Please refer to Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Important Questions given below. These solved questions for Chemical Reactions and Equations have been prepared based on the latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. We have provided important examination questions for Class 10 Science all chapters.
Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. State one industrial application of reduction process.
Ans. It is used in the extraction of metals e.g.,
ZnO(s) + C(s) Heat Zn(s) + CO2(g)
Question. Balance the following chemical reaction :
MnO2 + HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O
Ans. MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Question. Balance the following chemical equation :
Pb(NO3)2(s) heat → PbO(s) + NO2(g) + O2(g)
Ans. 2Pb(NO3)2(s) heat → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Question. Give an example of decomposition reaction.
Describe an activity to illustrate such a reaction by heating.
Ans. Those reactions in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances are known as decomposition reactions.
Aim : To show thermal decomposition reaction of ferrous sulphate.
Material required : Ferrous sulphate crystals, dry test tube, burner

Procedure : 1. Take 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry test tube.
2. Observe the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals.
3. Heat the crystals of ferrous sulphate over the flame of a burner for some time.
4. Observe the crystals after heating for 5 minutes.

Observation : The pale green colour of ferrous sulphate crystals changes to reddish brown ferric oxide and smell of burning sulphur is observed.
Question. What change in colour is observed when white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight? What type of chemical reaction is this?
Ans. When white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight, its colour changes to grey due to the formation of silver.
2AgCl(s)sunlight → 2Ag(s)+Cl2(g)
White Grey
This type of reaction is called photodecomposition reaction.
Question. What happens chemically when quick lime is added to water?
Ans. Quick lime reacts vigorously with water to produce calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) releasing a large amount of heat (exothermic reaction).
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + heat
(Quick lime) (Slaked lime)
Question. What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride? State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction between them will not take place. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the type of reaction.
Ans. When an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride then, white precipitate of barium sulphate (BaSO4) is formed.
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
If the reactants are present in solid state then no reaction will take place between them. This type of reaction is called double displacement reaction or precipitation reaction.
Question. (i) What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate taken in a test tube?
(ii) What type of reaction is this?
(iii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction.
Ans. (i) When lead nitrate is added to potassium iodide then yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed along with potassium nitrate.
(ii) This type of reaction is called precipitation reaction in which one of the products formed is an insoluble substance.
(iii) Chemical reaction will be as follows :
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI2(s) ↓ + 2KNO3(aq)
(Yellow ppt.)
Question. In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double than that of gas collected over the other electrode?
Ans. In electrolysis of water, hydrogen (H2) gas is liberated at cathode while oxygen (O2) gas is liberated at anode. The overall reaction is
2H2O(l) Electric current → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
From the above reaction, it is clear that amount of H2 liberated is twice that of O2.
Question. Balance the following chemical equation :
Fe(s) + H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + H2(g)
Ans. 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Question. Balance the following chemical equation :
FeSO4 heat → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
Ans. 2FeSO4 heat → Fe O + SO + SO3
Question. What is an oxidation reaction? Identify in the following reaction : ZnO + C → Zn + CO
(i) the substance oxidised and
(ii) the substance reduced.
Ans. The reaction in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed or loss of electrons takes place is called an oxidation reaction.
In the reaction,

(i) Carbon is getting oxidised to carbon monoxide.
(ii) Zinc oxide is getting reduced to zinc.
Question. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid indicating the physical state of the reactants and the products.
Ans. Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Sodium Hydrochloric Sodium
carbonate acid chloride + CO2 (g)
Question. What is a redox reaction? When a magnesium ribbon burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash, is magnesium oxidised or reduced? Why?
Ans. A reaction in which oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously is called redox reaction.
On heating in oxygen/air, magnesium burns with a dazzling white light to give magnesium oxide.
2Mg + O2 heat → 2MgO
Here, magnesium is oxidised as addition of oxygen has taken place.
Question. (a) What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating?
(b) Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change?
Ans. (a) Ferrous sulphate crystals (FeSO4.7H2O) are light green in colour.
When it is heated, white colour solid is formed.
FeSO4 .7H2O heat → FeSO4 + 7H2O
(b) When anhydrous ferrous sulphate is further heated strongly, it decomposes to give ferrous oxide (Fe2O3) and oxides of sulphur.

This type of chemical reaction is known as decomposition react
Question. On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to copper oxide powder, the solution formed is blue green. Predict the new compound formed which imparts a blue green colour to the solution.
Ans. CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + 2H2O
Copper chloride solution imparts blue green colour to the solution.
Question. Hydrogen being a highly inflammable gas and oxygen being a supporter of combustion, yet water, a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is used to extinguish fire. Why?
Ans. H2O is a compound constituted of hydrogen of oxygen elements and being a compound it has different properties as compared to its constituting elements.
Question. Why is respiration considered as exothermic process?
Ans. Respiration is an exothermic process because energy is given out in respiration.
Question. On what basis is a chemical reaction balanced?
Ans. Chemical equation is balanced on the basis of law of conservation of mass.
Question. What change in colour is observed when white silver chloride is left exposed to sun¬light? State the type of chemical reaction in this change.
Ans. Grey coloured silver metal is formed and pungent smelling chlorine gas is evolved.
2AgCl(s) sunlight 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g)
Question. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Ans. We apply paint on iron articles to prevent them from corrosion and rusting. Paint prevents the contact between iron and moist air.
Question. What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Ans. Exothermic reactions are those reactions in which heat energy is released during the reaction. Examples:
(i) N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3 + Heat energy
(ii) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat energy
Endothermic reactions are those reactions in which heat energy is absorbed (needed) during the reaction. Examples:
(i) CaCO3 Heat⎯⎯→ CO2 + CaO (ii) 2AgCl → sunlight⎯⎯→ 2Ag + Cl2
Question. Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Ans. During respiration, glucose is decomposed into carbon dioxide gas and water vapours using oxygen gas from air in the living cells of our body and heat energy is released during this process. So respiration is a type of exothermic reaction.
Example, C6H12O6 + 6O2 Respiration → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Heat energy
Glucose
Question. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Ans. Balanced chemical equation. When the number of atoms of different elements on both sides of a chemical equation are equal, then it is called a balanced chemical equation.
A chemical equation needs to be balanced so that it follows “Law of Conservation of Mass” which states that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Question. A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Ans. The shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ is Copper (Cu).
When copper is heated in air, it becomes black due to the formation of copper oxide.
2Cu + O2 Heat→ 2CuO
(Reddish Brown) (Black)
Copper Copper (II) oxide
Question. Oil and fat containing packed food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Ans. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen to prevent them from spoiling. When such food items come in contact with air, they get oxidised. They become rancid and their smell and taste changes.
Question. Give one example of chemical reaction in which change in colour takes place.
Ans. Fe(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ⎯⎯→ FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Copper Sulphate Ferrous Sulphate Copper
(Blue colour) (Light-green colour) (Brown colour)
Question. Identify the type of reaction in the following example:
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) ⎯⎯→ 2H2O (l)
Ans. It is a combination reaction because in this reaction two substances combine to form a single substance.
Question. Write the balanced chemical equation with the state symbols of the following reaction: Solutions of Barium chloride and Sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble Barium sulphate and the solution of Sodium chloride.
Ans. BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) ⎯⎯→ BaSO4 (s) + 2 NaCl (aq)
Question. What happens chemically when quick lime is added to water?
Ans. Quick lime reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime with the release of large amount of heat.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) ⎯⎯→ Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat energy
Calcium oxide Calcium hydroxide
(Quick lime) (Slaked lime)
Question. What precautions would you take while handling quicklime?
Ans. (i) Quicklime can cause severe burns, therefore it should be handled with a spatula.
(ii) As reaction between quicklime and water is exothermic, water should be poured over quicklime slowly.
Question. In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Ans. When copper is mixed in silver nitrate AgNO3 solution, copper displaces the silver because copper is more reactive than silver.
2AgNO3 (aq) + Cu (s) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Short Answer Questions
Question. Why does a moist blue litmus paper turn red when it is brought near the mouth of the test tube in which ferrous sulphate crystals are being heated?
Ans. On heating ferrous sulphate crystals (FeSO4 . 7H2O) it decomposes to ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide. Ferric oxide is solid while sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide are gases. Both sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide are acidic and hence these gases turn the moist blue litmus red.
Question. Why is silver bromide stored in dark bottles in the laboratories? Write the chemical equation to justify your answer.
Ans. When silver bromide is exposed to light, it decomposes to form silver metal and bromine vapours.
2AgBr (s) light⎯⎯⎯→Decomposition 2Ag (s) + Br2 (g)
Pale yellow Greyish white Red brown
When light falls on pale yellow coloured silver bromide, it changes to greyish white due to the formation of silver metal. To prevent the decomposition of silver bromide, it is stored in dark bottles in the laboratories.
Question. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans. In a displacement reaction, less reactive element is displaced from its salt by a more reactive element.
For example: Copper (Cu) is displaced from CuSO4 by iron because iron (Fe) is more reactive.
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Copper sulphate Iron sulphate
In double displacement reaction exchange of ions takes place between two reactants to form two new products.
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
Sodium sulphate Barium chloride Barium sulphate Sodium chloride
Question. An iron nail is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate for about 30 minutes, state the change in colour observed. Give the reason for the change.
Ans. Iron is more reactive than Cu. So it displaces Cu from copper sulphate solution. Thus, blue colour of the CuSO4 solution fades and colour of the solution turns green due to the formation of ferrous sulphate Solution. This is a displacement reaction.
CuSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) ⎯⎯→ FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(Blue) (Green)
Question. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction and identify the type of reaction and define it.
‘Iron III oxide reacts with Aluminium and gives molten iron and aluminium oxide’.
Ans. Fe2O3 (s) + 2Al (s) ⎯⎯⎯→ 2Fe (l) + Al2 O3 (l) + Heat
• It is a displacement reaction which is highly exothermic. The amount of heat evolved is so large that the metal is produced in the molten state.
• The displacement reaction of iron (III) oxide with aluminium is known as thermite reaction.
Question. Identify the type of reaction from the following equations:
(i) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O (ii) Pb (NO3)2 + 2KI → PbI2 + 2KNO3
(iii) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 (iv) CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
Ans. (i) CH4 + 2O2 ⎯⎯⎯→ CO2 + H2O
Redox reaction
(ii) Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI ⎯⎯⎯→ PbI2 + 2KNO3
Double displacement reaction
(iii) CaO + H2O ⎯⎯⎯→ Ca(OH)2
Combination reaction
(iv) CuSO4 + Zn ⎯⎯⎯→ ZnSO4 + Cu
Displacement reaction
Question. A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed. Write the chemical reaction involved and also mention the type of reaction.
Ans.
AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq)
(White ppt.)
It is a double displacement reaction.
b. Change in temperature:
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Question. (a) A solution of substance X is used for white washing. What is substance X? Write the chemical reaction of X with water.
(b) Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution changes when iron nail is dipped in it?
Ans.
a. X is CaO, calcium oxide
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
b. It is because Fe displaces Cu from CuSO4 (blue)
solution to form FeSO4 (pale green) and reddish brown Cu metal gets deposited.
Question. Distinguish between a displacement reaction and a double displacement reaction. Identify the displacement and the double displacement reaction from the following reactions:
a. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
b. Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Ans.
Displacement Reaction: When a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Double displacement reaction: When two compounds exchange their ions to form two new compounds.
a. Double displacement reaction.
b. Displacement reaction.
Question. Balance the following reactions:
a. BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
b. Ca(OH)2 + HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
c. Pb(NO3)2 → PbO + NO2 + O2
d. MnO2 + HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O
Ans.
a. BaCl2(aq) + H2SO4(dil) → BaSO4(s) + 2HCl (aq)
b. Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
c. 2Pb(NO ) (s) → Heat 2PbO(s) + 4NO (g) + O2 (g) Heat
d. MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Question. Write the balanced equation for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case:
a. Potassium bromide + Barium iodide → Barium bromide + Potassium Iodide
b. Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) → Hydrogen chloride(g)
Ans.
a. 2KBr(aq) + BaI2 → BaBr2(aq) + 2KI(aq)
It is double displacement reaction.
b. H2(g) +. Cl2(g) →sunlight 2HCl(g)
It is combination reaction.
Question. A zinc plate was put into solution of copper sulphate kept in a glass container. It was found that blue colour of the solution gets fader and fader with passage of time. After few days when zinc plate was taken out of the solution, a number of holes were observed on it.
a. State the reason for the changes observed on zinc plate.
b. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Ans.
a. Zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution to form colourless ZnSO4 and copper metal is deposited. Zinc gets consumed due to which holes are formed.
b. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Question. Define combination reaction. Give one example of a combination reaction which is also exothermic.
Ans.
Combination reaction: The reaction in which two or more elements or compounds combine to form compound(s) e.g.,
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat
It is an exothermic, combination reaction.
Question. What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride? State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction between them will not take place.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the type of reaction.
Ans. White precipitate of BaSO4 is formed.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl (aq)
It is a double displacement reaction. If reactants are taken in solid state, products will not be formed.
Question. Two reactions are given below:
a. 2KI + Cl2 → 2KCl + I2
b. 2K + Cl2 → 2KCl
Identify the type of reaction, giving justification in each case.
Ans. a. Displacement reaction because Cl2 is displacing I2 from KI solution.
b. Combination reaction because K reacts with Cl2 to form potassium chloride.
Question. What is redox reaction? When a magnesium ribbon burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash, is magnesium oxidised or reduced. Why?
Ans. Redox reaction is a reaction in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously.
Mg is getting oxidised because it is gaining oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
Question. A student took a small piece of solid quick lime in a china dish and poured over it a small amount of water. List two changes he is likely to observe in the china dish immediately after pouring water.
Ans. When a small amount of water is poured on a piece of quick lime—
• it reacts vigorously with water and a hissing sound is produced and slaked lime is formed.
• the reaction mixture becomes hot as it is an exothermic reaction.
Question. While studying the double displacement reaction, the solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate are mixed together.
(i) What do you observe as soon as the two solutions are mixed together?
(ii) What will happen in the above observation made by you after ten minutes?
Ans. (i) The reaction mixture becomes white in colour and a precipitate is formed.
(ii) White precipitate settles down after 10 minutes.
Question. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Ans. Any reaction that produces a solid insoluble product is known as precipitation reaction.
For example: Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) solution when mixed solution of barium chloride (BaCl2). Then insoluble white precipitate of barium sulphate (BaSO4) is formed.
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s)↓ + 2NaCl (aq)
Sodium Barium Barium sulphate Sodium
sulphate chloride (precipitate) chloride
Question. Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each:
(a) Oxidation (b) Reduction.
Ans. (a) Oxidation. The reactions in which the gain of oxygen takes place are called oxidation. Examples:
(i) 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO (ii) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
(b) Reduction. The reactions in which the loss of oxygen takes place are called reduction. Examples:
(i) ZnO + C → + CO (ii) CuO + H2 Heat⎯⎯→ Cu + H2O
Question. When hydrogen gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide, copper and steam are formed. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction and state (i) the substance oxidized and (ii) the substance reduced in the reaction. short (8)
(i) Substance oxidized = H2 (Hydrogen gas)
(ii) Substance reduced = CuO (Copper oxide)
Question. 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a boiling tube.
(i) State the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals both before heating and after heating.
(ii) Name the gases produced during heating.
(iii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Ans. (i) The colour of the ferrous sulphate crystals is green before heating and changes to brown after heating.
The colour of the crystals changes due to the formation of ferric oxide.
(ii) During heating sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3) are produced.
(iii) 2FeSO4 (s) light⎯⎯⎯→ Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
Ferric oxide
Question. Describe an activity to show a decomposition reaction in which light is used to decompose a reactant.
Write chemical equation of the reaction and state its one use.
Ans. Take about 2 g silver chloride in a china dish. It is first white in colour. Now place this china dish in sunlight for some time. After some time it is observed that white silver chloride turns grey. This is due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by light.
2AgCl sunlight⎯⎯⎯→ 2Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
Silver bromide also decomposes to silver and bromine by light.
2AgBr sunlight⎯⎯⎯→ 2Ag (s) + Br2 (g)
Use: This reaction is used in black and white photography.
Question. Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate
(c) Carbon dioxide is passed through lime water.
Ans. (a) 2Al (s) + 3H2SO4 (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ Al2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3H2 ↑
Aluminium sulphate
(b) Na2CO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ 2NaCl (aq) + CO2 + H2O
Sodium carbonate
(c) CO2 (g) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ CaCO3 (s) + H2O
Lime water (White ppt makes lime water milky)
Question. What type of material is formed when aqueous solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed. Give the balanced chemical equation involved. Name the type of reaction it is?
Ans. • A white precipitate of BaSO4 will be formed.
• Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
• It is a double displacement reaction.
Question. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them:
(i) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen gas to form ammonia.
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(iii) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and precipitate of barium sulphate.
(iv) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Ans. (i) 3H2 (g) + N2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
(ii) 2H2 S (g) + 3O2 (g) → 2H2O(l) + 2SO2 (g) (air)
(iii) 3BaCl2 (aq) + Al2 (SO4)3 (aq) → 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3BaSO4 (s)
(iv) 2K (s) + 2H2 O (l) → 2KOH (s) + H2 (g)
Question. Balance the following chemical equations:
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Ans. (a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question. (a) What is meant by balanced chemical equation? Why chemical equations are balanced?
(b) Balance the chemical equation given below:
Al2O3 + NaOH → NaAlO2 + H2O
Ans. (a) A balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products. It means a balanced chemical equation has equal masses of various elements in reactants and products.
According to law of conservation of mass, “Matter can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction”. Therefore the chemical equations are balanced to satisfy the law of conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
(b) Al2O3 + 2NaOH ⎯⎯⎯→ 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Question. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions :
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Ans. (a) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c) 2Al + 3CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
(d) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
Question. What will be the nature of solution formed when calcium oxide is dissolved in water? Name the substance formed when carbon dioxide gas is passed through this solution.
Ans. On dissolving calcium oxide in water, calcium hydroxide is formed. When a drop of this liquid is put on a red litmus paper, it turns blue. This shows calcium hydroxide is basic in nature. When carbon dioxide gas is passed through calcium hydroxide (lime water), it turns milky due to formation of calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ⎯⎯⎯→ CaCO3(s)↓ + H2O(l)
Lime water White ppt.
(Milkiness)
Question. Write an equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Ans. (i) Energy supplied in the form of heat. This reaction is also known as endothermic reaction.
CaCO3 (s) Heat⎯⎯→ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Lime stone Quick lime
(ii) Energy supplied in the form of light. This reaction is also known as photochemical reaction.
2AgBr (s) sunlight → 2Ag (s) + Br2 (g)
Silver bromide
(iii) Energy supplied in the form of electricity. This reaction is also known as electrolytic reaction.
2H2O Electricity → 2H2 + O2
Water Hydrogen Oxygen
Question. Solid calcium oxide was taken in a container and water was added slowly to it.
(i) State two observations made in the experiment.
(ii) Write the balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
Ans. (i) Solid calcium oxide was taken in a container and water was added to it.
Observations:
• The mixture produces a hissing sound.
• The beaker feels to be quite hot.
(ii) CaO (s) + H2O ⎯⎯⎯→ Ca(OH)2 + Heat
Calcium oxide Calcium hydroxide
(lime) (slaked flame)
Question. Select (i) combination reaction (ii) decomposition reaction and (iii) displacement reaction from the following chemical equations:
(i) ZnCO3 (s) → ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
(ii) Pb (s) + CuCl2 (aq) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu (s)
(iii) NaBr (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgBr (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
(iv) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl (g)
(v) Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
(vi) 3H2 (g) + N2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
(vii) CaCO3 (s) Heat⎯⎯⎯→ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Ans. (i) Decomposition reaction (ii) Displacement reaction
(iii) Double displacement reaction (iv) Combination reaction
(v) Displacement reaction (vi) Combination reaction
(vii) Decomposition reaction
Question. State the kind of chemical reactions in the following examples:
(i) Digestion of food in stomach
(ii) Combustion of coal in air
(iii) Heating of limestone
Ans. (i) Digestion of food in stomach. During digestion, the complex food is broken into simpler form.
Therefore it is a type of decomposition reaction.
(ii) Combustion of coal is air. During combustion the coal burns in air to form CO2, H2O along with the evolution of heat. Thus, it is a type of exothermic decomposition reaction.
(iii) Heating of limestone. When limestone is heated strongly, it breaks into CO2 and lime. Thus it is a type of thermal decomposition reaction.
Question. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
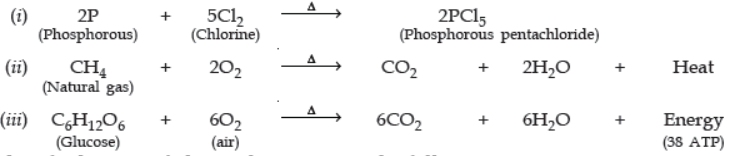
(i) Phosphorus burns in chlorine to form phosphorus pentachloride.
(ii) Burning of natural gas.
(iii) The process of respiration.
Ans.
Question. A student adds a spoon full of powdered sodium hydrogen carbonate to a flask containing ethanoic acid. List two main observations, he must note in his note book, about the reaction that takes place. Also write chemical equation for the reaction.
Ans. When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to a flask containing ethanoic acid, then — brisk effervescence will be formed because of CO2 gas escaping from the reaction mixture.
— evolution of colourless and odourless gas. Some amount of heat is evolved during the reaction.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 ⎯⎯⎯→ CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Long Answer Questions
Question. (a) What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride? State the physical conditions of reactants in which reaction between them will not take place. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and also mention the type of reaction.
(b) What changes in the colour of iron nails and copper sulphate solution do you observe after keeping the iron nails in copper sulphate solution for about half an hour?
Ans. (a) When barium chloride solution is added to sodium sulphate solution, then a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride solution:
BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
(Barium chloride) (Sodium sulphate) (Barium sulphate) (Sodium chloride)
(white ppt.)
It is an example of a double displacement reaction. In this displacement reaction, two compounds— barium chloride and sodium sulphate react to form two new compounds—barium sulphate and sodium chloride. An exchange of ions takes place in this reaction.
For example, the barium ions (Ba2+) of barium chloride react with sulphate ions (SO4 2-) of sodium sulphate to form barium sulphate (Ba2+ SO4 2– or BaSO4). In this reaction, barium sulphate is formed as a white, insoluble solid which separates out suddenly from solution.
Reaction will not take place if the reactants are in a solid state.
(b) When iron nails are dipped in copper sulphate solution, then iron sulphate solution and copper metal are formed:
CuSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) ⎯⎯⎯→ FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(Copper sulphate) Iron (Iron sulphate) (Copper)
(Blue solution) (Grey) (Greenish solution) (Red-brown)
In this reaction, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The deep blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of light green solution of iron sulphate. This displacement reaction occurs because iron is more reactive than copper. Also a brown substance will be deposited on the iron nail. This substance is nothing but copper metal.
Question. You are provided with a container made up of aluminium. You are also provided with solutions of dil HCl, dil HNO3, ZnCl2 and H2O. Out of these solutions which solution, can be kept in the aluminium container? Name the type of reaction taking place.
Ans. (i) Dilute HCl cannot be kept in aluminium container because aluminium metal reacts rapidly with dil HCl to form aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas.
2Al (s) + 6HCl (dil) ⎯⎯⎯→ 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
(Displacement reaction)
(ii) Dil HNO3 cannot be kept in aluminium container because aluminium metal reacts with dil HNO3 to form aluminium nitrate and the hydrogen liberated in this reaction is oxidised to water and nitric acid itself is reduced to any of the oxides of nitrogen. (Displacement reaction)
(iii) ZnCl2 solution also cannot be kept in aluminium container because Al is more reactive than Zn, therefore more reactive Al displaces less reactive Zn from its solution (ZnCl2).
2Al (s) + 3ZnCl2 (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ 2AlCl3 + 3Zn
(Displacement reaction)
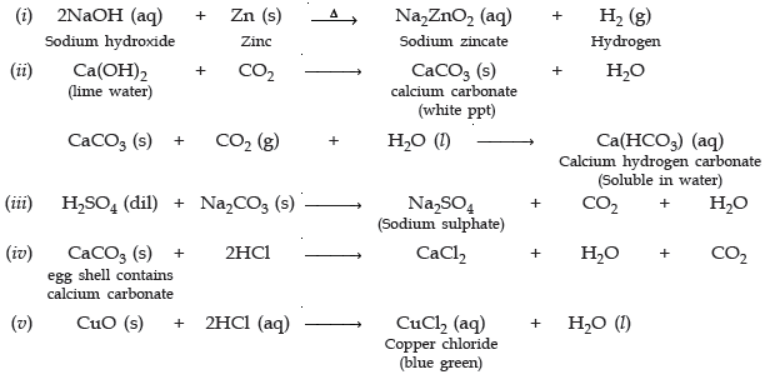
Question. Write balanced chemical equations for the following statements:
(i) NaOH solution is heated with zinc granules.
(ii) Excess of carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water.
(iii) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with sodium carbonate.
(iv) Egg shells are dropped in hydrochloric acid.
(v) Copper (II) oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans.
Question. Explain the following terms with one example each:
(a) Corrosion (b) Rancidity.
Ans. (a) Corrosion. When a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acid, oxygen, etc. and forms an irreversible metallic compound, it is said to corrode and this process is called corrosion.
Example: Rusting of iron is a common example of corrosion.
Conditions of corrosion—
(i) presence of moisture (water); and
(ii) presence of air or acids.
(b) Rancidity. When fats and oils are oxidised in air they become rancid and their smell and taste changes. This phenomenon is called rancidity.
Prevention from rancidity. Antioxidants are added to food containing fats and oils to prevent them from oxidation.
Example: An inert gas such as nitrogen is added to prevent the packed chips from getting oxidised.
Question. What is the difference between burning of magnesium ribbon in air and heating of ferrous sulphate crystals? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans.

Question. Identify the type of chemical reactions in the following processes:
(i) Barium chloride solution is mixed with copper sulphate and a white precipitate is formed.
(ii) On heating copper powder in a china dish, the surface of copper powder becomes black.
(iii) On heating green ferrous sulphate crystals, reddish brown solid is left as residue and a gas having smell of burning sulphur is evolved.
(iv) Iron nails when left dipped in blue copper sulphate solution become brownish in colour and blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades away.
(v) Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing large amount of heat.
(vi) Silver nitrate solution reacts with sodium chloride solution and a white precipitate is formed.
Ans. (i) BaCl2 (aq) + CuSO4 (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ BaSO4 (s)↓ + CuCl2 (aq)
(white ppt)
• Double displacement reaction.
• Characterised by the formation of precipitate.
(ii) 2Cu + O2 Heat⎯⎯⎯→ 2CuO
(Black)
In this reaction, Cu is changing into CuO. This is the addition of oxygen. So this is an oxidation reaction.
(iii) When green coloured ferrous sulphate is heated strongly, it decomposes to form brown coloured ferric oxide. A smell of burning sulphur is also obtained due to the formation of sulphur dioxide. In this reaction, one substance is splitting up into three substances so this is a decomposition reaction.

Iron displaces Cu from copper sulphate solution as iron is more reactive than copper. Therefore this is a displacement reaction.
(v) CaO (s) + H2O (l) ⎯⎯⎯→ Ca(OH)2
This is a combination reaction as two compounds quick lime and water combine to form a single compound slaked lime.
(vi) When silver nitrate solution is added to NaCl solution, then a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed.
AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ AgCl (s) + NaNo3 (aq)
(white ppt)
This is a double displacement reaction as two compounds react to form two new compounds.
Question. What happens when:
(a) solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed?
(b) an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution for 20 minutes?
Ans. (a) When solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed. It is a double displacement reaction.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 ⎯⎯⎯→ BaSO4 + 2NaCl
Sodium sulphate Barium chloride Barium sulphate Sodium chloride
(b) When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, following reaction takes place
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Iron Copper sulphate Ferrous sulphate Copper
In the above reaction, iron ions (Fe2+) being more reactive displaces copper ions (Cu2+) and a new compound ferrous sulphate is formed.
Question. (i) While studying the combination reaction on adding water to quick lime, name the product formed and write its colour.
(ii) While studying the decomposition reaction by heating ferrous sulphate crystals in a test-tube, a product is formed in the test-tube. Name the product and write its colour.
Ans. (i) Quicklime (CaO) reacts vigorously with water to form slaked lime [Ca(OH)2] which is white in colour.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) Combination ⎯⎯→ Ca(OH)2 (s)
Calcium oxide Calcium hydroxide
(Quick lime) (Slaked lime) (white)
(ii) When ferrous sulphate is heated strongly, it decomposes to form brown coloured ferric oxide and sulphur dioxide gas and sulphur trioxide gas.
2FeSO4 (s) Δ ⎯⎯→ Decomposion Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
Ferrous sulphate Ferric oxide
(green colour) (brown)
Question. A student performed the experiment of heating ferrous sulphate crystals in a boiling tube. He smelt fumes of a pungent gas and saw colours of ferrous sulphate disappear.
(i) Write the chemical formula of the pungent gas.
(ii) Why does the colour of crystal disappear?
(iii) Identify the nature of this chemical reaction.
Ans. (i) SO2 → Sulphur dioxide
SO3 → Sulphur trioxide
(ii) Ferrous sulphate crystals contain 7 molecules water of crystallization (FeSO4.7H2O). These crystals are green in colour. When these crystals are heated, they first lose 7 molecules of water of crystallization to form anhydrous ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) which is white in colour.
(iii) It is a thermal decomposition reaction
2FeSO4 Heat⎯⎯⎯→ Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
Green (decomposition)
because in this reaction one substance is splitting up into three substances on heating.
Question. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans. In a decomposition reaction, one substance breaks up into two or more chemical substances, while in a combination reaction two or more substances combine to form one single substance. So these two reactions are called opposites of each other.
Examples of decomposition reaction:
(i) CaCO3 (s) Heat→ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Lime stone Quick lime
(Calcium carbonate) (Calcium oxide)
(ii) 2Pb(NO3)2 (s) Heat⎯⎯→ 2PbO (s) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Lead nitrate Lead oxide Nitrogen dioxide Oxygen gas
Examples of combination reaction:
(i) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) Heat⎯⎯→ 2NH3 (g) + energy
Nitrogen Hydrogen Ammonia
(ii) Burning of hydrogen in oxygen of air to make water
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) Burning→ 2H2O (l)
Question. (a) A substance X, an oxide of a metal, is used extensively in the cement industry. This element is found in our bones also. On treatment with water it forms a solution which turns red litmus blue.
Identity X and also write the chemical reaction involved.
(b) Choose a metal from the following metals which reacts only with hot water: Sodium, magnesium, iron.
Mention the products formed during the reaction.
Ans. (a) ‘X’ is Calcium oxide (CaO). Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form Calcium hydroxide
(slaked lime)
CaO (s) + H2O (l) ⎯⎯⎯→ Ca(OH)2 + Heat
lime Slaked lime
(b) Magnesium reacts with hot water to form Magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Mg (s) + 2H2O (l) ⎯⎯⎯→ Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
(hot) Magnesium Hydrogen
hydroxide
Question. Name the substance oxidised and the substance reduced, and also identify the oxidising agent and reducing agents in the following reaction:
(a) 3MnO2 + 4Al → 3Mn + 2Al2O3
(b) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(c) SO2 + 2H2S → 3S + 2H2O
Ans.
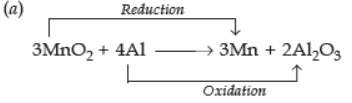
Substance oxidised = Al
Substance reduced = MnO2
Oxidising agent = MnO2
Reducing agent = Al

Substance oxidised = CO
Substance reduced = Fe2O3
Oxidising agent = Fe2O3
Reducing agent = CO

Substance oxidised = H2S
Substance reduced = SO2
Oxidising agent = SO2
Reducing agent = H2S
Question. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case:
(a) Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide (aq) æ æ æ Æ Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium bromide (s)
(b) Zinc carbonate (s) → Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
(c) Hydrogen (g) + Chlorine (g) → Hydrogen chloride (g)
(d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) → Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
Ans. (a) 2KBr (aq) + Ba I2 (aq) → 2K I (aq) + BaBr2 (aq) [Double displacement reaction]
(b) ZnCO3 (s) → ZnO (s) + CO2 (g) [Decomposition reaction]
(c) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl (g) [Combination reaction]
(d) Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) [Displacement reaction]
Question. (a) In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double that of gas collected over the other electrode?
(b) (i) What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate taken in a test tube?
(ii) What type of reaction is this?
(iii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction.
Ans. (a) In electrolysis of water (H2O), the hydrogen goes to one test tube and oxygen goes to another. The two electrodes collect H and O separately.
Since water (H2O) consists of 2 parts of hydrogen and 1 part of oxygen, so, the volume of hydrogen gas (H2) collected over cathode (negative electrode) is double the volume of oxygen gas (O2) collected over anode (positive electrode).
(b) (i) When potassium iodide solution is added to lead nitrate solution, then a yellow precipitate of lead iodide is produced along with potassium nitrate solution.
(ii) This is a double displacement reaction.
(iii) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) ⎯⎯⎯→ PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
Lead nitrate Potassium Lead iodide
iodide (yellow ppt)
Question. Mention the rules for writing a chemical equation illustrating with the help of example.
Ans. Rules for writing a chemical equation:
(i) The method of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of the substances involved in it is known as a chemical equation.
(ii) The substances which combine or react are known as reactants.
(iii) The new substances produced in a reaction are known as products.
(iv) The arrow sign (→) pointing towards the right hand side is put between the reactants and products.
This arrow indicates that the substances written on the left hand side are combining to give the substances written on the right hand side in the equation.
For example:
Zinc metal reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas.
Zinc + Sulphuric acid ⎯⎯⎯→ Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
Putting the symbols and formulae of all the substances in the above words gives equation,
Zn + H2SO4 ⎯⎯⎯→ ZnSO4 + H2
↓ ↓
Reactants Products


