Please refer to Human And Health Disease Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Human And Health Disease Notes and Questions
Food :
The food we eat is made up of complex molecules. These molecules are first broken down by digestive
enzymes (digestion) into simpler molecules. The simpler mol- ecules are then absorbed (absorption) in
the intestine, and they reach the blood stream. Blood carries them to the cells, which take them in
(assimilation) according to their needs. Thus, the purpose of taking food, i.e., the function of food, is to
supply nutrients to the cells.
Carbohydrates :
Ÿ Carbohydrates are the cheapest source of energy. One gram of carbohydrate yields
4.2 kilocalories of energy on respiration (controlled oxidation).
Ÿ Carbohydrates are more suitable for the production of energy in the body than proteins and fats
because carbohydrate molecules contain relatively more oxygen than the others, hence
require less molecular oxygen for oxidation. Athletes, laborer’s doing heavy work and
mountaineer’s should take high carbohydrate diet.
Fats :
Ÿ When fats are oxidized in the body, they produce energy. The energy obtained is more than
twice as much as that obtained from the same amount of carbohydrate. One gram of fat
gives about 9.3 kcal of energy.
Ÿ Certain fatty acids that we need are produced by the cells in the body from the
carbohydrates in our diet. They are called nonessential fatty acids. But there are a few
types of fatty acids that cannot be synthesized in our body. They are called essential fatty
acids. The later are present in many unsaturated vegetable oils like groundnut oil and
sunflower oil. Linoleic, linolenic and arachidonic acids are essential fatty acids. They are
constituent’s of structural lipids including membrane lipids.
Proteins :
Ÿ Proteins are formed from chemical units called amino acids. Proteins in our food are digested and
broken up into the constituent amino acids. These amino acids are absorbed in the small intestine
and transported by the blood to different parts of the body. They are then rejoined in specific
sequences to form different proteins in the cells. Hair, muscles, enzymes, haemoglobin,
antibodies and hormones are all proteins synthesized by the cells.
Ÿ Essential amino acids are those, which cannot be synthesized by the animal body and must be
supplied with food in adequate amounts. These are methionine, threonine, tryptophan, valine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine and phenylalanine.
Ÿ Nonessential amino acids are those, which are synthesized, in the animal body,
particularly from carbohydrate metabolism. They need not be supplied in the diet, e.g.,
glycine, alanine, serine, cysteine, tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid and glutamic acid.
Minerals :
Ÿ We need many metals and non- metals for the various reactions taking place in our body.
These are collectively called minerals. Just seven minerals comprise 60-80% of all the
minerals needed by the body. These are calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium,
phosphorus, sulphur and chlorine. The remaining minerals include iron, iodine, copper,
zinc, manganese, cobalt, molybdenum, selenium, chromium and fluorine.
Vitamins:-
Ÿ Vitamins are organic substances required regularly in minute quantities in diet for normal
metabolism, health and growth. Dr. Casmir Funk suggested the name “vitamin” in 1912.
They are usually required as coenzymes or precursors of coenzymes.
Ÿ Vitamins are usually divided into two categories on the basis of their solubility in two different
solvents: (i) fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K) and (ii) water soluble vitamins (B and C).
Roughage :
Ÿ Roughage is the dietary fibre made up of cellulose. Salad, vegetables and fruits are
sources of roughage. Cellulose is not digested, but helps in the movement of food and
faecal matter along the alimentary canal. Corn (bhutta) and whole broken wheat (dalia) are
good sources of roughage. Lack of roughage cause constipation.
• A balanced diet in one that provides all the nutrients required by the body in the correct
proportions.
HUMAN DISEASE
Disease :
The word disease (dis-ease) literally means distrubed ease or uncomfortable. Thus disease
can be defined as “Malfunctioning of the body or a part of it due to one reason or the other”.
Or
Disease is a condition of the body or a part of it in which functions are disturbed or deranged.
Factors affecting health :
1. Intrinsic factors- Disease causing factors which exist within human body.
(i) malfunctioning or improper functioning of body parts.
(ii) Genetic disorder
(iii) Hormonal imbalances
2. Extrinsic factors – Factors which enter the human body from outside.
(i) Unbalanced diet
(ii) Disease causing pathogens
(iii) Environmental pollutants
(iv) Tobacco, alcohol and narcotic drugs.
Types of Diseases :
Ÿ Acute Disease:-
A disease that occurs suddenly and lasts for a short period of time is called an acute disease
e.g. common cold, Malaria disease.
Ÿ Chronic Disease:-
A disease that lasts for a long time is called chronic disease e.g. tuberculosis.
Ÿ Noninfectious disease:-
A disease that is not caused by an infectious agent is called a noninfectious disease.
Disease like diabetes, cancer, anaemia and arthritis are noninfectious.
Ÿ Communicable disease:- An infectious diseases that can be spread from one infected individual to another is called
a communicable disease. An infectious disease can be spread from an
infected person to a healthy person in many ways such as through food, water, air, direct
contact, through a disease carrier like a mosquito, etc.
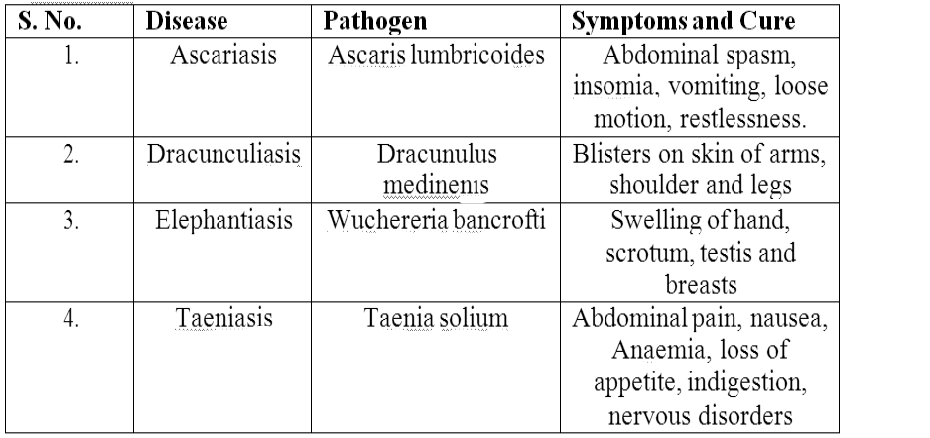
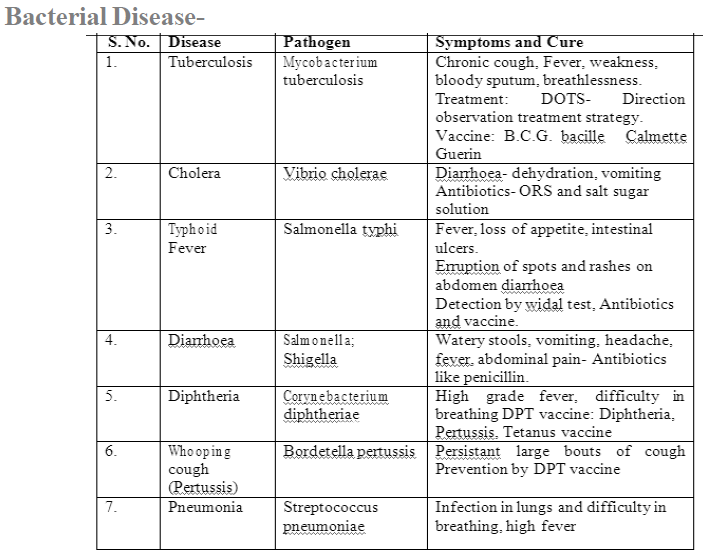
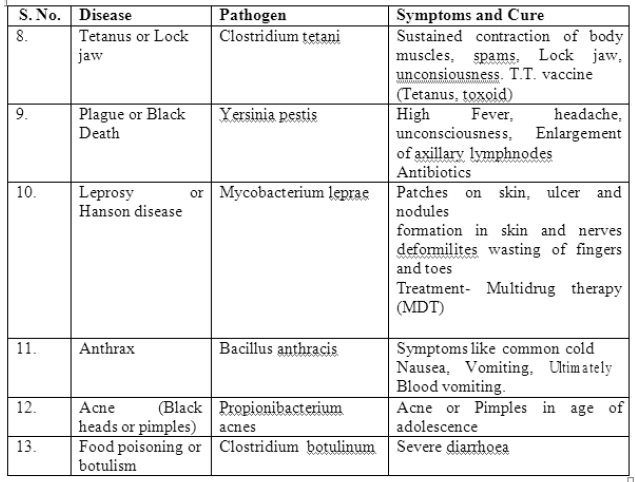
NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS
Balanced Diet :
A balanced diet is the first condition necessary for good health. A balanced diet is one that provides all
the nutrients required by the body in correct proportions. The nutrients required by our body are
proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals. When our diet lacks one or more of these
nutrients, we get deficiency diseases. For example, if our diet lacks the mineral iron, we may get a
disease called anaemia. A balanced diet prevents deficiency disease. It also increases our ability to
fight infections in general.
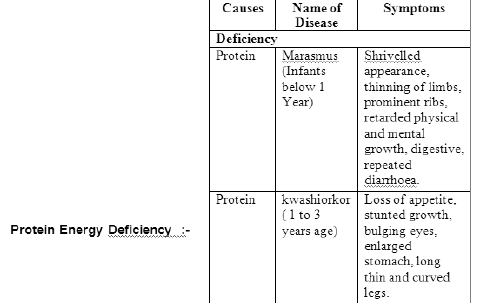
Minerals Deficiency:-
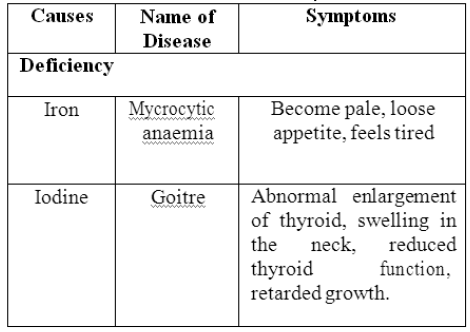
2. Vitamins Deficiency:- Fat –
Soluble vitamins
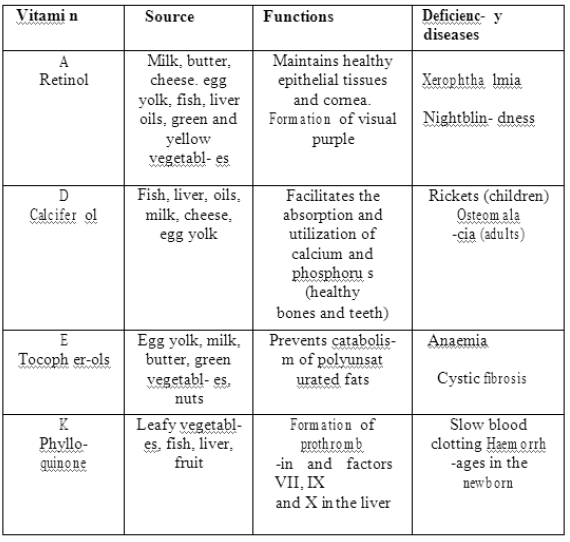
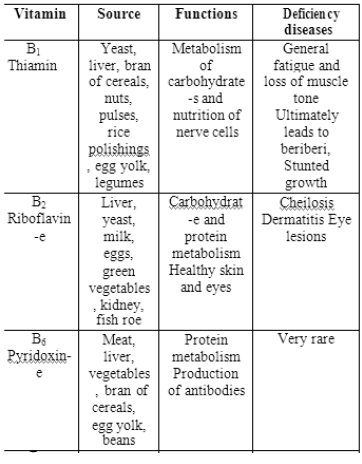
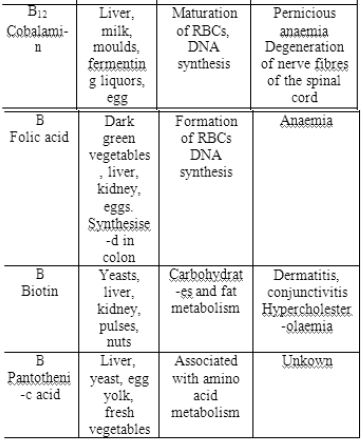

Vaccination :
Jenner took some pus with a sterile needle from the cowpox rash of an infected girl and injected
it into scratches made in the skin of an uninfected boy, who soon got cowpox. After he recovered,
Jenner injected the boy’s arm with pus from the spots of a person suffering from smallpox.
Luckily, the boy did not get smallpox and Jenner’s experiment was successful. The modern
term ‘vaccination’ comes from the Latin
words vacca which means cow and ‘vaccinia’ which means cow pox. It tells us how
Jenner made the first vaccine aganist smallpox using the microbes of cowpox, a similar but
less severe disease.
Pulse polio programme :
The pulse polio programme is an immunization drive against polio. Polio is a disease of the
muscles and nerves which can cause paralysis. To prevent polio, oral vaccine are given
periodically to all children under 5 years of age in our country. This is an effort to eradicate polio,
so no child will be infected by the polio virus.
Smallpox vaccine :
An immunization programme was carried out earlier to eradicate smallpox. Earlier, in
smallpox epidemics people were afraid of going near someone suffering from it. Smallpox
was controlled and eradicated with the help of a vaccine.
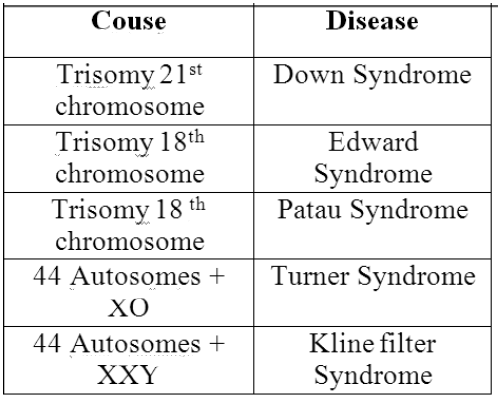
Genetic Disease:-
MCQs for NCERT Class 7 Science Human And Health Disease
Question: A healthy person is one who is free from –
(A) disease
(B) mental tension
(C) disease and mental tension
(D) bacteria
Answer:
disease and mental tension
Question: Fruit and vegetables bought from the market-
(A)may be coated with pesticides
(B) may carry germs
(C) may carry eggs of worms
(D) all the above
Answer:
all the above
Question: Breathing polluted air causes diseases of the
(A) nervous system
(B) circulatory system
(C) respiratory system
(D) digestive system
Answer:
respiratory system
Question; Which disease is likely to occur in crowded areas ?
(A) Non infectious
(B) Infectious
(C) Genetic
(D) Deficiency disease
Answer:
Infectious
Question: What kind of a disease is arthritis?
(A) An acute disease
(B) A chronic disease
(C) An infectious disease
(D) A communicable disease
Answer:
A chronic disease
Question: Which of the following is due to external causes ?
(A) Jaundice
(B) Diabetes
(C) Arthritis
(D) Cataract
Answer:
Jaundice
Question: Houseflies are the vectors of –
(A) cholera
(B) malaria
(C) dengue
(D) cataract
Answer:
cholera
Question: Mosquitoes spread –
(A) influenza
(B) rabies
(C) malaria
(D) AIDS
Answer:
malaria
Question: Tuberculosis is caused by –
(A) a bacterium
(B) a virus
(C) a protozoan
(D) AIDS
Answer:
a bacterium
Question: A type of rhabdovirus causes
(A) AIDS
(B) TB
(C) influenza
(D) rabies
Answer:
rabies
Question: The infectious agents responsible for which diseases can be spread when the
patient coughs?
(A) AIDS, TB and hepatitis
(B) TB, influenza and cholera
(C) TB and influenza
(D) TB and hepatitis
Answer:
TB and influenza
Question: The diseases that can be transmitted through body fluids are –
(A) AIDS and hepatitis B
(B) TB and typhoid
(C) influenza and cholera
(D) cholera and rabies
Answer:
AIDS and hepatitis B
Question: Leprosy is also famous as –
(A) Koch’s disease
(B) Hensen’s disease
(C) Pertussis
(D) Cholera
Answer:
Hensen’s disease
Question: Typhoid fever is caused by –
(A)Giardia
(B) Salmonella
(C) Shigella
(D) Escherichia
Answer:
Salmonella
Question: One of the following is the correct match for diseases and causative agents –
(A) AIDS- Bacillus
(B) Syphylis- Treponema pallidum
(C) Malaria – Trypanosoma
(D) Gonorrhoea- Virus
Answer:
Syphylis- Treponema pallidum
Question: Genus Aedes is a vector of –
(A) Filaria
(B) Dengue
(C) Malaria
(D) Elephantiasis
Answer:
Dengue
Question: Sleeping sickness is caused by –
(A) Entamoeba
(B) Gregarina
(C) Trypanosoma
(D) Plasmodium
Answer:
Trypanosoma
Question: Yersinia causes –
(A) plague
(B) Whoophing cough
(C) Leprosy
(D) Syphilis
Answer:
plague
Question: Which of the following is not a water borne disease
(A) Asthma
(B) Cholera
(C) Amoebiasis
(D) All of these
Answer:
Asthma
Question: Leprosy is caused due to –
(A)Clostridium
(B) Salmonella
(C) Mycobacterium
(D) Bacillus
Answer:
Mycobacterium
Question: Which of the following does not spread AIDS by –
(A) having sex with unknown person
(B) kissing on lips
(C) transfusing infected blood
(D) taking unsterlized injections
Answer:
kissing on lips
Question: The disease marasmus in children is caused due to the deficiency of –
(A) carbohydrates
(B) proteins
(C) fats
(D) vitamins
Answer:
proteins
Question: Which disease has been totally eradicated from India
(A) Plague
(B) Small pox
(C) Tuberculosis
(D) none above
Answer:
Small pox
Question: Pick up the set of bacterial diseases –
(A) Tetanus, typhoid, tuberculosis
(B) Small pox, influenzae, tetanus
(C) Meningitis, measles, syphyllis
(D) None above
Answer:
Tetanus, typhoid, tuberculosis
Question: Diphtheria is caused by –
(A) bacteria
(B) virus
(C) nematodes
(D) fungi
Answer:
bacteria
Question: About 70% of our energy requirement should be met by
(A) vitamins (
B) fats
(C) proteins
(D) carbohydrates
Answer:
carbohydrates
Question: The energy produced by 1 g of carbohy drate is
(A) 4.6 cal
(B) 4.2 kal
(C) 9 joules
(D) 9.2 kcal
Answer:
4.2 kal
Question: Endemic disease is caused by –
(A) bacteria
(B) environment
(C) human culture
(D) immoral society
Answer:
bacteria
Question: The term non- essential amino acid’s is applied to fatty acids that are
(A) synthesized in the body
(B) water- soluble
(C) required by the body but not essetial
(D) useless
Answer:
synthesized in the body
Question: Cholesterol is synthesised in
(A) Brunner ’s
(B) Pancreas
(C) liver
(D) Spleen
Answer:
liver
Question: Gastroenteritis is a disease caused by –
(A) virus
(B) fungi
(C) algae
(D) bacteria
Answer:
bacteria
Question: Vitamins are
(A) inorganic substances that cannot be synthesised by animal
(B) inorganic substances that can be synthesised by the animal
(C) organic substances that cannot be synthesised by animal
(D) organic substances that can be synthesised by animal
Answer:
organic substances that cannot be synthesised by animal
Question: Anaemia is related to
(A) iodine deficiency
(B) food adulteration
(C) iron deficiency
(D) all of these
Answer:
iron deficiency
Question: Ascariasis is a disease caused by –
(A) bacteria
(B) fungal growth
(C) worms
(D) None of these
Answer:
worms
Question: In goitre, there is swelling of the
(A) eyes
(B) limbs
(C) abdomen
(D) thyroid gland
Answer:
thyroid gland
Question: Kwashiorkor is likely in children who get
(A) low- iron diet
(B) low- vitamin diet
(C) low- fat diet
(D) low- protein diet
Answer:
low- protein diet
Question: An example of an air borne disease from the following is –
(A) cholera
(B) small pox
(C) typhoid
(D) AIDS
Answer:
small pox
Question: Deformed bones are associated with
(A) pellagra
(B) beriberi
(C) anaemia
(D) rickets
Answer:
rickets
Question: A balanced diet has
(A) vegetarian and non- vegetarian dishes
(B) salty and sweet dishes
(C) carbohydrates, fats and proteins
(D) all nutrients, water and roughage
Answer:
all nutrients, water and roughage
Question: Syphilis is an example of –
(A)water- borne disease
(B) advanced form of jaundice
(C) air- borne disease
(D) veneral disease
Answer:
veneral disease
Question: Which of the following nutrients do not provide energy for animals?
(A) Fats
(B)Carbohydrates
(C) Vitamins
(D) Proteins
Answer:
Fats
Question: Night blindness is due to
(A) excessive drinking of alcohol
(B) excess secretion of adrenals
(C) vitamin A deficiency
(D) inheritance by X-chromosome
Answer:
vitamin A deficiency
Question: The common housefly is responsible for causing many water- bornediseases. It role is
that of a –
(A) carrier
(B) vector
(C) causative agent
(D) none of these
Answer:
vector
Question: Vitamin A is responsible for
(A) rhodopsin
(B) night blindness
(C) pellagra
(D) cirrhosis
Answer:
night blindness
Question: Cod liver oil is source of
(A) vitamin B
(B) vitamin C
(C) iodine
(D) vitamin A
Answer:
vitamin A
Question: Insects like cockroach and spider are responsible for food poisoning and diseases. They
play the role of a-
(A) vector
(B) causative agent
(C) carrier
(D) All of these
Answer:
vector
Question: Vitamin B 2 is related with
(A) FMN
(B) NAD
(C) NADH
(D) ATP
Answer:
FMN
Question: Pernicious anaemia failure of erythrocytes to mature is mainly due to lack of
(A) vitamin K
(B) thiamine
(C) pyridoxine
(D) cyanocobal
Answer:
cyanocobal
Question: Botulism is caused by –
(A) Salmonella typhae
(B) Clostridium botulinum
(C) Crasticium botulinum
(D) Staphylococci
Answer:
Clostridium botulinu
Question: Castle intrinsic factor relates to intestinal absorption of
(A) cobalamin
(B) thiamine
(C) riboflavin
(D) pyridoxine
Answer:
cobalamin
We hope the above Human And Health Disease Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


