Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which of the following methods of contraception protects from acquiring sexually transmitted diseases?
(a) Surgery
(b) Condoms
(c) Copper T
(d) Oral pills
Answer
B
Question. The transfer of pollen from the anther to stigma is called………………….
(a) Fusion
(b) fertilization
(c) Pollination
(d) Vegetative propagation
Answer
C
Question. The process of release of eggs from the ovary is called
(a) Menstruation
(b) Reproduction
(c) Ovulation
(d) Insemination
Answer
C
Question. Which among the following diseases is not sexually transmitted?
(a) Syphyllis
(b) Hepatitis
(c) HIV-AIDS
(d) Gonorrhea
Answer
B
Question. Factors responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on slices of bread are
(i) large number of spores
(ii) availability of moisture and nutrients in bread
(iii) presence of tubular branched hyphae
(iv) formation of round shaped sporangia
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Cloning is a mode of :
(a) sexual reproduction
(b) asexual reproduction
(c) both a and b
(d) none
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(а) pollination, fertilisation, seedling, embryo
(b) seedling, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
(c) pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seedling
(d) embryo, seedling, pollination, fertilisation
Answer
C
Question. Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
(a) pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
Answer
B
Question. Vegetative propagation refers to formation of new plants from———-.
(a) stem, roots, flowers
(b) stem, roots, leaves
(c) stem, flowers, fruit
(d) stem, leaves, flowers
Answer
B
Question. Plants like banana, rose ,jasmine ,orange have lost the capacity to produce
(a) Seeds
(b) Buds
(c) Flowers
(d) Roots
Answer
A
Assertion (A) And Reason (R) Type Questions
Following statements consists of two statements- Assertion (A) and Reason (R) . Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question. Assertion (A): Spores are unicellular bodies.
Reason(R) : The parent body simply breaks up into smaller pieces on maturation.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: The off springs produced by sexual reproduction is likely to adjust better in
environmental fluctuation.
Reason: During the fusion of gametes there is a mixing of genetic material from two parents.
Answer
A
Case Study Based Question
Read the following and answer the questions:
Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
Question. What does the incidence sited in the paragraph indicate?
(a). Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant.
(b). Bryophyllum an propagate vegetatively through leaves.
(c). Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d). Both (a) and (b).
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?
(a) Guava
(b) Begonia
(c) Ginger
(d) Mint
Answer
B
Question. Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then
which part?
(a) Roots
(b) Stems
(c) Flowers
(d) Fruits
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following plant is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(a). Potato
(b) Snake plant
(c) Rose
(d) Water hyacinth
Answer
C
Read the following and answer the questions:
The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of population.
Question. What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys
(a) Broadening of shoulders
(b) Development of mammary glands
(c) Broadening of waist
(d) High pitch of voice
Answer
A
Question. Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
(a) Low pitch voice
(b) Appearance of moustaches and beard
(c) Development of mammary glands
(d) Broadening of shoulders
Answer
C
Question. Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body
(a) Condoms
(b) Diaphragms
(c) Oral pills
(d) Both a) and b)
Answer
C
Question. What should be maintained for healthy society
(a) Rate of birth and death rate
(b) Male and female sex ratio
(c) Child sex ratio
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Short Answer Type Question
Question. Name the male and female gametes in animals. What is fertilization and where does it take place in human females ?
Answer. Male Gamete: Sperm (= spermatozoan) Female Gamete: Ovum.
Fertilization: It is the fusion of two compatible gametes (e.g., sperm and ovum) to form diploid zygote during sexual reproduction.
In human females fertilization occurs in fallopian tube
Question. What is placenta? State its two roles during pregnancy.
Answer. Placenta is a spongy vascular structure formed by the joint activity of maternal and foetal tissues in the wall of uterus that connects foetus with uterus.
Roles: Providing nutrition to the foetus. Taking away wastes of the foetus.
Question. Explain various steps of budding in yeast.
Answer. Budding is a form of asexual reproduction usually observed in yeast.
• During this process, a small protrusion appears on the upper portion of the body of the organism. This bulge is called a bud.
• The bud gradually grows in size and forms an individual cell.
• From this newly budded cell, another bud appears at the tip.
• This process continues and a chain of
Role in evolution – some variations is produced in the new organisms during reproduction which play an important role in evolution. yeast cells is obtained.
Question. What is the importance of reproduction?
Answer. Importance of reproduction –
Maintenance of the existence – Organisms are maintaining their existence on the earth since their origin, million year ago, only because of reproduction.
b) Preservation of species – Species (a group of similar organisms) are preserved because of reproduction. It is possible because reproducing organisms produce new individuals which are very similar to themselves.
Question. What are the limitation of the asexual mode of reproduction? differentiate between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Answer. In asexual reproduction very little variation occurs within generation. Asexual reproduction has a lesser significance for evolution of species.
Asexual reproduction involves only a single individual. It does not require two sexes.
Sexual reproduction involves two different individuals, male and female sexes. The offspring is produced due to fission of male and female gametes.
Question. Define the terms unisexual and bisexual giving one example of each.
Answer. The flowers which contain only the male or female reproductive organs are called unisexual flowers. They are called incomplete flowers. To reproduce they undergo cross-pollination. Examples: Papaya, White mulberry and Watermelon.
The flowers which contain both male and female reproductive organs are known as full or bisexual flowers. They will self-pollinate themselves.
Examples: Tulip, Sunflower and Lily.
Long Answer Type Question
Question. (a) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower.
(b) Label pollen grain, male germ- cells, pollen tube and female germ-cell in the above diagram.
(c) How is zygote formed?
Answer. a and b
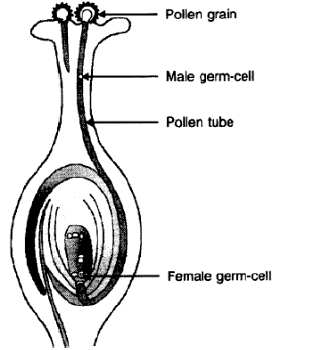
C. Zygote is formed when male gamete fuses with the egg
Question. How are spores produced in sporangium of Rhizopus?
Answer. a) A spore is a small microscopic structure with a thick wall.
b) Spores are generally formed in a structure called sporangium which reassembles formed in a structure called sporangium which resemble blob on – a – stick.
c) Sporangia are formed at the tip of erect fungal hypha.
d) In each sporangium, a nucleus divides several times producing a large number of nuclei. Nuclei get surrounded by a little cytoplasm and develop into thick – walled cells or spores.
e) The wall of sporangium breaks to release the spores in air.
f) On germination in the presence of moist surface, each spore gives rise to a new organism.

Question. List any three differences between pollination and fertilisation.
Answer.
