Students can refer to the following Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ questions with Answers provided below based on the latest curriculum and examination pattern issued by CBSE and NCERT. Our teachers have provided here a collection of multiple choice questions for Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 covering all topics in your textbook so that students can assess themselves on all important topics and thoroughly prepare for their exams
Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ questions with Answers
We have provided below Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ PDF questions with answers which will help the students to go through the entire syllabus and practice multiple choice questions provided here with solutions. As Light Reflection and Refraction MCQs for Class 10 Science pdf download can be really scoring for students, you should go through all problems provided below so that you are able to get more marks in your exams.
Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ questions
Question: The diameter of the reflecting surface of spherical mirror is called its
(a) aperture
(b) focal length
(c) radius of curvature
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question: If the magnification of a lens has a positive value, the image is
(a) real
(b) virtual and erect
(c) inverted
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question: A ray of light travelling in air falls obliquely on the surface of a calm pond. It will
(a) go into the water without deviating from its path
(b) deviate away from the normal
(c) deviate towards the normal
(d) turn back on its original path
Answer
C
Question: An object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between the image and the pole is
(a) equal to f
(b) greater than f but less than 2f
(c) equal to 2f
(d) greater than 2f
Answer
C
Question: Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) The height of the object is taken to be positive as the object is usually placed above the principal axis.
(b) The height of the image should be taken as positive for both virtual and real image.
(c) A negative sign in the value of the magnification indicates that the image is real.
(d) A positive sign in the value of the magnification indicates that the image is virtual.
Answer
B
Question: The focal length, f R2 = is valid
(a) for convex mirror but not for concave mirror.
(b) for concave mirror but not for convex mirror.
(c) for both convex and concave mirrors.
(d) neither for convex mirror nor for concave mirror.
Answer
C
Question: If the magnification of a lens has a negative value, the image is
(a) real and inverted
(b) virtual
(c) erect
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question: The image of the distant object is obtained on a screen by using a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror can be determined by measuring the distance between
(a) the object and the mirror
(b) the object and the screen
(c) the mirror and the screen
(d) the mirror and the screen as well as that between the object and the screen
Answer
C
Question: Two lenses of power +2.50 D and –3.75 D are combined to form a compound lens. Its focal length in cm will be
(a) 40
(b) –40
(c) 80
(d) –80
Answer
D
Question: Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
(a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
(b) Convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c) Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other
(d) Concave mirror as well as concave lens
Answer
A
Question: Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(c) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer
B
Question: Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form a real image larger than the actual object?
(a) When the object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of curvature
(b) When object is kept at a distance less than its focal length
(c) When object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
(d) When object is kept at a distance greater than its radius of curvature
Answer
C
Question: Which one of the following ray diagrams is c orrect for the ray of light incident on a lens as shown in figure?

Answer
B
Question: You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
(a) Kerosene
(b) Water
(c) Mustard oil
(d) Glycerine
Answer
D
Question: Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in Figure?
Answer
A
Question: A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. He finds the image of his head bigger, the middle portion of his body to be of same size and that of the legs smaller. Which of the following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top?
(a) Plane, convex and concave
(b) Convex, concave and plane
(c) Concave, plane and convex
(d) Convex, plane and concave
Answer
C
Question: A ray of light that strikes a plane mirror PQ at an angle of incidence of 30°, is reflected from the plane mirror and then strikes a second plane mirror QR placed at right angles to the first mirror. The angle of reflection at the second mirror is
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Answer
C
Question: Which position of the object will produce a magnified virtual image, if a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm is being used?
(a) 10 cm
(b) 20 cm
(c) 30 cm
(d) 35 cm
Answer
A
Question: A man runs towards the plane mirror at 2 ms–1. The relative speed of his image with respect to him will be
(a) 2 ms–1
(b) 4 ms–1
(c) 8 ms–1
(d) 10 ms–1
Answer
B
Question: A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed
(a) At the focus
(b) Between focus and centre of curvature
(c) Between focus and pole
(d) Beyond the centre of curvature
Answer
C
Question: Two big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he finds that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B remains the same
(a) Mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
(b) Mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
(c) Mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
(d) Mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
Answer
C
Question: An object is placed 20 cm in front of a plane mirror. The mirror is moved 2 cm towards the object. The distance between the positions of the original and final images seen in the mirror is
(a) 2 cm
(b) 4 cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) 22 cm
Answer
B
Question: A ray of light passes from a medium X to another medium Y. No refraction of light occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium Y at an angle of
(a) 120°
(b) 90°
(c) 45°
(d) 0°
Answer
B
Question: A lens of focal length 12 cm forms an erect image, three times the size of the object. The distance between the object and image is
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 36 cm
Answer
B
Question: If an object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens, the image formed is slightly smaller than the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 19 cm from the lens, the image formed is slightly larger than the object. The approximate focal length of the lens is
(a) 20 cm
(b) 18 cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) 5 cm
Answer
C
Question: A ray of light is travelling in a direction perpendicular to the boundary of a parallel glass slab. The ray of light
(a) Is refracted towards the normal
(b) Is refracted away from the normal
(c) Is reflected along the same path
(d) Does not get refracted
Answer
D
Question: A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
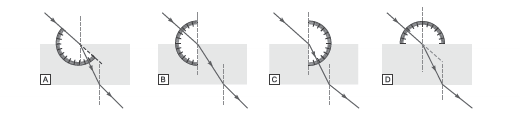
Answer
B
Question: A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab for three different values of angle of incidence (∠i) namely 30°, 45° and 60°. He extends the direction of incident ray by a dotted line and measures the perpendicular distance ‘l’ between the extended incident ray and the emergent ray.
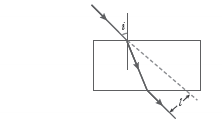
He will observe that
(a) ‘l’ keeps on increasing with increase in angle of incidence
(b) ‘l’ keeps on decreasing with increase in angle of incidence
(c) ‘l’ remains the same for all three angles of incidence
(d) ‘l’ is the maximum for ∠i = 45° and is less than this value for ∠i = 30° and ∠i = 60°.
Answer
A
Question: A student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get a correct measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by following the labelling indicated in figure

Answer
D
Question: Focal length of plane mirror is
(a) At infinity
(b) Zero
(c) Negative
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question: A concave mirror gives real, inverted and same size image if the object is placed
(a) At F
(b) At infinity
(c) At C
(d) Beyond C
Answer
C
Question: Image formed by plane mirror is
(a) Real and erect
(b) Real and inverted
(c) Virtual and erect
(d) Virtual and inverted
Answer
C
Question: In optics, an object which has higher refractive index is called
(a) Optically rarer
(b) Optically denser
(c) Optical density
(d) Refractive index
Answer
B
Question. The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence :
(a) always
(b) sometimes
(c) under special conditions
(d) never
Answer
A
Question. The figure given alongside shows the image of a clock as seen in a plane mirror. The correct time is :
(a) 2.25
(b) 2.35
(c) 6.45
(d) 9.25
Answer
D
Question. A concave mirror cannot be used as :
(a) a magnifying mirror
(b) a torch reflector
(c) a dentist’s mirror
(d) a rear view mirror
Answer
D
Question. A boy is standing in front of and close to a special mirror. He finds the image of his head bigger than normal, the middle part of his body of the same size, and his legs smaller than normal. The special mirror is made up of three types of mirrors in the following order from top downwards :
(a) Convex, Plane, Concave
(b) Plane, Convex, Concave
(c) Concave, Plane, Convex
(d) Convex, Concave, Plane
Answer
C
Question. In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at :
(a) a flat surface
(b) a bent-in surface
(c) a bulging-out surface
(d) an uneven surface
Answer
C
Question. One of the following does not apply to a concave mirror. This is :
(a) focal length is negative
(b) image distance can be positive or negative
(c) image distance is always positive
(d) height of image can be positive or negative
Answer
C
Question. In order to obtain a magnification of, –2 (minus 2) with a concave mirror, the object should be placed :
(a) between pole and focus
(b) between focus and centre of curvature
(c) at the centre of curvature
(d) beyond the centre of curvature
Answer
B
Question. The focal length of a spherical mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm is :
(a) 10 cm
(b) 15 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 30 cm
Answer
B
Question. The image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect and magnified. The position of object is :
(a) at focus
(b) between focus and centre of curvature
(c) at pole
(d) between pole and focus
Answer
D
Question. In order to obtain a magnification of, – 0.6 (minus 0.6) with a concave mirror, the object must be placed :
(a) at the focus
(b) between pole and focus
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) beyond the centre of curvature
Answer
D
Question. Linear magnification produced by a concave mirror may be :
(a) less than 1 or equal to 1
(b) more than 1 or equal to 1
(c) less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
(d) less than 1 or more than 1
Answer
B
Question. Magnification produced by a convex mirror is always :
(a) more than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) equal to 1
(d) more or less than 1
Answer
B
Question. Magnification produced by a plane mirror is :
(a) less than one
(b) greater than one
(c) zero
(d) equal to one
Answer
D
Question. The power of a lens is + 2.0 D. Its focal length should be :
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 40 cm
Answer
b
Question. If a spherical lens has a power of, – 0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) – 4 cm
(b) – 400 mm
(c) – 4 m
(d) – 40 m
Answer
c
Question. A ray of light passes from glass into air. The angle of refraction will be :
(a) equal to the angle of incidence
(b) greater than the angle of incidence
(c) smaller than the angle of incidence
(d) 45°
Answer
B
Question. A ray of light travelling in air goes into water. The angle of refraction will be :
(a) 90°
(b) smaller than the angle of incidence
(c) equal to the angle of incidence
(d) greater than the angle of incidence
Answer
B
Question. In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be :
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
Answer
C
Question. A converging lens is used to produce an image of an object on a screen. What change is needed for the image to be formed nearer to the lens ?
(a) increase the focal length of the lens
(b) insert a diverging lens between the lens and the screen
(c) increase the distance of the object from the lens
(d) move the object closer to the lens
Answer
C
Question. When an object is kept at any distance in front of a concave lens, the image formed is always :
(a) virtual, erect and magnified
(b) virtual, inverted and diminished.
(c) virtual, erect and diminished
(d) virtual, erect and same size as object
Answer
C
Question. When sunlight is concentrated on a piece of paper by a spherical mirror or lens, then a hole can be burnt in it. For doing this, the paper must be placed at the focus of :
(a) either a convex mirror or convex lens
(b) either a concave mirror or concave lens
(c) either a concave mirror or convex lens
(d) either a convex mirror or concave lens
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following can form a virtual image which is always smaller than the object ?
(a) a plane mirror
(b) a convex lens
(c) a concave lens
(d) a concave mirror
Answer
C
Question. The laws of reflection hold true for:
(a) plane mirrors only
(b) concave mirrors only
(c) convex mirrors only
(d) all reflecting surfaces
Answer
D
Question. Rays from the sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that the size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror.
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror.
(c) Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror.
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror.
Answer
B
Question. While determining the focal length of a concave mirror, you try to focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on the screen. The image formed on the screen, as compared to the object, should be:
(a) erect and highly diminished
(b) inverted and enlarged
(c) erect and enlarged
(d) inverted and highly diminished
Answer
D
Question. A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on the screen placed behind a convex lens. He then removed the screen and tried to look through the lens in the direction of the object. He would now observe:
(a) a blurred image on the wall of the laboratory
(b) an erect image of the tree on the lens
(c) no image as the screen has been removed
(d) an inverted image of the tree at the focus of the lens
Answer
D
Question. A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of the combinations for the magic mirror from top to bottom.
(a) Plane, convex and concave
(b) Convex, concave and plane
(c) Concave, plane and convex
(d) Convex, plane and concave
Answer
C
Question. In order to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object on screen, the position of the screen should be:
(a) parallel to the plane of concave mirror
(b) perpendicular to the plane of concave mirror
(c) inclined at an angle 600 to the plane of mirror
(d) in any direction with respect to the plane of concave mirror
Answer
A
Question. A student carries out the experiment of tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for two different values of angle of incidence ∠i = 300 and ∠i = 450. In the two cases the student is likely to observe the set of values of angle of refraction and angle of emergence as:
(a) ∠r =300, ∠e = 200 and ∠r = 450, ∠e = 280
(b) ∠r =300, ∠e = 300 and ∠r = 450, ∠e = 450
(c) ∠r =200, ∠e = 300 and ∠r = 280, ∠e = 450
(d) ∠r =200, ∠e = 200 and ∠r = 280, ∠e = 280
Answer
C
Question. A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces:
(a) a convergent beam of light
(b) a divergent beam of light
(c) a parallel beam of light
(d) a patch of coloured light
Answer
C
Question. In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed:
(a) between the pole and the focus of the reflector
(b) very near to the focus of the reflector
(c) between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
(d) at the centre of curvature of the reflector
Answer
B
Question. An optical device has been given to a student and he determines its focal length by focusing the image of the sun on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the sun. Select the correct statement about the device.
(a) Convex mirror of focal length 12 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 24 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
(d) Convex lens of focal length 12 cm
Answer
C
Question. A student has focussed on the screen a distant building using a convex lens. If he has selected a blue coloured building as obJect, select from the following options the one which gives the correct characteristics of the image formed on the screen.
(a) Virtual, erect, diminished and green shade
(b) Real, inverted, diminished and in violet shade
(c) Real, inverted, diminished and in blue shade
(d) Virtual, inverted, diminished and in blue shade
Answer
C
Question. Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A: from mirror to the screen
Student B: from building to the screen
Student C: from building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly:
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Answer
A
Question. A teacher sets up the stand carrying a convex lens of focal length 15 cm at 42.7 cm mark on the optical bench. He asks four students A, B, C and D to suggest the position of screen on the optical bench so that a distinct image of a distant tree is obtained almost immediately on it. The positions suggested by the students were as:
(A) 12.7 cm
(B) 29.7 cm
(C) 57.7 cm
(D) 72.2cm
Answer
A
Question. A student determines the focal length of a device ‘Xn by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object. The device ‘Xn is
(a) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Answer
D
Question. To determine the approximate focal length of the given convex lens by focussing a distant obcect (say, a sign board), you try to focus the image of the object on a screen. The image you obtain on the screen is always:
(a) erect and laterally inverted
(b) erect and diminished
(c) inverted and diminished
(d) virtual, inverted and diminished
Answer
C
Question. Where should an object be placed in front of the concave mirror so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image ?
Answer
Between pole and focus
Question. For which positions of the object does a concave mirror produce an inverted, magnified and real image ?
Answer
Between focus and centre of curvature
Question. Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
Question Parallel rays of light are reflected by a concave mirror to a point called the ………… principal
Answer
focus
Question The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ……….to the mirror.
Answer
principal focus
Question If the magnification has a plus sign, then image is……………and………….
Answer
virtual ; erect
Question. If the magnification has a minus sign, then the image is…………and………….
Answer
real ; inverted
Question A concave mirror………….rays of light whereas a convex mirror……….rays of light.
Answer
converges ; diverges
Question. When light is reflected, the angles of incidence and reflection are………. .
Answer
equal
Question For a convex mirror, parallel rays of light appear to diverge from a point called the………. principal focus
Question Name the spherical mirror which has :
(a) virtual principal focus.
(b) real principal focus.
Answer
(a) Convex mirror (b) Concave mirror
Question. Out of convex mirror and concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind the mirror ?
Answer
Convex mirror
Question. Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Answer
16 cm

Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ PDF with answers has been gathered for students to rehearse. Students can prepare this MCQ on light Class 10 PDF. Each question has four choices with answers. Firstly, Solve all these Questions and check your answer with the right answer. If your answers do not match with the right answer, Don’t worry try again because You need to prepare daily to score higher marks in the Class 10 Physics Exam.
We hope you liked the above Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ questions. In case you have any questions, please post them in the comments section below. Our faculty will provide you a response.
We hope this Reflection of Light MCQ Pdf shared with you will help you to get good marks in your exam. We have also other study material like NCERT Solutions, NCERT Book, Exam Question, and simpler paper of Class 12. If You want to score higher in your exam, So practice all this study material and if you have any problem in regard to the Reflection of Light MCQ Pdf then, write it in the comment box and we will guide you as much as possible.