + OH at 298 K is
(a) E° = RT/F In Kw
(b) E° = – RT/F In [PH2 )1/2 [OH–]
(c) E° =_ RT/F In [PH2 ]1/2 /[H+ ]
(d) E° = – RT/F In Kw
Answer
A
Question. Molar conductivities (L°m) at infinite dilution of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. (L°m) for CH3COOH will be
(a) 425.5 S cm2 mol–1
(b) 180.5 S cm2 mol–1
(c) 290.8 S cm2 mol–1
(d) 390.5 S cm2 mol–1
Answer
D
Question. An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to
(a) increase in ionic mobility of ions
(b) 100% ionisation of electrolyte at normal dilution
(c) increase in both i.e., number of ions and ionic mobility of ions
(d) increase in number of ions.
Answer
A
Question. The equivalent conductance of M/32 solution of a weak monobasic acid is 8.0 mho cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mho cm2. The dissociation constant of this acid is
(a) 1.25 × 10–6
(b) 6.25 × 10–4
(c) 1.25 × 10–4
(d) 1.25 × 10–5
Answer
D
Question. Kohlrausch’s law states that at
(a) infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to conductance of an electrolyte whatever be the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
(b) infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
(c) finite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
(d) infinite dilution each ion makes definite contribution to equivalent conductance of an electrolyte depending on the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte.
Answer
A
Question. Equivalent conductances of Ba2+ and Cl– ions are 127 and 76 ohm–1 cm–1 eq–1 respectively. Equivalent conductance of BaCl2 at infinite dilution is
(a) 139.5
(b) 101.5
(c) 203
(d) 279
Answer
A
Question. The specific conductance of a 0.1 N KCl solution at 23°C is 0.012 ohm–1 cm–1. The resistance of cell containing the solution at the same temperature was found to be 55 ohm. The cell constant will be
(a) 0.918 cm–1
(b) 0.66 cm–1
(c) 1.142 cm–1
(d) 1.12 cm–1
Answer
B
Question. On heating one end of a piece of a metal, the other end becomes hot because of
(a) energised electrons moving to the other end
(b) minor perturbation in the energy of atoms
(c) resistance of the metal
(d) mobility of atoms in the metal.
Answer
A
Question. On electrolysis of dil. sulphuric acid using platinum (Pt) electrode, the product obtained at anode will be
(a) hydrogen gas
(b) oxygen gas
(c) H2S gas
(d) SO2 gas.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a merit of Ni–Cd cell over lead storage battery?
(a) Ni–Cd cell can be re-used.
(b) Ni–Cd cell is comparatively economical to manufacture
(c) Ni–Cd cell has comparatively longer life
(d) All the above are the merits of Ni–Cd cell over lead storage battery.
Answer
C
Question. The ion of least limiting molar conductivity among the following is
(a) SO42-
(b) H+
(c) Ca2+
(d) CH3COO–
Answer
D
Question. Molar conductivities (∧0m) at infinite dilution of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. ∧0m for CH3COOH will be
(a) 425.5 S cm2 mol–1
(b) 180.5 S cm2 mol–1
(c) 290.8 S cm2 mol–1
(d) 390.5 S cm2 mol–1
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements regarding fuel cell is incorrect?
(a) These cells are eco-friendly.
(b) These cells convert energy of combustion of fuels like H2, CH4, CH3OH etc., directly into electrical energy.
(c) H2 – O2 fuel cell is used in Apollo space programme.
(d) Fuel cells produce electricity with an efficiency of about 100%.
Answer
D
Question. The electric charge for electrode decomposition of one gram equivalent of a substance is
(a) one ampere per second
(b) 96500 coulombs per second
(c) one ampere for one hour
(d) charge on one mole of electrons
Answer
D
Question. In electrolysis of NaCl when Pt electrode is taken then H2 is liberated at cathode while with Hg cathode it forms sodium amalgam. This is because
(a) Hg is more inert than Pt
(b) more voltage is required to reduce H+ at Hg than at Pt
(c) Na is dissolved in Hg while it does not dissolve in Pt
(d) conc. of H+ ions is larger when Pt electrode is taken
Answer
B
Question. When 9650 coulombs of electricity is passed through a solution of copper sulphate, the amount of copper deposited is (given at. wt. of Cu = 63.6)
(a) 0318g
(b) 3.18 g
(c) 31.8g
(d) 63.6g
Answer
B
Question. A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane, directly into electrical energy is known as :
(a) Electrolytic cell
(b) Dynamo
(c) Ni-Cd cell
(d) Fuel Cell
Answer
D
Question. A solution of copper sulphate (CuSO4) is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. The mass of copper deposited at the cathode (at. mass of Cu = 63u) is
(a) 0.3892g
(b) 0.2938g
(c) 0.2398g
(d) 0.3928g
Answer
B
Question. When 0.1 mol MnO42– is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise MnO42– to MnO4– is
(a) 96500 C
(b) 2 × 96500 C
(c) 9650 C
(d) 96.50 C
Answer
C
Question.The weight of silver (at wt. = 108) displaced by a quantity of electricity which displaces 5600 mL of O2 at STP will be
(a) 5.4 g
(b) 10.8 g
(c) 54.9 g
(d) 108.0 g
Answer
D
Question. Electrolysis of a salt solution was carried out, after some time solution turned yellow than salt can be
(i) NaCl (ii) KCl
(iii) RbCl (iv) KBr
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following represents variation of molar conductance of electrolyte with (concentration)½ respectively for weak and strong electrolyte ?


Weak acid Strong acid
(a) (iv) (v)
(b) (ii) (iv)
(c) (i) (ii)
(d) (iii) (ii)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Electrodes made up of gold participates in the chemical reaction.
(b) Electrolytic products of NaCl are Na and Cl2 whereas of aqueous NaCl are NaOH, Cl2 and H2.
(c) During electrolysis at cathode, reaction with higher value of E+ is preferred.
(d) All of the above statements are incorrect.
Answer
A
Question. During electrolysis of sulphuric acid, which of the following processes is possible at anode?

Answer
B
Choose the correct option based on following statements.
(i) Process A is preferred at higher concentration of sulphuric acid.
(ii) Process B is preferred at higher concentration of sulphuric acid.
(iii) Process A is preferred for dilute sulphuric acid.
(iv) Process B is preferred for dilute sulphuric acid.
(v) Both A and B are equally possible at higher concentration.
(a) (v) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (ii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (v) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Faraday’s laws of electrolysis will fail when
(a) temperature is increased
(b) inert electrodes are used
(c) a mixture of electrolytes is used
(d) None of these cases
Answer
D
Question. Three faradays electricity was passed through an aqueous solution of iron (II) bromide. The weight of iron metal (at. wt = 65) deposited at the cathode (in gm) is
(a) 56
(b) 84
(c) 112
(d) 168
Answer
B
Question. During the charging of lead storage battery, the reaction at anode is represented by

Answer
B
Question. In a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, combustion of hydrogen occurs to
(a) produce high purity water
(b) create potential difference between two electrodes
(c) generate heat
(d) remove adsorbed oxygen from elctrode surfaces
Answer
B
Question. The electrolyte used in Leclanche cell is
(a) paste of KOH and ZnO
(b) 38% solution of H2SO4
(c) moist paste of NH4Cl and ZnCl2
(d) moist sodium hydroxide
Answer
C
Question. How many moles of Pt may be deposited on the cathode when 0.80 F of electricity is passed through a 1.0 M solution of Pt4+?
(a) 1.0 mol
(b) 0.20 mol
(c) 0.40 mol
(d) 0.80 mol
Answer
B
Question. A current strength of 9.65 amperes is passed through excess fused AlCl3 for 5 hours. How many litres of chlorine will be liberated at STP? (F = 96500 C)
(a) 2.016
(b) 1.008
(c) 11.2
(d) 20.16
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following cells can convert chemical energy of H2 and O2 directly into electrical energy?
(a) Mercury cell
(b) Daniell cell
(c) Fuel cell
(d) Lead storage cell
Answer
C
Question. Hydrogen-Oxygen fuel cells are used in space craft to supply
(a) power for heat and light
(b) power for pressure
(c) oxygen
(d) water
Answer
B
Question. Prevention of corrosion of iron by zinc coating is called
(a) electrolysis
(b) photoelectrolysis
(c) cathodic protection
(d) galvanization
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following pair(s) is/are incorrectly matched?
(i) R (resistance) – ohm (Ω)
(ii) Ρ (resistivity) – ohm metre (Ωm)
(iii) G (conductance) – seimens or ohm (S)
(iv) k (conductivity) – seimens metre–1 (Sm–1)
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) only
Answer
C
Question. The best way to prevent rusting of iron is
(a) making it cathode
(b) putting in saline water
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Among the following cells:
Leclanche cell (i)
Nickel-Cadmium cell (ii)
Lead storage battery (iii)
Mercury cell (iv)
primary cells are
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. In electrolysis of dilute H2SO4 using platinum electrodes
(a) H2 is evolved at cathode
(b) NH2 is produced at anode
(c) Cl2 is obtained at cathode
(d) O2 is produced
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following metals is not produced by electrochemical reduction?
(a) Na
(b) Fe
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Answer
B
Question. In the electrolytic cell, flow of electrons is from
(a) cathode to anode in solution
(b) cathode to anode through external supply
(c) cathode to anode through internal supply
(d) anode to cathode through internal supply
Answer
D
Question. The correct order of E0M2+ /M values with negative sign for the four successive elements Cr, Mn, Fe and Co is
(a) Mn > Cr > Fe > Co
(b) Cr < Fe > Mn > Co
(c) Fe > Mn > Cr > Co
(d) Cr > Mn > Fe > Co
Answer
A
Question. If salt bridge is removed from two half-cells the voltage
(a) drops to zero
(b) does not change
(c) increases gradually
(d) increases rapidly
Answer
A
Question. Consider the following relations for emf of a electrochemical cell:
(i) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iii) emf of cell = (Reduction potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iv) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (i)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Standard potentials (Eº) for some half-reactions are given below :
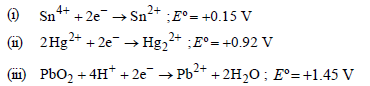
Based on the above, which one of the following statements is correct ?
(a) Sn4+ is a stronger oxidising agent than Pb4+
(b) Sn2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Hg22+
(c) Hg2+ is a stronger oxidising agent than Pb4+
(d) Pb2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Sn2+
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Both electronic and electrolytic conductance depends on the nature of conducting material.
(b) Both electronic and electrolytic conductance varies similarly with temperature.
(c) Electronic conductance is independent but electrolytic conductance depends on the amount of the conducting substance.
(d) All the above statements are incorrect.
Answer
B

We hope you liked MCQ on Electrochemistry Class 12 with Answers provided above. Incase you have any questions please post them in the comments section below and our Chemistry teachers will provide a response.

