Please refer to Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science Important Questions given below. These solved questions for Human Eyes and Colourful World have been prepared based on the latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. We have provided important examination questions for Class 10 Science all chapters.
Class 10 Science Human Eyes and Colourful World Important Questions
Question. The phenomenon of light responsible for the working of the human eye is
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) power of accommodation
(d) persistence of vision.
Answer
B
Question. The image formed on the retina of human eye is
(a) virtual and erect
(b) real and inverted
(c) virtual an inverted
(d) real and erect
Answer
B
Question. The change in the focal length of human eye is caused due to
(a) ciliary muscles
(b) pupil
(c) cornea
(d) iris
Answer
A
Question. The human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) cornea.
(b) iris.
(c) pupil.
(d) retina.
Answer
D
Question. The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
(a) 25 m.
(b) 2.5 cm.
(c) 25 cm.
(d) 2.5 m.
Answer
A
Question. The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) pupil.
(b) retina.
(c) ciliary muscles.
(d) iris.
Answer
C
Question. The light sensitive cell present on retina and is sensitive to the intensity of light is:
(a) cones
(b) rods
(c) both rods and cones
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following colours is least scattered by fog, dust of smoke?
(a) Violet
(b) Blue
(c) Red
(d) Yellow
Answer
C
Question. The coloured light that refracts most while passing through a prism is
(a) Yellow
(b) Violet
(c) Blue
(d) Red
Answer
B
Question. Which part of the eye refracts light entering the eye from external objects?
(a) Lens
(b) Cornea
(c) Iris
(d) Pupil
Answer
B
Question. The amount of light entering the human eye is controlled by
(a) Ciliary muscles
(b) Pupil
(c) Cornea
(d) Iris
Answer
B
Question. The focal length of human eye lens can be changed due to
(a) Iris
(b) Ciliary muscles
(c) Contact lens
(d) Spectacles
Answer
B
Question. The persistence of vision for normal eye is
(a) (1/10) th of a second
(b) (1/16) th of a second
(c) (1/6) th of a second
(d) (1/18) th of a second
Answer
B
Question. The following illustration represents the

(a) Correction of eye defect
(b) working of a simple microscope
(c) both (a) and
(b) (d) none of the above
Answer
B
Question. The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) presbyopia
(b) accommodation
(c) near-sightedness
(d) far-sightedness
Answer
B
Question. Colour blindness is caused due to
(a) lack of rod cells
(b) absence of optic nerve
(c) lack or cone cells
(d) none of these
Answer
C
Question. Long-sightedness or hypermetropia can be corrected by
(a) Contact lens
(b) Concave lens
(c) Convex lens
(d) Bifocal lens
Answer
C
Question. The part of eye that determines the colour of the eye of a person is
(a) Pupil
(b) Cornea
(c) Retina
(d) Iris
Answer
D
Question. The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is
(a) 25 m
(b) 20 m
(c) 25 cm
(d) 20 cm
Answer
C
Question. The glass has greater refractive index for
(a) Violet light
(b) Green light
(c) Blue light
(d) Red light
Answer
A
Question. The colour of sky is blue during day time, red during sunset and black at night. This is due to
(a) Scattering of light
(b) Small particles present in atmosphere
(c) Atmospheric refraction
(d) All of the above.
Answer
D
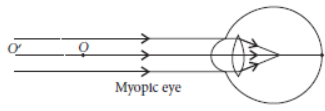
Question. The eye defect represented by the figure is
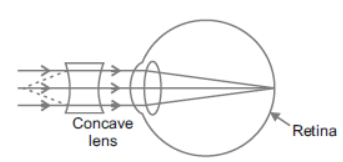
(a) Myopia
(b) Hypermetropia
(c) Cataract
(d) Presbyopia
Answer
A
Question. A student of class 10, is not able to see clearly the black board Question when seated at a distance of 5 m from the board, the defect he is suffering from is
(a) Myopia
(b) Hypermetropia
(c) Presbyopia
(d) Astigmatism
Answer
A
Question. The component of white light with greatest wavelength is
(a) Violet
(b) Red
(c) Green
(d) Blue
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What holds the crystalline lens in the human eye?
Answer : Ciliary muscles.
Question. Define least distance of distinct vision.
Answer : The minimum distance at which the objects can be seen clearly without any strain is called least distance of distinct vision. It is the near point of eye and is equal to 25 cm.
Question. What is persistence of vision?
Answer : When the image is formed on retina it remains there for 1/16th of a second and this property of eye is called persistence of vision.
Question. Define the power of accommodation of human eye.
Answer : The ability of eye to see nearby as well as far off objects at the same time is called power of accommodation.
Question. In which type of eye defect far point of the eye gets reduced?
Answer : Myopia.
Question. In which type of eye defect near point of the eye becomes more than 25 cm?
Answer : Hypermetropia.
Question. What is the diameter of human eye?
Answer : 2.3 cm
Question. Name the light sensitive part of the eye where image of an object is formed.
Answer : Retina
Question. What is the function of iris?
Answer : Iris controls the size of the pupil.
Question. What is dispersion of light?
Answer : The splitting of light into its various components (i.e., 7 colours) is called dispersion of light.
Question. Which part of the human eye helps in changing the thickness of lens?
Answer : Ciliary muscles.
Question. Name the disease in which crystalline lens of human eye becomes opaque.
Answer : Cataract.
Question. Distinguish between presbyopia and hypermetropia.
Answer :
| S.No. | Hypermetropia | Presbyopia |
| 1. 2. 3. | Only far-sightedness. Eye ball becomes short or the focal length increases. Corrected by using convex lens. | It can be only far-sightedness or both far and short-sightedness. Ciliary muscles become weak and able to adjust the focal length. Corrected by using bifocal lens. |
Question. Which is the range of vision of normal eye?
Answer : 25 cm to infinity.
Question. What is Tyndall effect?
Answer : Scattering of light in the nature due to small particles present in the atmosphere is called Tyndall effect.
Short Answer Type Questions
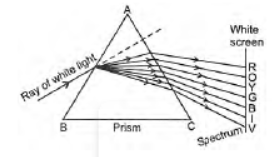
Question. A narrow PQ of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram. Trace it on your answer sheet and show the path of the emergent beam as observed on the screen DE.
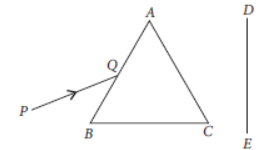
(i) Write the name and cause of the phenomenon observed.
(ii) Where else in nature is this phenomenon observed?
(iii) Based on this observation, state the conclusion which can be drawn about the constituents of white light.
Answer:
(i) The phenomenon of the splitting up of the white light into its constituents colours is called dispersion of light. Dispersion of light is caused due to, different constituents colours of light after different refractive indices to the material of the prism.
(ii) The formation of rainbow is caused by the dispersion of the white sunlight into its constituent colours.
(iii) Based on the dispersion of white light into its constituents colours, we can conclude that (a) The white light consists of seven colours (b) The violet light suffers maximum deviations and the red light suffers minimum deviation.
Question. About 3.5 crore people in the developing world are corneal blind. About 30 lac blind children below the age of 12 can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. What can a student of your age do in order to create awareness about this fact among people of your locality and why?
Answer: To create awareness among the people, we as a student can do the following.
(i) Organise a team of 3-4 members for eyedonation champion.
(ii) We can organise a play to aware people about the importance of donating an eye.
(iii) We can demonstrate poster and banner and take a walk around the area.
We must spread such awareness to encourage people to donate their eyes after their death so that the children below 12 years have to see this world as they are the future of our country.
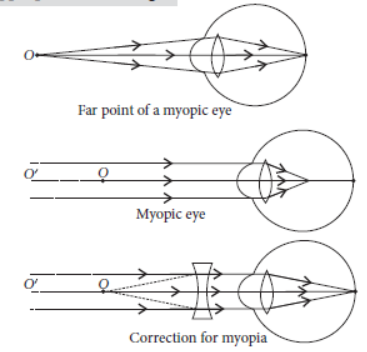
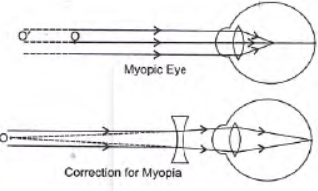
Question. (a) Draw a diagram to show the formation of image of a distant object by a myopic eye.
How can such an eye defect be remedied?
(b) State two reasons due to which this eye defect may be caused.
(c) A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond a distance of 1.5 m. What would be the power of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
Answer:

This defect can be correct by using concave lens.
(b) Myopia can be caused due to the following reasons.
(i) Excessive curvature of the eye lens
(ii) Elongation of the eyeball
(c) The far point of this myopic person is 1.5 m (This means a person can see a distant object kept at infinity clearly if the image of the object is formed at his infinity i.e., at 1.5 m)
u = ∞, v = –1.5 m, f = ?

Question. Name the three common defects of vision.
What are their causes? Name the type of lens used to correct each of them.
Answer: Three common defects of vision are
(i) Myopia
(ii) Hypermetropia
(iii) Presbyopia
Myopia can be caused due to following reasons.
(a) Elongation of eyeball.
(b) Excessive curvature of eye lens.
Hypermetropia can be caused due to following reasons.
(a) Shortening of eyeball.
(b) Focal length of eye lens becomes too long.
Presbyopia is caused due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of eye lens due to ageing.
Correction of these defects:
(i) Myopia can be corrected by using concave lens of appropriate focal length.
(ii) Hypermetropia can be corrected by using convex lens of appropriate focal length.
(iii) Presbyopia can be corrected by using bifocal lens.
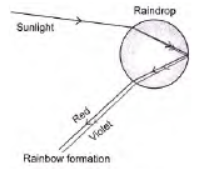
Question. Draw a labelled diagram to explain the formation of a rainbow in the sky.
Answer: A rainbow is a natural spectrum caused by dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets, present in the atmosphere.

Question. In the figure given a narrow beam of white light is shown to pass through a triangular glass prism. After passing through the prism it produces a spectrum XY on a screen.
(a) State the colour seen at X and Y.
(b) Why do different colours of white light bend through different angles with respect to the incident beam of light?
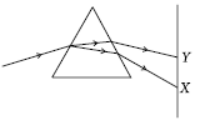
Answer: (a) At X, violet colour is seen and at Y, red colour is seen.
(b) Different colour of white light bend through different angles with respect to the incident of light because the refractive index of glass is different for different colours.
Question. What is meant by spectrum of white light?
How can we recombine the components of white light after a prism has separated them?
Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
Answer: Spectrum of white light is the ordered distribution of frequency or wavelength of the colour of white light.
We can recombine the components of white light after splitting, by placing inverted prism in the path of spectrum.
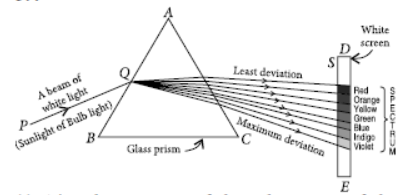
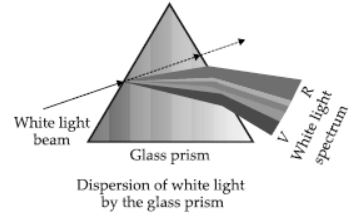
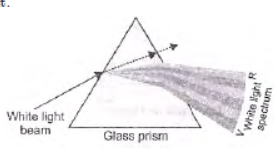
Question. What is ‘dispersion of white light’? State its cause. Draw a ray diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
Answer: Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours due to refraction is known as dispersion of white light.
Cause of dispersion : When a beam of white light enters a prism, it gets refracted and splits into seven constituent colours. The splitting of the light ray occurs due to the different bending angle for each colour. Thus, each colour ray when passing through the prism bends at different angles with respect to the incident beam, thus gives rise to a spectrum.
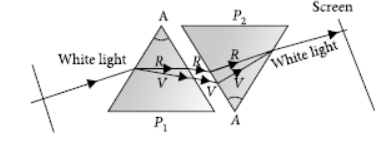
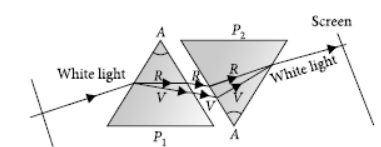
Question. State the cause of dispersion of white light passing through a glass prism. How did Newton showed that white light of sun contains seven colours using two identical glass prisms. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged together in inverted position with respect to each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the focus of the first prism.
Answer: Newton was the first to use a glass prism to obtain the spectrum of a whitelight. He then placed a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism. This allowed all the colours of the white light to pass through the second prism combining to form a white light emerging from the other side of the second prism. This made him believe that white light was composed of different colours.
Question. (a) Why do the component colours of incident white light split into a spectrum while passing through a glass prism, explain.
Answer: (a) When a beam of light incidents on a prism, it first gets refracted and splits into seven constituent colors. The splitting of the light ray occurs due to the different bending angle for each colour. Thus each colour ray when passing through the prism bends at different angles with respect to the incident beam. This gives rise to the formation of the spectrum.
Question. With the help of a labelled diagram, explain why the sun appears reddish at the sun-rise and the sun-set.
Answer:

At sun-rise and the sun-set, light from the sun passes through thicker layers of air and larger distance in the earth’s atmosphere. As the red colour has longest wavelength hence, it is least scattered by the air and dust particles. So, the sun appears reddish.
Question. What is a spectrum? How can we recombine the components of white light after a glass prism has separated them? Illustrate it by drawing a diagram.
Answer: Spectrum : The band of the colored components of a light beam is called its spectrum.
We recombine the components of white light by placing a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to first prism.

On passing white light to the first prism it splits into colours of the spectrum. Then this spectrum is allowed to pass through a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism. Then, we found a beam of white light.
Question. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a rainbow and mark the point where (i) dispersion, (ii) internal reflection occurs.
Answer: (i) Point A denotes dispersion and (ii) point B denotes internal reflection.

Question. Explain the formation of rainbow in the sky with the help of a diagram.
Answer: After a rain-shower, the sunlight gets dispersed by tiny droplets, present in the atmosphere. The water droplets acts like a small prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflectit internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop. Due to dispersion of light and internal reflection different colours reach the observer’s eye.

Question. Give reasons:
(i) The extent of deviation of a ray of light on passing through a prism depends on the colour.
(ii) Lights of red colour are used for danger signals.
Answer: (i) The extent of deviation of a ray of light on passing through a prism depends on the colour because the refractive index of glass for different colour is different. It depends on wavelength of a particular light.
(ii) Since the wavelength of light is maximum in the spectrum, its penetration power in the air is maximum and so we can see red colour from further distances. Thus, danger signal uses red colour.
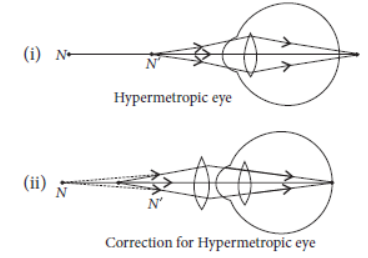
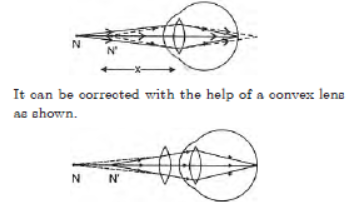
Question. What is hypermetropia? State the two causes of hypermetropia. With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect hypermetropia
(ii) correction of hypermetropia by using a lens
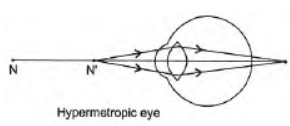
Answer: Hypermetropia : It is a defect in an eye in which a person is not able to see nearby object distinctly but can see far objects clearly.
Hypermetropia is caused due to following reasons:
(a) Shortening of the eyeball
(b) Focal length of crystalline lens is too long.
Question. What eye defect is myopia? Describe with a neat diagram how this defect of vision can be corrected by using a suitable lens.
Answer: Myopia is also known as near-sightedness. A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly.
Myopia can be corrected by using concave lens of appropriate focal length.
Question. (a) Trace on your answer sheet the path of a monochromatic ray AO incident on a glass prism and mark the angle of deviation.

(b) If AO were a ray of white light, (i) describe what will you observe on the screen BC placed near the prism
(ii) write the name of this phenomenon
(iv) what does it prove about the constituents of white light?
Answer: (a)
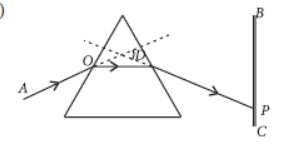
Here, in the figure, ∠D is the angle of deviation of the given monochromatic light by the glass prism.
(b) If AO were a ray of light, then
(i) On screen BC, a spectrum will be observe consisting of seven colours arranged from bottom to top as follows.
Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red (VIBGYOR)
(ii) The phenomenon is known as dispersion of light.
(iv) It proves that a white light consists of seven colours and lower the wavelength higher will be the deviation of light.
Question. (a) A person cannot read newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from.
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
(b) We see advertisements for eye donation on television or in newspapers. Write the importance of such advertisements.
Answer: (a) The person is suffering from hypermetropia.
(b) It is important to advertise for eye donation on television or in newspaper because
(i) Few people are unaware about the fact that there can be an eye transplant through which blind people can see this colourful and beautiful world.
(ii) To encourage them to donate their eye by spreading awareness about it through television or newspaper.
Question. Explain in brief the reason for each of the following:
(a) Advanced sun-rise (b) Delayed sun-set
Answer: (a, b) : The Sun is visible to us about 2 minutes before the actual sunrise, and about 2 minutes after the actual sunset because of atmospheric refraction. By actual sunrise, we mean the actual crossing of the horizon by the Sun. Figure shows the actual and apparent positions of the Sun with respect to the horizon. The time difference between actual sunset and the apparent sunset is about 2 minutes. The apparent flattening of the Sun’s disc at sunrise and sunset is also due to the same phenomenon.

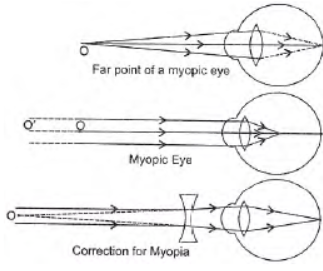
Question. A student suffering from myopia is not able to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m.
(a) List two possible reasons due to which this defect of vision may have arisen.
With the help of ray diagrams, explain
(i) Why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes?
(ii) The type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision and how this defect is corrected by the use of this lens.
(b) If, in this case, the numerical value of the focal length of the corrective lens is 5 m, find the power of the lens as per the new Cartesian sign convention.
Answer: (a) The two possible reasons due to which the defect of vision arises are :
excessive curvature of the eye lens elongation of the eye ball.
(i) A student with myopia has the far point nearer than infinity, thus, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina. In the given case the student is not able to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes are formed in front of the retina hence, it appears blurred.
(ii) This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power as it brings the image back on to the retina, thus the defect is corrected.

Question. Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Answer: Planets do not emit light. However, they become visible due to reflection of light falling on them. The planets are much closer to the earth and thus can be considered as the extended source of light. The fluctuations in the light coming from various points of the planet due to atmospheric refraction get averaged out. As a result, no twinkling of planets is seen.
Question. Explain giving reason why the sky appears blue to an observer from the surface of the Earth. What should the appearance of the sky be during the day for an astronaut staying in the international space station orbiting the Earth? State reason to justify your answer.
Answer: When sunlight passes the atmosphere, the fine particles in air scatter blue colour more strongly than red. This scattered blue light enters our eye and the colour of clear sky appears blue. For an astronaut staying in the international space station orbiting the Earth, the appearance of the sky will be black due to absence of air molecules to scatter the light coming from the Sun.
Question. State the difference in colours of the sun observed during sunrise/sunset and noon. Give explanation for each.
Answer: During sunrise or sunset, the suns rays pass through a maximum length of the atmosphere.
Most of the blue and shorter wavelength get scattered. Only the red colour of light reaches the observer. That is why the Sun observed during sunset and sunrise appear red. At noon, the distance to be travelled is least. All wavelengths are scattered equally and hence sun appears white.
Question. Draw a ray diagram to explain the term angle of deviation.
Answer: The emergent ray bends at an angle to the direction of the incident, thus the angle between them is known as angle of deviation (D).

Question. How does eye control the amount of light entering it?
Answer : The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the pupil and further the size of the pupil is controlled by iris.
Question. Why can’t we see object very close to our eye?
Answer : The objects are seen only when the image forms on retina when the light rays pass through the lens. The lens has its fixed ability of changing the focal length with the help of ciliary muscles.
Ciliary muscles cannot be contracted beyond a certain limit to change the focal length of eye lens. The objects kept very close to our eye cannot be focused by ciliary muscles.
Question. What is night blindness and colour blindness?
Answer : When a person lacks rod cells in retina he is not able to see the objects clearly in less/dim light, such a defect is called night blindness.
When a person lacks cone cells in retina he is not able to see/distinguish between different colours, such a defect of eye is called as colour blindness.
Question. What is myopia? How can it be corrected?
Answer : Myopia is an eye defect also called short-sightedness. In this type of defect person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see far off objects clearly. It may be caused due to the increase in the size of eye ball or due to the decrease in the focal length of the eye lens.
Correction–It can be corrected by using concave lens of appropriate focal length.
Question. The image formed on retina is inverted but we see the object erect. Why?
Answer : The image formed on retina is inverted, this image is formed on the light sensitive cells called rods and cones of the retina which generates electrical signals. This signal reaches brain via optic nerve. It is the brain that interprets this image and while processing the image it helps in perceiving objects as they are.
Question. Why do birds fly back to their nest in the evening?
Answer : Birds lack light sensitive cells called rods, due to lack of these cells they cannot see the objects clearly in less/dim light.
Question. Why are two eyes more helpful for us to see as compared to one?
Answer : Two eyes are more helpful as one eye gives only a view of 150° angle where as two eyes increase the view by making it wide to 180° angle. Two eyes also helps us to see the objects in dim light or darkness clearly. Two eyes give stereoscopic vision helping us assess the depth of vision.
Question. When white light enters the prism, which colour of light deviates/bends the least and which colour bends the most?
Answer : The light that bends the least is red colour and the light that bends the maximum is violet colour light.
Question. Explain the phenomenon which causes twinkling of stars.
Answer : The phenomenon is atmospheric refraction. In this case the star are point source illuminated objects which are very far from us when light travels through atmosphere it bends, and due to this the amount of light entering the eye is different each time which gives the twinkling effect.
Question. The sun appears to be red at the time of sunset and sunrise. Give the reason.
Answer : Sun appears red during sunset or sunrise because at this time the sun is far from the earth and the light that reaches the earth from the sun scatters the most and all other colours of light gets scattered. The least scattered light is red and it enters our eye.
Question. Give reason for early sunrise and delayed sunset.
Answer :

Sun being far off the light rays entering our eye gets refracted several times due to the atmosphere and the sunrise and sunset are seen to us due to the bending of light and that light enters our eye to visualise the sun at that particular point.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Draw a neat labelled diagram of human eye and explain the working of each part of it.
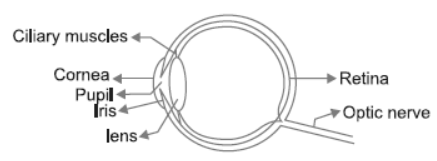
Answer : Working of Human eye
Human eye consists of various parts which helps us in seeing the objects, the function of various parts are:
(a) Cornea: It is the transparent membrane which refracts the light entering our eye.
(b) Iris: Iris controls the size of pupil.
(c) Pupil: It allows the light entering our eye to pass through it.
(d) Lens: Adjusts the focal length of the eye to see the objects at different places.
(e) Ciliary muscles: Helps in changing the focal length of the lens.
(f) Retina: It is the screen of the eye on which image is formed. It consists of rods and cones.
(g) Optic nerve: It carries the electrical signals from retina to brain.
Question. Describe with the help of diagram, how the refraction of light takes place through a glass prism.
Answer :
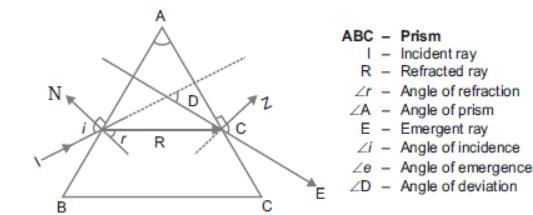
The incident ray I when enters the prism it gets refracted, bends and form ∠ r with the normal. Angle of refraction is smaller than the angle of incidence. The incident ray bends towards the normal, as it passes from rarer medium to denser medium. When this refracted ray passes from denser medium to rarer medium it bends away from the normal. This emergent ray has bent out at an angle to the direction of incident ray.
This angle is called the angle of deviation ∠D.
Question. Write the importance of ciliary muscles in the human eye. Name the defect of vision that arises due do gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles in old age. What type of lenses are required by the persons suffering from this defect to see the objects clearly?
Akshay, sitting in the last row in his class, could not see clearly the words written on the blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. He could now see the words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it soft to send the message to Akshay’s parents advising them to get his eyesight checked.
In the context of the above event, answer the following questions:
(a) Which defect of vision is Akshay suffering from? Which type of lens is used to correct this defect?
(b) State the values displayed by the teacher and Salman.
(c) In your opinion, in what way can Akshay express his gratitude towards the teacher and Salman?
Answer: Ciliary muscles modifies the curvature of eye lens and hence adjusts its focal length. This enables us to see objects.
The defect of vision is presbyopia, person suffering from this defect should wear bifocal lenses. These lenses consists of both concave and convex lenses.
(a) Akshay is suffering from myopia or nearsightedness.
He should use concave lens to correct this defect.
(b) Teacher and salman are concerned and caring.
(c) Akshay can show his gratitude by saying thank you.
Question. In presbyopia, we use bi-focal lens with upper portion concave lens and lower portion convex lens. Why is the arrangement so?
Answer : The upper portion is concave lens so that our eyes can see the distant objects. When the rays come parallel from infinity it will pass through the upper part of spectacles.
Whereas for the lower part consists of convex lens which facilitates our eye to see the near objects.
Question. (a) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Colour of the clear sky is blue.
(ii) The sun can be seen about two minutes before actual sunrise.
(iii) We cannot see an object clearly if it is placed very close to the eyes.
(b) What is presbyopia? Write two causes of this defect
Answer : (a) (i) Clear sky appears blue because the white light of sun when enters the earth’s atmosphere the large number of molecules present in the earth’s atmosphere scatter the light. As blue light scatters the maximum it reaches our eyes.
(ii) The sun is visible to us 2 minutes before the actual sunrise because of atmospheric refraction. When the sun is below the horizon, the light travelling from rarer to denser medium bends and reaches our eyes creating an impression that it is above the horizon.
(iii) A normal human eye has a near point of 25 cm, anything closer to it is not seen clearly.
(b) Presbyopia: This defect is caused due to ageing. The person suffering from this disease cannot see nearby as well as far off objects. It is caused due to weakening of ciliary muscles. The lens is not able to change the focal length. It can be corrected by using bi-focal lens.
Long Answer Questions
Question. A person can see distant signboards clearly but cannot read clearly a book which is at 25 cm from his eye.
Giving reason identify the defect. Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate this defect and its correction.
Answer : Eyes defect is hypermetropia. Its causes are due to
a. shortening the eye ball
b. increase in focal length of eye lens.

Question. What is meant by scattering of light? Use this phenomenon to explain why the clear sky appearsn blue or the sun appears reddish at sunrise.
Answer :
a. Scattering of light is phenomenon by which beam of light is spreaded in many direction when it interacts with particle of matter. When sunlight strikes molecules in atmosphere, the light is redirected in many direction.
b. Scattering of blue colour is most due to shorter wavelength, where as scattering of red colour is least. All colours scattered in the sky and redb colour light reaches to earth, due to this sun appears reddish.
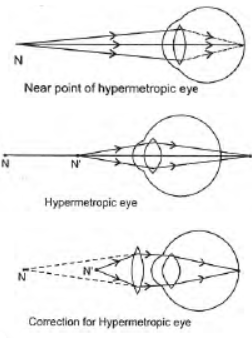
Question. A person is unable to read a book clearly when kept at a distance of 25 cm from his eye. Name the defect.
How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagrams for (i) defective eye (ii) corrected eye and explain them.
Answer :
The person cannot read a book at a distance of 25 cm from his eyes. So he is suffering from long sightedness/ hypermetropia. It can be corrected by using convex lens of suitable focal length.
Question. With the help of a diagram, explain the formation of a rainbow in the sky.
Answer :
The water droplets in the atmosphere act like small prisms. These droplets refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally and finally refract it again when it comes out of the rain drop.
Due to distortion of sunlight and internally reflection, different colours reach to the observer.
Question. With the help of scattering of light, explain the reason for the difference in colours of the Sun as it appears during sunrise/sunset and noon.
Answer :
At the time of sunrise or sunset it appears red where as at noon it appear white when it is overhead because at sunrise or sunset blue colour and other shorter wavelength light get scattered away while passing through the atmosphere. Scattering of longer wavelength is least which reach to the earth. Due to this sun appears red during morning and evening time.
When sun is overhead at noon, sun rays travels smaller distance, due to little scattering of blue and violet colour wavelength almost all wavelengths reach to earth and due to this sun appears white.
Question. State the cause of dispersion, when white light enters a glass prism. Explain with a diagram.
Answer :
When white light passes through a prism it splits into its constituent colours, because each coloured light has different speed in prism. Prism has different refractive index for these light rays and so deviates through different angles when emerge out from the prism.
Deviation for violet colour (shortest wavelength) is most and for red colour (largest wavelength) deviation is least.
Question. (a) Explain the phenomenon of scattering of light.
State the factor on which colour of scattered light depends.
(b) List any two natural phenomenon based on scattering of light.
Answer :
(a) Scattering of light is the phenomenon due to which light gets deflected by the atoms or molecules of different atmospheric gases and suspended particles present in atmosphere. Scattering depends upon size of the particles of the medium through which light passes.
(b) Two natural phenomenon based on scattering are (i) Reddish colour of sky during sunrise and sunset, (ii) Blue colour of sky.
Question. A person cannot see objects farther than 12 m from the eye clearly. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from and the lens that should be used for correction of this defect. Illustrate with the help of a diagram, how this lens will correct the defective vision?
Answer : He is myopic. Myopia can be corrected by using concave lens.
Question. A person cannot read a book at distances less than 50 cm. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from.
How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation:
a. by defective eye and
b. after using corrective lens.
Answer :
a. Either the hypermetropic eyeball is too short or b. The ciliary muscle is unable to change the shape of the lens enough to properly focus the image i.e., the focal length of the eye lens is too long. This
defect is called hypermetropia.
Question. (a) What is meant by dispersion of white light? Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
(b) Light of two colours A and B pass through a prism. A deviates more than B from its path of incidence. Which colour has a higher speed in the prism?
Answer :
(a) Splitting of white light into its constituent colours when it is passed through a prism is called dispersion of white light.
(b) B
Question. (a) A student is unable to see clearly the worlds written on the blackboard placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from State the possible causes of this defect and explain the method of correcting it.
(b) Why do stars twinkle? Explain.
Answer :
(a) Defects of vision: Myopia or short sightedness.
Reasons: Excessive curvature of eye lens and elongation of eye ball.
Correction: Using a concave lens myopic
(b) Due to atmospheric refraction stars twinkle. The density of atmospheric layers keep changing due to which point sized star sometimes appear brighter or dimmer with changing position. Due to this, stars appears twinkling.
Question. Account for the following:
a. Part of the human eye that helps in changing the focal length of the eye lens.
b. The condition resulting due to the eye lens becoming cloudy.
c. The factors on which colour of the scattered white light depends.
d. The range of vision of a normal eye.
e. The sky appears dark to the astronauts in the space.
Answer :
a. Ciliary muscles.
b. Cataract.
c. Size of the suspended particles in the medium through which white, light passes.
d. 25 cm to infinity is the range of vision of normal eye.
e. Due to absence of atmosphere in the space, there is no scattering and hence space appears black/ dark.
Question. (a) If a person wears lens of power – 6D for distant vision and for correcting his near vision he needs a lens of +2D. Determine the focal length of the lenses in both the case.
(b) Give reason for the following natural phenomenon:
(i) Stars twinkle
(ii) Planets do not twinkle
(iii) Stars appear raised in the sky.
Answer :
(a) (i)
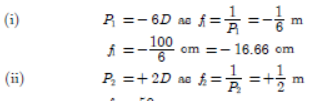
(b) (i) Due to continuous changes in the densities of the atmospheric layers the apparent position of the star also changes; which make the light coming from the distant point sized
star brighter and dimmer. The light coming from the stars therefore gives a shaking appearances, which gives the impression of twinkling of a star.
(ii) Since the planets are closer to us. Due to this they appear a combination of large point-sizes source of light, and change in the path of light coming from the planets is not significant. So planets do not appear twinkling.
(iii) Due to atmospheric refraction, a star appears to be slightly higher than its actual position in sky.
Question. (a) State the reasons which lead to hypermetropia.
With the help of suitable diagram, explain this defect of vision and its correction.
(b) Draw diagram of an experimental arrangement for observing scattering of light in colloidal solution.
Name the two chemicals used in this activity.
Answer :
a. In hypermetropia a person cannot see near by objects clearly. Its is due to shortening of the eye ball or due to increase in focal length of eye lens.
To correct hypermetropia, a convex lens of suitable focal length is needed.
Question. What is meant by scattering of light? Mention the factor on which it depends. Explain why the colour of the clear sky is blue? An Astronaut in space finds sky to be dark. Explain reason for this observation.
Answer :
(a) Scattering of light is the phenomenon due to which light gets deflected by the atoms, molecules or particles of the medium when light falls on them. These are known as scatterer particles.
(b) Factors on which scattering depends are the size of the atoms, molecules of the scatterer.
(c) When sunlight falls on the atoms or molecules of the gases shorter wavelengths J like of blue colour get scattered more due to which sky appears blue.
In space there is no atmosphere, so there is no scattering hence the sky appears dark/black.
Question. (a) Demonstrate an activity with a well labelled diagram to prove that white light is made up of seven colours.
(b) Which colour of light bends least and which one the most while passing out from the prism. Also state the reason for the same.
Answer : (a) To demonstrate that white light is made up of seven colours, take a prism. Allow white light to fall on its one focus through a pin hole. Rotate the prism until the coloured light emerge out from the prism. Collect these coloured lights on a screen or white sheet of paper. This prove that white light is made up of seven colours.
(b) Violet colour deviates most whereas red colour deviates least because they have different speeds in prism they have different refractive indices and hence have different angle of deviation.


