Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which of the following is biodegradable waste ?
(a) DDT
(b) Aluminium can
(c) Plastic bag
(d) Cow dung
Answer
D
Question. In a given food chain if the amount of energy at the fourth trophic level is 6 kJ, what will be the energy available at the producer level?
(a) 6000 kJ
(b) 20 kJ
(c) 60 kJ
(d) 600 kJ
Answer
A
Question. Accumulation of non-biodegradable pesticides in the food chain in increasing amount at each higher trophic level is known as:
(a) Eutrophication
(b) Pollution
(c) Biomagnifications
(d) Accumulation
Answer
C
Question. The % of solar radiation absorbed by all green plants for photosynthesis is about ———–.
(a) 1%
(b) 5%
(c) 8%
(d) 10%
Answer
A
Question. O2 ——— UV ———→ O + O
O+O2 ———→ O3 (Ozone) The role of UV rays in this reaction is ———
(a) To Split Oxygen molecule
(b) To unite oxygen molecule
(c) To Destroy Ozone
(d) None
Answer
A
Question. In 1987 the ———————- Succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC Production
(a) UNESCO
(b) UNEP
(c) UNCTED
(d) UNICEF
Answer
B
Question. O3———???———→ O2 + (O+O) which substance catalyzes the reaction?
(a) Chlorine
(b) Sulphur dioxide
(c) Hydrogen sulphide
(d) Neon
Answer
A
Question. Which group of waste materials can be classified as nonbiodegradable ?
(a) Plant waste, used tea bags
(b) Polyethene bags, plastic toys
(c) Used tea bags, paper straw
(d) Old clothes, broken footwear
Answer
B
Question. Environment includes:
(a) Land, air, water
(b) Light, temperature, rainfall
(c) Plants, animals, microbes
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Study the image and answer the questions given below.

A. Which of the following chemicals cause Biological Magnification :
(a) DDT
(b) BHC
(c) All non biodegradable pesticides and chemicals
(d) Plastics
Answer
C
B. What may happen if all the Rabbits disappear from the ecosystem :
(a) Bird population declines
(b) Snake population declines
(c) Bird and snake population declines
(d) Bird and snake population declines and grass grow abundant
Answer
D
C. Find out the energy available to the bird :
(a) 100KJ
(b) 10 KJ
(c) 1KJ
(d) . 5KJ
Answer
B
D. Which trophic level may have higher Biological Magnification :
(a) Grass
(b) Snake
(c) Bird
(d) Rabbit
Answer
B
Assertion Reason Type Of Questions
(a) If both Assertion and reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion
(c) If Assertion is true but the Reason is false
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Question. Assertion – Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level
Reason – Autotrophs or producers are the first trophic level in the ecosystem
Answer
A
Question. Assertion – Water, soil, temperature, light, minerals are the abiotic factors in the ecosystem
Reason – Biotic factors interact with abiotic factors in an ecosystem to sustain
Answer
A
Question. Assertion-Enzymes are very essential for digestion of food materials in our body. Specific enzymes are needed for the breakdown of a particular substance
Reason – We will not get energy if we try to eat coal
Answer
A
Question. Assertion – A sparrow when feeds on seeds, it is a primary consumer, but when it feeds on an insect, it belongs to secondary consumer.
Reason – The ecological pyramids (trophic levels) are not always reliable
Answer
A
Question. Assertion – Ozone layer is seen at the Stratosphere of atmosphere, which is harmful to plants and animals.
Reason – The Ozone layer that is found in the troposphere of atmosphere is good to the plants and animals
Answer
D
Question. Assertion – In Sea waters the number of Primary Producers is more than that of Primary consumers
Reason – In Sea water the Primary consumers are more than that of Primary Producers
Answer
B
Question. Assertion – Forests, Grass lands, Rivers, Meadows, Estuaries are natural ecosystems
Reason – Artificial ecosystems are manmade ecosystems
Answer
A
Question. Assertion – Only the green plants can prepare their own food by means of photosynthesis
Reason – Some Bacteria derive their nutrition by autotrophic means
Answer
B
Case Study Questions
Pollution Of River Ganga
The belief the Ganga River is “holy” has not, however, prevented over-use, abuse and pollution of the river. All the towns along its length contribute to the pollution load. It has been assessed that more than 80 per cent of the total pollution load (in terms of organic pollution expressed as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)) arises from domestic sources, i.e., from the settlements along the river course. Due to over-abstraction of water for irrigation in the upper regions of the river, the dry weather flow has been reduced to a trickle.
Rampant deforestation in the last few decades, resulting in topsoil erosion in the catchment area, has increased silt deposits which, in turn, raise the river bed and lead to devastating floods in the rainy season and stagnant flow in the dry season. Along the main river course there are 25 towns with a population of more than 100,000 and about another 23 towns with populations above 50,000. In addition, there are 50 smaller towns with populations above 20,000. There are also about 100 identified major industries located directly on the river, of which 68 are considered as grossly polluting. Fifty-five of these industrial units have complied with the regulations and installed effluent treatment plants (ETPs) and legal proceedings are in progress for the remaining units. The natural assimilative capacity of the river is severely stressed. The principal sources of pollution of the Ganga River can be characterized as follows:
• Domestic and industrial wastes. It has been estimated that about 1.4 × 106 m3 d-1 of domestic wastewater and 0.26 × 106 m3 d-1 of industrial sewage are going into the river.
• Solid garbage thrown directly into the river.
• Non-point sources of pollution from agricultural run-off containing residues of harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
• Animal carcasses and half-burned and unburned human corpses thrown into the river. • Defecation on the banks by the low-income people.
• Mass bathing and ritualistic practices.
Question. Accumulation of toxic substances at higher trophic levels of an ecosystem through the food chain in water bodies affects which of the following organisms more?
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Small fishes
(d) Large fishes
Answer
D
Question. When toxic chemicals and nutrients get deposited in the water bodies, which of the following gases get depleted in the water bodies?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Both oxygen and carbon dioxide
(d) Nitrogen
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following activities may pollute the river water more?
(a) Bathing using detergent and soap
(b) Discharging animals excreta
(c) Deposit flowers and leaves as the part of puja
(d) Bathing without soap and detergent
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following organisms grow abundant in water when the water get mixed with nutrients like sulphates, phosphates etc.?
(a) Algae
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Small fishes
(d) Large fishes
Answer
A
Question. Green Algae and Diatoms are the major producers of Aquatic ecosystem .Which of the following will be more in the aquatic ecosystem:
(a) Small fishes
(b) Large fishes
(c) Algae and phytoplankton
(d) Tadpole
Answer
A
Question. Phyto plankton (60000kj) ———-→ Zooplankton (6000kj)—→Small fishes (600kj)—→Large fish(———-?????—–). Find out the energy available to
large fish.
(a) 60Kj
(b) 6kj
(c) 0.6 Kj
(d) 61Kj
Answer
A
Question. The source of Primary energy source to the aquatic organisms is —————
(a) Algae
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Sun
(d) Moon
Answer
C
Question. The harmful metals that get mixed with the water bodies from the industrial units’ are :
(a) Iron and copper
(b) Mercury and lead
(c) Sodium and potassium
(d) Magnesium and cobalt
Answer
B
Question. The Ganga Action Plan is to ——————–
(a) Make Ganga water free from garbage
(b) Minimise the use of soap and detergents in water bodies like Ganga
(c) Make awareness among the people to save Ganga
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. This will be the best method to protect our River water bodies-
(a) Grow trees along the bank of Rivers
(b) Grow small fishes in River water
(c) Permitted level of sand mining
(d) Making Flats or Malls near the River
Answer
A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Define ecosystem and name its components.
Answer. The living and non-living components of an area interact with each other to form an ecosystem. Components of ecosystem are: Biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living)
Question. What is natural and artificial ecosystem? Give one example each
Answer. Natural ecosystem: Self-sustaining ecosystem formed by the interaction of living and non living things in an area. Eg: Forest or pond Artificial ecosystem: An ecosystem which is formed or modified by human intervention. Crop field or aquarium.
Question. What is food chain? Construct an aquatic food chain showing four trophic levels.
Answer. Food chain is formed by a series of organisms feeding on one another.
Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small fish → Bird.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. List two causes of depletion of ozone layer. Mention any two harmful effects of depletion of this layer.
Answer. Two causes of depletion of ozone layer are as follows:
a. Use of CFC’s
b. Use of Halogens
Harmful effects of ozone depletion:
a. Due to depletion of ozone UV radiation reaches the earth. This UV radiation causes skin cancer, damage to eyes and immune system.
b. Ozone depletion may also lead to variation in global rainfall, ecological disturbances and wildling of global food supplies.
Question. What are decomposers? Write any two consequences of decomposers are removed from the ecosystem?
Answer. Decomposers are organisms that live on dead and decaying matter. They convert complex organic material into simple materials and mix with soil. Eg: fungi, bacteria Some of the consequences if decomposers are removed from soil are
a. Dead organisms will pile up.
b. There will be no replenishment of soil.
Question. How is ozone formed in the higher level of the atmosphere? “Damage to ozone layer is a cause of concern”. Justify this statement.
Answer. Ozone is formed due to action of UV rays on oxygen molecules to form free oxygen atom which subsequently combines with another molecule of oxygen to form ozone. The reaction is:
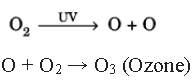
Ozone depletion is a cause of concern because it protects us from the harmful ultraviolet radiations of the Sun by absorbing them. The UV rays can cause skin cancer, ageing, cataract, etc. to human beings if they are not absorbed by ozone due to ozone depletion.
Question. Make a diagrammatic representation showing various trophic levels.
Answer.
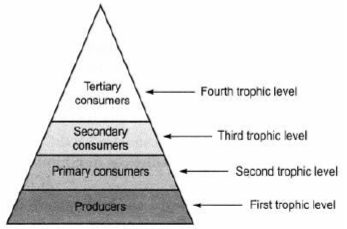
Long answer Type Questions
Question. In a food chain, if 10000 Joules of energy is available to the producer, how much energy will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer it to the tertiary consumer?
Answer. Energy which will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer it to the tertiary consumer are a. Energy available to producers = 10,000 Joules.
Energy transfer to producer = 1% of 10,000 Joules = 100 Joules.
b. According to Ten per cent law, Energy transfer to primary consumer = 10100 × 100 = 10 Joules.
c. Energy transfer to secondary consumer = 10100 × 10 = 1 Joule.
d. Energy transfer to tertiary consumer = 10100 × 1 = 0.1 Joule
Question. “Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional”. Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body
Answer. Because the energy moves progressively through the various trophic levels and is no longer available to the previous trophic level. The energy captured by autotrophs does not revert to the solar input.
a. Pesticides, used for crop protection when washed down into the soil/ water body, are absorbed by the plant along with water and minerals
b. Plants are consumed by animals and these chemicals get into animal body
c. Being non-biodegradable, these chemicals get accumulated progressively in the food chain and into our body
d. As we go into higher levels of food chain amount of harmful substances will increase in the body of organisms as a result of biomagnification.