Please refer to Life Processes Class 10 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 10. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 10 Science Life Processes Notes and Questions
Class 10 Science Life Processes MCQs
Question. Which of the following parts of a kidney contains the lowest concentration of urea ?
(a) Lop of Henle
(b) Branches of renal vein
(c) Bowman’s capsule
(d) Glomerulus
Answer
B
Question. Uriniferous tubules of a kidney are concerned with formation of
(a) glucose
(b) amino acids
(c) hormones
(d) urine
Answer
D
Question. Excretion is removal of
(a) CO2
(b) harmful and useless ingredients
(c) extra water
(d) metabolic wastes
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is used in measuring transpiration ?
(a) Photometer
(b) Cobalt chloride paper
(c) Bell – jar
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. Translocation of solutes primarily takes place through
(a) phloem
(b) xylem
(c) cortex
(d) pith.
Answer
A
Question. Muscle cells engaged in vigorous activity build up a high concentration of
(a) lactic acid
(b) pyruvic acid
(c) alcohol
(d) cholesterol
Answer
A
Question. Main function of kidney is
(a) passive absorption
(b) ultrafiltration
(c) selective reabsorption
(d) Both B and C
Answer
D
Question. Ammonia is converted into urea in
(a) kidney
(b) spleen
(c) liver
(d) nephron
Answer
C
Question. Function of loop of Henle is
(a) conservation of water
(b) formation of urine
(c) filtration of blood
(d) passage of urine
Answer
A
Question. Urea is transported through
(a) RBCs
(b) WBCs
(c) Plasma
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. Major function of contractive vacuole is
(a) excretion
(b) circulation
(c) osmoregulation
(d) all the above
Answer
C
Question. Which one is a accessory excretory organ
(a) Liver
(b) Stomach
(c) Intestine
(d) Heart
Answer
A
Question. The process of respiration is concerned with
(a) liberation of oxygen
(b) liberation of carbon dioxide
(c) liberation of energy
(d) intake of oxygen
Answer
C
Question. The common immediate source of energy for cellular activity is
(a) NAD
(b) ATP
(c) DNA
(d) RNA
Answer
B
Question. The tissue respiration refers to
(a) inspiration
(b) external respiration
(c) internal respiration
(d) expiration
Answer
C
Question. If the CO2 concentration in the blood increases, the rate of breathing will
(a) decrease
(b) stop
(c) increase
(d) have no effect
Answer
C
Question. Vocal cards occur in
(a) pharynx
(b) glottis
(c) bronchial tube
(d) larynx
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following gases makes the most stable combination with the hemoglobin of red blood cells.
(a) CO2
(b) CO
(c) O2
(d) N2
Answer
B
Question. Volume of air inspired or expired with each normal breath is called
(a) tidal volume
(b) inspiratory capacity
(c) total lung capacity
(d) residual volume
Answer
A
Question. Most of the carbon dioxide in the blood is carried in the form of
(a) carbonic acid
(b) bicarbonates
(c) carbaminohaemoglobin
(d) dissolved CO2
Answer
B
Question. Breathing rate in mammals in controlled by a part of the brain called the
(a) thalamus
(b) hypothalamus
(c) medulla oblongata
(d) cerebellum
Answer
C
Question. In anaerobic respiration
(a) O2 is taken in
(b) CO2 is taken in
(c) O2 is given out
(d) CO2 is given out
Answer
D
Question. Disease called pleurisy is due to
(a) inflammation of pleura
(b) inflammation of trachea
(c) inflammation of alveoli
(d) none of these above
Answer
A
Question. Leaves respire with the help of
(a) lenticles
(b) stomata
(c) plasmodesmata
(d) cuticle
Answer
B
Question. Correct statement is
(a) roots of plant respire through lenticles and stomata.
(b) stem of plant respire through lenticles
(c) both A and B are correct
(d) both A and B are incorrect
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristic of good respiratory surface ?
(a) Thin and moist
(b) Large surface area
(c) Close to oxygen and gas transport
(d) Thick and dry surface
Answer
D
Question. Respiration in yeast
(a) takes place in the presence of oxygen
(b) yields lactic acid and carbon dioxide
(c) in anaerobic and produces carbon dioxide
(d) takes place only in darkness
Answer
C
Question. In man, which of the following structures is analogous to the spiracles of cockroach ?
(a) Alveoli
(b) Lungs
(c) Bronchioles
(d) Nostrils
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following prevents collapsing of trachea ?
(a) Diaphragm
(b) Ribs
(c) Cartilaginous ring
(d) Muscles
Answer
C
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion(A) is followed by a statement of reason(R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason(R)are true and reason(R)is the correct explanation of assertion(A)
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason(R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason(R) is false
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R)is true
1. Assertion (A): The excretory unit of kidney is nephron.
Reason(R): It carries out filtration, selective absorption and tubular secretion to form urine in kidney.
Answer
A
2. Assertion (A): The oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is separate in the heart of mammals.
Reason(R): This allows efficient supply of oxygen to all tissues.
Answer
A
3. Assertion (A): Herbivores have larger small intestine as compared to carnivores.
Reason(R): Complete digestion of food takes places in small intestine.
Answer
B
Very short Answer Questions
Question. How is the wall of small intestine adapted for performing the function of absorption of food?
Ans. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption.
Question. Out of a goat and tiger, which one will have a longer small intestine? Justify your answer.
Ans. Goat because herbivores eating grass needs a longer small intestine to allow the cellulose to be digested.
Question. Bile juice does not have any digestive enzyme but still plays a significant role in the process of digestion. Justify the statement.
Ans. Bile juice makes the food alkaline for the action of Trypsin. Bile salts break the large globules of fat.
Question. In birds and mammals the left and right side of the heart is separated. Give reasons.
Ans. The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
Question. What is the role of acid in our stomach?
Ans. HCl of gastric juice disinfects the food and make the medium acidic for proper functioning of pepsin.
Question. Mention the respiratory unit of lungs and excretory unit of kidneys.
Ans. Respiratory unit of lungs-Alveoli
Excretory unit of kidneys-Nephrons
Question. Where does aerobic respiration occurs in a cell?
Ans. Aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria of the cell.
Short Answer Type Questions
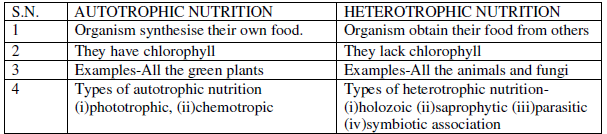
Question. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans.
Question. What is photosynthesis? Explain its mechanism.
Ans. Photosynthesis– A process in which green plants takes carbon dioxide and water and converts them into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
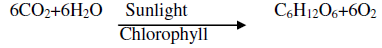
Mechanism:
(i)Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii)Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
(iii)Splitting of water molecules (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen.
(iv)Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrate.
Question. What is transpiration? List its two functions.
Ans.The loss of water in the form of vapour from aerial parts/leaves/stems is known as transpiration.
Functions:
(i)It helps in the absorption and upward movement of water.
(ii)Movement of dissolved minerals from root to leaves.
(iii)It helps in the temperature regulation or cooling of the plant.
Question. (i)Draw the diagram of cross section of a leaf and label the following parts:
(a)Cuticle (b) Chloroplast
(ii)A gas is released during photosynthesis. Name the gas and also state the way in which the gas is evolved.
(iii)In certain group of plants, stomata remain closed during day. How is food synthesized by such plants?
Also name them.
Ans.(i)

(ii)Oxygen gas is evolved during photosynthesis. Oxygen gas is evolved by splitting of water
2H2O → 2H2 + O2
(iii)They take take up CO2 at night through stomata, which open during night and produce an intermediate organic acid which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by chlorophyll during the day and breaks up to release of CO2 .The CO2 so produced internally is used in photosynthesis during day when stomata are closed. Example-desert pant
Question. (a)What is translocation? Why is it essential for plants?
(b)Where do the substances in plants reach as a result of translocation?
Ans. (a)Translocation is the process of movement of materials from leaves to all other parts of the plant body.
(b)As a result of translocation, the substances in plants reach to the storage organs of roots, fruits and seeds and to growing organs.
Question. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.

Question. Draw the diagram of alimentary canal of man and label it.

Question. How do carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human.
Ans. (i)Carbohydrates: -The human saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase which digests starch. In duodenum, pancreatic juice which contains digestive enzymes like pancreatic amylase breaks down the starch. It is digested in jejunum by intestinal juice.
(ii)Protein-In stomach, proteins are digested by gastric juice. The enzyme pepsin breaks down proteins into amino acid and in jejunum by intestinal juice which contain trypsin. It also convert protein into amino acid.
(iii)Fats-In duodenum and jejunum fats are digested by pancreatic juice aided by bile salts.
Question. How does aerobic respiration differs from anaerobic respiration?
Ans.

Question. Explain the three pathways of breakdown of glucose in living organisms.
Ans.
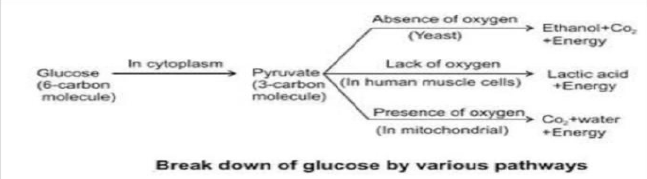
In the very first stage the Glucose which is a 6-carbon molecule is breaks into pyruvate which is a 3-carbon molecule in the cytoplasm. After that they are broken down by three different pathways to release energy.
(i)In the absence of oxygen in Yeast.
(ii)In the lack of oxygen in human muscle
(iii)In the presence of oxygen in mitochondria.
Question.Draw the diagram of human respiratory system and label its parts.
Ans.
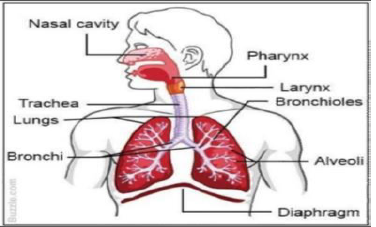
Question. List two types of the transport system in human being and write the functions of any one of these.
Ans.(i)Blood circulatory system (ii)Lymphatic system
Function of blood circulatory
(i)Transport of oxygen (ii)Transport of digested food (iii)Transport of carbon dioxide
(iv)Transport of nitrogenous waste (v)Transport of salts
Functions of lymphatic system
(i)Carries digested and absorbed fat.
(ii)Drains extra fluid from tissue back into the blood.
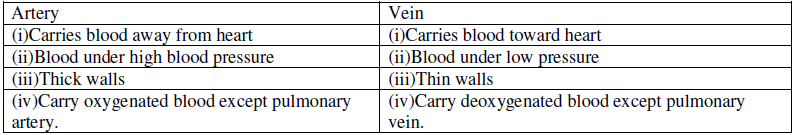
Question. Write three types of blood vessels. Give one important feature of each.
Ans.(i)Arteries-No valves, thick walled, carry oxygenated blood away from heart.
(ii)Veins-Presence of valves, thin walled, carry deoxygenated blood towards heart.
(iii)Capillaries-Very fine blood vessels, found in tissues, site for material exchange
Long Answer Type Questions
Question.(a)Mention any two components of blood.
(b)Trace the movement of oxygenated blood in the body.
(c)Write the function of valve present in between atria and ventricles.
(d) Differentiate between an artery and a vein.
Ans.(a)Plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
(b)Lungs → left side of the heart → aorta → body organs
(c)Valve prevents back flow of blood.
(d)
Question. (a)Draw a sectional view of the human heart and label on it Aorta, right ventricle, pulmonary vein, pulmonary artery
(b)Explain the process of double circulation.
Ans. (a)
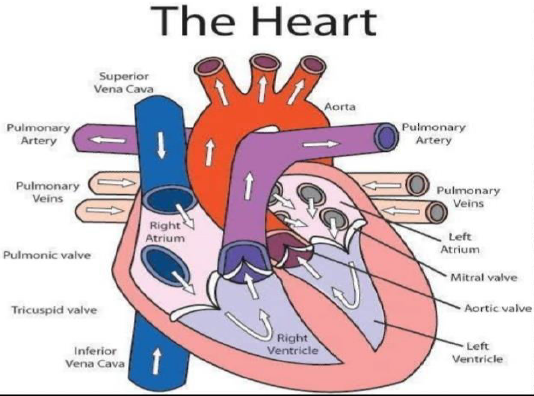
(b) In human beings, the blood goes through the heart twice during each cycle i.e. The blood passes through the human heart two times to supply once to the whole body.So,it is called Double circulation.
Importance: –
It is necessary for human being to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood because this makes their circulatory system more efficient and helps in maintaining constant body temperature.

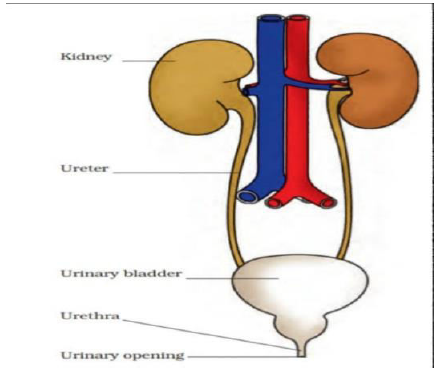
Question. (a)Define excretion.
(b)Name the basic filtration unit present in the kidney.
(c)Draw excretory system in human beings and label the following organs of excretory system which perform following functions:
(i) form urine
(ii) is a long tube which collects urine from kidney.
(iii) store urine until is passed out
Ans.(a)Excretion: Process involved in removal of nitrogenous/harmful metabolic waste from the body.
(b)Basic filtration unit present in the kidney is nephron.
(c)Diagram of human excretory system:
Question. (i)Draw a diagram of an excretory unit of a human kidney and label the following:
Bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus, Collecting duct, renal artery
(ii)Write the important function of the structural and functional unit of kidney.
(iii)Write any one function of an artificial kidney.
Ans. (i)
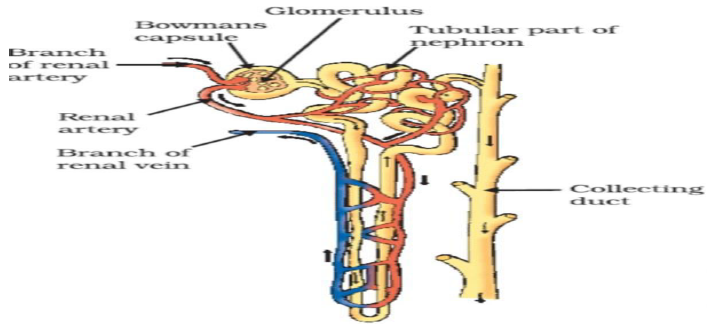
(ii) Function of nephron is filtration, re-absorption and secretion.
(iii) Function of artificial kidney:
Help to remove harmful wastes, extra salts and water. It controls blood pressure. Maintain the balance of sodium, potassium salts in a patient whose kidneys have failed.

We hope the above Life Processes Class 10 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science


