Please refer to National Income Accounting Class 12 Economics notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Economics books for Class 12. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 12 Economics National Income Accounting Notes and Questions
Q.1 Output means……………unless stated otherwise
a) Gross output at MP b) Net output at MP
c) Gross output at FC d) None of these
Ans: Gross output at MP
Q.2 Which of the following is not a component of domestic income?
a) Operating surplus b) Compensation of employees
c) Net factor income from abroad d) Mixed income
Ans: Net factor income from abroad
Q.3 If factor cost is greater than marker price, it means that
a) Indirect taxes < subsidies b) Indirect taxes > subsidies
c) Indirect taxes = subsidies d) None of these
Ans: Indirect taxes < subsidies
Q.4 An Indian farmer produces wheat without incurring cost of inputs and sells for Rs. 1,000 to a miller who grinds wheat into flour and sells for Rs1,200 to baker. The baker sells bread to consumers for Rs. 1,600. Total value added is Rs.
a) 1600 b) 2200
c) 1000 d) 1400
Ans: 1600
Q.5 Which of the following is not true about final goods?
(a) Final gods satisfy wants of ultimate consumers and producers.
(b) Final goods have direct demand as they satisfy the wants directly.
(c) Final goods are subject to further transformation in the process of production.
(d) Final goods are neither used up as raw-material nor for resale in the same year.
Ans: C
Q.6 Following is an example of final good:
(a) Flour used by a banker in making biscuits
(b) Unsold stock of goods lying with the sellers
(c) Tires purchased by a transport company
(d) Mobile sets purchased by a mobile dealer
Ans: Unsold stock of goods lying with the sellers.
Q.7 Which out of the following is not included in estimation of NI?
(a) Subsidized Lunch (b) Old-age Pension
(c) Free Medical facilities (d) Construction of a house
Ans: Old-age Pension
Q.8 Which of the following is included in compensation of employees?
(a) Dearness Allowance
(b) Tools given to employees to be used during work
(c) Payment by insurance company to an injured employee
(d) Contribution by employee to provident fund
Ans: Dearness Allowance
Q.9 ‘Commodity service method’ is another name for:
(a) Expenditure method (b) Income method
(c) Value – added Method (d) None of these
Ans: Value-added Method
Q.10 Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Bread is always a consumer good
(b) All producer goods are not capital goods
(c) Transfer income is received for providing a good or service in return
(d) Interest paid by a household on car loan from a bank is a factor payment
Ans: All producer goods are not capital goods
Q.11 When will GDP of an economy be equal to GNP?
Ans: GDP and GNP will be equal when the ‘net factor income from abroad’ is zero.
Q.12 When is the net domestic product at market price less than the net domestic product at factor cost?
Ans: When net indirect taxes are negative i.e., subsidies are more than indirect taxes.
Q.13 If NDPFC is Rs 1,0000 crores and NFIA is (-) Rs 500 crores, how much will be the national income?
Ans: National Income = 10000 + (-500)
= Rs 9500 Crore
Q.14 If the domestic factor income is Rs 50,000 crores and the national income is Rs 45,000 crores, how much will be the net factor income from abroad?
Ans: Net factor income from abroad = 45,000 – 50,000 = (-) Rs 5000 Crore
Q.15 If compensation of employees in a firm constitutes 65% of net value added at factor cost of a firm, find the proportion of operating surplus.
Ans: 100% – 65% = 35% (assuming mixed income is zero).
Q.16 14. What is the rationale for not taking into account the value of intermediate goods in the measure of GDP?
Ans: To avoid the problem of double counting.
Q.17 When is the net domestic product at market price less than the net domestic product at factor cost?
Ans: When net indirect taxes are negative i.e., subsidies are more than indirect taxes.
Q.18 What is Nominal GDP?
Ans: It is money value of final goods and services produced in a year at prices of the current year.
Q.19 What is GDP deflator?
Ans: It is measured as the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP, multiplied by 100.
GDP Deflator=Nominal GDP/Real GDP*100.
Q.20 What is Green GNP?
Ans: It refers to estimation of GNP that accounts for or taken into consideration certain parameters like environmental pollution and exploitation of natural resources.
Q.21 Explain how ‘externalities’ are a limitation of taking gross domestic product as an index of welfare.
Ans: When the activities of somebody result in benefits or harms to others with no payment received for the benefit and no payment made for the harm done, such benefits and harms are called externalities.
Activities resulting in benefits to others are positive externalities and increase welfare; and those resulting in harm to others are called negative externalities, and thus decrease welfare.
GDP does not take into account these externalities.
For example, construction of a flyover or a highway reduces transport cost and journey time of its users who have not contributed anything towards its cost. Expenditure on construction is included in GDP but not the positive externalities flowing from it. GDP and positive externalities both increase welfare. Therefore, taking only GDP as an index of welfare understates welfare. It means that welfare is much more than it is indicated by GDP.
Similarly, GDP also does not take into account negative externalities. For examples, factories produce goods but at the same time create pollution of water and air. River Yamuna, now a drain, is a living example. The pollution harms people. The factories are not required to pay anything for
harming people. Producing goods increases welfare but creating pollution reduces welfare. Therefore, taking only GDP as an index of welfare overstates welfare. In this case, welfare is much less than indicated by GDP.
Q.22 With reasons state whether the followings will be included in the estimation of National Income of a country?
(a)Commission on sale of second-hand goods.
(b)Scholarship given by the government to the students.
(c)Income earned by an Indian resident working in Russian Embassy situated in India.
(d)Subsidized lunch served to workers in a factory.
Ans: (a)Yes, this will be included in the national income as it is a factor income
(b)No, it will not be included as it is transfer payments
(c)Yes, it will be included as the income is earned by Indian resident
(d)Yes, it will be included as it is a part of the compensation of employees
Q.23 Calculate National Income by Income and Expenditure method.

Ans: Income Method:
NDPFC= Compensation of employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed income of self employed
NDPFC = xiii + (ix+x+xii) + ii
NDPFC = 400 + (60+200+340) +100
NDPFC = 1100 ————————————————- (i)
National Income or NNPFC = NDPFC + NFIA
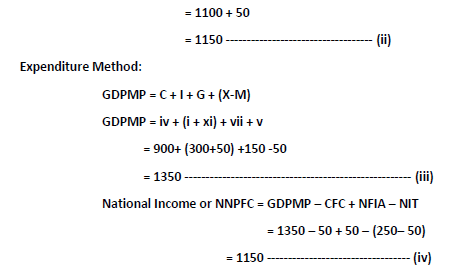
∴The estimated National Income is Rs.1150 crores
Q.24 From the following data calculate GNP at FC by

Ans: GNPFC (a) Income Method :
= (ii) + (vi) + (viii) + (x) + (xi)
NNPFC = 1850 + 400 + 500 + 1100 + (– 50) = 3800
GNPFC = 3800 + 100 = 3900 Crores
(b) Exped. Method = (i) + (iii) + (iv) + (v) + (ix) + (xi) – (xii)
500 + 100 + 1100 + 2600 + (– 100) + (– 50) – 250
= 3900 Crore
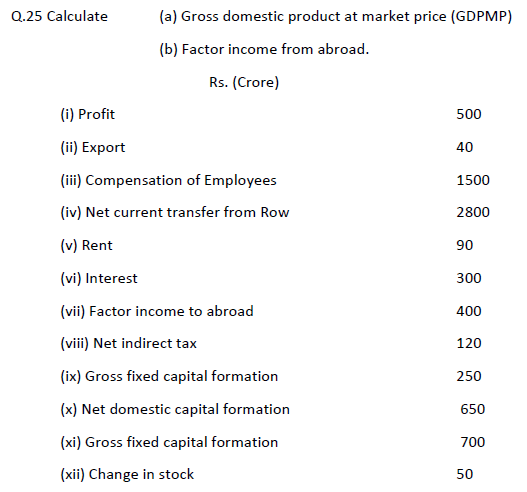
Ans: (a) GDPMP :
NDPFC = (iii) + (v) + (vi) + (vii)
= 1500 + 500 + 300 + 400
= 2700 Crores
GDPMP = NDPFC + CFC + NIT
CFC = (GFCF + S) – 650
= (700 + 50) – 650= 100
NIT = 250
GDPMP = 2700 + 100 + 250= 3050
(b) FIFA
GNPFC = GDPMP + NFIA – NIT
2800 = 3050 + NFIA – 250
NFIA = 0
NFIA = FIFA – FIPA
0 = FIFA – 120
FIFA = 120 Crores

We hope the above National Income Accounting Class 12 Economics are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics

