Please refer to the Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development with answers provided for Class 10 Social Science. These solved case study based questions are expected to come in the Class 10 Economics exam in the current academic year. We have provided Case study for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters here. You should practise these solved case studies to get more marks in examinations.
Chapter 1 Resources and Development Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
On the Basis of the Status of Development Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example, the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these have not been developed properly. Developed Resources: Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility. Identify at least two resources from each category. Do you know that India has got the right to mine manganese nodules from the bed of the Indian Ocean from that area which lies beyond the exclusive economic zone. Identify some other resources which are international in nature. Stock: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are included among stock. For example, water is a compound of two gases; hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have advanced technical ‘know-how’ to use it for this purpose. Hence, it can be considered as stock. Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. River water can be used for generating hydroelectric power but presently, it is being utilised only to a limited extent. Thus, the water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be used in the future.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Which one of the following statements is true about the term resources?
(a) Resources are free gifts of nature.
(b) They are the functions of human activities.
(c) All those things which are found in nature.
(d) Things which cannot be used to fulfill our needs.
Answer
B
(ii) Identify the correct basis of the Status of Development potential resources.
| Basis | Potential resources |
| (a) resources | 1. No appropriate technology to use them |
| (b) stock | 2. Not utilised |
| (c) developed resource | 3. Subset of the stock |
| (d) reserves | 4. Surveyed (quantity and quality) |
Choose the correct option-
(a) (a)-1, (b)–3, (c)–2, (d)–4
(b) (a)–2, (b)–1, (c)–4, (d)–3
(c) (a)–3, (b)–1, (c)–4, (d)–2
(d) (a)–4, (b)–2, (c)–3, (d)–1
Answer
B
(iii) Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation are __________.
(a) Potential Resources
(b) Individual Resources
(c) Developed Resources
(d) Stock
Answer
C
(iv) Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called:
(a) Renewable resources
(b) Reserve
(c) Community resources
(d) Non-renewable resources
Answer
D
2. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy – agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic – needs inputs of energy. The economic development plans implemented since Independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy to remain operational. As a result, consumption of energy in all forms has been steadily rising all over the country. In this background, there is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources are the twin planks of sustainable energy. India is presently one of the least energy efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources. For example, as concerned citizens we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles; switching off electricity when not in use, using power-saving devices and using non-conventional sources of energy. After all, “energy saved is energy produced”.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) How will using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles help us?
(a) saving resources
(b) saving energy
(c) saving vehicles
(d) all the above
Answer
B
(ii) There is an urgent need of _________ development.
(a) unsustainable
(b) sustainable
(c) non-energy
(d) none of the above
Answer
B
(iii) Meaning of sustainable:
(a) viable
(b) temporary
(c) conserve
(d) none of the above
Answer
D
(iv) What is considered to be the basic requirement of economic development?
(a) resources
(b) energy
(c) technology
(d) citizens
Answer
B
3. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
We have shared our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generations too. Ninety-five per cent of our basic needs for food, shelter and clothing are obtained from land. Human activities have not only brought about degradation of land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to land. Some human activities such as deforestation, over grazing, mining and quarrying too have contributed significantly in land degradation. Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country. There are many ways to solve the problems of land degradation. Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent. Planting of shelter belts of plants, control on over grazing, stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes are some of the methods to check land degradation in arid areas. Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) In which of the follo wing States mining has caused severe land degradation?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Jharkhand
(c) Kerala
(d) Uttarakhand
Answer
B
(ii) In which of the following states is overgrazing responsible for land degradation?
(a) Jharkhand and Orissa
(b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
(c) Punjab and Haryana
(d) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
Answer
B
(iii) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation
(b) Deforestation
(c) Over-irrigation
(d) Overgrazing
Answer
C
(iv) One of the following which does not check land degradation-
(a) control on overgrazing
(b) creating shelter belts
(c) deforestation
(d) afforestation
Answer
C
4. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Resource planning is a complex process which involves: (i) identification and inventor of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources. (ii) evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans. (iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans. India has made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning right from the First Five Year Plan launched after Independence. The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region, but mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. There are many regions in our country that are rich in resources but these are included in economically backward regions. On the contrary there are some regions which have a poor resource base but they are economically developed. The history of colonisation reveals that rich resources in colonies were the main attractions for the foreign invaders. It was primarily the higher level of technological development of the colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the colonies. Therefore, resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes.
India has experienced all this in different phases of colonisation. Therefore, in India, development in general, and resource development in particular do not only involve the availability of resources, but also the technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) What was main attraction of foreign invaders to India?
(a) architecture
(b) resource
(c) irrigation method
(d) spices
Answer
B
(ii) Resource planning is essential for __________ existence of all forms of life.
(a) ecological balance
(b) sustainable
(c) exploitation
(d) None of these
Answer
B
(iii) Which of the following is essential for sustainable existence of all forms of life?
(a) Resource planning
(b) Resource management
(c) Resource extraction
(d) Resource generation
Answer
A
(iv) From which Five Year Plan has India made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning?
(a) First Five Year Plan
(b) Fifth Five Year Plan
(c) Annual Plans
(d) Tenth Five Year Plan
Answer
A
5. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow Non-Renewable Resources: These occur over a very long geological time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use. On the Basis of Ownership Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue. In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals. Make a list of resources owned by your household. Community Owned Resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there. National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Which one of the following is not the community owned resource?
(a) Burial grounds
(b) Grazing grounds
(c) Privately owned house
(d) village ponds
Answer
C
(ii) Match the following
| 1. Renewable resource | (a) wells |
| 2. Individual resource | (b) Ocean |
| 3. National resource | (c) solar energy |
| 4. International resource | (d) plantation |
Choose the correct option:
(a) 1–(a), 2–(c), 3–(d), 4–(b)
(b) 1–(c), 2–(d), 3–(a), 4–(b)
(c) 1–(b), 2–(a), 3–(c), 4–(b)
(d) 1–(d), 2–(c), 3–(a), 4–(b)
Answer
D
(iii) Which among the following is a type of resources classified on the basis of exhaustibility?
(a) National and individual
(b) Renewable and non-renewable
(c) Biotic and abiotic
(d) Potential and reserves
Answer
B
(iv) Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called:
(a) Renewable resources
(b) Reserve
(c) Community resources
(d) Non-renewable resources
Answer
D
6. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue.
In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals.
Community owned resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there.
National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land.
All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and
resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Which one of the following is an example of Biotic Resources?
(a) Rock
(b) Mountain
(c) Mineral
(d) Flora
Answer
D
(ii) The resources which are owned by the community are:
(a) plantation
(b) pasture land
(c) ponds
(d) all the above
Answer
D
(iii) The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone can be termed as which of the following types of resource?
(a) Individual resources
(b) Community owned resources
(c) National resources
(d) International resources
Answer
D
(iv) On the basis of ownership, plantations can be better considered as which of the following types of resources?
(a) Individual resource
(b) Community owned resource
(c) National resource
(d) International resource
Answer
A
Resources and Development
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question. Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Biotic
(c) Flow
(d) Non-renewable
[Answer : (d)
Question. Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put?
(a) Replenishable
(b) Human-made
(c) Abiotic
(d) Non-renewable
[Answer : (a)
Question. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation
(b) Deforestation
(c) Over-irrigation
(d) Overgrazing
[Answer : (c)
Question. In which one of the following States is terrace cultivation practised?
(a) Punjab
(b) Plains of U.P.
(c) Haryana
(d) Uttaranchal
[Answer : (d)
Question. In which of the following States is black soil found?
(a) Jammu & Kashmir
(b) Gujarat
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Jharkhand
[Answer : (b)
Question. What percentage of our land should be under forest according to the National Forest Policy (1952)?
(a) 33
(b) 22.5
(c) 31
(d) 30
[Answer : (a)
Question. Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have appropriate technology to access them are called:
(a) Potential resource
(b) Stock
(c) Developed resource
(d) Reserves
[Answer : (b)
Question. India’s territorial water extends upto a distance of:
(a) 12 km
(b) 12 nautical miles
(c) 200 nautical miles
(d) 19.2 miles
[Answer : (b)
Question. Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called:
(a) Renewable resources
(b) Reserve
(c) Community resources
(d) Non-renewable resources
[Answer : (d)
Question. Land that is left uncultivated for more than five agricultural years is called:
(a) Pasture land
(b) Culturable waste land
(c) Current fallow
(d) Barren land
[Answer : (b)
Question. Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as:
(a) Net sown area
(b) Forest cover
(c) Waste land
(d) Gross cropped area
[Answer : (d)
Question. The total degraded land in our country is:
(a) 133 million hectares
(b) 130 million sq. km.
(c) 140 million hectares
(d) 130 million hectares
[Answer : (d)
Question. In which of the following States mining has caused severe land degradation?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Jharkhand
(c) Kerala
(d) Uttarakhand
[Answer : (b)
Question. The main cause of land degradation in Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh is:
(a) Mining
(b) Over irrigation
(c) Deforestation
(d) Over grazing
[Answer : (b)
Question. Which is the most common soil of Northern India?
(a) Black soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Red soil
[Answer : (c)
Question. Red soil is mostly found in:
(a) Parts of Jammu & Kashmir
(b) Upper Ganga Plains
(c) Eastern and Southern part of Deccan Plateau
(d) None of the above
[Answer : (c)
Question. Red soil is reddish in colour due to:
(a) high clay content.
(b) presence of kankar nodules in the subsoil.
(c) diffusion of iron in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
(d) high moisture content.
[Answer : (c)
Question. Which of the following is not important for soil formation?
(a) Relief
(c) Parent rock
(c) Climate
(d) Duration of day
[Answer : (d)
Question. Black soil is also called:
(a) Bangar
(b) Khadar
(c) Regur
(d) Humus
[Answer : (c)
Question. Black soils are common in:
(a) Deccan trap region
(b) Kashmir Valley
(c) Ganga Valley
(d) Northern Plains
[Answer : (a)
Question. Laterite soil is very useful for growing:
(a) Rice, wheat and mustard
(b) Tea, coffee and cashewnut
(c) Pulses, sugarcane and resin
(d) None of the above
[Answer : (b)
Question. Black soil is deficient in
(a) Calcium carbonate
(b) Magnesium
(c) Potash
(d) Phosphoric contents
[Answer : (d)
Question. Which of the following soils has self-aeration capacity?
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Mountain soil
(c) Black soil
(d) Red soil
[Answer : (c)
Question. Ploughing along the contour lines to decelerate the flow of water down the slopes is called:
(a) Strip cropping
(b) Sheet erosion
(c) Contour ploughing
(d) Terrace cultivation
[Answer : (c)
Question. Which of the following is not a measure for soil conservation?
(a) Strip cropping
(b) Terrace cultivation
(c) Shelter belts
(d) Overdrawing of ground water
[Answer : (d)
Assertion-Reason Questions
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
1. Assertion. Alluvial soil is ideal for growth of paddy, wheat, cereal and pulse crops.
Reason. Alluvial soil is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture.
Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Alluvial soil contains adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops. It is porous and this property makes it ideal for the growth of wheat, paddy, cereal and pulse crops.
2. Assertion. The availability of resources is not the only necessary condition for the development of any region.
Reason. Not only availability of resources but also corresponding change in technology is necessary for the development of any region.
Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. Thus, both resources and advanced technologies contribute in development of a region.
3. Assertion. Resources are free gifts of nature. Reason. Resources like soil, air, water are easily available in nature.
Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Resources are not free gifts of nature but are present due to interaction of human beings with nature, technology and institutions. They are a function ofhuman activities. They transform material available in our environment into resources.
4. Assertion. Land is a natural resource of utmost importance.
Reason. Land can be used for various purposes.
Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Land is a natural resource of utmost importance as it supports human life and wild life, economic activities like agriculture, mining, transport and communication system.
5. Assertion. Resource planning is an easy process in India.
Reason. Resource planning involves planning structure, identification and inventory of resource across the regions.
Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Resource planning is not an easy but a very complex process as it involves surveying, mapping,
quantitative and qualitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
6. Assertion. Soil is the most important renewable natural resource.
Reason. Soil supports different types of living organisms on earth.
Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Soil is a living system. Soil helps to grow plants,
supports natural vegetation and economic activities like agriculture. Its universal usage proves that it is the most important renewable natural resource.
7. Assertion. Processes of soil formation and erosion go simultaneously and create a balance between the two.
Reason. The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is soil erosion.
Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Soil formation and erosion go simultaneously but this balance is disturbed due to human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining. Natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion.
8. Assertion. Arid soil is unsuitable for cultivation.
Reason. Arid soil is generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. It restricts the filtration of water.
Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Due to dry climate and high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture that is why it becomes unfit for cultivation.
9. Assertion. Control on mining activities does not control land degradation.
Reason. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, deforestation has occurred due to overgrazing, not mining.
Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Activities of mining cause land degradation because mining sites are abandoned after excavation work.
This results in over-burdening. Mining activities in the mentioned states has contributed to deforestation.
10. Assertion. Terrace cultivation does not restrict erosion.
Reason. Running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. This helps to cultivate crops.
Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Terraces, out on slopes in forms of steps break up the force of the wind, thus preventing erosion. The gullies render cultivation in those lands impossible
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Give one example of the main commercial crop cultivable in laterite soil.
Ans. Tea/coffee.
Question. Which type of soil is most suitable for growing the crop of cashew nut ?
Ans. Soil for the growth of Cashew nuts: Red Laterite soil.
Question. Classify resources on the basis of exhaustibility.
Ans. On the basis of exhaustibility, resources can be classified as:
1. Renewable/ Non-exhaustible resources
2. Non-renewable/ Exhaustible resources.
Question. Read the features of a soil and name the related soil:
1. This soil ranges from red to brown in colour.
2. It is generally sandy in texture and is saline.
3. It lacks humus and moisture.
Ans. Arid soil is the soil that has all these features.
Question. “Degradation of land is a cause of worry.” Give one reason to support the statement.
Ans. Degradation of land is a cause of worry because it can cause ecological imbalance.
Question. How is overgrazing responsible for land degradation in Gujarat?
Ans. Overgrazing is responsible for land degradation in Gujarat because the extensive grazing for long and repeated periods leaves less time for propre vegetation to grow and thus the land and it is soil particles are left loose thereby degrading the overall quality of the land. Related Theory Overgrazing refers to what happens when livestock feeds on pasture to the point where there is no vegetation left.
Question. “Conservation of resource is vital for development.” Give one example regarding the statement.
Ans. Conservation of resources: afforestation, water treatment.
Question. How are mining activities responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand?
Ans. Mining activities are responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand because mining sites are abandoned after the excavation work is complete, leaving deep scars on the land. Related Theory To get rid of this land degradation, proper management of wastelands and control of mining activities needs to be initiated.
Question. Water is a compound of two inflammable gases, hydrogen and oxygen, which can be used as a rich source of energy. However, we do not have the required technical ‘know-how’ to use them for this purpose. What kind of resources can these gases be put in?
Ans. The gases can be put in: The Stock Resources.
Question. Highlight the reason for land being known as the utmost important natural resource.
Ans. Land is known as the utmost important natural resource because all economic activities are performed on land and it also supports natural vegetation and wildlife.
Question. Give one example of community owned resources.
Ans. Village grazing grounds, public parks and picnic spots.
Question. This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows. They are well- known for their capacity to hold moisture. in addition, they are rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime. they are made up of extremely fine i.e. clayey material.
Read the details given in the source above and identify the kind of soil whose features have been mentioned.
Ans. Black Soil Explanation: Black soil is also known as ‘Regur Soil’ or ‘Cotton Soil’ as it is good for the cultivation of cotton crop in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat in India.
Question. Favourable conditions for wind energy exist in Western Rajasthan and Gujarat, but they have not been utilised and developed to the maximum. It falls in which category of resources?
Ans. Wind energy received in Western Rajasthan exist as: Potential Resources.
Question. Which soil is most retentive of moisture?
Ans. Black Soil retains the most moisture.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. ‘‘Resource planning is a complex process.’’ Support the statement with arguments.
Ans. Resource planning is a complex process because:
(1) Resource planning involves identifying resources which are available in different parts of the country. This is a time consuming process as it involves surveying and mapping various regions of the country. Then, the quality and quantity of the available minerals also needs to be estimated.
(2) Resource planning is a complicated process as it involves the use of specialised technology, skill sets and requires setting up many institutions for the execution of resource development plans.
(3) One of the daunting tasks is to match and align resource development plans with national development plans. Related Theory Resource planning is the judicious use of resources. Resource planning becomes more important in a country like India, where resources are not distributed properly.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘alluvial soil’ found in India.
Ans. Features of the alluvial soil are as:
(1) It is formed by the deposition of the river load as it flows from its upper to its lower course.
(2) It is light and porous, therefore easily tillable.
(3) It is a fertile soil as it is rich in minerals, especially potash and lime.
(4) It is suitable for the growth of a large variety of rabi and kharif crops.
(5) Soils in the drier areas are more alkaline.
Question. Classify resources of the basis of their origin.
Ans. Types of resources on the basis of origin are as follows:
(1) Biotic Resources: These resources are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc.
(2) Abiotic Resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example, rocks and metals etc.
Question. Describe the different steps of resource planning.
Ans. The different steps of resource planning are :
(1) Doing proper and strategic surveying, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of resources, leading to identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country.
(2) Resource development plans are implemented by evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional setup. (3) The overall development plans are then matched and coincided with development plans.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘black soil’ found in India.
Ans. Features of the black soil found in India are:
(1) Black soil is black in colour and is also known as regur soil.
(2) Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil.
(3) It is fine textured and clayey in nature.
(4) It is formed from weathered lava rocks , which also gives it its black colour.
(5) It has high water retention power.
Question. Mention three problems that are associated with the indiscriminate use of resources.
Ans. The following three problems are the result of indiscriminate use of resources:
(1) Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals.
(2) Accumulation of resources in few hands, which in turn has divided the society into two segments-rich and poor.
(3) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Question. ‘Sustainable Development is a crucial step for the development of a country’. Explain with suitable examples.
Ans. Sustainable development is crucial for development of a country as it:
(1) Promotes use of renewable resources like solar energy, tidal energy, etc
(2) Puts a check on over usage of resources
(3) Promotes protection and conservation of resources for future generation
Question. Describe the importance of judicious use of resources.
OR
Why should we use natural resources properly and judiciously? Explain your views.
Ans. The importance of judicious use of resources are : (1) Multiple environmental and socioeconomic problems may arise if resources are used in an indiscriminate manner. (2) Most of the resources are non-renewable. The continuous usage of these resources may result in exhaustion of the resources. This may stunt development and growth of the people. (3) It will enhance the status of a person and would not impede development in general for future generations. They have to be used with caution.
49. What were the main features of the Earth Summit held at Rio de Janeiro in 1992?
Ans. Three main features of the Earth Summit of 1992 held at Rio de Janeiro:
(1) It was the first international Earth Summit in which more than 100 heads of states met.
(2) The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
(3) This Convention endorsed the global, Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is meant by conservation of resources? Mention any four steps taken at global level to conserve resources.
Ans. Resources are vital for development and also to satisfy human needs and aspirations. But irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important. Even once Mahatma Gandhi raised his concern about resource conservation in these words, “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses. Steps taken at global level for the conservation of resources are as follows:
(1) The club of Rome advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968.
(2) In 1974, Gandhi ji’s philosophy was presented by Schumacher in his book ‘Small is Beautiful’.
(3) In 1987, the Brundtland Commission Report introduced the concept of sustainable development as a means for resource conservation.
(4) In 1992, the first Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil made significant contribution towards the conservation of resources.
Question. What is land degradation? Suggest any four steps to control land degradation.
Ans. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation. This has serious repercussions on society and the environment. Following steps can be taken to control the land degradation:
(1) Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent
(2) Planting of shelter belts of plants.
(3) Control on over grazing, stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes
(4) Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Question. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development? Explain.
Ans. Sustainable economic development means development that is viable keeping the requirements of both the present and future generations at par. It is a development that doesn’t compromise with the environment, provides equal opportunities to grow, utilises resources for both the present and upcoming generations. The issue of sustainability is important for development because without the same, man will use resources without care, destroying the environment, preventing all chances of survival and development in future. If not for sustainability, people would start exploiting finitely available resources and end up finishing them soon, thus destroying Earth’s balance. Global warming, ozone layer depletion and environmental pollution have been caused due to this ignorance. Sustainability is vital for maintaining global peace and quality of life. So, the need of the hour is to use resources wisely so, as to sustain our planet Earth.
Question. What is resource planning? Why is resource planning essential? Explain.
Ans. Resource planning is a technique of proper utilisation of resources which aimed at sustainable development. Resource planning is essential because of the following reasons:
(1) Most of resources available on earth are limited in supply.
(2) The resources available to us are distributed unevenly all over the country.
(3) Overutilization of the resources may lead to environmental pollution and depletion of resources as well. Therefore, planning of resources can reduce pollution and overutilization of resources as well.
(4) Planning of resources can lead to have a balanced development at national, state, regional and local levels.
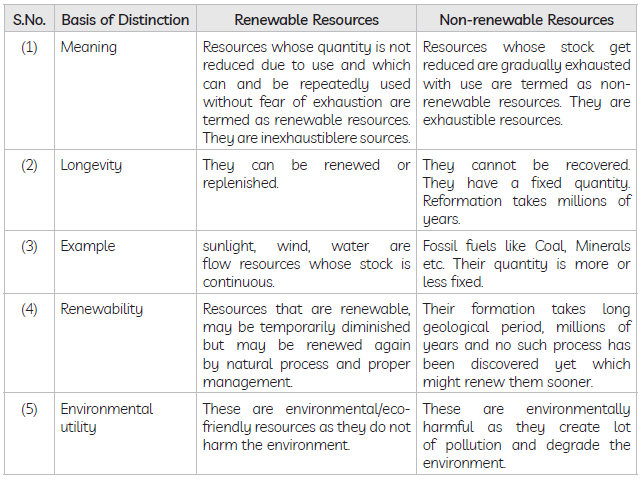
Question. Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable resources. Give examples.