Please refer to Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 10. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 10 Science Human Eyes and Colourful World Notes and Questions
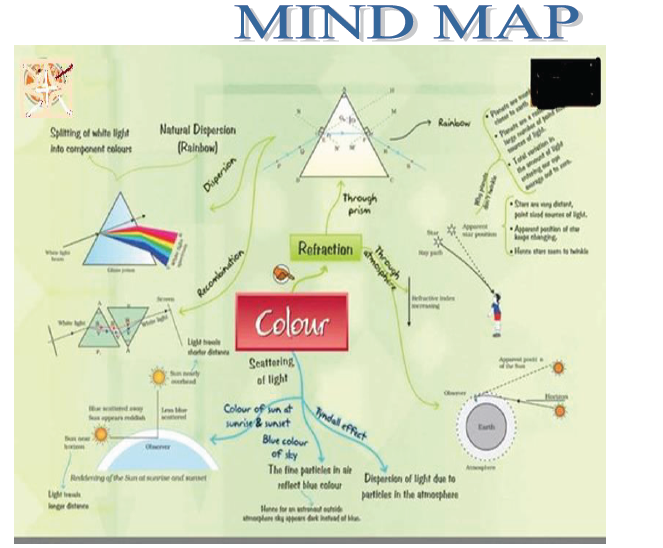


Dispersion of white light by a glass prism: The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its seven constituent colors when it passes through a glass prism is called dispersion of white light. The various colours seen are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red. The sequence of colours remembers as VIBGYOR. The band of seven colours is called the spectrum. The different component colour of light bends at a different angle with respect to the incident angle. The violet light bends the east while the red bends most.
Issac Newton: He was the first, who obtained spectrum of sunlight by using glass prism. He tried to split the spectrum of white light more by using another similar prism, but he could not get any more colours.
He repeated the experiment using second prism in inverted position with respect to the first prism. It allowed all the colours of spectrum to pass through second prism. He found white light emerges on the other side of second prism.
Rainbow: It is the spectrum of sunlight in nature. It is formed due to the dispersion of sunlight by the tiny water droplet, present in the atmosphere.
Formation of the rainbow: The water droplets act like small prism. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop. Due to the dispersion of light and internal reflection, different colours reach the observer’s eye.
Red colour appears on top and violet at the bottom of rainbow.
A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of Sun.
At ‘A’ – Refraction and dispersion take place.
At ‘B’ – Internal reflection takes place.
At ‘C’ – Refraction and dispersion take place.

Twinkling of Star: It is also due to atmospheric refraction.
Distant star act like a point source of light. As the beam of starlight keeps deviating from its path, the apparent position of star keeps on changing because physical condition of earth’s atmosphere is not stationary.
Hence, the amount of light enters our eyes fluctuate sometimes bright and sometime dim. This is the “Twinkling effect of star”.
Color of Sunrise and Sunset: While sunset and sunrise, the colour of the sun and its surrounding appear red. During sunset and sunrise, the sun is near to horizon, and therefore, the sunlight has to travel larger distance in atmosphere. Due to this, most of the blue light (shorter wavelength) is scattered away by the particles. The light of longer wavelength (red colour) reaches our eye. This is why sun appears red in colour.
Why the danger signal or sign is made of red colour?
Red colour scatteres the most when strikes the small particle of fog and smoke because it has the maximum wavelength (visible spectrum). Hence, from large distance also, we can see the red colour clearly.
At noon sun appears white: At noon, the sun is overhead and sunlight would travel shorter distance relatively through the atmosphere. Hence, at noon, the sun appear white as only little of the blue and violet colours are scattered.

Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which of the following colors is least scattered by fog, dust of smoke?
a. Violet
b. Blue
c. Red
d. Yellow
Answer
C
Question. The colored light that refracts most while passing through a prism is
a. Yellow
b. Violet
c. Blue
d. Red
Answer
B
Question. At noon the sun appears white as
(a) light is least scattered.
(b) All the colors of the white light are scattered away.
(c) Blue color is scattered the most.
(d) Red color is scattered the most.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the formation of a rainbow?
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion
(b) Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
(a) dispersion of light by water droplets
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
(d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
Answer
C
Question. Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
(a) Ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere.
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
(c) scattering of light by dust particles
(d) internal reflection of light by clouds.
Answer
B
Question. The clear sky appears blue because
(а) blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere.
(b) Ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere.
(c) Violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colors by the atmosphere.
(d) light of all other colors is scattered more than the violet and blue color lights by the atmosphere.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colors of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colors of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
Answer
C
Question. The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in color. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colors, the red light
(a) Is scattered the most by smoke or fog.
(b) Is scattered the least by smoke or fog.
(c) Is absorbed the most by smoke or fog.
(d) Moves fastest in air.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Total internal reflection of light
(d) Reflection of light from the earth.
Answer
B
Question. The bluish color of water in deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of sky in water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea.
Answer
C
Question.A student traces the path of a ray through a glass prism for four different values of angle of incidence. On analyzing the diagrams, he is likely to conclude that the emergent ray
(a) is always parallel to the incident ray.
(b) Is always perpendicular to the incident ray
(c) Is always parallel to the refracted ray
(d) Always bends at an angle to the direction of incident ray.
Answer
D
Question. A student is observing the diagram showing the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism. He would find that for all angles of incidence the ray of light bends:
(а) towards the normal while entering into the prism and away from the normal while emerging out of the prism
(b) away from the normal while entering into the prism and towards the normal while emerging out of the prism.
(c) Away from the normal while entering as well as while emerging out of the prism.
(d) Towards the normal while entering as well as while emerging out of the prism.
Answer
A
Question. In the following diagram, the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism is shown:
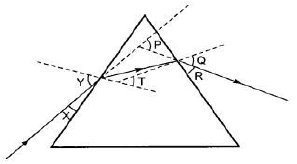
In this diagram the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation respectively are (select the correct option):
(a) X, R and T
(b) Y, Q and T
(c) X, Q and P
(d) Y, Q and P
Answer
D
Question. After tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass prism a student marked the angle of incidence (∠i), angle of refraction (∠r), angle of emergence (∠e) and the angle of deviation (∠D) as shown in the diagram. The correctly marked angles are:

(a) ∠i and ∠r
(b) ∠i and ∠e
(c) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠i, ∠r and ∠e
Answer
B
Question. While performing the experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism, four students marked the incident ray and the emergent ray in their diagrams in the manner shown below.

The correct path of the rays has been shown by:
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer
C
Question. Stars appears to be twinkling because of
(a) atmospheric refraction
(b) reflection
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) spectrum
Answer
B
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
Direction – In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion is given by the corresponding statement of Reason. Of the statements, mark the correct answer as
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
(e) If Assertion and Reason both are false.
1. Assertion: Tyndall Effect is an optical phenomenon of light used to explain atmospheric refraction.
Reason: The tiny particles of dust disperse sunlight in it falls through foliage in a forest.
Ans. C
2. Assertion: On a clear summer night twinkling of stars is observed.
Reason: The twinkling of stars is caused by dispersion of star light by the atmosphere.
Ans. C
3. Assertion: On mid-day, the colour of the sunlight becomes white.
Reason: No atmospheric refraction is caused due to overhead sun.
Ans. A

Give the answers according to information of the Sun position (Raipur) given in the above chart.
1. Duration of the Sun and the Moon dated 5 th January 2021.
Ans : Sun 10h:53m:39s Moon 14h:7m:21s
2. Write the date in which the Sun was present for longer time.
Ans : 11th
3. Date in which the sun rised earliest ?
Ans : 1st
4. Difference between the day length from 1st January and 2nd January.
Ans : 19s
Question. A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a rain shower. It is caused by dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets, present in the atmosphere. A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun. The water droplets act like small prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop.

Due to the dispersion of light and internal reflection, different colours reach the observer’s eye. You can also see a rainbow on a sunny day when you look at the sky through a waterfall or through a water fountain, with the Sun behind you.
A. Rainbows are caused due to:
a. scattering of white light
b. dispersion of white light
c. reflection of white light
d. None of the above
Ans: b
B. The colours are in the order in rainbow:
a. Violet, blue, green, yellow, indigo, orange and red
b. Violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red
c. Violet, green, blue, yellow, indigo, orange and red
d. Violet, blue, green, yellow, indigo, orange and red
Ans: b
C. What is the shape of a rainbow?
a. straight line
b. circle shape
c. arc shape
d. Oval shape
Ans: c
D. Water droplet act like as:
a. tiny prism
b. tiny glass slab
c. tiny lens
d. tiny mirror
Ans: a
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Which phenomenon is responsible for making the path of light visible?
Answer: Tyndall effect is responsible for making the path of light visible.
Question. Why is red color selected for danger signal lights?
Answer: Because the red light has the largest wavelength of all colors, it is the least dispersed. Because of this, much of the light gets reflected back and can travel longer distances through clouds, fog, dust etc. to effectively enter our eyes.
Question. What will the color of the sky be for an astronaut staying in the international space station orbiting the earth?
Answer: For an astronaut staying in the international space station orbiting the Earth the color of the sky will be black because the light reaching it does not scatter.
Question. Light of two colors A and B pass through a glass prism. A deviates more than B from its path of incidence. Which color has a higher speed in the prism?
Answer: Color B has higher speed than that of color A.
Question. Explain why the planets do not twinkle but the stars twinkle?
ANS: The planets are much closer to the earth. A planet can be considered as a collection of large number of point-sized sources of light. So the total variation in the amount of light entering our eye from all the individual point-sized sources will average out to zero thereby nullifying the twinkling effect.
Question. Name the three phenomenon of light responsible for the formation of rainbow in the sky.
Answer: Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection of light.
Question. When white light passes through a glass prism; seven colors namely red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet are seen on the white screen. All these colors have different angles of deviation. Explain why?
Answer: Speed of color in a medium depends upon its wavelength. All the colors have different wavelength. The red color has the longest wavelength and violet color has the last wavelength.
Therefore, red color has the highest speed in the glass prism and the violet color has the lowest speed in the glass prism. Hence, all colors of white light are refracted by different amounts while passing through the glass prism. Therefore, all the colors have different angles of deviations.
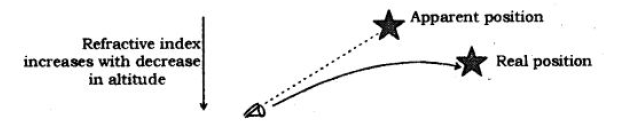
Question. Explain with the help of a diagram, how we are able to observe the sunrise about two minutes before the Sun gets above the horizon
Answer: The Sun can be seen about two minutes before sunrise because when the Sun is slightly below the horizon, the Sun’s light coming from less dense air to more dense air is refracted downwards as it passes through the atmosphere. Thus due to this atmospheric refraction, the Sun appears to be raised above the horizon when actually it is slightly below the horizon.
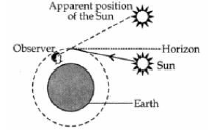
Question. Nitin and his four friends were sitting on his roof on a pleasant day. All of them were enjoying Ludo. Suddenly Aryu saw seven colors in the sky. He jumped with joy and shouted “Look, there is an Indradhanush in the sky”. Then Nitin explained all about the rainbow. After that every one clapped for him.
(a) What information is given by Nitin to his friends about a rainbow?
(b) Is it possible to obtain rainbow phenomenon on the earth?
(c) Which term is used for the seven colors of the rainbow?
Answer:
(a) Rainbow is a natural phenomenon in which an arch of seven colors visible in the sky is produced by the dispersion of white sunlight by raindrops in the atmosphere. Each raindrop acts as a tiny glass prism splitting the sunlight into seven colors.
(b) Yes, in daily life, when white light of the Sun is passed through a glass prism, it splits into seven colors.
(c) The band of seven colors obtained by the splitting of white light is called spectrum.
(d) The red color appears at the top of the rainbow whereas violet color appears at its bottom.
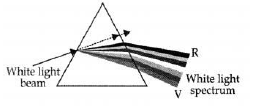
Question.(a) Draw a labeled ray diagram to illustrate the dispersion of a narrow beam of white light when it passes through a glass prism.
(b) A star appears slightly higher (above) than its actual position in the sky. Illustrate it with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer: (a)
(b) Light from a star is refracted as it leaves vacuum and enters the earth’s atmosphere. Air at higher altitudes is rarer and is denser nearer to the earth’s surface. Thus when light coming from the star comes down, the dense air bends the light more. Due to this refraction of star’s light, the star appears to be at a higher position.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question. A narrow beam PQ of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram.
(i) Write the name and cause of the phenomenon observed.
(ii) Where else in nature is this phenomenon observed?
(iii) Based on this observation, state the conclusion which can be drawn about the constituents of white light.

Answer: (i) The phenomenon of splitting of white light into seven colors on passing through a glass-prism is called dispersion of light. The dispersion of white light occurs because colors of white light travel at different speeds through the glass prism.
(ii) Formation of rainbow is an example of dispersion of white light in nature.
(iii) The formation of spectrum of seven colors shows that white light is made up of lights of seven different colors mixed together. That is, white light is a mixture of seven colors (or seven colored lights), i.e., red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.

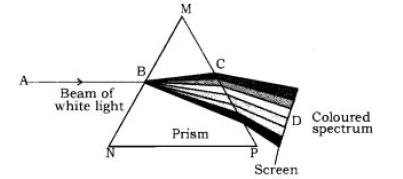
Question. State the cause of dispersion of white light passing through a glass prism. How did Newton show that white light of Sun contains seven colors using two identical glass prisms? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged together in inverted position with respect to each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the focus of the first prism.
Answer: White light is a mixture of lights of seven colors, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. The dispersion of white light occurs because colors of white light travel at different speeds through the glass prism. The amount of refraction depends on the speed of colored light in glass. When white light consisting of seven colors falls on a glass prism, each color in it is refracted by a different angle, with the result that seven colors are spread out to form a spectrum. The red light bends the least, while violet bends the most.
Newton’s experiment with two identical prisms:
* When a beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, a band of seven colors is formed on a white screen. This band of seven colors is called spectrum of white light.
* Newton showed that the seven colored lights of the spectrum can be recombined to give back white light.
* First he tried to split the colors of the spectrum of white light using a prism.
* He then placed a second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism. This allowed all the colors of the spectrum to pass through the second prism. He found a beam of white light emerging from the other side of the second prism.

Question. (a) Draw a ray diagram to explain the term angle of deviation.
(b) Why do the component colors of incident white light split into a spectrum while passing through a glass prism, explain.
(c) Draw a labeled ray diagram to show the formation of a rainbow.
Answer: (a) Angle of deviation is the angle between extended incident ray and extended emergent ray through a prism.
PQ = Incident Ray
RS = Emergent Ray
∠D = Angle of Deviation
(b) The incident white light splits into a seven colored spectrum as speed of different colored light waves is different when these pass through the prism.


We hope the above Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science


