Students can read the important questions given below for Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10 Social Science. All Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 10 Social Science Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Social Science Question Bank Class 10 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Which community in India is famous for protecting the black buck ?
Answer : Bishnois.
Question. Which organization of international level has classified existing plants and animal species of the world.
Answer : International Union for Conservation of National and Nature Resources (IUCN).
Question. What do you mean by madhuca insignis ?
Answer : Madhuca insignis means a wild variety of mahua.
Question. What was the aim of Chipko Movement ?
Answer : Forest conservation.
Question. Write the examples of endemic species.
Answer : Mithun, Nicobar pigeon and Andaman wild pig.
Question. Write the full form of JFM.
Answer : Joint Forest Management.
Question. How many species of fauna and flora are found in our country?
Answer : 81,000 species of fauna and 47,000 species of flora are found in our country.
Question. Name a few trees that are considered sacred in India ?
Answer : Peepal, Banyan and Mango.
Question. Which two factors are majorly responsible for depletion of forest resources ?
Answer : Grazing and fuel-wood collection.
Question. Sundarban National Park is located in which state ?
Answer : West Bengal.
Question. Write the examples of extinct species ?
Answer : Asiatic cheetah, Pink head duck.
Question. Name the state in which Corbett National Park is located.
Answer : Uttarakhand.
Question. How much forest area was converted into agricultural land all over India according to the Forest Survey of India between 1951 and 1980 ?
Answer : 26,200 sq. km.
Question. Write the examples of rare species ?
Answer : Hornbill, Himalayan brown bear, wild Asiatic buffalo and desert fox.
Question. Which conservation strategy do not directly involve community participation ?
Answer : Demarcation of wildlife sanctuaries.
Question. When was Project Tiger launched ?
Answer : In 1973.
Question. What is the main reason for the depletion of flora and fauna?
Answer : Insensitivity to our environment.
Question. Name an endangered species.
Answer : Black buck, Indian rhino, crocodile, Indian wild ass.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How have human activities affected the depletion of flora and fauna ? Explain.
Answer : (a) Habitat destructions agricultural expansion has resulted in destruction of habitat.
(b) Hunting is carried out illegally, thereby, decreasing the number of animals.
(c) Poaching is done and parts of animals are sold for profit.
(d) Overexploitation of resources, cutting of trees for profit motive without replanting and conserving.
(e) Environmental pollution caused by industries destroys soil and water.
(f) Poisoning the forest.
Question. Mention any four major threats to the population of tiger ? Explain the efforts made by the government to protect them.
Or
Write a brief note on ‘Project Tiger’.
Answer : Tiger is one of the key wildlife species in the faunal web. In 1973, the authorities felt that the tiger population had dwindled to 1,827 from an estimated 55,000 at the turn of the century. Major threats to tigers are poaching for trade, shrinking habitat, depletion of prey based species, growing human population, etc. ‘Project Tiger’ is one of the well- publicised wildlife campaigns in the world that was launched in 1973. In 1993, the population of tiger had dropped to 3,600. There are 39 tiger reserves in India. Corbett National Park in Uttarakhand, Sundarbans National Park in West Bengal, Bandhavgarh National Park in Madhya Pradesh, Sariska Wildlife Sanctuary in Rajasthan, Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam and Periyar Tiger Reserve in Kerala are some of the tiger reserves of India.
Question. Classify Indian forests into three categories. Write the main feature of each.
Answer : Classification of forests :
(a) Reserved Forest : They are regarded as most valuable as far as the conservation of forest and wildlife resources are concerned Jammu and Kashmir, Andhra Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal and Maharashtra have large areas of reserved forests.
(b) Protected Forest : Almost one-third of total forest area is protected forest. This forest land is protected from any further depletion. Bihar, Haryana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Odisha and Rajasthan have a bulk of it under protected forests.
(c) Unclassed Forests : There are other forests and wastelands belonging both government and private individuals and communities. All north eastern states and parts of Gujarat have high percentage of their forests as unclassed forests.
Question. ‘’Forests play a key role in the ecological system.’’ Highlight the values of forest in our life.
OR
Explain three reasons why we need to save the biodiversity of our planet ?
Answer : We need to save the biodiversity of our planet because :
(a) Human beings along with all living organisms form a complex web of ecological system in which they are only a part and are very much dependent on this system for their existence.
(b) The plants, animals and micro-organisms recreate the quality of the air we breathe, the water we drink and the soil that produces our food without which we cannot survive
(c) Forests play a key role in the ecological system as these are also the primary producers on which all other living beings depend.
Question. Write any three factors which are responsible for large scale deforestation in India.
Answer : Three factors which are responsible for large scale deforestation in India are :
(a) The greatest damage inflicted on Indian forests was during the colonial period due to the expansion of the railways, agriculture, commercial and scientific forestry and mining.
(b) Agricultural expansion continues to be one of the major causes of depletion of forest resources. Between 1951 and 1980, according to the Forest Survey of India, over 26,200 sq. km. of forest area was converted into agricultural land all over India.
(c) Substantial parts of the tribal belts, especially in the north- eastern and central India, have been deforested or degraded by shifting cultivation (Jhum), a type of ‘slash and burn’ agriculture.
Question. What is Joint Forest Management Programme ?Which was the first state to adopt this programme ?
Answer : (i) A programme which involves local communities in the management and restoration of degraded forests. It involves local communities and land managed by forest department.
(ii) This programme was first passed in 1988 by the state of Odisha.
Question. Distinguish between endangered species and vulnerable species of wild animals. Give one example of each.
Answer :

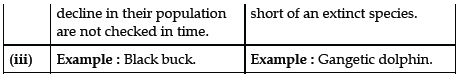
Question. What is Himalayan Yew ? Why is it under great threat at present ?
Answer : It is a medicinal plant.
(a) Over-exploitation of the tree has led to drying up of many yew trees in Himachal Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh.
(b) The biggest selling anti-cancer drug in the world, taxol, is extracted from it to treat cancers.
Question. What efforts or steps were taken by the government to protect forests and wildlife of the country ?
OR
Write a note on good practices towards conserving forest and wildlife.
OR
Explain any three measures taken by the Indian government to protect wildlife.
Answer : Measures taken by the Indian government to protect wildlife are :
(a) The Indian Wildlife Protection Act was implemented in 1972 with various provisions for protecting habitats.
(b) An all-India list of protected species was also published.
(c) To protect the remaining population of certain endangered species government has banned hunting, given legal protection of the habitats of those species and restricted trade in wildlife.
(d) Central and many state governments have established national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Question. “Large-scale development projects have also contributed significantly to the loss of forests.” Justify this statement with relevant examples.
Answer : (i) Since 1951, over 5000 sq km forest was cleared for river valley projects.
(ii) Clearing of forests is still continuing with projects like the Narmada Sagar Project in Madhya Pradesh which would inundate 40, 000 hectares of forest.
(iii) Mining is another important factor behind deforestation.
Question. Analyse the involvement of different traditional communities to conserve their own natural habitats in India.
Or
Describe how communities have conserved and protected forests and wildlife in India ?
Answer : (a) People of Sariska Tiger Reserve are fighting against mining.
(b) The villages of five districts of Alwar declared 1200 hectares of forest as the “Bhairodev Dakav Sonchuri”.
(c) People involved in “Chipko Movement” resisted deforestation.
(d) The Mundas and Santhals of Chhota Nagpur forest region worship trees like mahua and kadamba.
(e) People working some trades involved in joint forest management.
Question. Why do we need to conserve our forests and wildlife? Explain any two steps taken by the government to protect forests and wildlife resources.
Answer : (a) We need to conserve our forests and wildlife because :
(i) Conservation preserves the ecological diversity and our life support system – air, water and soil.
(ii) Conservation also preserves the genetic diversity of plants and animals for better growth of species and breeding.
(iii)It makes the planet Earth safe.
(b) Steps taken by the government to protect forests and wildlife resources :
(i) The Indian Wildlife Protection Act was implemented in 1972 with various provisions for protecting habitats.
(ii) Central and many state governments have established national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Question. What is Biodiversity ? Why is biodiversity important for human lives ? Explain.
Answer : Biodiversity is immensely rich in wildlife and cultivated species, diverse in form and function but closely integrated in a system through multiple network of interdependence. Biodiversity is important for human life because :
(a) It forms an ecological system keeping the air, water and soil in balance.
(b) It provides us medicines and different types of things which are useful for our survival.
(c) It makes the planet Earth safe.

