Please refer to Human Health and Diseases Class 12 Biology Important Questions given below. These solved questions for Human Health and Diseases have been prepared based on the latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. We have provided important examination questions for Class 12 Biology all chapters.
Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases Important Questions
Question. The toxic substance, ‘haemozoin’, related to the high fever and chill, is released during which of the following disease?
(a) Dengue
(b) Malaria
(c) Diphtheria
(d) Phenumonia
Answer
B
Question. The pathogens of genera, Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermorphyton are responsible for
(a) botulism
(b) conjunctivitis
(c) ringworms
(d) skin allergy
Answer
C
Question. Food poisoning is caused by
(a) Entamoeba histolytica
(b) Escherichia coli
(c) Clostridium botulinum
(d) Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Answer
C
Question. Vector for kala azar is:
(a) sandfly
(b) bedbug
(c) louse
(d) housefly
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a communicable disease?
(a) Malaria
(b) Diabetes
(c) Hypertension
(d) Kwashiorkar
Answer
A
Question. Mumps is a viral disease and painful swelling of
(a) parotid glands
(b) thyroid
(c) thymus
(d) sublingual glands
Answer
A
Question. In which of the following disease, there is always a time lag between the infection and appearance of the symptoms of that particular disease?
(a) AIDS
(b) Allergy
(c) Cancer
(d) Alcoholism
Answer
A
Question. Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by
(a) eating imperfectly cooked pork.
(b) tse-tse fly.
(c) mosquito bite.
(d) drinking water containing eggs of Ascaris.
Answer
D
Question. To which type of barriers under innate immunity, do the saliva in the mouth and the tears from the eyes, belong?
(a) Physical barriers
(b) Cytokine barriers
(c) Cellular barriers
(d) Physiological barriers
Answer
D
Question. Immunoglobulins are
(a) antigen
(b) antibodies
(c) antiseptics
(d) antibiotics
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statements regarding drugs are correct ?
(i) Heroin, commonly called smack, is obtained by acetylation of morphine.
(ii) Cocaine is obtained from the latex of Papaver somniferum.
(iii) Marijuana interferes with the transmission of dopamine.
(iv) Morphine is an effective sedative and pain killer.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the correct statement regarding the particular psychotropic drug specified?
(a) Barbiturates cause relaxation and temporary euphoria
(b) Hashish causes after thought perceptions and hallucinations.
(c) Opium stimulates nervous system and causes hallucinations.
(d) Morphine leads to delusions and disturbed emotions.
Answer
B
Question. The following four statements (i – iv) kidney transplant.
Identify the two correct statements.
(i) Even if a kidney transplant is proper the recipient may need to take immuno suppresants for a long time.
(ii) The cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection.
(iii) The B-lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft.
(iv) The acceptance or rejection of a kidney transplant depends on the specific interferons.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. Select the correct statement.
(a) Cocaine is given to patients after surgery as it stimulates recovery.
(b) Barbiturates when given to criminals make them tell the truth.
(c) Morphine is often given to persons who have undergone surgery as a pain killer.
(d) Chewing tobacco lowers blood pressure and heart rate.
Answer
C
Question. At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS?
(a) Within 15 days of sexual contact with an infected person.
(b) When the infecting retrovirus enters host cells.
(c) When viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase.
(d) When HIV replicates rapidly in helper T-lymphocytes and damages large number of these.
Answer
D
Question. Common cold differs from pneumonia in that
(a) pneumonia is caused by a virus while the common cold is caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae.
(b) pneumonia pathogen infects alveoli whereas the common cold affects nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs.
(c) pneumonia is a communicable disease whereas the common cold is a nutritional deficiency disease.
(d) pneumonia can be prevented by a live attenuated bacterial vaccine whereas the common cold has no
effective vaccine.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is correct regarding the number of helper T cells and the viral concentration in the blood?
(a) As the number of HIV increase, so do the numbers of helper T cells.
(b) As the number of HIV increase, the number of helper T cells decreases.
(c) As the concentration of HIV decreases, the number of helper T cells increases.
(d) There is no relationship between the concentration of HIV and the number of helper T cells.
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions
Question. Which one of the following is not correctly matched ?
(a) Culex pipiens – Filariasis
(b) Aedes aegypti – Yellow fever
(c) Female Anopheles – Leishmaniasis
(d) Glossina palpalis – Sleeping sickness
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is the correct match for diseases and its causative agents ?
(a) AIDS – Bacillus
(b) Syphilis – Treoponema pallidum
(c) Malaria – Trypanosoma
(d) Gonorrhoea – Virus
Answer
B
Question. Match the disease given in column I with the appropriate items (pathogen/ prevention/treatment) given in column II.
| Column-I (Diseases) | Column-II (Pathogen/prevention/treatment) |
| A. Amoebiasis | I. Lassa virus |
| B. Diphtheria | II. Use only sterilized food and water |
| C. Cholera | III. DPT vaccine |
| D. Rabies | IV. Use oral rehydration therapy |
(a) A – II; B – III;C – IV; D – I
(b) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
(c) A – II; B – IV; C – I; D – III
(d) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
Answer
A
Question. In which one of the following options the two examples (given in column I) are correctly matched with their particular type of immunity (given in column II)?
| Column I (Examples) | Column II (Type of immunity) |
| (a) Saliva in mouth and tears in eyes | Physical barriers |
| (b) Mucus coating of epithelium, urogential tract and HCl in stomach | Physiological barriers |
| (c) Polymorphonuclear leucocytes and monocytes | Cellular barriers |
| (d) Anti-tetanus and anti-snake bite injections | Active immunity |
Answer
C
Question. Select the correct match of the symptoms of diseases given in column I with their respective pathogen of the diseases given in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Appearance of dry, scaly lesions on various parts of the body such as skin nails and scalp. | I. Entamoeba histolytica |
| B. Chronic inflammation of the lymphatic vessel of lower limbs. | II. Ascaris lumbricoides |
| C. Fever, chills, cough, headache and in severe cases the lips and finger nails may turn gray to bluish in colour. | III. Haemophilus influenzae |
| D. Constipation, abdominal pain and cramps, stool with excess mucous and blood clots. | IV. Wuchereria bancrofti |
| E. Internal bleeding, muscular pain, fever, anaemia and blockage of intestinal passage. | V. Microsporum |
(a) A – I; B – II;C – III; D – IV; E – V
(b) A – III; B – V;C – II; D – IV; E – I
(c) A – III; B – I;C – V; D – II; E – IV
(d) A – V; B – IV;C – III; D – I; E – II
Answer
D
Diagram Type Questions
Question. Refer the given figure showing the mode of action of AIDS virus and identify the sequences labelled as A, B, C and D.

(a) A – Viral DNA introduced into cell; B – Viral DNA; C – Viral DNA incorporates into host RNA; D – New viral RNA produced
(b) A – Viral RNA introduced into cell; B – Viral RNA;C – Viral DNA incorporates into host DNA; D – New viral DNA produced
(c) A – Viral RNA introduced into cell; B – Viral DNA; C – Viral DNA incorporates into host DNA; D – New viral RNA produced
(d) A – Viral DNA introduced into cell; B – Viral RNA; C – Viral RNA incorporates into host DNA; D – New viral DNA produced
Answer
C
Question. The diagram given below shows an antibody molecule with their parts labelled as A, B, C, D, E & F. Identify the part marked as A, B, C, D, E and F.

(a) A-Antigen binding site; B-Variable region (of L-Chain); C – Constant region (of L-Chain); D – Light polypeptide chain (L-Chain); E-Heavy polypeptide chain (H-Chain); F – Disulfide bond.
(b) A – Antigen binding site; B-Constant region (of L-Chain); C – Variable region (of L-Chain); D – Light polypeptide chain (L-Chain); E-Heavy polypeptide chain (H-Chain); F – Disulfide bond.
(c) A-Antigen binding site; B-Variable region (of L-Chain); C – Constant region (of L-Chain); D -Heavy polypeptide chain (L-Chain); E – Light polypeptide chain (H-Chain); F – Hydrogen bond
(d) A-Antigen binding site; B-Variable region (of L-Chain); C – Constant region (of L-Chain); D – Light polypeptide chain (L-Chain); E – Heavy polypeptide chain (H-Chain); F – Hydrogen bond
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. A certain patient is suspected to be suffering from acquired immuno deficiency syndrome. Which diagnostic technique will you recommend for its detection?
(a) WIDAL
(b) ELISA
(c) MRI
(d) Ultrasound
Answer
B
Question. Hormone produced against allergic reaction is
(a) epinephrine
(b) nor-epinephrine
(c) glucocorticoid
(d) mineralocorticocoid
Answer
C
Question. If you keep the sanitary system around yourself sound then the disease which will not most probably break out is :
(a) cholera
(b) malaria
(c) beri-beri
(d) scurvy
Answer
A
Question. Which of these may cause hypothermia in humans ?
(a) Smoking
(b) LSD
(c) Dopamine
(d) Alcohol consumption
Answer
D
Question. Which part of the brain is not affected by alcohol?
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Medulla oblongata
(d) Pons varolii
Answer
D
Question. In alcoholics, liver gets damaged as it
(a) secretes more bile.
(b) stores excess of glycogen.
(c) accumulates excess of fats.
(d) all of the above.
Answer
C
Question. What is common between mumps, cholera and TB ?
(a) They are all bacterial diseases.
(b) They are all endemic diseases.
(c) They are all viral diseases.
(d) They are all communicable diseases.
Answer
D
Question. A person is injected with globulin against hepatitis. This is
(a) naturally acquired active immunity.
(b) naturally acquired passive immnity.
(c) artificially acquired active immunity.
(d) artificially acquired passive immunity.
Answer
C
Question. The best HLA (human leukocyte antigen) match for transplants in order of preference is
(a) sibling > twin > parent > unrelated donor
(b) twin > unrelated donor > parent > sibling
(c) twin > sibling > parent > unrelated donor
(d) sibling > parent > twin > unrelated donor
Answer
C
Question. The pathogen Microsporum responsible for ringworm disease in humans belongs to the same kingdom of organisms as that of
(a) Rhizopus, a mould
(b) Ascaris, a round worm
(c) Taenia, a tapeworm
(d) Wuchereria, a filarial worm
Answer
D
Question. A person is suffering from one disease and shows the following symptoms, like sustained high fever (39 to 40 degree Celsius), weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache and loss of appetite. His doctor confirmed that he is suffering from one bacterial infection.
On which of the following facts (given below) his doctor confirmed the bacterial infection.
(i) Salmonella typhi bacteria are responsible for the infection.
(ii) Streptococcus pneumonia is responsible for the infection.
(iii) By seeing the report which shows the positive result of Widal test.
(iv) The pathogen is transmitted through the bite of female Anopheles mosquito.
(v) As a result of infection, the alveoli get filled with fluid leading to severe problem in respiration.
(a) (i) and (iii) only
(b) (ii), (iii) and (v) only
(c) (ii), (iii), (iv) and (v) only
(d) (i), (ii), (iv) and (v) only
Answer
A
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Millions of chickens were killed in West Bengal, Orissa and Maharashtra recently. What was the reason?
Ans. Millions of chickens were killed (culled) in West Bengal, Orissa and Maharashtra because they were found to be infected with H5N1 virus, the causal organism of Bird Flu.
Question. How do interferons protect us?
Ans. Interferons protect non-infected cells from further viral infections, by creating cytokine barriers.
Question. What is an autoimmune disease? Give an example.
Ans. It is an abnormal immune response in which the immune system of the body starts rejecting its own body cells or ‘self’ cells and molecules. For example, rheumatoid arthritis.
Question. Define the term ‘health’. Mention any two ways of maintaining it.
Ans. Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being.
Good health is maintained by balanced diet/personal hygiene/regular exercise. (Any two)
Question. Malaria, typhoid, pneumonia and amoebiasis are some of the human infectious diseases.
Which ones of these are transmitted through mechanical carriers?
Ans. Malaria and amoebiasis are transmitted through mechanical carriers.
Question. Draw a well labelled diagram of an antibody molecule.
Ans.

Question. Name two STDs which can be transmitted through contaminated blood.
Ans. Hepatitis-B and AIDS are the two STDs which can be transmitted through contaminated blood.
Question. What are interferons?
Ans. Virus infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Why does a doctor administer tetanus antitoxin and not a tetanus vaccine to a child injured in a roadside accident with a bleeding wound? Explain.
OR
Why is a person with cuts and bruises following an accident administered tetanus antitoxin? Give reasons.
Ans. Tetanus is caused by a microbe which has a deadly and fast action. Action of vaccine is slow and this delay may become fatal. Therefore, antitoxins are administered which neutralise the effect of the bacterial toxin.
Question. How does spleen act as a lymphoid organ? Explain.
Ans. The spleen is a large bean-shaped organ. It mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes. It acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms. Spleen also has a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
Question. (a) Name the source plant of heroin drug. How is it obtained from the plant?
(b) Write the effects of heroin on the human body.
OR
Name an opioid drug and its source plant. How does the drug affect the human body?
Ans. (a) The source drug of heroin is poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
It is derived by acetylation of morphine, which is obtained from the latex of the poppy plant.
(b) Heroin is a depressant and slows down the body functions.
Question. When you go for a trek/trip to any high altitude places, you are advised to take it easy and rest for the first two days. Comment, giving reasons.
OR
Why do tribes who live in high altitude of Himalayas experience discomfort in respiration?
How do they get adapted to survive in such a situation?
Ans. At high altitudes it is advised to take easy due to low oxygen availability. This may also cause altitude sickness. It is also advised to take rest because body compensates the low oxygen availability during rest by increasing RBC production and decreasing the binding capacity of haemoglobin, in turn increasing the breathing rate.
Question. Explain the relationship between B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes in developing an immune response.
Ans. B-lymphocytes produce antibodies to fight pathogen.
T-lymphocytes do not produce antibodies but help B cells to produce them. They can also destroy pathogen directly.
Question. What would happen to immune system, if thymus gland is removed from the body of a person?
Ans. Thymus is the primary lymphoid organ. In thymus gland, immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. If thymus gland is removed from the body of a person, his immune system becomes weak. As a result the person’s body becomes prone to infectious diseases.
Question. How are auto-immune diseases different from immunodeficiency disease? Give one example of each in human.
Ans.
| S.No. | Auto-immune disease | Immunodeficiency disease |
| (i) | When the immune system of the body starts attacking ‘self-cells’ and molecules,the disease is called auto-immune disease. | When the immune system fails to function properly against pathogen or antigen, it is called immunodeficiency disease. |
| (ii) | For example, rheumatoid arthritis. | For example, AIDS. |
Question. In the metropolitan cities of India, many children are suffering from allergy/asthma. What are the main causes of this problem? Give some symptoms of allergic reactions.
Ans. Allergy is the exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment. In metropolitan cities lifestyle is responsible in lowering of immunity and sensitivity to allergens. More polluted environment increases the chances of allergy in children.
Some symptoms of allergic reactions are sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing.
Question. (a) Name the virus that causes AIDS in humans.
(b) Explain the sequence of events that follows when this virus attacks to cause immune deficiency in humans.
Ans. (a) Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
(b) (Life cycle of HIV).• It was first reported in U.S.A. in 1981 and in last 25 years, it has killed more than 25 million people.
• It is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
• HIV belongs to the group retrovirus.
• It has RNA genome enclosed in an envelope.
• Transmission of HIV occurs through following ways:
(i) By sexual contact with the infected person.
(ii) By transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products.
(iii) By sharing infected needles.
(iv) From infected mother to her child through placenta.
• It is not spread by more touch or physical contact. It only spreads through body fluids. Hence the infected persons should not be isolated from family and society.
Question. Name the two special types of lymphocytes in humans. How do they differ in their roles in immune response?
Ans. B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes are the lymphocytes in humans.
B-cells produce pathogen specific antibodies and are responsible for humoral immune response.
T-cells help the B-cells to produce antibodies and are responsible for cell-mediated immunity.
Question. Name the cells that act as HIV factory in humans when infected by HIV. Explain the events that occur in the infected cell.
OR
Name the type of cells the AIDS virus first enters into after getting inside the human body.
Explain the sequence of events that the virus undergoes within these cells to increase their progeny.
Ans. Macrophages/Helper T-cells act as HIV factory.
The virus enters macrophages or helper T-cells where RNA genome of the virus forms viral DNA with the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The viral DNA then gets incorporated into host cell’s DNA and directs infected cells to produce new virus particles.
Question. What is “withdrawal syndrome”? List any two symptoms it is characterised by.
Ans. It is the state experienced by addicts when their regular dose of alcohol/drug is abruptly discontinued. It is often characterised by anxiety, shakiness, nausea and sweating.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Name a human disease, its causal organism, symptoms (any three) and vector, spread by intake of water and food contaminated by human faecal matter.
Ans. (i) Typhoid
• It is caused by pathogenic bacterium Salmonella typhi.
• It is spread by contaminated food and water.
• It generally enters the small intestine and then migrates to other organs through blood.
(i) Malaria
• It is caused by a protozoan Plasmodium (P. vivax, P. malaria and P. falciparum).
• P. falciparum causes the most serious and fatal malignant malaria.
• The vector of Plasmodium is female Anopheles mosquito which transfers the sporozoites (infectious form).
• Treatment is by antimalarial drugs like quinine, chloroquin.
• Malaria can be prevented by killing mosquitoes by spraying DDT, BHC, etc., and using insect repellents, mosquito nets, etc.
(i) Ascariasis
• It is caused by an intestinal endoparasite of human, Ascaris lumbricoides, commonly called roundworm.
• Eggs of parasite are excreted along with faeces of infected person, which contaminates water, soil and plants.
• Infection takes place through contaminated vegetables, fruits and water.
Question. (a) Name the respective forms in which the malarial parasite gains entry into (i) Human body and (ii) Body of female Anopheles.
(b) Name the hosts where the sexual and the asexual reproductions of malarial parasites occur respectively.
(c) Name the toxin responsible for the appearance of symptoms of malaria in humans. Why do these symptoms occur periodically?
Ans. (a) (i) Sporozoite
(ii) Gametocytes.
(b) Sexual reproduction occurs in mosquito and asexual reproduction takes place in human body.
(c) The name of the toxin is ha Peamraoszitoeisn .a fter entering the fresh RBCs take 48 to 72hours to complete the erythrocytic cycle, rupturing the erythrocytes. They then burst to release toxic substance called haemozoin and the symptoms like chill and high fever occurs periodically.
Question. (a) Name the causative agent of typhoid in humans.
(b) Name the test administered to confirm the disease.
(c) How does the pathogen gain entry into the human body? Write the diagnostic symptoms and mention the body organ that gets affected in severe cases.
OR
Name the bacterium that causes typhoid. Mention two diagnostic symptoms. How is this disease transmitted to others?
Ans. Typhoid
• It is caused by pathogenic bacterium Salmonella typhi.
• It is spread by contaminated food and water.
• It generally enters the small intestine and then migrates to other organs through blood.
Question. (a) Name the causative agents of pneumonia and common cold.
(b) How do these differ in their symptoms ?
(c) Mention two symptoms common to both.
Ans. (a) Pneumonia is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae/Haemophilus influenzae and that of common cold is Rhinoviruses.
(b) Different symptoms:
| S.No. | Pneumonia | Common cold |
| (i) | Infects alveoli of lungs | Infects nose & respiratory passage |
| (ii) | Symptoms: Chills, lips/fingers may turn grey to black | Symptoms: Sore throat, hoarseness |
(c) Common symptoms:
(i) In both the cases the infected person is inflicted with cough.
(ii) In both the cases the patient suffers from headaches.
Question. (a) Name and explain any four lymphoid organs present in humans.
(b) Categorise the named lymphoid organs as primary or secondary lymphoid organs, giving reasons.
Ans. Components of immune system:
• Lymphoid organs
• Immune cells
• Soluble molecules like antibodies
• Lymphoid tissues
Question. Name any two organisms that are responsible for ringworms in humans. Mention twodiagnostic symptoms. Name the specific parts of the human body where these organisms thrive and explain why.
Ans. Microsporum/Trichophyton/Epideromophyton. (Any two) Symptoms: Dry/scaly lesion on skin/nails/scalp, intense itching.
These organisms thrive in body groin or between toes. They thrive better in heat/moisture/perspiration.
Question. (i) Write the scientific names of the two species of filarial worms causing filariasis.
(ii) How do they affect the body of infected person(s)?
(iii) How does the disease spread?
OR
Name the parasite that causes filariasis in human. Mention its two diagnostic symptoms. How is this disease transmitted to others?
Ans. Filariasis/Elephantiasis
• It is caused by filarial worms, Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi.
• Female Culex mosquito is the vector.
Question. Trace the life-cycle of malarial parasite in the human body when bitten by an infected female Anopheles.
Ans. Plasmodium falciparum is the malarial parasite.
Life cycle of Plasmodium
• Plasmodium requires two hosts to complete its life cycle—human and mosquito.
• The infected female Anopheles mosquito transfers the infectious form of Plasmodium, i.e.,sporozoites to the human body by biting.
• The sporozoites reach the liver cells, where they multiply.
• This is followed by their attack on red blood cells resulting in their rupture.
• The ruptured RBCs release a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for high recurring fever, chills and shivering.
• Sexual stages (gametocytes) develop in red blood cells, from where these parasites enter the female Anopheles mosquitoes when they bite an infected person.
• In the body of mosquitoes, they fertilise and multiply in the stomach wall.
• Sporozoites are now stored in the salivary gland of mosquito till it is again transferred to human body by a mosquito bite. After entering the human body, all the events are repeated.
Question. (a) Name the stage of Plasmodium that gains entry into the human body.
(b) Trace the stages of Plasmodium in the body of female Anopheles after its entry.
(c) Explain the cause of periodic recurrence of chill and high fever during malarial attack in humans.
Ans. (a) Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites.
(b) When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected person, the parasites enter the mosquito’sbody and undergo further development. The parasites multiply within them to form sporozoites that are stored in salivary glands until their transfer to human body.
(c) The rupture of RBCs release a toxic substance called haemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recur.
Question. Study a part of the life cycle of malarial parasite given alongside. Answer the questions that follow:
(a) Mention the roles of ‘A’ in the life cycle of the malarial parasite.
(b) Name the event ‘C’ and the organ where this event occurs.
(c) Identify the organ ‘B’ and name the cells being released from it.
Ans. (a) A—Gametocytes of Plasmodium enter the mosquito when it bites a malarial patient and feed on blood.
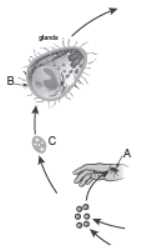
(b) C—Fertilisation. It occurs in the intestine of mosquito.
(c) B—Salivary gland of the female Anopheles mosquito. These release sporozoites of Plasmodium.
Question. Write the events that take place when a vaccine for any disease is introduced into the human body.
Ans. The vaccine contains proteins of pathogen or inactivated/weakened pathogen. When a dose of vaccine is introduced into the human body, it behaves as an antigen and the body produces antibodies in response to the antigen. This response generates active immunity. The antibodies thus produced will neutralise the pathogenic agents during actual infection. The vaccines also generate memory B-cells and T-cells that recognise the pathogen quickly on subsequent exposure and overwhelm the invaders with a massive production of antibodies.
Question. (a) It is generally observed that the children who had suffered from chicken-pox in their childhood may not contract the same disease in their adulthood. Explain giving reasons the basis of such an immunity in an individual. Name this kind of immunity.
(b) What are interferons? Mention their role.
Ans. (a) The first infection of chicken pox produces a primary response and antibodies are generated against chicken pox virus, subsequent encounter with the same virus elicits a highly intensified secondary response, due to the memory cells formed during the first encounter.
This kind of an immunity is active immunity.
(b) Proteins secreted by viral infected cells, which protects non-infected cells from viral infection are called interferous. When α-interferon is given to cancer patient it activates immune system and destroys tumour.
Question. (a) How does the human body respond when vaccine is introduced into it ?
(b) It is said that vaccinations are a must for a healthy society. Justify.
Ans. (a) B-cells assisted by T-cells produce antibodies against weakened antigens, which have been introduced as vaccine. These antibodies neutralise the pathogens (during actual infection) and also generate memory B-cells and T-cells.
(b) B and T memory cells recognise the pathogen in case of actual infection and produce antibodies to kill the pathogen. Thus the population will remain healthy if they are vaccinated prior to the infection.
Question. A person shows strong unusual hypersensitive reactions when exposed to certain substances present in the air, identify the condition. Name the cells responsible for such reactions. What precaution should be taken to avoid such reactions.
Ans. The condition is called allergy. Mast cells are responsible for such reactions.
To avoid such reactions following precautions must be taken.
(i) Use of drugs like antihistamine, adrenaline and steroids quickly reduces the symptoms.
(ii) Avoid contact with substances to which a person is hypersensitive.
Question. Your classmate complains of headache and cough. The doctor confirms that he is suffering from Pneumonia and not common cold, on the basis of certain symptoms. List these symptoms. Mention any two precautions to be followed to prevent the spread of this disease.
Ans. Doctor confirms pneumonia on the basis of the following symptoms—fever/chills/grey-blue lips and finger nails (any two).
It is not common cold as the following symptoms are not observed – Nasal congestion/sore throat/hoarseness (any two).
Precautions to be followed are:
(i) Cover the nose when near the patient.
(ii) Do not share glasses and utensils or articles used by the infected person.


