Students can read the important questions given below for Human Development Class 12 Geography. All Human Development Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 12 Geography Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Geography Question Bank Class 12 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Human Development Class 12
I. Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
The level of urbanisation is measured in terms of percentage of urban population to total population.The level of urbanisation in India in 2011 was 31.16 per cent, which is quite low in comparison to developed countries. Total urban population has increased eleven-fold during the twentieth century.Enlargement of urban centres and emergence of new towns have played a significant role in the growth of urban population and urbanisation in the country. But the growth rate of urbanisation has slowed down during last two decades.Urban centre with population of more than one lakh is called a city or class I town. Cities accommodating population size between one to five million are called metropolitan cities and more than five million are mega cities. Majority of metropolitan and mega cities are urban agglomerations.
Question. How much has the urban population increased during the 12th century?
(A) nine folds
(B) ten folds
(C) eleven folds
(D) twelve folds
Answer
C
Question. What was the level of urbanisation recorded in India in 2011?
(A) 31.14 %
(B) 31.15%
(C) 31.16%
(D) 31.17%
Answer
C
Question. Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai are examples of :
(A) Rural cities
(B) Metropolitan cities
(C) Transport cities
(D) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. An ___________is a continuous urban spread constituting a town and its adjoining outgrowths.
(A) urban agglomeration
(B) metro
(C) sub growth
(D) All of the Above
Answer
A
II. Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
The objective of the Smart Cities Mission is to promote cities that provide core infrastructure,a clean and sustainable environment and give a decent quality of life to its citizens. One of the features of Smart Cities is to apply smart solutions to infrastructure and services in order to make them better. For example, making areas less vulnerable to disasters, using fewer resources and providing cheaper services. The focus is on sustainable and inclusive development and the idea is to look at will act like a lighthouse to other aspiring cities.
Question. What is the purpose of the Smart Cities Mission?
(A) Economic growth
(B) Improve the quality of life of people
(C) Provide good environment
(D) All of the Above
Answer
D
Question. Name one Smart City in India?
(A) Kapurthala
(B) Agra
(C) Bhubaneswar
(D) Agra
Answer
C
Question. When was the Smart Cities Mission launched?
(A) 2015
(B) 2016
(C) 2017
(D) 2018
Answer
A
Question. What are the main features of the Smart Cities Mission?
(A) provide core infrastructure
(B) stop migration
(C) stop brain drain
(D) All of the Above
Answer
A
III. Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
Towns flourished since prehistoric times in India.Even at the time of Indus valley civilisation, towns like Harappa and Mohenjodaro were in existence.The following period has witnessed evolution of towns. It continued with periodic ups and downs until the arrival of Europeans in India in the eighteenth century.
Ancient Towns: There are number of towns in India having historical background spanning over 2000 years. Most of them developed as religious and cultural centres. Varanasi is one of the important towns among these. Prayagraj (Allahabad), Pataliputra (Patna), Madurai are some other examples of ancient towns in the country.Medieval Towns: About 100 of the existing towns have their roots in the medieval period. Most of them developed as headquarters of principalities and kingdoms. These are fort towns which came up on the ruins of ancient towns. Important among them are Delhi, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Lucknow, Agra and Nagpur.
Question. Name one town that existed in the Indus Valley Civilisation.
(A) Harappa
(B) Madurai
(C) Amritsar
(D) Lahore
Answer
A
Question. Where did evolution of the first towns begin?
(A) Near agriculturally fertile areas
(B) Near borders
(C) Near rivers
(D) Both (A) and (C ) are correct
Answer
D
Question. An example of ancient town is :
(A) Karwar
(B) Varanasi
(C) Vishakhapatnam
(D) Madras
Answer
B
Question. ___________ towns came up on the ruins of ancient town.
(A) Fort
(B) War
(C) Transport
(D) Trade
Answer
A
IV. Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions.
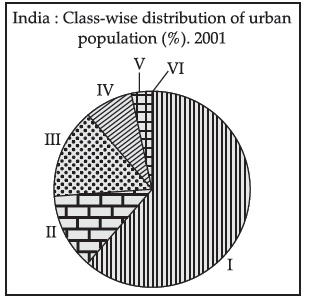
Question. Which class of towns constitutes the minimum share in distribution of urban population?
(A) II
(B) III
(C) IV
(D) VI
Answer
D
Question. Which class of towns constitutes more than 50% share of the urban population?
(A) I
(B) III
(C) IV
(D) V
Answer
A
Question. Which two classes of towns are likely to have similar distribution of urban population?
(A) I and III
(B) II and III
(C) I and IV
(D) III and V
Answer
B
Question. If Class I towns have a population size of 1,00,000 and more and Class III towns have a population size of 20,000 to 49,999, which of these is most likely to be the population size of Class V towns?
(A) 2,00,000 and more
(B) 75,000 to 99,999
(C) 50,000 to 74,999
(D) 5,000 to 9,999
Answer
D