Please refer to Periodic Classification Of Elements Class 10 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 10. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 10 Science Periodic Classification Of Elements Notes and Questions
Dobereiner’s Triads: This classification is based on the atomic mass. According to this, when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic masses, groups of three elements, having similar properties are obtained. The atomic mass of middle element of the triad being nearly equal to the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements.
For Example Li (6.9), Na (23), K (39).
Limitation: It fails to arrange all the known elements in the form of triads, even having similar properties.
Newland’s Law of Octaves: According to this ‘when elements are placed in order of increasing atomic masses, the physical and chemical properties of every 8th element are a repetition of the properties of the first element.’
Limitations :
* Law of octaves was applicable only up to calcium (only for lighter elements).
* Newland adjusted two elements in the same slot (e.g. Co and Ni), having different properties. For example; Co and Ni with Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine.
* According to Newland, only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in future.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table: Mendeleev’s periodic table is based on the physical and chemical properties of elements and their atomic masses.
Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
* Mendeleev’s left vacant places in his table which provided an idea for the discovery of new elements. Example: Eka-boron, Eka-aluminum and Eka-silicon.
* Mendeleev’s periodic table was predicted properties of several undiscovered elements on the basis of their position in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
* It is useful in correcting the doubtful atomic masses of some elements.
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
(a) Noble gases could accommodate in the Mendeleev’s periodic table without (a) No fixed position for hydrogen: No correct position of the hydrogen atom was in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Example: Position of hydrogen with alkali metals and halogens (17th group).
(b) No place for isotopes: Position of isotopes were not decided. Example: Cl-35 and Cl-37.
(c) No regular trend in atomic mass: Position of some elements with lower atomic masses before with higher atomic mass. Example: Ni-58.7 before Co-58.
* disturbing the periodic table after discovery.
* The Modern Periodic Table: In 1913, Henry Moseley showed that the atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
* Modern Period Law: The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic number.
Trends in Modern Periodic Table: Valency, Atomic size, metallic and non-metallic characters, and Electronegativity.
(i) Valency: The valency of an element is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of its atom (i.e. the combining capacity of an element is known as its valency).
In Period: On moving from left to right in a period, the valency first increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to zero (0).

In Groups: On moving from top to bottom in a group, the valency remains same because the number of valence electrons remains the same.
ii) Atomic size: Atomic size refers to radius of an atom. It is a distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom.
In Period: On moving from left to right in a period, atomic size decreases because nuclear charge increases.
Example: Size of second period elements: Li > Be > B > C > N > O > F
In Group: Atomic size increases down the group because new shells are being added in spite of the increase in nuclear charge.
Example ; Atomic size of first group element : Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs < Fr
(iii) Metallic character: It is the tendency of an atom to lose electrons
In Period: Along the period from left to right, metallic characters decreases because a tendency to lose electron decreases due to the increase in nuclear charge.
Example: Metallic character of second period elements: Li > Be > B > C >> N > O > F
In Group: Metallic character, when moving from top to bottom increases because the atomic size and tendency to lose electrons increases.
Example: First group element: Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs
(iv) Non-metallic character: It is tendency of an atom to gain electrons
In Period: Along the period from left to right, non-metallic character increases because tendency to gain electrons increases due to increase in nucleus charge.
Example; Non-metallic character of 2nd period elements: Li < Be < B < C < N < O < F
In Group: On moving from top to bottom in a group, non-metallic character decreases because atomic size increases and tendency to gain electrons decreases. Ex. Non-metallic character of 17th period element: F > Cl > Br > I
(v) Chemical Reactivity
In metals: Chemical reactivity of metals increases down the group because tendency to lose electrons increases. Example; Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs (1st group)
In non-metals: Chemical reactivity of non-metals decreases down the group because tendency to gain electrons decreases. Example: F > Cl > Br > I (17th group)
(vi) Electronegativity: It is tendency of an element to attract the shared pair of electrons towards it in a covalently bonded molecule. It increases with increase of nuclear charge or decrease in atomic size.
Along the period electro negativity increases. Example; Li < Be < B < C < N < O < F. Down the group electronegativity decreases. Example; Li > Na > K > Rb > Cs
F > Cl > Br > I

Multiple Choice Questions:
Question. According to Mendeleev periodic table, the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic function of their:
(a) Atomic Mass
(b)Atomic Numbers
(c) Atomic Volumes
(d) Densities
Answer
A
Question. Group-2 Metals are referred to as:
(a) Alkali Metals
(b) Alkaline earth Metals
(c) Chalcogens
(d) Halogens
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) K
(d) Ca
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following elements does not lose an electron easily?
(a) Na
(b) F
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Answer
B
Question. Elements P, Q, R and S have atomic numbers 11, 15, 17 and 18 respectively. Which of them are reactive non‑metals?
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) Q and R
(d) R and S
Answer
C
Question. The positions of four elements A, B, C and D in the modern periodic table are shown below. Which element is most likely to form an acidic oxide?

(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of the atomic radii of O, F and N?
(a) O < F < N
(b) N < F < O
(c) O < N < F
(d) F < O < N
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following elements has the largest atomic radii?
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) K
(d) Ca
Answer
C
Question. Elements belonging to same group have similar properties because:
(a) they have same number of valence electrons
(b) their atomic numbers go on increasing as we move down the group
(c) all of them are metallic elements
(d)None of the above
Answer
A
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
Directions: For questions given below, two statements are given – One labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason(R). select the correct answer from the codes (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below:
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(ii)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false
(iv) (A) is false but (R) is true
1. Assertion(A): The atomic and ionic radii generally decrease towards right in a period.
Reason (R): Across a period, nuclear charge increases.
Answer : (i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
2. Assertion(A): The elements of the same group have similar chemical properties.
Reason (R): The elements of the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
Answer : (i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
3. Assertion(A): Chlorine is the most electronegative element.
Reason (R): Electronegativity decreases down the group.
Answer : (iv) (A) is false but (R) is true
4. Assertion(A): On moving down the group, the basic nature of the oxides increases.
Reason (R): On moving down the group, metallic character increases.
Answer : (i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Very short answer Type Questions :
Question. Besides Gallium, which other elements have since been discovered to fill the gaps left by Mendeleev in his periodic table?
Answer: Scandium and Germanium
Question. Out of Li and K, which one have stronger metallic character and why?
Answer: ‘K’, because it can lose electrons easily due to larger size and less effective nuclear charge.
Question. On moving from left to right in the second period, what happens to the number of valence electrons?
Answer: Valence electrons keeps on increasing from left to right in the second period.
Question. What is place of metalloid in the periodic table?
Answer: They are placed between metals and non‑metals in a zig‑zag manner.
Question. Arrange the following metals in decreasing order of atomic size: Ca, Mg, Ba, Be
Answer: Ba > Ca > Mg > Be
Question. How does valency of an element vary across a period?
Answer: The valency of an element first increases and then decreases across a period.
Question. How does atomic size vary from left to right in a periodic table?
Answer: Atomic size decreases along a period from left to right in the periodic table.
Question. Which has smaller size: K(19) or Na(11); B(5) or C(6)?
Answer: Na(11) is smaller in size than K(19), C(6) is smaller in size than B(5).
Question. Write the number of valence electrons present in a nitrogen atom (147N).
Answer: It has 5 valence electrons.
Question. How does reactivity of metals vary down the group?
Answer: It increases down the group.
Question. Give any one difference in the electronic configuration of Group 1 and Group 2 elements.
Answer: Group 1 elements have 1 valence electron and are more reactive than Group 2 elements which have two valence electrons.
Question. Give the number of elements in 2nd and 5th period of modern periodic table.
Answer: 2nd period has 8 elements, 5th period has 18 elements.
Question. An element ‘A’ has atomic number 16. To which group and period does it belong?
Answer: It belongs to group 16 and third (3rd) period.
Question. Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration: 2, 8 in the modern periodic table?
Answer: It belongs to Group 18 and second period of the periodic table.
Question. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating the periodic table?
Answer: (i) Increasing order of atomic mass (ii) Formula of oxides and hydrides
Question. State modern periodic law.
Answer: Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
Question. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group in the periodic table?
Answer: It is because these are least reactive and resemble each other.
Question. Write two reasons responsible for late discovery of noble gases.
Answer: (i) They are less abundant in nature. (ii) They are least reactive.
Question. What was the basis of classification of elements by Newlands?
OR
Define Newlands’ law of octaves.
Answer: Elements were arranged in increasing order of atomic mass and every 8th element resembled with the first element.
Question. Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka‑silicon and Eka‑aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev.
Answer: GeCl4, GaCl3.
Question. Out of the three elements P, Q and R, having atomic number 11, 17 and 19 respectively, which two elements will show similar properties and why?
Answer: P(11): 2, 8, 1, Q(17): 2, 8, 7, R(19): 2, 8, 8, 1
‘P’ and ‘R’, because they have the same number of valence electrons.
Question. Write the number of horizontal rows in the modern periodic table. What are these rows called?
Answer: There are 7 horizontal rows. These are called periods.
Question. Write the formula which determines the maximum number of electrons that the shell of an atom can accommodate.
Answer: 2n2, where ‘n’ represents the number of electronic shell.
Question. The electronic configuration of two elements X and Y are 2, 8, 7 and 2, 8, 8, 3 respectively. Write the atomic numbers of X and Y.
Answer: 17 and 21 respectively.
Question. Explain, why the number of elements in the third period are 8.
Answer: It is because 3rd shell could accommodate a maximum of 18 electrons, but if it is the outermost shell it could not have more than 8 electrons. Therefore, this period has 8 elements.
Question. Name the element having electronic configuration 2, 8, 3. What is its valency?
Answer: Aluminium, its valency is equal to 3, because it lose 3 electrons to become stable.
Question. To which group and period should hydrogen be assigned?
Answer: It is placed in Group 1 and first period.
Question. Why was the system of classification of elements into triads not found suitable?
Answer: It is because all the elements discovered at that time could not be classified into triads.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Given below are four elements with their atomic numbers:

(a) Identify the element which belong to same group of Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange the given elements in decreasing order of atomic size.
(c) Write the formula of the oxide of ‘B’.
(d) Which of the above element is a metalloid?
Answer: (a) ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to same group. (b) B > D > A > C
(c) B2O (d) ‘D’ is a metalloid.
Question. What is meant by periodicity of properties of elements? Why are the properties of elements placed in the same group of periodic table similar?
Answer: The repetition of similar properties of elements after a certain interval of elements is called periodicity of properties.
Elements of the same group have same number of valence electrons, same valency and therefore posses similar chemical properties.
Question. The following table shows elements represented by the letters A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H: 12
(i) Which of the element has the atomic size (a) biggest and (b) smallest?
(ii) Which element has valency (a) 3 and (b) Zero
Answer: (i) (a) ‘A’ is biggest in size (b) ‘G’ is smallest in size
(ii) (a) ‘C’ has valency 3. (b) H has zero valency
Question. An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 16 of the modern periodic table.
(i) Determine the number of valence electrons and valency of ‘X’.
(ii) Molecular formula of the compound, when ‘X’ reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot structure.
(iii) Name the element ‘X’ and state whether it is metallic or non‑metallic.
Answer: (i) The element is S(16)—2, 8, 6, The number of valence electrons—6, Valency—2.

(iii) Sulphur, non‑metallic.
Question. Calcium is an element with atomic number 20
(i) Will it be a metal/non‑metal?
(ii) What will be its valency?
(iii) What would be formula of its chloride?
(iv) Will it be larger/smaller than K?
Answer: (i) It is a metal. (ii) Its valency is equal to 2.
(iii) CaCl2 is the formula of its chloride. (iv) It will be smaller than K.
Question. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Lithium atom is smaller than sodium atom.
(b) Chlorine (Atomic number 17) is more electronegative than sulphur (Atomic number 16).
Answer: (a) It is because Li(2, 1) has two shells whereas Na(2, 8, 1) has three shells.
(b) Chlorine is smaller in size and has more effective nuclear charge than sulphur, therefore it is more electronegative.
Question. Two elements ‘M’ and ‘N’ belong to Group I and II respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of M and N vary:
(a) size of their atoms (b) their metallic characters
(c) their valencies in forming oxides (d) formulae of their chlorides
Answer: (a) Size of ‘N’ is smaller than ‘M’.
(b) ‘M’ is more metallic than ‘N’.
(c) Valency of ‘M’ is 1 and valency of ‘N’ is 2.
(d) MCl and NCl2 are the formulae of their chlorides.
Question. In the following table, the position of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are given as they are in the modern periodic table as follows:

On the basis of above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the element which form only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a metal with the valency of 3.
(iii) Name the non‑metal with the valency of 3.
(iv) Out of B and C, whose atomic size is bigger and why?
(v) Write the common name for the family to which the elements D and F belongs to.
Answer: (i) E, (ii) B, (iii) C, (iv) B, … It has more number of shells, (v) Noble gases
Question. Based on the group valency of elements, state the formula of the following, giving justification for each.
(i) Oxides of Group 1 elements.
(ii) Halides of the elements of Group 13.
(iii) Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of Group 16.
Answer: (i) Group 1 elements can lose one electron to become stable, so its valency is equal to 1, M2O.
(ii) Group 13 elements have valency equal to 3, MCl3.
(iii) Group 2 elements have valency equal to 2, Group 16 elements have 6 valence electrons.

Question. An element ‘M’ with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with NO3 –, SO4 2– and PO4 3– radicals. Write the formulae of three compounds so formed. To which group and period of modern periodic table, ‘M’ belongs to? Will ‘M’ form covalent or ionic compounds? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: Mg(NO3)2, MgSO4, Mg3(PO4)2
It belongs to Group 2, 3rd period of the periodic table.
It will form ionic compounds because it can lose 2 electrons easily to form Mg2+ ions.
Question. Why lithium with atomic number 3 and potassium with atomic number 19 are placed in group one?
What will be atomic numbers of first two elements of second group?
Answer: K L M N
Li(3) 2, 1
K(19) 2, 8, 8, 1
Li and K are placed in Group 1 because both have 1 valence electron.
Be(4) and Mg(12) are first two elements of Group 2.
Question. An element belongs to third period and second group of the periodic table:
(a) State number of valence electrons in it. (b) Is it a metal or non‑metal?
(c) Name the element. (d) Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer: (a) 2, 8, 2 is the electronic configuration. The number of valence electrons = 2
(b) It is a metal
(c) Magnesium
(d) MgO is the formula of its oxide.
Question. State the reasons for the following:
(a) The elements of the same group have similar chemical properties.
(b) The elements of the same period have different properties.
Answer: (a) It is because they have the same number of valence electrons.
(b) It is because they differ in the number of valence electrons.
Question. (a) State two main characteristics of elements on which modern periodic table is based.
(b) No fixed position can be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table. Why?
Answer: (a) (i) Atomic number, (ii) No. of valence electrons
(b) It is because hydrogen resembles with Group 1 as well as Group 17 elements, therefore no fixed position can be assigned to it.
Question. What were the limitations of Newlands’ law of octaves?
Answer: (i) It was applicable upto Ca, i.e. lighter elements only.
(ii) New elements could not fit into Newlands’ octaves.
Question. Use Mendeleev’s Periodic table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements:
K, C, Al, Si, Ba
Answer: K2O, CO2, Al2O3, SiO2, BaO
Question. Study the data of the following three categories A, B and C.

(a) From the given three categories A, B and C, pick the one which forms Dobereiner’s Triads.
(b) Why did Mendeleev placed elements of category A, B and C in three different groups?
(c) Is Newland law of octaves applicable to all the three categories? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: (a) ‘A’ forms Dobereiner’s Triad.
(b) It is because they had different formula of oxides and hydrides.
(c) No, it was not applicable to elements after Ca(20) because after Ca every eighth element did not possess similar properties to first.
Question. Choose from the following: 6C, 8O, 10Ne, 11Na, 14Si
(a) Elements that should be placed in the same period.
(b) Elements that should be placed in the same group.
State the reason for your selection in each case.
Answer: (a) 6C, 8O, 10Ne belong to the same period because all these have 2 shells.
11Na, 14Si belong to the same period because both of these have 3 shells.
(b) 6C and 14Si belong to the same group because they have the same number of valence electrons and valency.
Question. The electrons in the atoms of four elements A, B, C and D are distributed in three shells having 1, 3, 5 and 7 electrons in the outermost shell respectively. State the period in which these elements can be placed in the modern periodic table. Write the electronic configuration of the atoms A and D and the molecular formula of compound formed when A and D will combine.
Answer: They belong to third period because these have 3 shells.
A has electronic configuration 2, 8, 1, valence electron 1, valency = 1
D has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7, valence electron 7, valency = 1
Formula: AD or A+D–
Question. (a) State modern periodic law.
(b) Elements A, B, C and D have atomic numbers 1, 8, 11 and 19 respectively. Choose the odd element and give reason for your answer.
Answer: (a) Modern Periodic Law: It states that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
(b) ‘B’ with atomic number 8 is an odd element because it has 6 valence electrons whereas others have 1 valence electron.
Question. An element ‘X’ belongs to the second group of periodic table. What is the formula of its chloride?
Answer : XCl2
Question. Where would you expect to find the element with atomic number 18 in the periodic table?
Answer : The element will bein-18th group and in the 3rd period of the periodic table.
Question. Name the elements present in first period.
Answer : Hydrogen and Helium.
Question. Out of lithium and potassium, which will have higher metallic character and why?
Answer : Potassium will have stronger metallic character than lithium because as we move from top to bottom in a group, the size increases which increases ease of liberation of electron.
Question. Write two achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Answer : (i) It could classify all the elements discovered at that time.
(ii) It helped in discovery of new elements.
Question. (a)Name the element with atomic number 17.
(b)To which period does it belong?
(c) To which group does it belong?
(d)Write its electronic configuration.
Answer :
(a) Chlorine
(b) 3rd
(c)17th
(d) 2,8,7
Question. Explain the basic character of oxide of elements down the group and across the period.
Answer : The basic nature decreases across the period. It changes from basic to acidic. The basic nature increases down the group.
These variations in acidic and basic nature of oxides can be related to electronegativity of the element. As the electronegativity of the element decreases down the group the basic character of the oxide increases.
Long Answer Questions
Question. An element X of group 15 exists as a diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K, in the presence of a catalyst to form a compound ammonia, which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(i) Identify the element X. How many valence electrons does it have?
(ii) Draw the electron dot structure of diatomic molecule of X. What type of bond is formed in it?
(iii) Draw the electron dot structure for ammonia and what type of bond is formed in it?
Answer: (i) ‘X’ is nitrogen. It has 5 valence electrons.

Question. The nucleus of five elements D, E, F, G and H are shown below:

(i) Identify D and E.
(ii) Identify the position of F and H in the periodic table.
(iii) What is the cause of similarity among the species D, G, H?
(iv) What will be the formula of compound formed between D and E?
(v) Which is largest in size among D, E, F, G and H?
Answer: (i) ‘D’ is lithium, E is fluorine.
(ii) F belongs to group 17, 3rd period.
H belongs to group 1, 4th period.
(iii) They have the same number of valence electrons, D(3) 2, 1; G(11) 2, 8, 1; H(19) 2, 8, 8, 1.
(iv) DE is the formula of the compound.
(v) H is largest in size due to the presence of four shells.
Question. (i) Which element can lose electrons most easily in 3rd period and why?
(ii) Why does tendency to lose electrons increases down the group?
(iii) What happens to the basic character of oxides down the group and why?
(iv) What happens to the acidic character of oxides along a period and why?
(v) Which group of elements can gain electrons most easily and why?
Answer: (i) Na, it is due to larger atomic size and least effective nuclear charge.
(ii) It is due to increase in atomic size and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
(iii) Basic character of oxides increases down the group due to increase in metallic character.
(iv) Acidic character of oxides increases along a period due to increase in non‑metallic character.
(v) Group 17 elements, due to smaller atomic size and more effective nuclear charge.
Question. An element X, which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(i) Identify the element X.
(ii) Write the electronic configuration of X.
(iii) Write the balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals.
(iv) What would be the nature (acidic/basic) of the oxides formed?
(v) Locate the position of the element in the modern periodic table.
Answer: (i) ‘X’ is sulphur. (ii) S(16): 2, 8, 6
(iii) 2FeSO4(s) heat → Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) SO2 and SO3 are acidic oxides and major air pollutants whereas Fe2O3 is a basic oxide.
(v) It belongs to group 16 and 3rd period.
Question. Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells, but different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This compound is added in a small amount to almost all the vegetable dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature, while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of D is almost neutral. Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(i) To which group or period of the periodic table do the listed elements belongs to?
(ii) What would be the nature of compound formed by the combination of elements B and F?
(iii) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
(iv) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state, at room temperature?
(v) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G are 3 and 7 respectively, then write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Answer: (i) They belong to the same period but different groups. ‘G’ belongs to Group 17. A and B belong to Group 1 and 2, … their oxides are basic. ‘C’ belongs to Group 13 due to 3 valence electrons. ‘D’ belongs to Group 14. E and F belong to group 15 and 16, respectively. ‘H’ belongs to group 18.
(ii) B and F will form an ionic compound.
(iii) A and B are metals.
(iv) G, H are gases at room temperature.
(v) CG3
Question. The position of certain elements in the Modern Periodic Table are shown below:
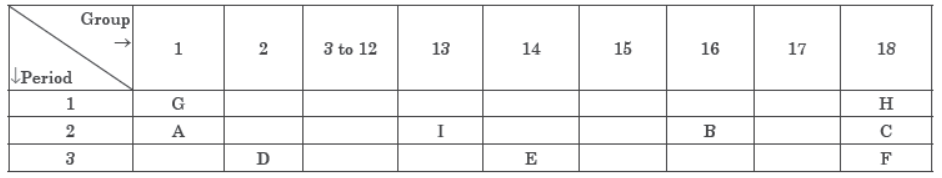
Using the above table answer the following questions giving reasons in each case:
(i) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a non‑metal with valency 2?
(iii) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(iv) Out of H, C and F which has largest atomic size?
(v) To which family does H, C and F belong?
Answer: (i) E will form only covalent compounds.
(ii) B is non‑metal with valency 2.
(iii) D is metal with valency 2.
(iv) ‘F’ has largest atomic radius.
(v) It belongs to noble gases.
Question. (a) Why do we classify elements?
(b) What were the two criteria used by Mendeleev in creating periodic table?
(c) Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in his periodic table?
(d) In Mendeleev’s periodic table, why was there no mention of noble gases like Helium, Neon and Argon?
(e) Would you place the two isotopes of chlorine, Cl‑35 and Cl‑37 in different slots because of their different atomic mass or in the same slot because their chemical properties are same? Justify your answer.
Answer: (a) It helps to study the properties of elements in a simpler way by studying the properties of 118 elements by studying properties of 18 groups and 7 periods.
(b) (i) Increasing order of atomic mass, (ii) Formula of oxides and hydrides of elements.
(c) These gaps were left for the undiscovered elements.
(d) Noble gases were not discovered by that time.
(e) They will be placed in same slot due to same properties.
Question. An element P (atomic number 20) reacts with an element Q (atomic number 17) to form a compound.
Answer the following questions giving reason:
Write the position of P and Q in the Modern Periodic Table and the molecular formula of the compound formed when P reacts with Q.
Answer: Atomic number of element P = 20
Electronic configuration of element P = 2, 8, 8, 2
Atomic number of element Q = 17
Electronic configuration of element Q = 2, 8, 7
The position of P in the Modern Periodic Table
Period (Number of shells) = 4
Group (Electrons in outer‑most shell) = 2
The position of Q in the Modern Periodic Table
Period (Number of shells) = 3
Group (Electrons in outer‑most shell) = (10 + 7) = 17
When P reacts with Q, it loses the two valence electrons (valency 2).
These two valence electrons are accepted by two Q atoms (valency 1).
Hence, the formula of the compound formed between P and Q is PQ2.
Question. Name the element which has
(a) the electronic configuration 2, 8, 1
(b) a total of two shells, with 4 electrons in the valence shell.
(c) total of three shells, with 3 electrons in valence shell.
(d) One shell which is completely filled with electrons.
(e) twice as many electrons in the second shell as in the first shell.
Answer: (a) Sodium (2, 8, 1) (b) Carbon (2, 4) (c) Aluminium (2, 8, 3)
(d) Helium (2) (e) Carbon (2, 4)
Question. On the basis of Mendeleev’s Periodic table, answer the following questions:
(a) Name the element which is in
(i) I group and III period. (ii) VII group and II period.
(b) Suggest the formula of the following:
(i) Oxide of nitrogen (ii) Hydride of oxygen
(c) In group VIII of the periodic table, why does cobalt with atomic mass 58.93 appear before nickel having atomic mass 58.71?
Answer: (a) (i) Na belongs to 1st group, IIIrd period. (ii) F belongs to VII group, IInd period.
(b) (i) N2O5 (ii) H2O
(c) It is because Co, Rh, Ir resemble with each other and Ni, Pd, Pt resembles with each other.
Similarity in properties were preferred over increasing order of atomic masses.
Question. An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystal and are major air pollutants.
i. Identify ‘X’.
ii. Write its electronic configuration.
iii. Write its balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals.
iv. What would be the nature (Acidic/Basic) of oxides formed?
v. Locate the position of the element in the periodic table.
Answer : (i) ‘X’ is Sulphur
(ii) Electronic configuration of X is: 2,8,6
(iii) 2FeSO4 —–→ Fe2O3+SO2 +SO3(iv)SO2 and SO3 are acidic oxides
(v) It belongs to group 16 and 3rd period.
Question. (a) Why do we classify elements?
(b)What were the two criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his periodic table.
(c)Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in his periodic table?
(d)In Mendeleev’s Periodic table, why was there no mention of Noble gases like He, Ne and Ar?
Answer : (a) classification of elements helps in systematic study of the properties if elements and in understanding and remembering the properties of elements.
(b) The two criteria are increasing order of atomic mass and similarity in the properties of elements.
(c) Mendeleev left gap in his periodic table for the undiscovered elements like Germanium and Gallium
(d) There was no mention of gases like He, Ne and Ar as they were not known at that time, and were discovered much later
CCT Based Questions
Question. Dobreiner triads and Newlands law of Octaves were early attempts at classifying elements into groups based on their properties. Dobreiner observed that groups of three elements(triads) could be formed in which all the elements shared similar physical and chemical properties. The identification of new elements made this model obsolete. Newly discovered elements did not fit into the triads. The British chemists John Newlands arranged then known elements in an ascending order of their atomic masses and observed that every 8th element had similar properties. On the basis of this observation, Newlands law of Octaves was formulated.
(a) What is the relationship in the atomic masses of elements of a Dobreiner triad?
(b) State Newlands law of Octaves.
(c) A and Bare the two elements having similar properties and obeying Newlands law of Octaves. How many elements are there in between A and B?
(d) Name the elements that form alkali metal triad.
Answer : (a) In the Dobreiner triads of elements, the atomic weight of the middle element is the arithmetic means of the other two.
(b) When the elements with lower atomic masses were arranged in order of their increasing atomic masses, the properties of every eighth element were similar to those of the first one.
(c) There are six elements in between A and B.
(d) Lithium, Sodium and potassium form alkali metal triad
Question. There are many observable patterns in the physical and chemical properties of elements as we descend in a group or move across a period in the periodic table. Such patterns are called Periodic trends. Major periodic trends include valency, atomic size, metallic and non-metallic properties.
(a) How does valency change on moving down in a group of modern periodic table?
(b) Why does atomic radius decrease on moving across a period in modern periodic table.
(c) how is metallic character related to the reactivity of metals.
(d) Discuss the variation of basic nature of oxides down the group.
Answer : (a) On moving down a group, valency remains the same as all the elements of the group have same number of valence electrons
(b) On moving from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases due to increase in nuclear charge.
(c) Greater the metallic character, greater is the reactivity.
(d) Basic nature of oxides increases down the group due to increase in metallic character.

We hope the above Periodic Classification Of Elements Class 10 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science


