Please refer to Environmental Issues Class 12 Biology notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Biology books for Class 12. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 12 Biology Environmental Issues Notes and Questions
Environment (Protection) Act : 1986
Chipko Movement of Garhwal Himalayas: 1974
Joint Forest Management (JFM): 1980s
Montreal Protocol (an international treaty in Canada): 1987 In India, the Air (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act (1981) was amended in 1987
Air Pollution
Causes and effects of air pollution:
- Particulate & gaseous air pollutants from smokestacks of thermal power plants, smelters, etc.
- According to Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), particulate size of less than 2.5μm in diameter (PM 2.5) causes greatest harm to human health.
- It causes respiratory problems, irritation, inflammations & damage to lungs and premature deaths.
Control of air pollution:
Air pollution can be controlled by following methods
1. Electrostatic precipitator:
- This device is very efficient, used to remove particulate matter from air.
- This device can remove 90% particulates which are present in industrial or thermal power plant’s exhausts.
- In this device, electrode wire at thousand volts are used and dust particles passed out through this device.
- Electrons released get attached to dust particles giving them negative charge.
- The collecting plates which are grounded attract these charged particles
2. Scrubber:
- This device is used to remove gaseous pollutant like sulphur dioxide.
- The exhaust is passed through a spray of water and lime, which on reacting with sulphur dioxide form precipitate
3. Catalytic converter:
- This is a device fitted in automobiles for reducing emission of gases.
- In catalytic converter, metals like rhodium and platinumpalladium acts as catalyst.
- Only unleaded petrol can be used in vehicle in which catalytic converter is fitted.
Noise Pollution
Control of Vehicular Air Pollution in Delhi: All the buses of Delhi were converted to run on CNG by the end of the 2002.
Other steps to reduce air pollution in Delhi include.
- Phasing out of old vehicles.
- Use of unleaded petrol and low sulphur petrol and diesel.
- Use of catalytic converters in vehicles.
- Application of Euro-IV norms for vehicles from April 1, 2010.
Auto Fuel Policy:
- The Government of India has laid out a road map to cut down the vehicular air pollution in many cities of India.
- The goal of this of aromatic hydrocarbons to 35% of the fuel.
- The Bharat Stage II was applied to all automobiles in all cities from April, 1,2005.
- The cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata have to meet Euro emission norms from April 1, 2005 and Euro IV Emission norms April, 1, 2010.
In India, the Air (Prevention & Control of Pollution)
Act (1981) was amended in 1987 to include noise as an air pollutant.
Water Pollution
The Government of India has passed the water (Prevention and control of pollution) Act, 1974 to safegaurd our water resources.
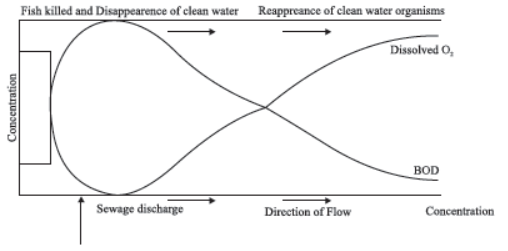
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
- BOD refers to the amount of oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidized by bacteria.
- In the given figure, the effect of sewage on some important characteristics of a river is shown:
Algal Bloom: Presence of large amounts of nutrients in water causes excessive growth of algae called an algal bloom.
Harmful effects of algal bloom are:
- Fish mortality
- Deterioration of water quality
- Toxic to animals and human beings.
Biomagnification
- It refers to increase or accumulation in concentration of toxic substances at successive tropic levels.
- Biomagnification of DDT in an aquatic food chain is given below:
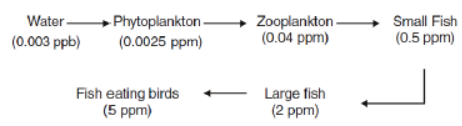
Harmful Effect:
- High concentration of DDT disturbs calcium metabolism in birds, which causes thinning of egg shell and their premature breaking, causing decline in birds population.
Eutrophication:
- It is the process of nutrient enrichment of water and subsequent loss of species diversity like fishes.
- Excess nutrients cause algal bloom which may cover the whole surface of water body and release toxins.
- It causes oxygen deficiency in water that leads to the death of aquatic animals like fishes.
Water hyacinth
- The water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is the most problematic aquatic weed (Terror of Bengal). They grow faster than our ability to remove them. They grow abundantly in eutrophic water bodies.
Solid Wastes
- Solid wastes refer to everything that goes out in trash.
- Municipal solid wastes are wastes from homes, offices, stores, schools, hospitals, etc., that are collected and disposed by the municipality.
- The municipal solid wastes include paper, food wastes, plastics, glass, metals, rubber, leather, textile, etc.
- Burning reduces the volume of the wastes, although it is generally not burnt to completion and open dumps often serve as the breeding ground for rats and flies.
- Sanitary landfills were adopted as the substitute for openburning dumps. In a sanitary landfill, wastes are dumped in a depression or trench after compaction, and covered with dirt every day.
- Hospital wastes contain disinfectants and other harmful chemicals, and also pathogenic micro-organisms. The incinerators are used to dispose hospital wastes.
Polyblend: A Remedy for Plastic Waste
- Ahmed Khan (A plastic sack manufacturer in Bangalore) developed Polyblend. It is a fine powder of recycled modified plastic. Polyblend is mixed with the bitumen and is used to lay roads.
- Blend of polyblend and bitumen enhances the bitumen’s water repellant properties and helps to increase road life.
Radioactive Wastes
- Use of nuclear energy has two very serious problems:
- Accidental leakage. E.g., The Three Mile Island and Chernobyl incidents
- Safe disposal of radioactive wastes.
- It has been recommended that storage of nuclear waste, after sufficient pre-treatment, should be done in suitably shielded containers buried within the rocks, about 500 m deep below the earth’s surface. However, this method of disposal is meeting stiff opposition from the public.
Greenhouse effect and Global Warming
- Increase in the level of greenhouse gases is mainly responsible for global warming (Increase in mean global temperature due to trapping of infrared radiation).
- Carbon dioxide, Methane, CFCs, N2O are the main gases that cause greenhouse effect.
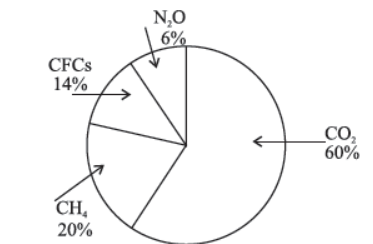
Fig: Contribution of various greenhouse gases to total global warming
Harmful effect of Global Warming:
- Melting of glaciers
- Over many years, this will result in a rise in sea level that can flood the coastal areas.
Measures to Control Global Warming:
- Minimize the use of fossil fuel.
- Improving efficiency of energy usage.
- Reducing deforestation.
- Planting trees.
Ozone Depletion
- Bad ozone (troposphere) – Harms plants and animals
- Good ozone (stratosphere) – acts as a shield absorbing UV rays from sun.
- Ozone gas is continuously formed by the action of UV-rays on molecular oxygen and also degraded into molecular oxygen in stratosphere.
- The thickness of the ozone-layer in a column of air from the ground to the top of the atmosphere is measured in terms of Dobson units (DU).
- Ozone layer absorbs the harmful UV-rays. These rays cause the skin cancer, damages genes, cause inflammation of cornea.
- Chlorofluorocarbons deplete the ozone layer. The part of atmosphere with lesser concentration of ozone is called ozone hole.
Steps leading to ozone depletion
- UV-rays split CFCs and release atomic chlorine (Cl)
- UV-rays also split ozone into oxygen.
- Chlorine atoms trap oxygen atoms and ozone is not formed again from oxygen. This leads to depletion of ozone in the stratosphere.
- Ozone Hole: Large area of thinned ozone layer over Antarctica.
Electronic Wastes (e-waste)
e-wastes are irreparable; includes computer and other electronic goods. Disposal of e-wastes:
- Buried in landfills
- Incineration.
- Recycling.
- El Nino effect
- Rise in temperature leading to deleterious changes in the environment and resulting in odd climatic changes is El Nino effect.
Adverse effect:
- Increased melting of polar ice, submerging of coastal areas, flood, loss of habitat leading to loss of biodiversity.
Degradation by Improper Resource Utilisation and MaintenanceSoil erosion and desertification
Soil erosion and desertification
- Human activities like over-cultivation, deforestation, grazing and poor irrigation practices, leads to soil erosion. It results in arid patches of land and desertification.
- Increased urbanization also creates desertification.
Water logging and soil salinity:
- These are the problems as a part of Green Revolution.
- Irrigation without proper drainage of water leads to water logging in the soil.
- It draws salt to the surface of the soil. The salt is deposited on the land surface or collects at the plant roots. This damages the agriculture.
Deforestation
Reasons of deforestation
- Conversion of forest to agricultural land.
- For timber, firewood, cattle ranching, etc.
- Slash & burn agriculture (Jhum cultivation) in the northeastern states of India. In this, the farmers cut down the trees of the forest and burn the plant remains. The ash is used as a fertiliser and the land is then used for farming or cattle grazing.
Consequences of deforestation:
- CO2 concentration in the atmosphere is enhanced because trees that could hold a lot of carbon in their biomass are lost with deforestation
- Loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction
- Disturbs hydrologic cycle
- Soil erosion & Desertification
- Reforestation: The process of restoring a forest that once existed in the past. It may occur naturally in a deforested area. However, we can speed it up by planting trees.
Chipko Movement of Garhwal Himalayas
- In 1974, local women participated to protect trees from the axe of contractors by hugging them.
- The Government of India in 1980s has introduced the concept of Joint Forest Management (JFM) after realizing the significance of participation by local communities.

We hope the above Environmental Issues Class 12 Biology are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology


