Students can read the important questions given below for Transport in Plants Class 11 Biology. Transport in Plants Class 11 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 11 Biology Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Class 11 Biology Question Bank Class 11 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions Transport in Plants Class 11 Biology
Objective Type Questions
Question. Process of plasmolysis is
(a) Always reversible
(b) Always irreversible
(c) Rarely reversible
(d) Usually reversible
Answer
D
Question. When a plant cell is placed in hypotonic solution, which of the following occurs?
(a) The cell takes up water and eventually bursts
(b) The cell takes up water until the osmotic potential equals the pressure potential of the cell
(c) Plasmolysis occurs
(d) Nothing occurs
Answer
B
Question. Initially solution in side A, with respect to side B, is
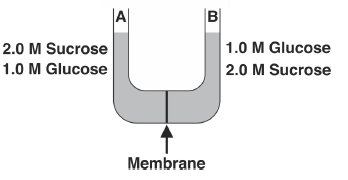
(a) Hypotonic
(b) Hypertonic
(c) Isotonic
(d) Iwer
Answer
C
Question. If a plasmolysed cell has O.P. 10, T.P. = -2, it’s DPD will be
(a) 8
(b) 12
(c) 10
(d) -2
Answer
B
Question. What would be Y of a fully flaccid cell?
(a) +3
(b) +2
(c) -3
(d) 0
Answer
D
Question. When a plasmolysed cell is placed in water or hypotonic solution, what happens?
(a) T.P. of cell decreases
(b) T.P. of cell becomes zero
(c) T.P. increases
(d) Water potential of cell decreases
Answer
C
Question. The process which brings about entry of water into seed coat when seeds are placed in water for germination is
(a) Diffusion
(b) Osmosis
(c) DPD
(d) Imbibition
Answer
D
Question. Water potential of imbibants is
(a) Highly positive
(b) Zero
(c) Highly negative
(d) Always positive
Answer
C
Question. Stomatal movement is not affected by
(a) O2 concentration
(b) Light
(c) Temperature
(d) CO2 concentration
Answer
A
Question. Go through the following facts
A. The pressure that is produced by swelling of wood had been used by prehistoric man to split rocks and boulders
B. The seedling is able to come out of soil due to development of a pressure. This pressure is-
(a) O.P.
(b) T.P.
(c) I.P.
(d) S.P.
Answer
C
Question. Mass or bulk flow of substance is called
(a) Active transport diffusion
(b) Translocation
(c) Diffusion
(d) Facilitated
Answer
B
Question. Multidirectional flow of a variety of organic and inorganic solutes occur through
(a) Xylem
(b) Vascular tissues
(c) Phloem
(d) Root
Answer
C
Question. Water moving through the apoplast from the soil to stele cells must crosses a plasma membrane in the cells of
(a) Root hairs
(b) Cortex
(c) Endodermis
(d) Only water
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is true about apoplast (the transport route through intercellular spaces and cell wall)?
(a) Cell membrane is involved
(b) Plasmodesmata are involved
(c) Minerals movement is regulated by
(d) Water and solutes can move by bulk flow
Answer
D
Question. Cell walls impregnated with water repellent suberin are found in the cells of
(a) Endodermis
(b) Pericycle
(c) Tracheids
(d) Root hairs
Answer
A
Question. The primary difference between the apoplast and the symplast is that the
(a) Apoplast is through non-living spaces and cell walls
(b) Apoplast relies on active transport
(c) Symplast is nonliving spaces and cell wall
(d) Apoplast prevents passive diffusion
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a component of the symplast?
(a) Sieve tube
(b) Endodermal cells
(c) Plasmodesmata
(d) Xylem tracheids
Answer
D
Question. All of the following increase the surface area available for absorption of water and minerals by a root except
(a) Mycorrhiza
(b) Numerous branches of root
(c) Root hair
(d) None
Answer
D
Question. The pathway for water that lies with the cell wall is
(a) The apoplastic pathway
(b) The casparian pathway
(c) The symplastic pathway
(d) The endodermal pathway
Answer
A
Question. Which one of following is incorrect?
(a) Movement through the apoplast does not involve crossing the cell membrane
(b) Water is absorbed along with mineral solutes, by the root hairs, purely by diffusion
(c) Apoplastic movement is dependent on the gradient
(d) Symplast is the system of adjacent cell wall
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the casparian strip ?
(a) The layer of endodermis
(b) The waxy layer between the endodermal cells
(c) The apoplast
(d) The layer of epidermal cells
Answer
B
Question. Guttation results from
(a) A high water potential of the leaves than of roots
(b) Root pressure causing water to flow up through xylem faster than it can be lost by transpiration
(c) The pressure flow of sap through phloem
(d) A water vapor breaks in the column of xylem sap
Answer
B
Question. As various ions from the soil are actively transported into vascular of root, water follows and increases the pressure inside the xylem. This positive pressure is called
(a) Mass pressure
(b) Root pressure
(c) Osmotic potential
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. Go through the four statement given below
A. Root pressure provides a light push in the overall process of water transport
B. Most plants meet their water need by transpiration pull
C. The greatest contribution of root pressure may be to re-establish the continuous chains of water molecules in the xylem vessel which often break under enormous tension created by transpiration
D. Guttation is the cause of transpiration pull
The correct statement are
(a) A,B,C,D
(b) A,B,C
(c) B,C,D
(d) B,C
Answer
B
Question. Water potential measures the tendency of water to
(a) Evaporate
(b) Move from one place to another
(c) Condense
(d) Adhere
Answer
B
Question. To develop root pressure energy is used to
(a) Actively transport minerals into root cells
(b) Evaporate water in the laves
(c) Condense water in the xylem
(d) Create suction in the xylem
Answer
A
Question. The lowest water potential in the system are
(a) Root hairs
(b) Vascular cylinders of root
(c) Tracheids of the stem
(d) Leaves
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a major factor in the movement of xylem sap up in a tall tree?
(a) Plasmodesmata
(b) Cohesion of adhesion
(c) Tension
(d) Transpiration
Answer
A
Question. The fact that water transport continues as long as leaves are alive and active indicate that
(a) Leaves pump water
(b) Leaves are necessary for transport of water
(c) Roots are active
(d) Water is needed for leaves to remain alive
Answer
B
Question. The transpiration driven ascent of sap depends on which of the following physical properties of water?
(a) Cohesion
(b) Surface tension
(c) Adhesion
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is a difference between transport by xylem and transport by phloem?
(a) Active transport moves xylem but not phloem sap
(b) Transpiration moves phloem sap but not xylem sap
(c) Xylem sap moves up; phloem sap moves down
(d) Xylem moves from sugar source to sink but phloem does not
Answer
C
Question. In plants, the area outside the plasma membrane, but still within plant is called
(a) Interstitial area
(b) Apoplast
(c) Stele
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. Imagine a twig from a tree examine the cut surface of the twig with a magnifying glass you locate a vascular tissue and observe a growing droplet of fluid exuding from the cut surface. The fluid is probably
(a) Phloem sap
(b) Xylem sap
(c) Guttation fluid
(d) Only water
Answer
A
Question. The last thing all water and solute molecules must pass through before they can enter the vascular system and move upward to leave is
(a) Endodermis
(b) Stoma
(c) Epidermis
(d) Root hair
Answer
A
Question. Unloading of mineral ions occurs the fine vein ending through
(a) Diffusion only
(b) Active transport only
(c) Diffusion and active transport
(d) Facilitated diffusion and active transport
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not part of the transpiration cohesion adhesion mechanism of ascent of sap?
(a) The loss of water from the mesophyll cells, which initiate a pull of water molecules from the neighboring cells
(b) Hydrophilic wall of narrow tracheids and xylem vessel that help to raise the column of water against the force of gravity
(c) Reduction of water in the surface film of mesophyll due to transpiration
(d) The active pumping of water into the xylem of root
Answer
D
Question. Which one(s) aid(s) stomatal movement?
(a) Heterogeneous nature of cell wall
(b) Unique shape of guard cell
(c) Radial orientation of cellulosic micro fibril in the guard cell
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is correct?
A. The immediate cause of stomatal movement is a change in the turgidity of guard cell
B. Higher vapour pressure in substomatal chamber and intercellular space with respect to atmospheric vapour pressure does not favour transpiration
C. Forces generated by transpiration create pressure sufficient to lift a xylem sized water column over 130 meters high
D. Under low humidity, optimum temperature, guard cells are turgid, moist soil, transpiration would be high
Options :
(a) All
(b) A,B and D are correct
(c) No one is correct
(d) Only D is correct
Answer
C
Question. The casparian strip
A. Limit the pathway available to water and solutes, forcing them to enter the symplast
B. Surrounds the pericycle
C. Is made of suberin
The correct statement is-
(a) All
(b) None
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following criteria does not pertain to facilitated transport?
(a) Requirement of special membrane proteins
(b) High selectivity
(c) Transport saturation
(d) Uphill transport
Answer
D
