Please refer to the Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting Important Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Accountancy for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these Important based Class 11 Accountancy Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Mention any four components of a computer system.
Ans. The four elements/components of a computer system are
(i) Hardware Computer hardware consists of physical components such as keyboard, mouse, monitor and processor. These components can be physically touched.
These are electronic and electromechanical components. These are the basic components of a computer that collectively form a system.
(ii) Software It is the set of instructions that makes the computer work. Software is held on the computer’s hard disk, CD-ROM, DVD or on a diskette (floppy disk) and is loaded from the disk into the computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory), as and when required. It is the hypothetical or imaginary part of computer which is used with hardware to make computer perform operations.
(iii) Humanware/People People interacting with the computer and executing the program or software are known as humanware. They constitute the most important part of the computer system and they are system analyst programmers and operators.
(iv) Procedures A specified series of actions or operations, which have to be executed in the same manner, in order to always achieve the desired result in same circumstances. There are three types of procedures which constitute part of computer system and they are hardware oriented procedure, software oriented procedure and internal procedure.
Question. Give two examples each of the organisation where ready-to-use, customised and tailored accounting packages respectively are suitable to perform the accounting activity.
Ans. (i) Ready-to-use accounting packages are best suitable for small and conventional business.
(ii) Customised accounting packages are best suitable for large and medium business.
(iii) Tailored accounting packages are best suitable for large and typical business.
Question. Write a short note on secondary storage devices.
Ans. Secondary storage devices refers to storage devices that serve as an addition to the computer’s primary storage, RAM and cache memory. It consists of non-volatile memory that allow users to permanently store data even if computer is turned off or there is a ower cut. It is also known as backup storage device, external storage, etc.
Secondary storage devices are as follows
(i) Online storage media
(ii) Near line storage device
(iii) Offline storage media or distribution media
Question. Briefly explain the need of computers in accounting.
Ans. The advent of globalisation has resulted in the rise in business operations. Consequently, every medium and large size organisation requires well established information system in order to generate information required for decision-making and achieving the organisational objectives.
This made information technology to play vital role in supporting business operations.
Question. An organisation can choose from number of softwares available. What are the factors taken in consideration before sourcing an accounting software?
Ans. The following factors are usually taken in consideration before sourcing an accouning software
(i) Flexibility The software system must be flexible in respect of data handling and report preparing.
(ii) Maintenance Cost The accounting software must be such which has less maintenance cost.
(iii) Size of Organisation The accounting software must be according to need and size of the organisation.
(iv) Easy to Adaptation The accounting software must be such which is easy to apply in organisation.
Question. Write a short note on the following
(i) Operating system
(ii) Utility programme
Ans. (i) Operating System It is an integrated set of specialised programmes that is meant to manage the resources of a computer and also facilitate the operation. It creates a necessary interface that is an interactive link between the user and the computer hardware.
(ii) Utility Programme It is a set of computer programmes which are designed to perform certain supporting operations. It is also known as system utility. Most major operating systems
come with several pre-installed utilites like disk storage, disk cleaners, disk space analysers, etc.
Question. Explain briefly the functions of a computer.
Ans. Computer performs following functions which are as follows
(i) Input Information or data that is entered into a computer is called input. It sends data and instructions to the CPU.
(ii) Processing It is sequence of actions taken on data to convert it into information which is meaningful to the user.
(iii) Output It makes processed data available to the user. It is mainly used to display the desired result to the user as per input instructions.
Question. Define computerised accounting system. Also, mention any three features of this system.
Ans. An accounting information system that processes the financial transactions and events as per Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to produce reports as per user requirements is referred to as a computerised accounting system.
Features of computerised accounting system are as follows (any three)
(i) Online input and storage of accounting data.
(ii) Printout of purchases and sales invoices.
(iii) Logical scheme for codification of accounts and transactions. Every account and transaction is assigned a unique code.
(iv) Grouping of accounts is done from the very beginning.
Question. Mention the steps involved in designing accounting reports.
Ans. The various steps involved in designing accounting reports from accounting data are as follows
Step 1 Definition of Objectives The reports should clearly define the objectives, who are the users of the report and the decision to be taken on the basis of report.
Step 2 Structure of Report The information to be contained therein and the style of presentation.
Step 3 Querying with the Data Base The accounting information queries must be clearly defined and the methodology to be adopted while interacting with the database.
Step 4 Finalising the Report The report should be completely ending with proper analysis and suggestion.
Question. What is a management information system?
Ans. It is the most commonly used form of information system. Management Information System (MIS) is a system that provides the necessary information required for managing an organisation effectively and in taking various decisions.
MIS is viewed and used by management at many levels such as operational, tactical and strategic. MIS is supportive of the institution’s long-term strategic goals and objectives.
Management information system is basically concerned with processing data into information which is then communicated to various departments in an organisation for appropriate decision-making. Data → Information → Communication → Decision he purpose of management information system is to rovide the right information, to the right person, at the right place, at the right time, in the right form, at the right cost.
Question. What do you mean by codification of accounts?
Ans. Each account is given a separate code based on the group and sub-group to which it belongs. The account can be classified as belonging to incomes group, expenses group, assets group or liabilities group.
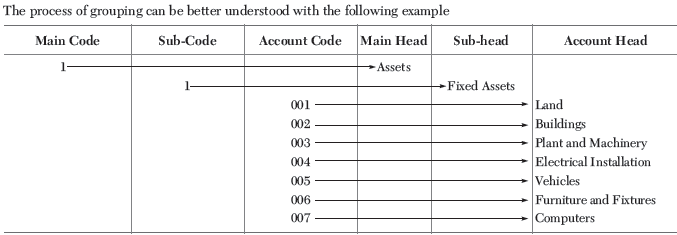
hus, code for land account will be 11001 and for building account it will be 11002 and so on.
Question. Define memory unit along with its types.
Ans. Memory Unit In this unit, data is stored before being actually processed. The processing of data is accomplished either through batch processing or real-time processing, which are explained below
(i) Batch Processing It applies to large and voluminous data that is accumulated off-line from various units i.e., branches or departments. The entries accumulated data is processed in one shot to generate the desired reports according to the requirement.
(ii) Real-time Processing It provides online outcome in the form of information and reports without time lag between the transaction and its processing.
Question. Define procedures as an element/component of computer system. Also, discuss the types of procedures.
Ans. A specified series of actions or operations which have to be executed in the same manner, in order to always achieve the desired result in same circumstances are referred to as procedures.
There are three types of procedures which constitute part of computer system
(i) Hardware-oriented Procedure It provides details about components and their method of operation.
(ii) Software-oriented Procedure It provides a set of instructions required for using the software of omputer system.
(iii) Internal Procedure It is instituted to ensure smooth flow of data to computers by sequencing the operation of each sub-system of overall computer system.
Question. Briefly explain any four components of a computer hardware.
Ans. The various components of a computer hardware are
(i) Motherboard The main electronic division of the computer with the help of which other components or peripherals, that are also a part of the operating system, communicate with each other is motherboard.
(ii) Processor It is the processing unit that controls all the components attached to the computer system. It is also known as CPU (Central Processing Unit).
(iii) Primary Storage Memory Alternatively referred to as volatile memory, internal memory and main memory. It is a storage location that holds emory for short period of time while the computer is running, e.g. RAM.
(iv) Keyboard It is an input device which is used to input text into the computer in the CUI. On the keyboard, keys are placed in a special sequence.
Question. The use of computers in any database oriented application has four basic requirements. Briefly discuss them.
Ans. The use of computers in any database oriented application has four basic requirements as mentioned below
(i) Front-end Interface It is an interactive link between the user and database oriented software through which the user communicates to the back-end database.
(ii) Back-end Database It is the data storage system that is hidden from the user and responds to the requirement of the user to the extent the user is authorised to access.
(iii) Data Processing It is a sequence of actions that are taken to transform the data into useful information for decision-making.
(iv) Reporting System It is an integrated set of objects that constitute the report.
Question. Write a short note on accounting information system.
Ans. AIS is a subsystem of management information system. It enables users to collect, store, manage, process, retrive and report financial data to its internal and external users.
AIS can be used by following
(i) Business analyst
(ii) CEO/CFO
(iii) Accountants
(iv) Regulators
(v) Auditors
(vi) Managers
This system allow its users to track all accounting and business activities of an entity. It helps to manage the organisation efficiently and effectively by combining modern technology resources together with traditional accounting controls and methods.
Question. Briefly explain any four limitations of a computer system.
Ans. Following are the limitations of computer system
(i) Lack of Decision-making Decision-making involves a lot of understanding, information intelligence and ability to decide making it a complex process which can’t be performed by computer.
(ii) Lack of Emotions Computer do not have any feelings as they are devoid of human heart or soul, since it is a machine.
(iii) Lack of Common Sense Computers fail to understand the logical aspect of problem and just keep on working as per it’s programming.
(iv) Lack of Intelligence Quotient Computers cannot think themselves and need to be directed before each and every step.
They operate on the basis of instructions given by human beings.
Question. Mention any four disadvantages of computerised accounting system.
Ans. (i) Cost of Training In a computerised accounting system, the use of complicated accounting softwares generally require specialised staff. It also involves huge training cost to understand use of hardware and software on a continuous basis.
(ii) Staff Opposition Whenever the accounting system is computerised, a high degree of objection is observed from the existing accounting staff.
(iii) Ill Effects on Health Various health problems like bad backs, eye strain, muscular pains, etc are developed due to the extensive use of computer systems.
(iv) Inability to Check Unanticipated Errors Computers are not capable to detect unanticipated errors as they lack the capability to judge.
Question. Write a short note on CPU.
Ans. Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the main part of a computer system. It is also called the brain of the computer. It processes the given data according to the instructions and arranges the information in a manner which provides easier retrieval of the data when required by the user.
It has two main units as described below
(i) Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) It is responsible for performing all the arithmetic calculations such as addition, subtraction, division, multiplication and exponentiation. In addition to this, it also performs logical operations involving comparisons among variables and data items.
(ii) Control Unit This unit is responsible for controlling and coordinating the activities of all other units of the computer system.
Question. With the help of a diagram, show the relationship of the accounting system with the other functional management information system.
Ans. Every accounting system is essentially a part of the Accounting Information System (AIS) which in turn is a part of the broader system viz. the organisation’s management information system.
Inspite of the accounting information system, other functional management information systems are manufacturing information system, human resource information system and marketing information system.

The diagram shown above entails the four widely recognised functional areas of management.
An organisation operates in a given environment surrounded by the suppliers and customers.
The informational needs emerge from the business processes stratified into functional areas where accounting is one of them. The Accounting Information System (AIS) receives and provides information to the various sub-systems of the institutional/integrated MIS.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. ‘‘An organisation is a collection of interdependent decision-making units that exists to pursue organisational objectives’’. In the light of this statement, explain the relationship between information and decisions. Also, explain the role of transaction processing system in facilitating the decision-making process in business organisations.
Ans. An organisation consists of various interdependent decision-making units at every level of management and department. All these separate departments take decisions for their respective fields to achieve the desired common organisational objectives.
The organisation as a whole needs to set its targets, draft plans and formulate various policies. These activities are based on the information (in the form of data) regarding the past experiences and expected future conditions. It is on the basis of this information that an organisation allocates its resources and attempts to accomplish its determined targets. Thus, it
can be said that on one hand, information facilitates the decision-making process while on the other hand, past decisions act as a pool of information in the future.
In this aspect, information forms the most crucial part of today’s business environment. In this context, Transaction Processing System (TPS) has emerged as crucial component of the business operations.
Transaction Processing System (TPS) refers to a computerised system that records, processes, validates and stores routine transactions that occur in various functional areas of a business on daily basis. This system facilitates the decision-making in a business organisation through the following processes
(i) Data Collection It refers to the collection of data.
(ii) Data Editing It refers to checking data for correctness.
(iii) Data Validation It refers to verifying data for any errors and rectifying those errors.
(iv) Data Manipulation It refers to processing and analysing data on a pre-set design.
(v) Data Storage It refers to the processing of stored data in the database.
(vi) Report Generation It refers to generating reports in hard copy or soft copy in a pre-designed format.
(vii) Query Support It refers to the process whereby the user of TPS can raise a query and extract the data to get report.
Question. Describe the various types of accounting software along with their advantages and limitations.
Ans. Types of accounting software are
(i) Readymade Softwares These are the softwares that are developed not for any specific user but for the users in general e.g., Tally, Ex, Busy. Advantages of readymade software are
(a) The cost of installation of these softwares is generally low and number of users is limited.
(b) Ready-to-use software is relatively easier to learn and people (accountant) adaptability is very high.
(c) The training needs are simple and sometimes the vendor (supplier of software) offers the training on the software free.
(d) As these softwares are available off-the-shelf, time required in developing a ‘tailor made software’ is saved.
Limitations of readymade software are
(a) The level of secrecy is relatively low and the software is prone to data frauds.
(b) These softwares offer little scope of linking to other information systems.
(c) These softwares use laser printers which are costly than dot matrix printers.
(ii) Customised Softwares Customised softwares means modifying the readymade softwares to suit the specific requirements of the user.
Advantages of customised softwares are
(a) Secrecy of data and software is high in customised software.
(b) Linkage to other information system is available on the basis of need of the enterprise.
Limitations of customised softwares are
(a) The cost of installation and maintenance is relatively high because the high cost is to be paid to the vendor for customisation.
(b) Since the need to train the software users is important, the training costs are therefore high.
(iii) Tailored Softwares The softwares that are developed to meet the requirement of the user on the basis of discussion between the user and developers.
Advantages of tailored softwares are
(a) The secrecy and authenticity checks are robust in such softwares.
(b) Such softwares offer high flexibility in terms of number of users.
(c) As these softwares are developed according to specification of the user, it takes care of the specific needs of the enterprise.
(d) These softwares can be effectively linked to some other information system.
Limitations of tailored softwares are
(a) These softwares require specialised training to the users.
(b) The cost of maintenance and development of such softwares is much higher as compared to readymade and customised software.
(c) The results will be misleading, in case the accounts are grouped in an incorrect manner.
Question. Define a computerised accounting system. Distinguish between a manual and computerised accounting system.
Ans. A computerised accounting system is that accounting information system that processes the financial transactions and events as per Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to produce reports as per requirements of the user.
The differences between a manual and computerised accounting system are

Question. ‘‘A computer system possesses some characteristics, which in comparison to human beings, turn out to be its capabilities.’’ In the light of this statement, discuss the characteristics / capabilities of a computer system.
Ans. The above said statement is correct. The characteristics/capabilities of a computer system are as follows (any four)
(i) Speed The amount of time, a computer takes to accomplish a task or an operation refers to its speed.
In comparison to human beings, computers require far less time to perform a task. Generally, human beings take into account a second or minute as unit of time. But computers have such a fast operating capability that the relevant unit of time is fraction of a second.
Modern computers are capable of performing a 100 million calculations per second and that is why the industry has developed Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS) as the criterion to classify different computers according to speed.
(ii) Accuracy The degree of exactness with which computations are made and operations are performed is referred to as its accuracy. Most of the errors in Computer Based Information System (CBIS) occurs because of bad programming, erroneous data and deviation from procedures, which are caused by human beings. Errors attributable to hardware are normally detected and corrected by the computer system itself.
(iii) Reliability It refers to the ability with which the computers remain functional to serve the user. Computer systems are more reliable than human beings as they are well-adapted to perform repetitive operations and are immune to tiredness, boredom or fatigue. However, there can be failures of computer system due to various internal and external reasons.
(iv) Versatility The ability of computers to perform a variety of tasks is referred to as versatility. Task can be simple as well as complex. Computers are usually versatile unless designed for a specific application. A general purpose computer is capable of being used in any area of applications such as business, industry, scientific, statistical, technological, communications and so on and when installed in an organisation, can take over the jobs of several specialists because of its versatility.
(v) Storage and Retrieval It refers to the amount of data, which a computer system can store and access.
The computer systems, besides having instant access to data, have huge capacity to store such data in a very small physical space, e.g. CD-ROM. A typical mainframe computer system is capable of storing and providing one billion of characters and thousands of graphic images.
Question. What are the components of an accounting information system?
Ans. Accounting information system generally has following main components
(i) People The people in an AIS are simply the system users.
(ii) Procedure It is the methods and instructions of collecting, storing, retrieving, processing data and communicating information to its users.
(iii) Data All relevant financial and business information required by the users is data. Data included in an AIS depend on the nature of business. Generally, it includes information
relating to purchases and sales, debtors and creditors, revenues and expenses, assets and liabilities. These are used to prepare accounting information that are relevant for its users.
(iv) Information Technology Infrastructure It includes the hardware and software programmes used to operate AIS. Quality, reliability, flexibility and security are the key components of an effective AIS software.
(v) Internal Control It refers to the security measures that protect data against unauthorised computer access and to limit access of data only to an authorised user. AIS must have internal controls system.
