Please refer to Reproduction Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Reproduction Notes and Questions
Reproduction is a process by which every living organism produce an organism like their own.
• Types of reproduction :
(a) Asexual reproduction : In this type of reproduction only one parent organism either mother or father
produces new organism.
(b) Sexual reproduction : In this type of reproduction both parent are involved & produces new organisms.
• Asexual reproduction in unicellular organism :
1. Binary fission : During this process, two daughter organisms of equal sizes are formed from one parent
by the division of the parent body. This is the most common method of reproduction in algae, fungi and
bacteria (fig.).

Multiple fission: Sometimes the nucleus divides into many daughter nuclei. The daughter nuclei arrange
at the periphery of the parent cell, and a bit of cytoplasm around each daughter nuclei is present.
Nucleus develops an outer membrane. Finally, the multinucleated body divides into many daughter
cells. e.g. Blue green algae.

(2) Budding : In this type of reproduction, a small outgrowth appears on the body of the organism. This
outgrowth is called a bud. The buds grow and finally detach from the parent body and begin to live as
independent organisms.
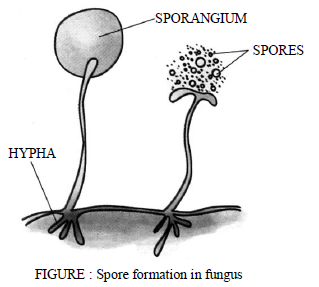
(3) Fragmentation : This takes place in algae like spirogyra and oscillatory. The filament of the alga
breaks into two or more pieces called fragments, and the process is known as fragmentation. Each
fragment the grows into a new plant.

(4) Spore formation : Some lower plants such as ferns, mosses, lichens and fungi reproduce through
spore formation under unfavourable conditions. Spores are tiny, microscopic bodies, which are covered
by hard protective coats. The protective coats enable them to tide over adverse environmental
conditions. When favourable conditions return, each spore gives rise to a new individual.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
When reproduction takes place only from the vegetative parts of plant known as vegetative reproduction.
(a) Natural vegetative propagation.
(b) Artificial vegetative propagation.
→ Natural vegetative propagation :
• Natural propagation by leaf : Vegetative propagation by leaves can be seen in very few plants like bryophyllum and begonia. In these plants buds are produced on leaf margins. These buds after falling on the ground grow into new plants.
• Natural propagation by stem : Underground stems are modified for storage of food. ?These
underground stems produce several new plants from their buds. Modified stems like tuber, bulb, rhizome and corm help the plants to multiply.
• Natural propagation by root : Roots also help in vegetative propagation. For example, sweet
potato and dahlia give rise to new plants from their fleshy roots. (figure)
→ Artificial vegetative propagation :
• Grafting : In this commonly practiced method a new variety is obtained from the mother plant
(figure). In this process a detached part of one plant is inserted into the stem or the root
system of another plant.

The short piece of detached shoot containing several buds is called scion. The lower portion of the plant that is fixed to the soil by its roots system is called the stock. They establish vascular connection with each other after a few days.
• Layering : In this method a young branch is bent towards the ground and covered with moist
soil. After some days, new roots develop from the covered part, which is in contact with the
soil. This is called a layer and the process is called layering. The branch is then separated from
the parent plant and allowed to grow into a new independent plant.

• Cutting : In this method a healthy young branch of a plant having leaf buds is cut out and
planted in moist soil (figure). The branch develops root and grows into a new plant. Bougainvillea,
sugarcane, rose and grapes are grown from cuttings.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
Flower is a reproductive part of plant. Which contain male & female sex organ & produce ovum & pollen
grain. A normal flower consists of four whorls namely sepals, petals, androecium and gynoecium (figure).
The androecium is the male reproductive part of the flower. Androecium may consist of one or more
tube-like stamens. Each stamen consists of thin stalk called filament and a two-lobed head called the
anther. Anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes. The pistil or gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower. Each pistil consist of stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules.

POLLINATION
Pollination is the process by which pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred to the
stigma of the same flower or another flower.
• Types of pollination :
There are two types of pollination which are described below :
• Self-Pollination or Autogamy :
It is the process of transfer of pollen from anther to the stigma of the same flower or to the stigma of
another flower of the same plant.

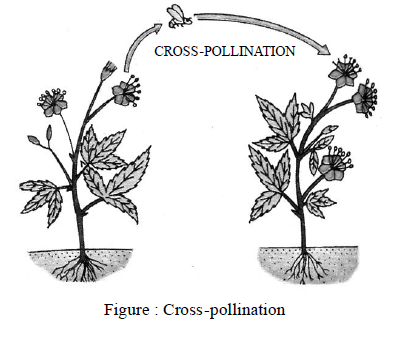
• Cross-pollination or Allogamy :
It is the process of transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower of another
plant of the same species or sometimes of very closely related species.
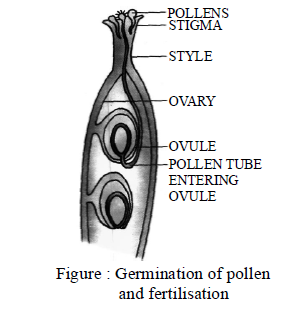
FERTILISATION
After successful pollination the stigma secretes nutrients for the lodged pollen grains. The pollen grains
absorb these nutrients and grow to form a thin tube called pollen tube. This grows into the stigma in
down the style (figure). It grows until it reaches the ovule and enters inside it. The pollen tube
contains two male gametes. After reaching the ovule, it releases the male gametes, one of which
fused with the egg to form the zygote. This process of fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete
is called fertilization. The zygote develops into an embryo.
FRUIT & SEED FORMATION
After fertilization the ovary grows into a fruit and the ovules inside it become seeds. The other parts of
the flower such as sepals, petals, and stamens fall off. A fruit is actually a biologically ripened ovary.
Olympiad Problems NCERT Class 7 Science Reproduction
Question: A method in which roots are initiated on the stem while still attached with the parent plant is called –
(A) grafting
(B) budding
(C) layering
(D) tissue culture
Answer:
layering
Question: Hydra reproduces by –
(A) budding
(B) spore formation
(C) binary fission
(D) fragmentation
Answer:
budding
Question: Pollen grains are produced in –
(A) anther
(B) filament
(C) stigma
(D) style
Answer:
anther
Question: Seeds in a matured ovary develop from –
(A) ovule
(B) stigma
(C) ovum
(D) pollen grains
Answer:
ovule
Question: Seeds and fruits dispersed by wind have –
(A) wings
(B) hairs
(C) censer mechanism
(D) all of these
Answer:
hairs
Question: Ferns, mosses, lichen and fungi reproduce through –
(A) spore formation
(B) binary fission
(C) budding
(D) fragmentation
Answer:
spore formation
Question: A plant can be grown from tissue-culture is –
(A) orchid
(B) pear
(C) grapevine
(D) cherry
Answer:
orchid
Question: Stigma, style and ovary are the parts of –
(A) androecium
(B) gynoecium
(C) anther
(D) sepals
Answer:
gynoecium
Question: Which does not belong to bisexual flower ?
(A) mustard
(B) rose
(C) petunia
(D) papaya
Answer:
papaya
MCQs for NCERT Class 7 Science Reproduction
Question: In which of the following plants vegetative reproduction takes place with the help of bulbils?
(A) Colocasia
(B) Zingiber
(C) Agave
(D) Vallisneria
Answer:
Agave
Question: Scion is a term in relation to
(A) layering
(B) cutting
(C) grafting
(D) micropropagation
Answer:
grafting
Question: Which of the following is propagated by means of cutting?
(A) Sugarcane
(B) Coffee
(C) Citrus
(D) All of these
Answer:
All of these
Question: Stem cuttings are commonly used for propagation in
(A) rubber
(B) mangoes
(C) sugarcane
(D) jasmine
Answer;
sugarcane
Question: A method in which roots are induced on the stem while it is still attached to the parent plant is called
(A) layering
(B) cutting
(C) grafting
(D) vivipary
Answer:
layering
Question: During grafting root stock is generally derived from a plant
(A) efficient in water and mineral absorption
(B) resistant to diseases
(C) that grows strong and healthy branches
(D) all of the above
Answer
all of the above
Question: What is parthenogenesis?
(A) Development of fruit without hormones
(B) Development of fruit without fertilisation
(C) Development of egg without fertilisation
(D) Development of embryo without fertilisation
Answer:
Development of egg without fertilisation
Question: What is micropropagation?
(A) Germination of seed with cotyledons above the soil
(B) A technique to obtain new plants by cultivating the cells or tissues in culture medium
(C) The mature stage of endosperm
(D) To manufacture hormones
Answer:
A technique to obtain new plants by cultivating the cells or tissues in culture medium
Question: Pollination is best defined as
(A) the transference of pollens from anthers to stigma
(B) the germination of pollen grains
(C) visiting of flowers by ants
(D) the growth of pollen tube in the ovule
Answer:
the transference of pollens from anthers to stigma
Question: Pollination is a characteristic of
(A) angiosperms
(B) pteridophytes
(C) bryophytes
(D) all of the above
Answer:
angiosperms
Question: Self-pollination means
(A) germination of pollens within the anther
(B) transference of pollens from anthers to the stigma within the same flower
(C) transference of pollens from one flower to another on the same plant
(D) presence of male and female sex organs in the same flower
Answer:
transference of pollens from anthers to the stigma within the same flower
Question: When pollen of a flower is transferred to the stigma of another flower of the same plant the pollination is
referred to as
(A) autogamy
(B) allogamy
(C) xenogamy
(D) geitonogamy
Answer:
geitonogamy
Question: Cross-pollination is advantageous because it results in
(A) formation of weaker progeny
(B) formation of better progeny
(C) formation of male offspring
(D) formation of female offspring
Answer:
formation of better progeny
Question: Fertilisation means
(A) transfer of male gamete to female gamete
(B) adhesion of male and female reproduction organs
(C) fusion of nuclei of male and female gametes
(D) the shedding of gametes from a reproductive organ
Answer:
fusion of nuclei of male and female gametes
Question: Which of the following event is NOT directly affected by light in a vegetable garden?
(A) Seed germination
(B) Food manufacture
(C) Fertilisation
(D) Flowering
Answer:
Fertilisation
Question: Fertilisation in which male gametes are carried through pollen tube is known as
(A) chalazogamy
(B) siphonogamy
(C) syngamy
(D) porogamy
Answer:
siphonogamy
Question: Double fertilisation is characteristic of
(A) angiosperms
(B) algae
(C) gymnosperms
(D) bryophytes
Answer:
angiosperms
Question: The group of petals is called:-
(A) sepals
(B) calyx
(C) root
(D) None of these
Answer:
None of these
Question: During grafting, the portion of plant that is grafted is called:-
(A) stock
(B) scion
(C) stalk
(D) stem
Answer:
scion
Question: In roses, the method commonly used to produce new plants is:-
(A) tissue culture
(B) cutting
(C) layering
(D) None of these
Answer:
cutting

We hope the above Reproduction Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


