Please refer to Agriculture Class 10 Social Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Social Science books for Class 10. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 10 Social Science Agriculture Notes and Questions
Technological and Institutional reforms :
– Consolidation of holdings, co-operation and abolition of zamidari, etc. were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after independence.
– Land reform was the main focus of our first five year plan.
– The green revolution based on the use of package technology and the white revolution (operation flood) were some of the strategies initiated to improves the lot of Indian agriculture.
– Development in few selected areas. In the 1980s and 1990s, a comprehensive land development progreamme was initiated, which includes both institutional and technological reforms.
– Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire and disease.
– Establishment of Grameen Banks, cooperative societies and banks for providing loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest.
– Kissan credit cards and personal accident insurance schemes introduced.
– Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers were introduced on radio and T.V.
– The government also announces minimum support price.
– Remunerative and procurement prices for important crops to check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middleman.
Contribution of Agricultures to the National Economy, Employment and Output :
– Agriculture backbone of Indian Economy.
– Share in the gross domestic product.
– Providing employment.
– Livelihood to the population.
– The government of India made concerted efforts to modernize agriculture.
– Establishment of Indian council of Agricultural Research, agricultural universities.
– Veterinary services and animal breading centres.
– Horticulture development.
– Research and development in the field of meteorology and weather forecast.
Question. By which name is specialized cultivation of fruits and vegetables known?
Answer
Horticulture
Question. Describe ‘Jhumming cultivation’ in one sentence.
Answer
Slash and burn cultivation in the NE region of India.
Question. How can small and marginal farmers be supported by the government?
Answer
Loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest, Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and crop insurance etc.
Question. By which other name is ‘slash and burn’ agriculture known?
Answer
Jhum cultivation
Question. India is the largest producer as well as consumer of which agricultural product in the world ?
Answer
Pulses
Question. What soil is perfect for the growth of cashew nuts?
Answer
For the best production deep, well-drained sandy or sandy-loam soil is recommended.
Question. What are the growing conditions required for the main staple food crop of India? Mention the main growing regions.
Answer
(i) Growing conditions required for rice :
(a) High temperature (above 25°C). It is a Kharif crop.
(b) High humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm.
(ii) Main growing regions : Northern plains, north eastern India, Coastal areas, deltaic plains and river valleys.
Question. How many cropping seasons are found in India? Name them and write a short note on each.
Answer
The three cropping seasons in India are:
(i) Rabi (ii) Kharif (iii) Zaid Rabi
These are characterized as :
(i) The kharif season largely coincides with Southwest Monsoon under which the cultivation of tropical crops such as rice, cotton, jute, jowar, bajra and tur is possible.
(ii) The rabi season begins with the onset of winter in October-November and ends in March- April. The low temperature conditions during this season facilitate the cultivation of temperate and subtropical crops such as wheat, gram and mustard.
(iii) Zaid is a short duration summer cropping season beginning after harvesting of rabi crops.
Question. Name the two most important staple food crops of India. Name the states where they are produced. Write the geographical conditions required for their growth.
Answer
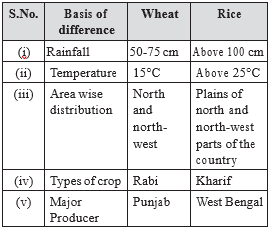
The most important staple crops are rice and wheat. The states where they are grown and geographical conditions for the production of rice and wheat are :
| Parameter | Rice | Wheat |
| States where grown (major states in decreasing order) | West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab and Odisha | Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh |
| Soil | Clay or clay loam (Good water retention capacity) | Well-drained fertile soil, heavy textured soil with lime, clayey loamy soil or black soil |
| Temperature | Above 25° C | 10° – 15°C during growth and 25° – 28°C at ripening |
| Rainfall | Above 100 cm | 50-75 cm |
Question. Define plantation agriculture. Explain any four characteristics of plantation agriculture.
Answer
Plantation agriculture : It is a type of commercial farming practised in tropical and sub- tropical regions. It was introduced by the British in India.
Characteristics :
(i) A single crop is grown over a large area.
(ii) It is capital intensive and done with cheap labour.
(iii) All produce is used as raw materials in various industries. Crops are tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana, etc.
(iv) Plantation has interface of agriculture and industry both.
Question. Explain rubber cultivation in India under the following heads :
(i) Importance
(ii) Geographical conditions
(iii) Producing states.
Answer
(i) Importance : Many industries depend upon rubber as their raw material especially transport industry.
(ii) Geographical conditions :
(a) It is an equatorial crop, but under special conditions, it is also grown in tropical and subtropical areas. It requires moist and humid climate with rainfall of more than 200 cm and temperature above 25°C.
(iii) Rubber producing states are Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Garo hills of Meghalaya.
Question. Describe any four geographical conditions required for the growth of tea. Mention the two major tea producing states of South India.
Answer
Tea : Grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates.
Soil type : Deep and fertile, well drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter.
Climate : Warm and moist, frost-free climate throughout the years.
Rainfall : Frequent showers throughout the year. Two states : Assam, West Bengal, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh, Meghalaya and Tripura.
Question. Which are the two major cotton producing states of North? Describe four geographical conditions required for the growth of cotton.
Answer
Maharashtra, Gujarat, MP. etc., are the major cotton producing states.
Geographical conditions required for the cultivation of cotton are:
(i) It grows well in drier parts of the black cotton soil of the Deccan plateau.
(ii) It requires high temperature (21°C – 30°C).
(iii) It requires light rainfall or irrigation (50-100 cm).
(iv) It requires 210 frost free days and bright sunshine for its growth.
Question. Compare the geographical conditions required for the production of cotton and jute.
Answer
| S. No. | Cotton | Jute |
| (i) | Cotton requires more than 21° C of temperature. | Jute requires 30°C temperature. |
| (ii) | Rainfall : 50 – 100 cm. | Rainfall : About 150 cm. |
| (iii) | Frost free days are a must during picking days. | Hot and humid climate is required. |
| (iv) | Loamy and black soil is required. | W e l l-dra in e d fertile loamy soil is required. |
| (v) | Mainly grown in Maharashtra and Gujarat. | Grown in eastern state of the country as W.B. |
Question. Explain any four features of primitive subsistence agriculture in India.
Answer
Features of primitive subsistence agriculture in India are :
(i) It is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools.
(ii) Tools which are used are basically traditional tools such as hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(iii) This type of agriculture totally depends upon monsoon.
(iv) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift to another plot of land.
Question. Explain any four features of intensive subsistence agriculture in India.
Answer
(i) Intensive subsistence farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land. In this type of farming, the agricultural production is increased by using high doses of biochemical inputs and better agricultural inputs.
(ii) Features of intensive farming :
(a) High yielding variety (HYV) seeds and modern chemical inputs and irrigation are used to increase the production.
(b) The per hectare yield is very high.
(c) More than one crop is cultivated during a year.
(d) In Indian this kind of farming is seen in Kerala.
Question. Which is the leading coffee producer state in India?
Answer
Karnataka
Question. What is the importance of millets?
Answer
In addition to their good nutritional value, an important feature of these crops is that they require much less water to grow than rice and wheat. They can be successfully cultivated in semi-arid tropics and on poor soils.
Question. Which crop is the major crop of rabi ?
Answer
Wheat
Question. Mention the sowing period of Kharif crops.
Answer
The kharif cropping season is from July – October during the south-west monsoon.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘Rabi crop season.’
Answer
(a) Rabi crops are also known as winter crops. They are sown from October to December and harvested from April to June.
(b) Wheat, barley, pea, gram and mustard are the important rabi crops. Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhan and Uttar Pradesh are the important producers of rabi crops.
(c) Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western disturbances helps in the success of these crops. However, the success of the green revolution in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the above mentioned rabi crops.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘Kharif crop season.’
Answer
(a) Kharif crops are also known as summer crops. They are sown at the beginning of monsoon and harvested in September-October.
(b) Paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur, moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soybean are important kharif crops. Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are important rice growing states.
(c) In Assam, West Bengal and Orissa; three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are called Aus, Aman and Boro.
Question. Categories the following as ‘Rabi crops’ and ‘Zaid crops’ :
(i) Wheat
(ii) Watermelon
(iii) Fodder crops
(iv) Mustard
(v) Cucumber
(vi) Peas
Answer
| Rabi Crops | Zaid Crops |
| Wheat, pea, and mustard | Watermelon, cucumber, fodder crops |
Question. What is the importance of pulses in our country? Why are pulses grown as a rotation crop ?
Answer
India is the largest producer and consumer of pulses in the world. Pulses are rich in proteins and are the main source of protein for vegetarians India. It is second important constituent of Indian diet after cereals.
Pulses are mostly grown in rotation with other crops because
(i) Pulses need less moisture and survive even dry conditions.
(ii) Being leguminous crops, all these crops help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air.
(iii) Major pulse producing states are : Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh
Question. Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of ‘wheat’ in India.
Answer
Wheat requires a cool growing season and a bright sunshine at the time of ripening. It requires 50 to 75 cm of annual rainfall evenly distributed over the growing season. Fertile alluvial soil or mixed soil and plain land or gentle slope is ideal for wheat cultivation.
There are two important wheat-growing zones in the country – the Ganga-Satluj plains in the northwest and black soil region of the Deccan. The major wheat-producing states are Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
Question. Explain any two geographical conditions required for the cultivation of pulses. Name any two important pulses producing states.
Answer
Pulses are mostly grown in rotation with other crops because
(i) Pulses need less moisture and survive even in dry conditions.
(ii) Being leguminous crops, all these crops help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air.
Major pulse producing states are : Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
Question. Give an account of rice cultivation in India, under the following heads:
(a) Climatic condition
(b) Soil requirement
(c) Two major rice producing states
Answer
(a) Climatic condition : It is a kharif crop which requires high temperature (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
(b) Soil requirement : Rice is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. The preferred soil type is clayey or clayey -loam.
(c) Two major rice producing states : West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh
Question. Give an account of oilseeds in India. State the importance of groundnut and name the states where it is grown.
Answer
Importance of oil seeds :
(i) These are edible and used as cooking medium. (ii) Also used as raw material in production of soaps, cosmetics and ointments.
(iii) India is the largest producers of oil seeds. Groundnut :
(i) Kharif crop
(ii) Accounts for half of the total oilseed production in India.
(iii) State : Andhara Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Question. Name any four oilseeds produced in India. Explain the importance of oilseeds in our day to day life.
Answer
(i) Groundnut (ii) Mustard (iii) Coconut (iv) Sesame (v) Soyabean, Sunflower, etc.
Importance of oilseeds : Most of these are edible in the form of oil. Used as raw material for manufacturing paints, varnishes, soaps, perfumes etc,. oil cake is used as cattle feed and fertiliser.
Question. What are millets? Give brief description of the climatic conditions and producing states of the millets grown in India.
Answer
Millets are coarse grains but have high nutritional value e.g., ragi-rich in iron, calcium.
(i) Jowar – Rain fed crop mostly grows in moist area.
(ii) Bajra – grows well on sandy soils and shallow black soil.
States producing – Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Gujrat, Haryana and U.P.
(iii) Ragi – grows well in dry region on red, black, sandy and loamy soils.
States producing – Tamil Nadu, Himachal
Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim.
Question. Which crop is known as the ‘golden fibre’? Explain any two geographical conditions essential for the cultivation of this crop. Mention its any four uses.
Answer
(i) Jute is called the golden fibre.
(ii) Geographical conditions :
(a) Grows well in drained fertile soil of the flood plains where the soil is renewed every year.
(b) High temperature is required during the time of growth.
Uses : Can be used to manufacture gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets and other artefacts.
Question. Explain the geographical conditions required for the cultivation of pulses. Name any two important pulses producing states.
Answer
Pulses are mostly grown in rotation with other crops because
(i) Pulses need less moisture and survive even in dry conditions.
(ii) Being leguminous crops, all these crops help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air.
Major pulse producing states are : Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
Question. Mention any two geographical conditions required for the growth of maize crop in India. Describe any three factors which have contributed to increase in maize production.
Answer
(i) Geographical conditions required for the growth of maize crop in India : (a) It is a kharif crop which requires temperature between 21°C to 27°C.
(b) It grows well in alluvial soil.
(ii) Use of modern inputs such as HYV seeds, fertilisers and irrigation have contributed to the increased production of maize.
Question. Explain any three geographical conditions required for the growth of rice in India. How is it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall? Explain with examples.
Answer
(i) Three geographical conditions for the growth of rice :
(a) It requires high temperature (above 25°C).
(b) Annual rainfall above 100 cm.
(c) High humidity
(ii) It is possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall with the help of irrigation as done in Punjab and Haryana.
Question. What are the climatic conditions required for the growth of rice?
Answer
(i) Three geographical conditions for the growth of rice :
(a) It requires high temperature (above 25°C).
(b) Annual rainfall above 100 cm.
(c) High humidity
(ii) It is possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall with the help of irrigation as done in Punjab and Haryana.
Question. “Wheat and rice farming in India are fairly different from each other”. Explain
Answer
Question. Describe four geographical conditions required for the growth of sugarcane. Name two major sugarcane producing states of North India.
Answer
Geographical conditions required for the growth of sugarcane in India are :
(i) It is a tropical as well as sub-tropical crop so it requires a hot and humid climate.
(ii) Temperature of 24°C to 27°C.
(iii) It requires an annual rainfall between 75 to 100 cm.
(iv) It can be grown on a variety of soils.
Major sugarcane producing states of North India are : Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Question. Which factors has helped Punjab and Haryana to grow more and more of rice?
Answer
Development of dense canal network and inputs like fertilizers and pesticides.
Question. Explain any three steps for agriculture reforms taken by the Government of India, after the independence.
Answer
Three steps were as follows :
From the earliest days agriculture was given great importance in the “five year plans”. Other important steps included : 1. Abolishment of zamindari system. The right to own the land was given to the actual cultivators which then led to the increase in the production.
1. Abolishment of zamindari system. The right to own the land was given to the actual cultivators which then led to the increase in the production.
2. Cooperative societies were formed which provided quality seeds and fertilizers to farmers at low price.
3. Another act called ‘land ceiling act’ was passed, according to which the land could not be held by a person beyond a defined limit.
The important institutional reforms carried out by the Government of India have been as follows :
(i) Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire and disease.
(ii) Establishment of Grameen (regional rural) banks, cooperative societies and banks for providing loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest. (iii) Establishment of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), agricultural universities, veterinary services and animal breeding centers, horticulture development, research and development in the field of meteorology and weather forecasting etc.
Question. Describe any three technological and institutional reforms made in the field of agriculture in India.
Answer
(i) Land reforms : Collectivisation, consolidation of land holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari.
(ii) Agricultural reforms : Green revolution and white revolution.
(iii) Land development programmes : Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone etc., establishment of Grameen banks.
(iv) Issuing of Kisan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme, etc.
(v) Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers on radio and TV.
Question. The government of India has introduced various institutional and technological reforms to improve agriculture in the 1980’s and 1990. Support this statement with examples.
Answer
The various institutional reforms introduced by the government in the interest of farmers are mentioned below:
(i) Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, and disease.
(ii) Establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies and banks for providing loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest.
(iii) Kisan Credit Card (KCC), Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) schemes are introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers.
(iv) Special weather bulletins and agricultural program for farmers have been introduced on the radio and television.
(v) The government also announces minimum support price, remunerative and procurement prices for important crops to check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middlemen.
The technological advancements gave birth to Green Revolution, White Revolution or Operation Flood. Considering the importance of agriculture the Government of India took steps to modernize agriculture. Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) was established. The government encourages through various institution the use of –
(a) Soil testing facilities
(b) Technology such as drip irrigation
(c) Better seeds, fertilizers and pesticides
Question. Explain any five initiatives taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Answer
The main initiatives include :
(i) Land reforms : Collectivisation, consolidation of land holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari.
(ii) Agricultural reforms : Green revolution and white revolution.
(iii) Land development programmes : Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, etc., establishment of Grameen banks, Cooperative societies and banks for providing loans.
(iv) Issuing of Kisan Credit Card and Personal
Accident Insurance Scheme, etc.
(v) Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers on radio and TV.
(vi) Government announces Minimum support Price (MSP) and remunerative and procurement prices to check exploitation.
(vii) The government provides HYV seeds and fertilisers.
(viii) Government provides technical assistance and training for farmers.
(ix) Soil testing facilities, cold storage and transportation for farmers.
Question. Why has the agriculture sector in India got a major set back in spite of increase in the G.D.P. growth rate? Analyse the reason.
Answer
(i) More and more land is used for construction of factories, warehouses and shelters which have reduced the land under cultivation.
(ii) Soil gets degraded by the use of pesticides, fertilizers, etc. Irrigation, often leads to water logging and salinity.
(iii) Today Indian farmers are facing a big challenge from international competition.
(iv) Our government is reducing the public investment in agriculture, subsidy on fertilizers have decreased.
(v) Reduction in import duties on agricultural products have proved detrimental to agriculture in our country.
Question. Why is agriculture called the mainstay of Indian economy?
Answer
(i) Agriculture is the mainstay of Indian economy because about 67% of our population depends directly or indirectly on agriculture.
(ii) It provides raw materials to the industries. (iii) India earns foreign exchange by exporting agricultural products.
(iv) It contributes about 17% to other gross domestic product.
(v) It provides food to the Indian population.
Question. Why has Indian agriculture started to decline in the trend of food production? How can we overcome this problem?
Answer
Indian agriculture started a decline in the trend of food production because :
(i) More and more land is used for construction of factories, warehouses and shelters. This has reduced good land under cultivation.
(ii) Soil gets degraded by the use of pesticides, fertilizers, over-irrigation, etc., which leads to water logging and salinity.
Remedial measures:
(i) Use of agricultural techniques which are environmentally sustainable.
(ii) Use of biotechnology in modifying different crops and increase the yield per hectare. It reduces dependence on insecticides and also require less water.
Notes For NCERT Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture


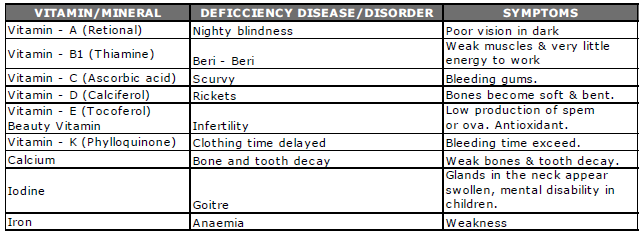
• Slash and burn’ agriculture- Clears a patch of forest land and produce crops, when the soil fertility decreases the farmer shifts and clear a fresh patch of land, known by different names in different parts of India- like Jhumming,mostly done in the Northeastern-states
• Rabi Crops-Sown in Winter from October to December and harvested in Summer from April to June-eg. Wheat, Barley, Peas, Gram
• Kharif Crops- Grown with the onset of the Monsoon, harvested in September October- eg. paddy, Maize, Jowar, Bajra
• Zaid Crops- in between Rabi and Kharif season-short season during the summer months- eg.water melon, cucumber.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Write the uses of jute. Why is it losing its market in India today?
Answer: It is known as the golden fibre. It is used in making gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets and other artefacts. Due to its high cost, it is losing market to synthetic fibres and packing materials, particularly the nylon.
2. List the two beverage crop of India and write the climatic conditions need for its growth.
Answer: Tea- Well drained soil,rich in humus and organic matter-Warm-moist-frost freedays,frequent showers evenly distributed over the years Coffee- Cool climate,hilly region – Well drained soil
Long Answer Questions
Question 1. Explain any five features of Indian agriculture.
Answer: Intensive subsistence, labour intensive farming, high doses of bio chemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining high yield. The right of inheritance has led to division of land among successive generations.

We hope the above Agriculture Class 10 Social Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science


