Students can refer to the following Human Eye and Colourful World MCQ Questions for Class 10 with Answers provided below based on the latest curriculum and examination pattern issued by CBSE and NCERT. Our teachers have provided here a collection of multiple-choice questions for The Human Eye and The Colourful World Class 10 covering all topics in your textbook so that students can assess themselves on all important topics and thoroughly prepare for their exams
The Human Eye and Colourful World MCQ Questions for Class 10 Questions with Answers
We have provided below Human Eye and Colourful World MCQ Questions for Class 10 with answers which will help the students to go through the entire syllabus and practice multiple choice questions provided here with solutions.
As The Human Eye and Colourful World MCQ for Class 10 Science pdf download can be really scoring for students, you should go through all problems provided below so that you are able to get more marks in your exams.
Question: A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in figure. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?

Answer
B
Question: The splitting of white light into different colours on passing through a prism is called
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) dispersion
(d) deviation
Answer
C
Question: Which of the following is a natural phenomenon which is caused by the dispersion of sunlight in the sky?
(a) Twinkling of stars
(b) Stars seem higher than they actually are
(c) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset
(d) Rainbow
Answer
D
Question: The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of sky in water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
Answer
C
Question: The effect of glass prism is only to separate the seven colours of
(a) White light
(b) light from bulb
(c) Sunlight
(d) All
Answer
D
Question: Sunlight is a mixture of __ visible colours
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) none
Answer
C
Question: Name the scientist who was the first to use a glass prism to obtain the spectrum of sunlight.
(a) Isaac Newton
(b) Einstein
(c) Kepler
(d) Hans Christian Oersted
Answer
A
Question: When Newton colour disc is rotated fast, the different colours ________.
(a) Can be separated
(b) Can be differentiated
(c) Cannot be differentiated
(d) None
Answer
C
Question: When a ray passes through a prism __________.
(a) It goes undeviated
(b) It remain parallel to a base
(c) It bends towards the base
(d) None
Answer
C
Question: The _________ colour is at the top and _________ colour is at the bottom of spectrum.
(a) Red, Violet
(b) Red, Blue
(c) Violet, red
(d) None
Answer
A
Question: When a beam of white light passes through the prism
(a) velocity of violet rays is greater than that of red rays
(b) velocities of violet and red rays are equal to each other
(c) velocity of violet rays is smaller than that of red rays
(d) velocities of violet and red rays do not change
Answer
B
Question: Which of the following is correct for the order of colours present in white light
(a) VIBGYOR
(b) VIYGOBR
(c) VBIYORG
(d) VIGBOYR
Answer
B
Question: The angle between two refracting surfaces of prism is called the angle of
(a) Prism
(b) Emergence
(c) Deviation
(d) Incidence
Answer
A
Question: The angle at which the ray gets deviated is called
(a) Angle of deviation
(b) Angle of dispersion
(c) Angle of emergence
(d) refracted angle
Answer
A
Question: The broad wavelength range of visible spectrum is-
(a) 4000-8000Å
(b) 2000-4000Å
(c) 10000-20000Å
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question: For which colour, refractive index of glass is maximum?
(a) Red
(b) Violet
(c) Green
(d) Yellow
Answer
B
Question: A transparent refracting material which is bounded by two plane refracting surfaces is
(a) Prism
(b) Convex lens
(c) Glass slab
(d) None
Answer
A
Question: Which image shows the deviation of light in a prism?
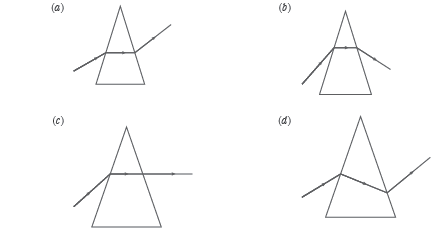
Answer
B
Question: The image shows a light ray incident on a glass prism.
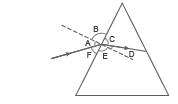
Answer
A
The various angles are labeled in the image. Which angle shows the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively?
(a) A and D
(b) C and F
(c) D and F
(d) B and E
Answer
B
Question: Red colour of the sun at the time of sunrise and sunset is because-
(a) Red colour is least scattered
(b) Blue colour is least scattered
(c) Red colour is scattered the most
(d) All colours are equally scattered
Answer
A
Question: The sun appears two minutes before the actual sunrise due to atmospheric refraction. How does sunlight travel from space to atmosphere?
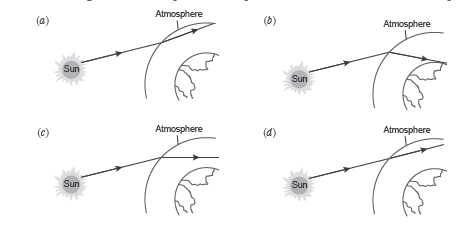
Answer
B
Question: A ray of light is incident on one face of the prism, as shown.

How will the ray of light disperse in the prism?
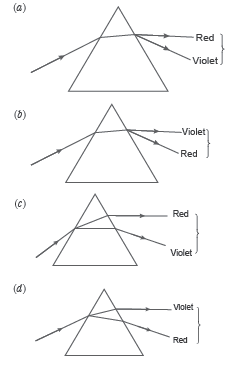
Answer
C
Question: Which option justifies that the sun appears red at sunrise and sunset?
(a) The distance between the sun and earth reduces.
(b) The white light disperses into seven colours, only red enters the atmosphere.
(c) Red has high wavelength, so it travels longer distance.
(d) Red scatters highest by the atmosphere.
Answer
C
Question: The image shows the dispersion of the white light in the prism.
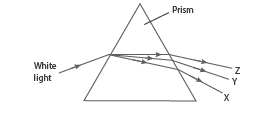
What will be the colours of the X, Y and Z? We can see a rainbow on a sunny day when y
(a) X: green; Y: violet; Z: red
(b) X: violet; Y: green; Z: red
(c) X: red; Y: violet; Z: green
(d) X: red; Y: green; Z: violet
Answer
B
Question: White light passes through an equilateral prism then
(a) dispersion takes place at first refracting surface and refraction at second refracting surface
(b) refraction takes place at first refracting surface and refraction at second refracting surface
(c) dispersion takes place at both refracting surfaces
(d) refraction takes place at both refracting surfaces
Answer
A
Question: Two identical prism PQR and P’Q’R’ are given. White light is passed through PQR as shown below.

Which of the following position of P’Q’R’ will again yield white light?
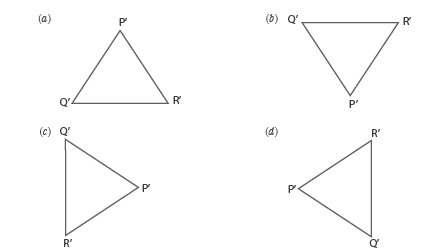
Answer
C
51. The day is longer on the earth by about 4 minutes because
(a) the earth is round in shape
(b) the earth rotates on its axis
(c) the earth has atmosphere
(d) the earth revolves around the sun
The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Answer
C
Question. After testing the eyes of a child, the optician has prescribed the following lenses for his spectacles :Left eye : + 2.00 D Right eye : + 2.25 D The child is suffering from the defect of vision called :
(a) short-sightedness
(b) long-sightedness
(c) cataract
(d) presbyopia
Answer
B
Question. A person got his eyes tested. The optician’s prescription for the spectacles reads :
Left eye : – 3.00 D Right eye : – 3.50 D
The person is having a defect of vision called :
(a) presbyopia
(b) myopia
(c) astigmatism
(d) hypermetropia
Answer
B
Question. A student sitting on the last bench in the class cannot read the writing on the blackboard clearly but he can read the book lying on his desk clearly. Which of the following statement is correct about the student ?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
(d) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
Answer
D
Question. A man driving a car can read a distant road sign clearly but finds difficulty in reading the odometer on the dashboard of the car. Which of the following statement is correct about this man ?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
(d) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
Answer
A
Question. The defect of vision in which the eye-lens of a person gets progressively cloudy resulting in blurred vision is called :
(a) myopia
(b) presbyopia
(c) colourblindness
(d) cataract
Answer
D
Question. A person cannot see distant objects clearly. His vision can be corrected by using the spectacles containing :
(a) concave lenses
(b) plane lenses
(c) contact lenses
(d) convex lenses
Answer
A
Question. A person finds difficulty in seeing nearby objects clearly. His vision can be corrected by using spectacles containing :
(a) converging lenses
(b) diverging lenses
(c) prismatic lenses
(d) chromatic lenses
Answer
A
Question. The animal which does not have eyes that look sideways is :
(a) Horse
(b) Chicken
(c) Lion
(d) Fish
Answer
C
Question. With both eyes open, a person’s field of view is about :
(a) 90°
(b) 150°
(c) 180°
(d) 360°
Answer
C
Question. Having two eyes gives a person :
(a) deeper field of view
(b) coloured field of view
(c) rear field of view
(d) wider field of view
Answer
D
Question. A beam of white light is shone onto a glass prism. The light cannot be :
(a) deviated
(b) dispersed
(c) focused
(d) refracted
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following colour of white light is least deviated by the prism ?
(a) green
(b) violet
(c) indigo
(d) yellow
Answer
D
Question. The colour of white light which is deviated the maximum on passing through the glass prism is :
(a) blue
(b) indigo
(c) red
(d) orange
Answer
B
Question. The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a glass prism is called :
(a) refraction
(b) deflection
(c) dispersion
(d) scattering
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following coloured light has the least speed in glass prism ?
(a) violet
(b) yellow
(c) red
(d) green
Answer
A
Question. The coloured light having the maximum speed in glass prism is :
(a) blue
(b) green
(c) violet
(d) yellow
Answer
D
Question. As light from a far off star comes down towards the earth :
(a) it bends away from the normal
(b) it bends towards the normal
(c) it does not bend at all
(d) it is reflected back
Answer
Question. We can see the sun before the actual sunrise by about :
(a) 5 minutes
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 2 hours
(d) 20 minutes
Answer
B
Question. The twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric :
(a) reflection of light
(b) dispersion of light
(c) interference of light
(d) refraction of light
Answer
D
Question. The atmospheric refraction of light causes the twinkling of :
(a) planets only
(b) stars only
(c) planets and stars
(d) stars and satellites
Answer
B
Question. A student sitting in the last row of the class-room is not able to read clearly the writing on the blackboard.
(a) Name the type of defect he is suffering from.
(b) How can this defect by corrected ?
Answer
(a) Myopia (Short-sightedness) (b) Concave lens
Question. Name the defect of vision in a person :
(a) whose near point is more than 25 cm away.
(b) whose far point is less than infinity
Answer
(a) Hypermetropia (b) Myopia
Question. Your friend can read a book perfectly well but cannot read the writing on blackboard unless she sits on the front row in class.
(a) Is she short-sighted or long-sighted ?
(b) What type of lenses–converging or diverging–would an optician prescribe for her
Answer
(a) Short-sighted (b) Diverging lenses
Question. A man can read the number of a distant bus clearly but he finds difficulty in reading a book.
(a) From which defect of the eye is he suffering ?
(b) What type of spectacle lens should he use to correct the defect ?
Answer
(a) Hypermetropia (Long-sightedness)
(b) Convex lens
Question. In the formation of spectrum of white light by a prism :
(i) which colour is deviated least ?
(ii) which colour is deviated most ?
Answer
(i) Red (ii) Violet
Question. Which colour of the spectrum has (a) longest wavelength, and (b) shortest wavelength ?
(a) Red (b) Violet
Question. What is the colour of the sunlight :
(a) scattered by the dust particles in the atmosphere ?
(b) scattered by the air molecules in the atmosphere ?
Answer
(a) White (b) Blue
Question. How much is our field of view :
(a) with one eye open ?
(b) with both eyes open ?
Answer
(a) About 150° (b) About 180°
Question. Out of animals of prey and predators, which have their eyes :
(i) at the front of their head ?
(ii) on the opposite sides of their head ?
Answer
(i) Predators (ii) Animals of prey
Question. Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye :
(a) carries signals from an eye to the brain.
(b) muscles which change the shape of the eye-lens.
(c) a hole in the middle of the iris.
(d) a clear window at the front of the eye.
(e) changes shape to focus a picture on the retina.
Answer
(a) Optic nerve (b) Ciliary muscles (c) Pupil (d) Cornea (e) Eye-lens
Question. What is the name of :
(a) the curved, transparent front surface of the eye ?
(b) the light-sensitive layer in the eye ?
Answer
(a) Cornea (b) Retina
Question. Name the part of the eye :
(a) which controls the amount of light entering the eye.
(b) on which the image is formed.
(c) which changes the focal length of eye-lens.
Answer
(a) Iris (b) Retina (c) Ciliary muscles
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
Question When a ray of light enters a prism, it bends……………..the normal ; as it leaves the prism, it bends ………… the normal.
Answer
towards ; away from
Question White light is composed of………….colours. The colour of white light deviated through the largest angle by a prism is…………..
Answer
seven; violet
Question. We can see the sun about………….minutes before the actual sunrise and about………….minutes after the actual sunset because of atmospheric……………
Answer
two ; two ; refraction
Question. Having two eyes gives a …………….field of view.
Answer
wider
Question. A short-sighted person cannot see ………….. objects clearly. Short-sightedness can be corrected by using ……………lenses.
Answer
distant ; concave
Question. A long-sighted person cannot see ………….. objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using ………….. lenses.
Answer
nearby ; convex
Question. Having two eyes enables us to judge……………..more accurately.
Answer
distances
Question. As light rays pass from air into a glass prism, are they refracted towards or away from the normal ?
Answer
Towards the normal
Question. Which phenomenon makes us see the sun :
(b) a few minutes after actual sunset ?
Answer
Atmospheric refraction of sunlight
Question. Atmospheric refraction causes advance sunrise and delayed sunset. By how much time is :
(b) sunset delayed ?
Answer
(b) About 2 minutes
Question. Which of the two is scattered more easily : light of shorter wavelengths or light of longer wavelengths ?
Answer
Light of shorter wavelength

