Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Gene is a sequence of nucleotides
(b) During the process of gene expression, DNA is first copied into RNA
(c) Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence
(d) Genes cannot acquire mutations in their sequence
Answer
D
Question. The process where characteristics are transmitted from parent to offspring is called:
(a) Variation
(b) Heredity
(c) Gene
(d) Allele
Answer
B
Question. In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2 is
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 1
(d) 2 : 1
Answer
C
Question. Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following:
(i) Round, yellow, (ii) Round, green
(iii) Wrinkled, yellow (iv) Wrinkled, green
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is totally impossible outcome of Mendel’s Experiment?
(a) 3 tall 1 short
(b) 24 tall 8 short
(c) 8 tall 0 short
(d) 4 tall 1 medium height-
Answer
D
Question. The number of sex chromosomes in zygote of human is_______.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. A character which is expressed in hybrid is ________.
(a) Dominant
(b) Recessive
(c) Co-dominant
(d) Epistatic
Answer
A
Question. The exchange in genetic material takes place in _____.
(a) Vegetative propagation
(b) Asexual reproduction
(c) sexual reproduction
(d) budding
Answer
C
Question. What will be the number of chromosomes present in each gamete produced by the plants if the palisade cells of a species of plant contain 28 chromosomes in all?
(a) 56
(b) 28
(c) 14
(d) 4
Answer
C
Question. The following results were obtained by a scientist who crossed the F1 generation of pure-breeding parents for round and wrinkled seeds.

(a) 1881
(b) 22572
(c) 2508
(d) 5643.
Answer
D
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) type questions.
Following questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question. Assertion(A) : Variations are seen in offspring produced by sexual and asexual reproduction.
Reason (R) : DNA molecule generated by replication is not exactly identical to original DNA.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : When pea plants (pure line) having round yellow seeds are crossed with pure line plants having wrinkled green seeds, then all pea plants obtained in F1, generation bear wrinkled green seeds.
Reason: Round and yellow seeds are dominant to wrinkled and green seeds.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion :Selfing of a plant for several generations helps plant breeders to obtain pure breeding varieties.
Reason: Pure breeding plants are heterozygous for many traits.
Answer
C
Case Study questions
Read the passage and answer the given five questions
Pea plant is also tiny, easy to grow, and produces a big number of offspring. Pea plants can have tall plants or dwarf plants. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a tall plant with using pollen from plant with dwarf plant. The resulting pea pod has all tall plants.
Question. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
(1) The allele for tallness is dominated over that of dwarfness.
(2) The plant with tallness is heterozygous.
(3) The plant with dwarfness is homozygous.
(a) 1 only
(b)1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following crosses will give tall and dwarf plants in same proportion?
(a) TT x tt
(b) Tt x tt
(c) TT x Tt
(d) tt x tt
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) TTXTT
(b) Tt x Tt
(c) Tt x TT
(d) Tt x tt
Answer
D
Question. State the ratio of tall plant to dwarf plants in F2 genertion.
(a) 2:2,
(b) 1:3
(c) 3:1,
(d) 4:0
Answer
C
Question. The characters which does not appear in the first filial generation are called
(a) Recessive characters
(b) Dominant characters
(c) Lethal characters
(d) Non-mendelian characters.
Answer
A
Very short answer type questions
Question. Name the information source for making proteins in the cells.
Answer. Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in cells.
Question. What is meant by contrasting traits or characters?
Answer. The characters which always appear in two opposing conditions are called contrasting characters. Tall and dwarf are two contrasting traits for the plant height.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits − blood group A or O − is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer. The give information is not enough to tell us which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant. In blood heredity, blood Type A is always dominant and blood Type O is always recessive. Here, father’s Blood group can be AA (homozygous) or AO (heterozygous) genotypically, where as that of mother can only be OO. For daughter to be born with blood group O, she must receive O type gene one each from father and mother. For this father must have heterozygous AO blood group and mother must have homozygous blood group OO.
Question. How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer. Mendel performed an experiments in which he took a tall plant with round seeds and a short plant with wrinkled-seeds. In F1, They were all tall and had round seeds. Tallness and round seeds were thus dominant traits. When, he used these F1 progeny to generate F2 progeny by self-pollination, he found that some F2 progeny were tall plants with round seeds, and some were short plants with wrinkled seeds. At the same time there tall plants, but had wrinkled seeds, while others were short, but had round seeds. Thus, Mendel’s experiments show that the tall/short trait and the round seed/wrinkled seed trait are independently inherited.
Question. The chromosome number of the sexually reproducing parents and their offspring is same.”” Justify the statement.
Answer. n sexually reproducing organisms, male and female gametes /reproductive cells with only half the number of chromosomes (as in the parent cell) are produced. during fertilization, when male and female gametes fuse to give to a zygote, original number of chromosomes are restored.
Question. Genes controls traits ‘ . Explain this statement with an example.
Answer. Genes controls traits by synthesizing the specific enzyme. Plant height depends on the amount of a particular plant hormone. The amount of plant hormone made will depends on enzyme. If enzyme work efficiently the plant will be tall. if the gene for that enzyme has an alteration that makes enzyme less efficient, the amount of hormone will be less and plant will be short.
Question. Differentiate between phenotype and genotype?
Answer. Genotype – It is the complete heritable genetic identity of an organism. It is the set of alleles that are carried by the organism. It also includes non expressed alleles.
Phenotype – It is the description of the actual physical characteristics of an organism or the expressed form of the genotype.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is variation? How is variation created in a population? What is the importance of variation for survival of a species?
Answer.
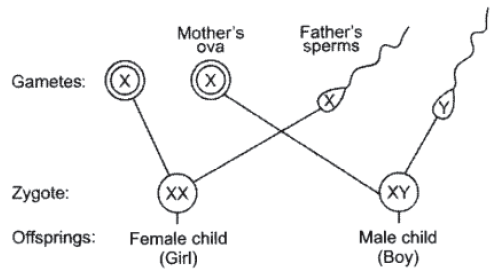
Question. With the help of a flow chart explain in brief how the sex of a newborn is genetically determined in human beings. Which of the two parents, the mother or the father, is responsible for determination of sex of a child?
Answer. In human beings, the sex of the individual is genetically determined. Sex chromosome of male is XY and of female is XX. Sex of a child depends on what happens at fertilisation.
The woman produces eggs having X chromosome while the man produces 50% sperms having X chromosome and 50% sperms having Y chromosome. Man therefore, actually determines the sex of the new born baby.
Question. (a) Why did Mendel choose garden pea for his experiments? Write two reasons.
b) ‘Different species use different strategies to determine sex of a newborn individual. It can be environmental cues or genetically determined.’ Explain the statement by giving example for each strategy.
Answer. Heredity – Transmission of characters from one generation to another or from parents to offspring.
Gene – It is the basic unit of inheritance. It consists of a sequence of DNA, which is the genetic material. Genes can mutate and can take two or more alternative forms.
Alleles – The alternative forms of genes. They affect the same characteristics or traits in alternate forms. They are located on the same place of the chromosome. eggs are kept determines whether the developing animal in egg is male or female.
(ii) In some animals like snail, individual can change sex.
Genetical Cue: A child who inherits an X-chromosome from her father will be a girl and one who inherits a Y- chromosome from the father will be a boy.