SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Why is Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation describe as natural genetic engineering in plants?
Answer.(i) Agrobacterium tumefaciens pathogen of dicot plants is able to deliver a piece of DNA known as T-DNA to transform normal plant cell into tumour.
(ii) Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been modified into a cloning vector, which is no more pathogenic to the plant but still able to use the mechanism to deliver genes into a variety of plants.
iii. Since this process occur without human intervention, it is described as natural genetic engineering.
Question. DNA being hydrophilic cannot pass through cell membrane of a host cell. Explain how does recombinant DNA get introduced into the host cell to transform the later?
Answer.(i)Chemical and heat shock method
-the bacterial cells are treated with specific concentration of divalent cation such as calcium, rDNA is forced into such cells by incubating rDNA on ice, followed by placing them briefly at 420c and placing them back on ice.
(i)Microinjection-In this method rDNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell
(ii)Biolistics or gene gun-In this the target cells are bombarded with high velocity particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA
Question. Which enzymes are used for releasing macromolecules (DNA) from cell envelope?
Answer.Lysozyme for bacteria, cellulase for plant cell and chitinase for fungus.
Question. Name the enzymes used in Bacteria, Plants and fungus for isolating DNA?
Answer.Lysozyme for bacteria, cellulase for plant cell and chitinase for fungus.
Question. What are the other macromolecules associated with DNA?
Answer.RNA, proteins, polysaccharides and also lipids
Question. Name the enzyme used to cut DNA?
Answer.restriction enzymes,
Question. Why is the enzyme cellulase needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and not from animal cells?
Answer.The enzyme cellulase breaks down cellulose which is present in cell walls of plants but absent in animal cells.
Question. Give the full form of PCR. Who developed it?
Answer.PCR is a polymerase chain reaction. It was developed by Kary Mullis in 1985.
Question. How many PCR cycles are adequate for proper amplification of DNA segment?
Answer.20-30 cycles.
Question. Name the source of the DNA polymerase used in PCR technique.
Answer.The DNA polymerase used in PCR is Taq polymerase extracted from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus.
Question. Why we prefer the usage of Taq polymerase in PCR technique?
Answer.It is a thermostable enzyme that can withstand high temperature used in the denaturation and separation of DNA strands. Hence, it can be used for a number of cycles in amplification.
Question. Name the bacterium that yields thermostable DNA polymerase.
Answer.The thermostable DNA polymerase can be produced with the help of a bacterium which is named Thermus aquaticus.
Question. Name the technique used for amplification of DNA?
Answer.The DNA amplification can be done by the technique named the Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Question. Biotechnological techniques can help to diagnose the pathogen much before the symptoms of the disease appear in the patient. Suggest any two such techniques
Answer.1. PCR – Polymerase chain reaction
2. ELISA – Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Question. Why is the primer required in PCR added at the 3’ end of DNA template?
Answer.The dna polymerase can catalyse polymerisation reaction in 5’ to 3’ direction only. The free 3’ end of the primer will provide linking site for new nucleotides.
Question. What are selectable markers? What is their use in genetic engineering?
Answer.A gene or other identifiable portion of DNA whose inheritance can be followed and used in the process of selection of transformed cells from non-transformed ones is called selectable marker.
A selectable marker is a gene inserted into a cell, in particular a bacterium or a cultured cell, which confers a trait appropriate for artificial selection.
Question. Name two main steps which are collectively referred to as down streaming process. Why is this process significant?
Answer.Separation and Purification.
This process is essential because before reaching into market, the product has to be subjected for clinical trial and quality control.
Question. What are recombinant proteins? How do bioreactors help in their production?
Answer.Any protein encoding gene is expressed in a heterologous host, is called recombinant protein.
Bioreactors help in the production of recombinant proteins on large scale. A bioreactor provides optimal conditions for achieving the desired recombinant protein by biological methods.
Question. How does a simply stirred tank bioreactor to differ from sparged stirred – tank’ bioreactor?
Answer.In the simply stirred tank bioreactor the stirrer facilitates the even mixing and the oxygen availability throughout the process, whereas for proper mixing throughout the reactor in the case of sparged stirred-tank bioreactor the air is found to be bubbled
Question. How is a continuous culture system maintained in a bioreactor?
Answer.In a continuous culture system, the used medium is drained out from one side while the fresh medium is added from the other to maintain the cells in their physiologically most active log/exponential phase. The continuous culture method produces larger biomass leading to a higher yield of the desired protein.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (3 MARKS)
Question. Explain the work carried out by Cohen and Boyer that contributed immensely to biotechnology.
Answer.They isolated antibiotic resistance gene by cutting out a piece of DNA from the plasmid.
The cutting of DNA at specific locations was done with the help of restriction enzymes popularly called as ‘molecular scissors.
The cut piece of DNA with antibiotic resistance gene was then linked with the plasmid DNA of Salmonella typhimurium acting as vector with the help of the enzyme DNA ligase.
This new autonomously replicating DNA created in vitro with linked fragment of antibiotic resistant gene is called recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA was then transferred into Escherichia coli, where it could replicate using the new host’s DNA polymerase enzyme. The ability to multiply copies of antibiotic resistance gene in E. coli was called cloning of antibiotic resistance gene in E. coli.
Question. With the help of diagrams show the different steps in the formation of recombinant DNA by the action of restriction endonuclease.
Answer.Fig 11.1 steps in the formation of recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease enzyme ECoRI Page 196 NCERT TEXT
Question. How are restriction endonuclease enzymes named? Write examples.
Answer.The naming of restriction enzymes is as follows:
The first letter of the name comes from the genus and the next two letters from the name of the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they are isolated.
The next letter comes from the strain of the prokaryote.
The roman numbers following these four letters indicate the order in which the enzymes were isolated from that strain of the bacterium.
eg.EcoR I is isolated from Escherichia coli RY 13
Question. How are DNA segments separated by gel electrophoresis be visualised and isolated?
Answer.-The separated DNA fragments are visualised after staining with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV light.
-The bright orange-coloured bands of DNA appears when ethidium bromide-stained gel is exposed to UV light.
-The separated bands of DNA are cut out from the gel piece and extracted from the gel piece. This is known as elution.
Question. List 6 recombinant proteins which are used in medical practice? Find where they are used as therapeutics.
Answer.

Question. How do bioreactors help in the production of recombinant proteins?
Answer.Small volume cultures cannot yield appreciable quantities of products. To produce these products in large quantities the development of ‘bioreactors’ was required where large volumes of (100-1000 L) of cultures can be processed. Thus, bioreactors can be thought of as vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products, using microbial, plant, animal, or human cells or individual enzymes. A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions like temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins and oxygen.
Question. Sketch the two types of bioreactors. What is the utility? Which is the common type of bioreactors?
Answer.
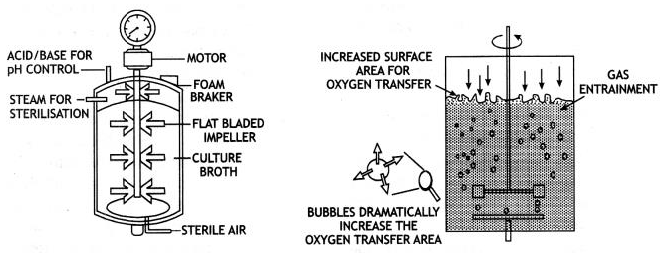
(a) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor (b) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor through which sterile air bubbles are sparged.
A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions (temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen).
One of the most commonly used bioreactors is of stirring type.
A stirred tank reactor is cylindrical or a container with a curved base which facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor. Alternatively, air can be passed through the reactor. It consists of agitator system, an oxygen delivery system, a foam control system, a temperature control system, pH control system and sampling ports so that small volumes of the culture can be withdrawn periodically.
Question. Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
Answer.Shake flasks are used for growing and mixing the desired materials on a small scale in the laboratory. A large scale production of desired biotechnological product is done by using ‘bioreactors’. Besides better aeration and mixing properties, the bioreactors have following advantages
(i) Small volumes of cultures are periodically withdrawn from die reactor for sampling.
(ii) It has a foam control system, pH control system and temperature control system.
(iii) Facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor.
Question. What are the components of a bioreactor?
Answer.The bioreactor has the following components:
• An agitator system.
• An oxygen delivery system.
• A foam control system.
• A temperature control system.
• pH control system and
• Sampling ports.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. With the help of diagrams enumerate the different steps in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer.• Isolation of genetic material which has the gene of interest.
• Cutting of gene of interest from genome and vector with the same restriction endonuclease enzyme.
• Amplifying gene of interest (PCR).
• Ligating gene of interest and vector using DNA ligase forming rDNA.
• Transformation of rDNA into the host cell.
• Multiplying host cell to create clones.
• Figure 11.2 Diagrammatic representation of recombinant DNA technology page 197 NCERT text book
Question. With the help of a neat labelled sketch, explain the formation of recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoR1.
Answer.DIAGRAM –Refer Page 196 Fig 11.1NCERT text
Restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
-The recognition site for EcoRI – 5′ – G A A T T C – 3′
3′ – C T T A A G – 5′
-Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands:
-The enzyme cuts both the vector DNA and the foreign DNA at the same site. EcoRI cuts the DNA between bases G and A only when the sequence GAATTC is present in the DNA.
-This leaves single-stranded portions at the end which are overhanging stretches called sticky ends.
-sticky end form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness of the end facilitates the action of enzyme DNA ligase. -Thus, Recombinant DNA is formed.
Question. a) Why are engineered vectors preferred by biotechnologists for transferring the desired genes into another organism?
(b) Explain how do “ori” selectable markers” and” cloning sites” facilitate cloning into a vector?
Answer..(a)Engineered vectors are preferred because they help easy linking of foreign DNA and selection of recombinants from non-recombinants.
(b)(i) Origin of replication (Ori)
-It is the sequence of DNA from where replication starts.
-Any piece of alien DNA linked to it is made to replicate within the host cell
-It also decides the copy number of linked DNA
(ii)Selectable marker
-The selectable marker is a gene in the vector, which helps in selecting the transformant/recombinant cells from the non-recombinants. Eg. the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics.
(iii)Cloning sites
-The vector should have very few, preferably single recognition sites to link the alien/foreign DNA.
Question. List the steps involved in rDNA technology
Answer.• Isolation of a desired DNA fragment.
• Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector.
• Transferring the recombinant DNA into the host.
• Culturing the host cells in a medium at large scale and extraction of the desired product.
Question. Any recombinant DNA with a desired gene is required in billion copies for commercial use. How is the amplification done? Explain.
Answer.Amplification of gene is done using polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). it is carried out in the following steps:
(i) Denaturation The double stranded DNA is denatured by applying high temperature of 95°C for 15 seconds. Each separated strand acts as a template.
(ii) Annealing Two sets of primers are added, which anneal to the 3′ end of each separated strand.
(iii) Extension DNA polymerase extends the primers by adding nucleotides complementary to the template provided in the reaction. Taq polymerase is used in the reaction, which can tolerate heat. All these steps are repeated many times to get several copies of the desired DNA.
Question. How is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus employed in recombinant DNA technology?
Answer.Thermus aquaticus, a bacterium yields DNA polymerase used in PCR in recombinant DNA technology.
(i) This enzyme remains active during the high temperature applied in the denaturation of double stranded DNA.
(ii) It extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction and the genomic DNA as template.
(iii) Repeated amplification is achieved by this enzyme. The amplified fragments, if desired can be used to ligate with a vector for further cloning.
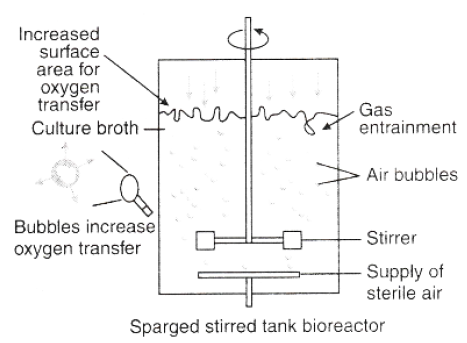
Question. What is bioreactor? Draw a labelled diagram of a sparged stirred bioreactor. Explain its functioning.
Answer.Bioreactors are vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products using microbial, plant or animal cells. A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions like temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins and oxygen. In a sparged stirred-tank bioreactor, the sterile air is sparged through the reactor. Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor has increased surface area for oxygen transfer than simple stirred-tank.
Question. What is downstream processing? Describe the steps in downstream processing.
Answer.The process of formulation, separation and purification of rDNA products made in Bioreactors is called downstream processing.
Steps in downstream processing.
i)Separation of biomass: the (microbial cells are separated from the culture medium. If the product is biomass then it is recovered for processing and spent medium is discarded. Cell mass is separated from the fermented broth by centrifugation or ultracentrifugation. When there is no aeration and agitation some of the microbial cells settle down in the fermentor.
Ii)Cell disruption: if desired product is intracellular the cell biomass can be disrupted so that the product is released.
iii)concentration of broth: The spent medium is concentrated if the product is extracellular.
iv)Initial purification of metabolites: methods for recovery of product from the clarified fermented broth -precipitation, solvent extraction, ultrafiltration, ion exchange chromatography, adsorption and solvent extraction.
v)Metabolite specific purification: Specific purification methods are used when desired metabolite is purified to a very high degree.
vi)De watering: When a low amount of product is found in very large volume of spent medium, volume is reduced by removing water to concentrate the product.it is done by vaccum drying or reverse osmosis.
vii) Polishing of metabolites: Final step of making the product to 98%-100% pure. Purified product is mixed with excipients. The formulated product is packed and sent to the market for the consumers.
Question. Sequentially state the process you would adopt for getting a recombinant protein?
Answer.i) Isolation of DNA (enzymes used), cutting the DNA,
ii)Separation of fragments,
iii)PCR,
iv)introducing into host cell,
v)obtaining gene product in the Bioreactor,
vi)downstream processing
Question. Describe the parts of a Simple stirred-tank bioreactor.
Answer.i)An agitator system
ii). oxygen delivery system
iii)Foam control system
iv)temperature control system
v) pH control system
vi) Sampling ports
vii) Cleaning and sterilization system.
viii). A sump and dump line for emptying of the reactor
Question. Draw well labelled diagrams of simple stirred tank bioreactor and sparged stirred tank bioreactor. distinguish between simple stirred tank bioreactor and sparged stirred tank bioreactor.
Answer.i) There is increased surface area for oxygen transfer in the Sparged Stirred bio reactor, whereas there is less surface area as compared to Sparged tank for oxygen area in Simple Stirred bio reactors.
ii). Bubbles increase the oxygen transfer area in Sparged whereas there is absence of oxygen bubbles in Simple stirred
DIAGRAM /CASE BASED QUESTIONS
Question. A schematic representation of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) up to the extension stage is given below. Answer the questions that follow:

(i) Name the process – A
(ii) Identify (b)
(iii) Identify C and mention its importance in PCR.
Answer.(i) A-Denaturation of the double stranded DNA.
(ii) B-Primers
(iii) C-DNA polymerase or Taq polymerase.
Importance in PCR: It extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction medium and the genomic DNA as the template. Taq polymerase is thermostable and withstands the high temperature used in denaturation process.
A – Heat
B – Primers
C – Deoxynucleotides
D – 30
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below
‘The vectors are DNA molecules that can carry a foreign DNA segment and replicate inside the host cell. Vectors may be plasmids, bacteriophages (viruses that attack bacteria), cosmids, yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) and viruses. The most widely used, versatile, easily manipulated vector PBR 322 is an ideal plasmid vector. Features that are required to facilitate cloning into a vector includes origin of replication (Ori) which is a specific sequence of DNA bases responsible for initiating replication, selectable marker genes and cloning sites.
Question. p in pBR 322 denotes that it is a
(a) plasmid
(b) prokaryote
(c) protist
(d) plant cell
Answer
A
Question. Ori is a specific DNA sequence that help in
(a) attachment of primers
(b) initiation of replication
(c) extension of DNA base
(d) initiation of denaturation.
Answer
B
Question. A and B shown in the figure respectively indicates
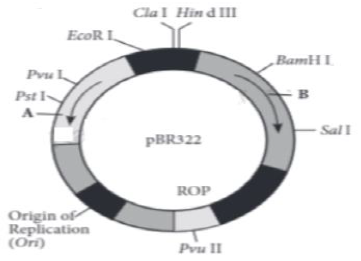
(a) Pvu II and Cla I
(b) ROP and Sal l
(c) ampR and tetR
(d) tetR and ampR.
Answer
C
Question. Selectable markers in vector
(a) are responsible for replication
(b) help in selecting transformants from non-transformants
(c) code for proteins involved in the replicating plasmids
(d) contain unique recognition sites.
Answer
C
Question. Plasmid vectors are
(a) dsDNA molecule
(c) present in bacteria and yeast
(b) extra-chromosomal
(d) all of these.
Answer
D
2. Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to 8(v) given below:
Rajat is a student of biotechnology. His professor tells him that for transformation with recombinant DNA the bacterial cells must be made capable of taking up DNA as DNA do not pass through membrane. While doing experiment in the lab, Rajat noticed that bacterial cells were not taking up the foreign DNA even after treating it with sodium ion. He asked his professor, the reason behind this. His professor explained that he should check the valency and charge of the ion that he is using for the treatment.
Question. It is difficult for DNA to pass through the membrane as
(a) it is a hydrophilic molecule
(b) it is a hydrophobic molecule
(c) it is a circular molecule
(d) it changes its shape when it comes in contact with host cell
Answer
A
Question. What type of ions are used for DNA mediated gene transfers?
(a) Divalent anions
(b) Divalent cations
(c) Monovalent cations
(d) Monovalent anions
Answer
B
Question. rDNA stands for
(a) reduced DNA
(b) red DNA
(c) recombinant DNA
(d) related DNA
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements with regard to DNA is correct?
(a) DNA is a positively charged molecule having two polynucleotide chains.
(b) Nitrogen bases of two polynucleotide chain form complementary pairs. i.e., A opposite G and T opposite (c)
(c) Backbone of DNA chain is built up of alternate deoxyribose sugar and phosphate group.
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: Competent host is essential for transformation with rDN(a)
Reason: Transfer of DNA in a prokaryotic cell is called transfection.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer
C
3.When you insert a piece of alien DNA into a cloning vector and transfer it into a bacterial, plant or animal cell, the alien DNA gets multiplie(d) In almost all recombinant technologies, the ultimate aim is to produce a desirable protein. Hence, there is a need for the recombinant DNA to be expresse(d) The foreign gene gets expressed under appropriate conditions. The expression of foreign genes in host cells involve understanding many technical details. After having cloned the gene of interest and having optimised the conditions to induce the expression of the target protein, one has to consider producing it on a large scale. Can you think of any reason why there is a need for large-scale production? If any protein encoding gene is expressed in a heterologous host, it is called a recombinant protein. The cells harbouring cloned genes of interest may be grown on a small scale in the laboratory. The cultures may be used for extracting the desired protein and then purifying it by using different separation techniques.
Question. Which of the following should be chosen for best yield if one were to produce a recombinant protein in large amounts?
(a) A continuous culture system
(b) A stirred-tank bioreactor without in-lets and out-lets
(c) Laboratory flask of the largest capacity
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The process of separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing is called
(a) upstream processing
(b) downstream processing
(c) bioprocessing
(d) postproduction processing
Answer
B
Question. Genetically engineered bacteria is used for the production of:
(a) Thyroxine
(b) Human insulin
(c) growth hormone
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Construction of recombinant DNA involves:
(a) cleaving and joining of DNA segments with endonuclease
(b) cleaving DNA segments with endonuclease and re-joining with ligase
(c) cleaving and re-joining DNA segments with ligase
(d) cleaving DNA segments with ligase and re-joining with endonuclease
Answer
B
Question. Any DNA molecule that has the ability to replicate in an appropriate host cell, to which the desired gene are integrated for cloning:
(a) Plasmid
(b) Linker
(c) Vector
(d) adapter
Answer
C
4.The cells can also be multiplied in a continuous culture system wherein the used medium is drained out from one side while fresh medium is added from the other to maintain the cells in their physiologically most active log/exponential phase. A stirred-tank reactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor. Alternatively, air can be bubbled through the reactor. If you look at the figure closely you will see that the bioreactor has an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system and a foam control system, a temperature control system, pH control system and sampling ports so that small volumes of the culture can be withdrawn periodically.

Question. Micro-organisms can be grown in the bioreactors by
(a) Support growth system
(b) Agitated growth system
(c) Suspende(d) growth system
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. The components of a bioreactor are:
(a) An agitator system
(b) An oxygen delivery system
(c) A foam control system
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The bioreactor is not capable of:
(a) Producing aseptic conditions
(b) Meeting containment regulations
(c) Controlling pH
(d) Produce electricity
Answer
D
Question. The small-scale bioreactors have volume of:
(a) 5-10 litres
(b) 10-20 litres
(c) 1-10 litres
(d) 1-20 litres
Answer
A
Question. Sparger in stirred tank bioreactor helps in:
(a) Proper gas distribution
(b) Proper mixing of medium
(c) Measuring temperature of medium
(d) Better sterility
Answer
A