Please refer to Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term 2 With Solutions Set B provided below. The Sample Papers for Class 10 Science have been prepared based on the latest pattern issued by CBSE. Students should practice these guess papers for class 10 Science to gain more practice and get better marks in examinations. The Term 2 Sample Papers for Science Standard 10 will help you to understand the type of questions which can be asked in upcoming examinations.
Term 2 Sample Paper for Class 10 Science With Solutions Set B
SECTION – A
1. (a) Lithium, sodium, potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements?
(b) Helium is an unreactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common?
Answer : (a) Lithium, sodium and potassium all react with water to form alkalies, i.e., lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide respectively with the liberation of
hydrogen gas.
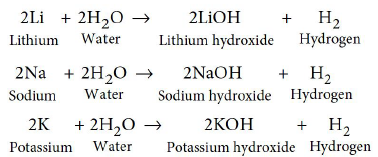
All these metals have one electron in their respective outermost shells. Thus, they have similar chemical properties.
(b) Helium and neon are noble gases and hence have extremely low chemical reactivity. The common thing in these gases is that they have their shells completely filled. Helium has only Kshell which is complete, i.e., has 2 electrons. Neon, on the other hand, has two shells, K and L. Both these shells are complete, i.e., K shell has 2 electrons and L shell has 8 electrons.
2. Define atomic radius. Give its units.
Answer : Ans: Atomic radius can be defined as the distance between the centre of nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom. Also, the atomic radius of a non-metallic element is defined as half of the distance between the nuclei of two similar atoms bound by a single covalent bond. Units = Å (angstrom) or pm (picometre) e.g., atomic radius of hydrogen atom = 37 pm.
OR
Two elements X and Y belong to group 1 and 2 respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of X and Y vary?
(i) Size of their atoms. (ii) Their metallic character.
Answer : X belongs to group-1 while Y belongs to group-2 of the same period hence, valency of X will be 1 and valency of Y will be 2.
(i) As we move along the period from left to right the size of the atoms decreases. Hence, X will be bigger than Y.
(ii) Across the period from left to right, the metallic character decreases. Hence, X is more metallic than Y.
3. We often observe domestic waste decomposing in the bylanes of residential colonies. Suggest ways to make the residents realise that the improper disposal of their waste is harmful to the environment.
Answer : Some of the ways to make people realise that the improper disposal of waste is harmful to the environment are :
(i) Conducting seminars about the negative effects of the wastes on environment.
(ii) Usage of pamphlets and posters for providing information on waste segregation.
(iii) Forming an eco-club in the society for spreading awareness about the ill-effects of improper disposal of waste.
OR
“A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time”. Explain with an example.
Answer : In an ecosystem, one organism may occupy more than one trophic level simultaneously.
One must remember that the trophic level represents a functional level, not a species level as such. A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time; for example, a sparrow is a primary consumer when it eats seeds, fruits, peas, etc. and a secondary consumer when it eats insects and worms.
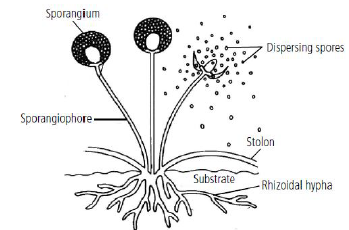
4. Draw a diagram showing spore formation in Rhizopus.
Answer :
5. Inheritance is the process by which characters are passed from the parent to progeny. It is the basis of heredity. What is meant by chemical basis of heredity?
Answer : Transmission of characters from one generation to another is termed as heredity. Carrier of hereditary information are genes that are segments of DNA. DNA (a chemical compound) is the chemical basis of heredity. Chemically, each gene has a specific sequence of nucleotides which determines its functional property.
Chromosome → DNA → genes → proteins.
These proteins (either functional or structural) express phenotype of the individual.
6. (a) What is meant by a magnetic field? Mention two parameters that are necessary to describe it completely.
(b) If field lines of a magnetic field are crossed at a point, what does it indicate?
Answer : (a) Magnetic field : It is defined as the space surrounding the magnet in which magnetic force can be experienced.
Necessary parameters are:
(i) Magnitude of magnetic field.
(ii) Direction of field lines.
(b) If field lines of a magnetic field are crossed at a point, it indicates that there are two directions of magnetic field at a point which is not possible.
7. Explain the following :
(a) Diamond is a covalent solid, yet has a high melting point.
(b) Diamond is used for making tools for cutting and drilling.
Answer : (a) It is a giant molecule containing a large number of carbon-carbon single covalent bonds (network structure). To break these covalent bonds, a large amount of energy is needed and hence diamond has a high melting point.
(b) Diamond is a good conductor of heat and is used for making cutting and drilling tools because the heat generated during cutting and drilling is easily absorbed by the network structure without overheating the diamond tool.
OR
(a) How many bonds are formed between two atoms of oxygen?
(b) How many single and double bonds are present in benzene molecule?
Answer : (a) Oxygen has the atomic number 8. Its electronic configuration is 2, 6 and it requires two more electrons to complete its octet. So, each atom of oxygen shares two electrons with another atom of oxygen. The two electrons contributed by each oxygen atom give rise to two shared pairs of electrons, thus it leads to formation of double bond between two oxygen atoms.
(b) Structure of benzene is

∴ Number of single bonds in benzene = 9
Number of double bonds in benzene = 3
SECTION – B
8. List two functions each of the following parts of human female reproductive system.
(a) Ovaries (b) Fallopian tubes (c) Uterus
Answer : (a) Ovaries : (i) It produces ovum.
(ii) It secretes female sex hormone.
(b) Fallopian tubes : (i) It conveys the ovum from the ovary to the uterus.
(ii) It acts as site for fertilisation.
(c) Uterus : (i) It nourishes the fertilised ovum which develops into the fetus.
(ii) It holds the fetus till the baby is mature enough for birth.
9. Crossing of a pea plant with purple flower and pea plant with white flowers, produces 50 plants with only purple flowers. On selfing, the plants produced 470 plants with purple flowers and 160 with white flowers. Explain the genetic mechanism accounting for the above results.
Answer : In this breeding experiment, ratio of purple to white flowers is approximately 3 : 1 in F2 generation. This ratio is according to Mendelian monohybrid cross. The cross further explains the following facts:
(i) F1 is represented only by dominant trait, i.e., purple flowered plants.
(ii) Both the traits, i.e., purple and white flower colour appear in F2 generation.
OR
Reproduction is linked to stability of population of a species. Justify the statement.
Answer : Reproduction is the only process to ensure the continuity of a species. During reproduction, DNA passes from one generation to the next. Copying of DNA takes place with consistency but with minor variations. This consistency leads to stability of species. Hence, reproduction is linked to stability of a species population. By reproduction, organisms produce large number of new individuals of their own kind out of which several get perished and only some survive. These surviving organisms replace the naturally dying members of the population. Hence, the population as a whole is not affected and remains stable.
10. List in a tubular form three differences between a voltmeter and an ammeter.
Answer : Difference between ammeter and voltmeter

OR
On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend and how?
Answer : The resistance (R) of a conductor depends upon :
(a) Its length (l), i.e., R ∝ l. Resistance of a conductor increases with increase in length of the conductor.
(b) Its cross-sectional area (A) i.e., R ∝ 1/A. Resistance of a conductor decreases with increase in cross-section area of a conductor.
(c) Nature of material : Conductors have small resistance as compared to other materials like semiconductors and insulators.
(d) Temperature : Resistance of conductors increases with increase in temperature.
11. (a) With the help of a suitable circuit diagram prove that the reciprocal of the equivalent resistance of a group of resistances joined in parallel is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
(b) In an electric circuit two resistors of 12 W each are joined in parallel to a 6 V battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
Answer : (a) Resistors in parallel : When resistors are connected in parallel.
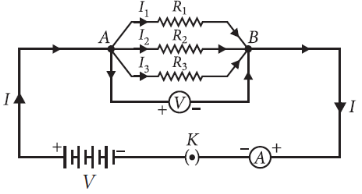
(i) The potential difference across their ends is the same.
(ii) The sum of current through them is the current drawn from the source of energy or cell.

Hence equivalent resistance in parallel combination is equal to the sum of reciprocals of the individual resistances.

12. Two pea plants – one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Answer :


Out of 160 seeds, 30 round green and 30 wrinkled yellow seeds are new combination of characters in F2 progenies.
The new combination of the characteristics are produced because of the independent assortment of seed shape and seed colour trait.
13. Farmers are advised to add biofertilizer in the soil instead of chemical fertilizers to combat the pollution. What are the harmful by-products of fertiliser industries? How do they affect the environment?
Answer : By-products are the products formed side by side with the production of main substances.
By-products from fertiliser industries are :
(i) NOx – Oxides of nitrogen
(ii) SO2 – Oxides of sulphur
Effects of these by-products are :
(i) Air pollution – Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur released by fertiliser industries cause air pollution as these gases are undesirable and create various harmful effects.
(ii) Acid rain – Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen i.e., SO2 and NOx are responsible for lowering the pH of rain creating acid rain. Acid rain consists of acids like nitric acid and sulphuric acid formed by dissolution of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur in water. Acid deposition is of two types – dry and wet. Acid rain has various harmful effects on our environment such as yellowing of marble, death of planktons, molluscs and fish (if below 5 pH), disturbance of food chains, etc.
SECTION – C
14. A hydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C10H22. A hydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. A hydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belong to the same homologous series.
(a) What is the molecular formula of (Q)?
(b) To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
(c) What is the trend of physical and chemical properties of compounds (P), (Q), (R)?
Answer : (a)Molecular formula of (Q) is C8H18 as it has two carbon atoms less than (P).
(b) Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are alkanes having general formula CnH2n+2.
(c) Compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong to same homologous series so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties. They have same general formula CnH2n+2. They differ by 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms.
OR
Write the molecular formula of preceding and succeeding homologues of hydrocarbon (R)?
Answer : Molecular formula of preceding member of compound (R) is C11H24 and succeeding member of (R) is C13H28.
15. Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.
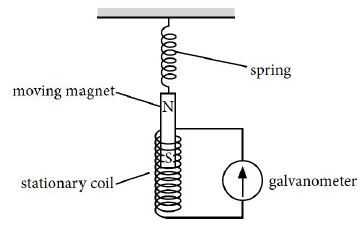
A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil.
He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil. Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following questions.
(a) What is the principle which Ansari Sir is trying to demonstrate?
(b) What will be observed when the Magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation.
(c) Consider the situation where the Magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
Answer : (a) Sir is trying to demonstrate the principle of Electromagnetic induction.
(b) There will be induced current in the coil due to relative motion between the magnet and the coil. Changing the magnetic field around the coil generates induced current.
(c) Using a stronger magnet, using a coil with more number of turns would lead to increase the deflection in the galvanometer.
OR
Is there any difference in the observations in the galvanometer when the Magnet swings in and then out of the stationary coil? Justify your answer.
Answer : When the magnet moves into the coil, the galvanometer shows a momentary deflection towards one side say left. When the magnet moves out of the coil, the galvanometer shows a momentary deflection now towards right. This is due to changing magnetic field associated with the coil as the magnet moves in and out.
The flux increases when the magnet goes in and it decreases when the magnet goes out.
Direction of induced current can be found by using Fleming’s right hand rule.
