Please refer to Crop Production & Management Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Crop Production & Management Notes and Questions
Introduction:
Food is the combination of various organic and inorganic substances which
is capable of providing,
• Energy for the various metabolic activities.
• Materials for repair / replacement of wornout tissues in the body.
• Materials for growth & reproduction.
• Regulatory substances, body secretions and metabolic activities, etc.
Sources of Food:
Classification of Crop Plants
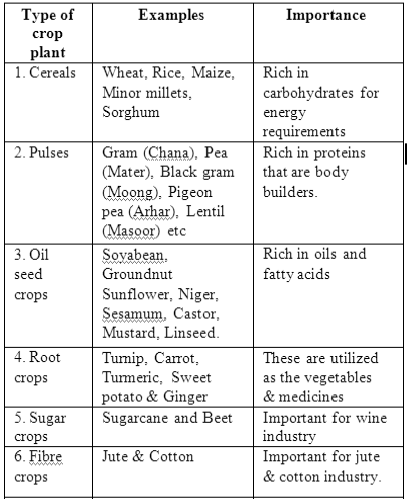
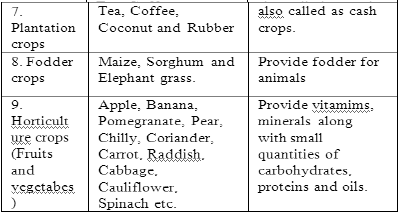
1. Agriculture:- Agre- Field. Culture- Cultivation
• It is the applied biological science which deal with the production of plants and
raising of livestock for human use is called agriculture.
• Involving soil cultivation.
• Crop Farming.
• Breeding and managment of crop and live stock.
Modern agriculture :
Modern agriculture is a combined effort of art, science and technology to provide food,
cloth and shelter to increasing human population, for improving the efficiency
of the agriculture process and contribute to increased output. These are as follows.
• Tools and machines are made and used.
• Building of dams and canals for irrigation.
• Development of new pest resistant and high yielding variety.
• Used fertilizer and pesticides for nutrition and protection of crop.
Crop:-
Plants of same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale known as crop.
Different types of crop require different climatic conditions. Crops are divided into two groups
based on growing season.
Kharif crop :
Sowing starts in summer or rainy season. They
are sown in June -July
Ex.- Rice, Cotton, Bajra, Jowar
Rabi crop :
Sowing starts in winter season They are
sown in October-November Ex.- Wheat,
Barley, Gram, Pea
Agricultural implements :
The tools which are used in cultivation of plants are known as agricultural implements.
Some of these tools are used manually whereas others are used with the help of some
animals like bullocks and camels. Now a d ayes t reactors and combine
harvesters help the farmers in their work
Agriculture practices:-
(1) Soil preparation:-
(a) Ploughing – by plough
(b) Levelling – by leveller.
(c)Manuring
(2) Sowing (3) Irrigation
(4) Weeding (5) Harvesting
(6) Threshing (7) Winnowing
(8) Storage.
(1) Soil preparation:
(a) Ploughing or Tilling – Process of loosening and turning of the soil is called ploughing or
tilling done by plough.
Advantages of ploughing:-
• It allows good root penetration so the plant is held firmly to the soil.
• It allows mixing of manure and fertilizer more uniformly.
• Roots are able to breathe more easily.
• Loosened soil promotes growth of worms and microbes which help to maintain the fertility of soil.
• Seeds are also able to germinate more easily.
Plough:- This is made of wood or iron and is drawn by a pair of bulls.It contains triangular
iron strip called ploughshare and main part of the plough is a long of wood called
ploughshaft. One end of the shaft is handle and other end is attached to a beam which is
placed on the bulls necks.
Hoe:- This is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod or wood or
iron. A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and work like a blade. It is
pulled by animals.
Cultivator:- Ploughing is done by tractor cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
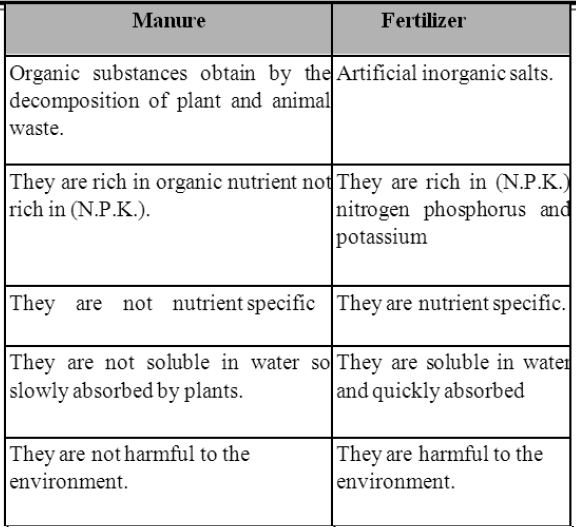
Manure or organic manure :
Organic substances are obtained from the decomposition of plant and animal wastes, which
added to soil in order to increase soil fertility, aeration and water holding capacity.
Types of manure :
(i) Farm yard manure : Consist of cattle dung, farm refuse, fallen leaves and wings.
(ii) Compost : Consist of rotten vegetable, sewage and sludge and animal refuse.
(iii) Green manure : These are fast growing herbaceous crops which are ploughed down and mixed with the soil, while still green.
Advantages of manure :
• Increase organic matter in soil and have low cost.
• Reduced soil erosion.
• Increase soil fertility, water holding capacity and aeration.
• Improve the texture of soil.
• Increase the number of friendly microbes.
Disadvantages of manure :
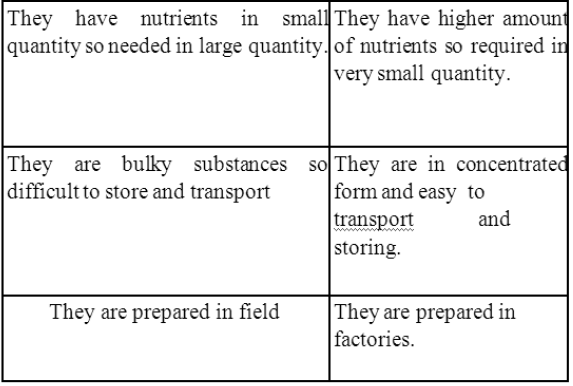
• They have low amount of nutrient.
• Manure are bulky and not easy to be absorbed.
Fertilizer :
These are commerically manufactured inorganic salts containing one or more essential plant
nutrients like N, P, K, which are used to increase soil fertility.
Advantages of fertilizers :
• They are nutrient specific and require in small amount.
• They are water soluble and absorbed by the plant easily.
Disadvantages of fertilizers:-
Fertilizers can change the chemical composition of soil and cause water pollution
(eutrophication).
Differences between manure and fertilizer:-
Sowing :
Process by which seeds are sown in the soil known as sowing. Before sowing good
quality (healthy and good variety) seeds are selected.
Sowing can be done by :
(i) Broad casting:- Seeds are scattered by hand or manually.
(ii) Traditional tool:- The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is shaped like a
funnel. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having
sharp ends. These ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there.
(iii) Seed drill- The other method is to use a seed drill. A simple seed drill consists of an iron
tube with a funnel at the top attached to the plough. Seeds are introduced into the
funnel opening and then released into the soil furrows made by a plough. By this method
seeds are sown at the correct depth and interval. It saves time and labour also.
Precaution during sowing seed.
è Use good quality, healthy and disease free seeds.
è Distance should be proper.
è Should be enough water in the soil.
Transplantation :
There are certain crops like paddy and some vegetables for which seeds are not directly
sown in the field. They are first germinated in nurseries and then the seedlings are
transferred to the main field. This process is known as transplantation.
Irrigation :
Supply of water to crop at different intervals is called irrigation. Sources of irrigation:- Well,
tube well, ponds, lakes, river, canal and dams.
Methods of irrigation :
Traditional methods –
(i) Moat (pulley system)
(ii) Chain pump
(iii) Dhekli
(iv) Rahat (lever system)
• These are cheaper and less efficient methods.
• Cattle and human labour is used
Modern methods of irrigation :
(i) Sprinkler system:-
• Useful for sandy soil and uneven land.
• Efficient system in the canal irrigated area of Haryana, Rajasthan, M.P.
• Spread water uniformly over plant and field.
• In this system the perpendicular pipes having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to main
line at regular intervals.
(ii) Drip system:- Boon in poor water region.
• Provide water to plants drop by drop at the root.
• Water is not wasted at all.
• Best irrigation technique for fruit crop, garden and trees.
Advantages of irrigation :
• Maintain the moisture of soil.
• Nutrient dissolved in water get transported to each part of plant.
Disadvantages of Excessive or Untimely Irrigation:-
All crop plants require water at different stages of their development. Plants require the
right amount of water at the right time.
• Excess of water (waterlogging) in the soil inhibits the process of germination of the seeds
as the seeds do not get sufficient air to respire.
• Roots do not grow well if there is waterlogging in the field.
Ÿ If the crop is irrigated when fully mature, it gets damaged. The plants, which are unable to resist
the strong winds, fall down affecting the yield. The falling down of the crop due to untimely
irrigation is termed as lodging. The excess from the field then has to be drained of immediately.
Crop protection management :
It includes eradication of pests, pathogens, weeds and other organisms that is
harmful to the crop plants.
Weeding :
Removal of weeds or desirable plants is called weeding.
(a) Mechanical control- It can be done by ploughing, burning and cutting of weeds before
they produce flower and seeds.
(b) Chemical control- By Spraying weedicides.
Biological control- By living organisms to destroy weeds. Cassia plant prevents
the growth of Parthenium weed. Herbivorous fish (Carps) feed on aquatic weeds (Hydrilla).
Cochineal insect used to remove opuntia.
Advantage :
• It does not cause pollution.
• Organisms are harmless to the main crop.
Pest- Organisms which damage or destroy cultivated plants or plant product. Ex. Insect,
Rats, Mites, Weeds, Fungi etc.
Pathogen- Disease causing organism. Ex. Bacteria, Fungi and Virus etc.
Weeds- Undersirable plant grow naturally. Ex.
Parthenium.
Pesticides or Biocides :
Chemical substances which are used to kill, control or repel pest.
Disadvantages of using pesticide :
Spray can affect wild life in a particular area. They can
enter the food chain. Water pollution.
Preventive measures avoiding use of pesticides – è
Crop rotation and multiple cropping.
• Use of pest and disease resistant hybrid varieties of crop plant.
• Sowing healthy seeds and summer ploughing.
• Selection of optimum time of cropping.
Harvesting:- The cutting of crop after its maturation called Harvesting, can done manually by
sickle or by a machine called harvester.
Threshing:- The process of beating out the grain from the crop is called threshing. A
combine machine can harvest and thresh.
Winnowing:- The process of separating the ch aff f r om t h e gr ain i s call ed
Storage:- There are two types of food materials perishable and non- perishable.
1. Perishable food materials:- Perishable food materials are those which get spoiled easily
when kept for sometime at room temperature. For example, vegetables, fruits, fish, meat
and milk.
2. Non- perishable food materials:- Non- perishable food materials are those which do not
get spoiled even kept for a long time at room temperature. For example, wheat flour, food,
grains, spices and sugar
Mode of storage :
There are two different modes of storage: dry storage and cold storage.
Dry storage :
• This method is used for storage of non- perishable food materials, Foodgrains are
dried in the sun to bring down the moisture content below 14% weight to prevent the
attack by pests. The dried foodgrains are then weighed, packed in gunny bags and transferred to properly ventilated halls called godowns or granaries. The gunny bags in the godown should be kept about 60 to 70 cm away from the walls and on wooden platforms about 10 to 15 cm above the ground. The godown must be
kept pests free by spraying various pesticides from time to time.Farmers store
foodgrains for their personal use in metal bins. Dried neem leaves are added in
the bin to prevent pest infestation.
• Grain silor are specially designed tall cylindrical structures for bulk storage of foodgrains. These
silor can store different stocks of foodgrains at different levels. The required foodgrain can
be taken out from the openings provided in the silor.
• Granaries and silor should be inspected from time to time to check for infestation of any kind. In
our country food grains are stored in large godowns by agencies like
Food Corporation of India, State Warehousing Corporation, etc.
Cold storage :
This method is used for storage of perishable food materials. These food material have very
short shelf- life so that these are usually stored at low temperature. Icebox fish etc. On commercial scale, the perishable food materials are stored in either a deep freezer or a cold storage.
Advantages of Food Storage :
• It prevents the food from being spoiled by the action of enzymes and microorganisms.
• It increases the storage period of food materials.
• It helps in the availability of season fruits and vegetables round the year.
• It makes the transportation of food materials easier.
• It helps to maintain prices in the market.
• It helps in maintaining buffer stock to meet any emergency in the country.
Precautions :
• They should be safe from moisture insect, rats, and microorganism.
• Grains are properly dried in the sun.
• Store grains in jute bags or metallic bins.
• Store in silos, granaries and godown with chemical treatment.
• Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains.
Cropping patterns :
Different ways of growing crops can be used to give maximum benefit.
(a) Mixed cropping- Growing two or more types of crop on same field. Products and wastes
from one crop can stimulate the growth of other crop in it.
Ex. Wheat – Gram, Sunflower – Groundnut Ragi –
Gram, Cotton crop – Groundnut.
(b) Intercropping:- Two or more crops grown in a definite row pattern is called intercropping.
(c) Crop rotation:- Process in which different crops are grown alternately in the same field.
Ex. Wheat – Gram
Green revolution :
Yield of crop per hectare has greatly increased due to the use of various improved techniques of
agriculture and better irrigation facilities.
• Developed new varieties of rice, wheat and maize that have increase food production of India.
• Father of green revolution in India – Dr. M.S. Swaminathan. (Produce Sharbati sonara variety of wheat)
Methods for the genetic improvement of crop plants:-
Plant breeding :
Branch of botany which deals with improvement in heredity of crop and production of new varieties.
Aim of plant breeding:-
• Increase in yield of seed, fibre and oil etc.
• Resistance to disease, pest, drought, frost and heat.
• Adaptibility to wider range of conditions.
• Change in maturity behaviour.
(i ) Selection- Economic plants having best desirable characters.
(ii) Hybridization- Cross breed of two genetically dissimilar varieties of crop plant
Hybridization may be :
• Inter specific hybridization- Between two different species. Ÿ Inter
generic hybridization – Between two different genera. Ex. Rabbage =
Radish + Cabbage
Triticale = Secale + Triticum Pomato
= Tomato + Potato
Animal husbandry:-
The branch of agriculture which deals with the management, breeding, feeding, weeding and
care of domestic animals is called animal husbandry. Important components of animal husbandry
are as follows:
• Proper feeding and clean drinking water.
• Clean and ventilated shelter.
• Prevention and care of animal diseases from spreading.
• Proper breeding of animals.Animals that provide food for human consumption may be listed as:
Dairy animals :
They include animals that provide milk e.g. cow, buffalo, goat, camel etc. India has the largest
population of milk producing animals but the total quality of milk produced by them used to be
comparatively low as compared to some other countries. But in recent years, with the efforts
of National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), it has greatly increased.
Milk is a highly nutritious food. It contains nearly all the nutrients required by us and is
called as complete food. Cow’s milk contains 3.6 % fat, 4% protien, 4.5 % sugar, 0.70 %
minerals and 87.20 % water. Milk is mostly obtained from cows and buffaloes.In order to
get more milk, the cows and buffaloes have been brought from other countries. They are
called exotic breeds while Indian breeds are called indigenous breeds. Efforts are being
made to produce better breeds of cows and buffaloes which produce more milk.
Poultry animals :
Eggs and meat are obtained from hen, duck and turkey. Over the year, the demand of eggs
and meat has increased considerably. Hence efforts are being made to improve the egg and
meat production.
Fish farming :
Fish and other varieties of sea food constitute a good source of nutritious food. The meat of
fish contains fat 2.6%, protien 19%, minerals 1.3% and water 77.20%. Fish provide nutritious
food, oil, fertilizers and many other useful products. The term fisheries includes fish and all
other edible aquatic animals like crabs, shrimps, lobsters etc.
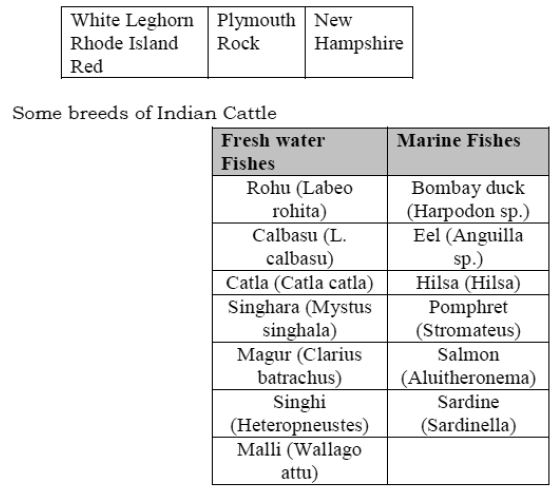
Both fresh water and marine (sea water) fish are used as food. Some fresh water fish are
catla, rohu singhara, calbasu, malli, magur etc. Some popular sea water fish are hisla,
pomfret and Bombay duck.
Meat providing live stock:- The main meat providing animals are goat, sheep, pig and
broilers.Goat’s meat is in great demand.
Honey bees:- Honey bees produce honey f r om t he n ectar of f l ower s. I ts constituents
are water, sugar, minerals and enzymes. Honey is used in various medicines. Rearing of
honey bees on a large scale is known as apiculture. Honey is highly nutritious product.
THE REVOLUTIONS :
1. Green revolution:- Production of good quality grains (wheat etc.) in the country to make it self sufficient.
2. Silver revolution:- Production of eggs by using high yielding breeds of hens.
3. White revolution:- For the enhancement of production of milk.
4. Blue revolution:- For the production of fish and food from water resources.
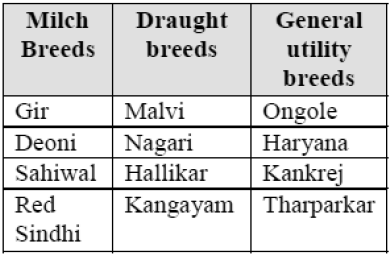
Some breeds of Indian Cattle
Some exotic breeds of Fowl
Major Animal Diseases :
Cattle Diseases

F Special Points:-
1 Vermicompost:- Vermicompost is the product of composting the organic matter with the
help of worms. Ex. Earthworm.
2. Eutrophication:- Excessive growth of algae (water bloom) due to the high
concentration of N.P.K. fertilizers in water is known as Eutrophication.
3. Buffer stock:- Grains are stocked for emergencies or buffer stock is the surplus stock of
grains which is preserved for times like drought and floods.
4. Organic farming:- Organic farming is a farming system with minimal or no use of
chemicals or fertilizers , pesticides, weedicides and maximum input of organic manure,
farm waste, biofertilizers, biopesticides like neem leaves or turmeric and healthy cropping
systems like crop rotation, inter cropping.
5. Macronutrients:- Essential elements which are utililzed by the plants in relatively large
quantities are called macronutrients or major nutrients. Macronutrients include Nitrogen,
Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium and Sulphur. Among them Nitrogen, Phosphorus
and Potassium are required in more amount, thus they are called primary elements.
Micronutrients:- These elements are needed by plants in a very small quantity (or traces)
and are called micronutrients or minor nutrients. For example Iron, Manganese, Boron,
Zinc, Copper, Molybdenum and Chlorine. Though micronutrients are needed in small
quantities as compared to macronutrients but both are equally important and essential
for the growth, development and maintenance of plants

MCQs for NCERT Class 7 Science Crop Production & Management
Question: Horticulture deals with –
(A) Production of crops
(B) Breeding of animals
(C) Study of soil
(D) Production of fruits and vegetables.
Answer:
Production of fruits and vegetables.
Question: Which one of the following is not true about ploughing –
(A) Loosens the soil
(B) Aerates the soil
(C) Makes the soil hard
(D) Allows easy penetration of roots into the soil
Answer:
Makes the soil hard
Question: Separating the grain from chaff is called –
(A) Winnowing
(B)Hybridisation
(C) Threshing
(D) Harvesting
Answer:
Winnowing
Question: Organic substances obtained from the decomposition of dead plants and animals wastes
are called-
(A) Fertiliser
(B) NPK
(C) Herbicide
(D) Manure
Answer:
Manure
Question: Biological methods of pest control involve-
(A) Spraying chemical to kill plants
(B) Killing pests by using other
(C) Spraying DDT
(D) Weeding
Answer:
Killing pests by using other
Question: Which one of the following is not a method to maintain the fertility of soil.
(A)Crop rotation
(B)Multiple cropping
(C) Fallow method
(D) Ploughing
Answer:
Ploughing
Question: Which one of the following can be used to prevent the disease called rust in wheat?
(A) An insecticide
(B) A rodenticide
(C) A fungicide
(D) A herbicide
Answer:
A fungicide
Question: Which of the following machines would you used to harvest a crop as well as to beat out
the grain from the chaff ?
(A)Mechanical harvester
(B) Combine
(C) Thresher
(D) Harrow
Answer:
Combine
Question: Denitrifying bacteria give out –
(A)Carbon
(B) Nitrogen
(C) Oxygen
(D) Hydrogen
Answer:
Nitrogen
Question: Plants get their nitrogen from the soil as –
(A)Nitrates
(B) Nitrogen dioxide
(C) Nitrogen oxide
(D) Nitric acid
Answer:
Nitrates
Question: First cultivated crop plants were-
(A)Cereal crop
(B) Pulses
(C) Fodder crop
(D) Fibre crop
Answer;
Cereal crop
Question: Transplantation is –
(A) Process of scattering the seed.
(B) Process of loosening and turning of soil
(C) Process of shifting of tiny sapling from the nursery to a field
(D) None of these
Answer:
Process of shifting of tiny sapling from the nursery to a field
Question: Which preventive measures avoid use of pesticides-
(A)Crop rotation (B) Use pest resistant varieties of crop plant
(C) Summer ploughing (D) All of these
Answer:
All of these
Question: Chemical substances which are used to kill insects –
(A) Fungicide
(B) Insecticide
(C) Weedicide
(D) All of these
Answer:
Insecticide
Question: Process of cutting of crop after its maturation-
(A) Threshing
(B) Harvesting
(C) Winnowing
(D) None of these
Answer:
Harvesting
Question: Transfer of seedlings from the nurseries to the main field is termed as –
(A) Sowing
(B) Weeding
(C) Transplantation
(D) Ploughing
Answer:
Transplantation
Question: The unwanted wild plants growing along with the crop plants are called –
(A) Seedlings
(B) Weeds
(C) Minor crops
(D) Grasses
Answer:
Weeds
Question: Vermicomposting involves –
(A)Cockroach
(B) Earthworm
(C) Leech
(D) Roundworm
Answer:
Earthworm
Question: Weedicides among the following are –
(A) 2, 4-D, Nitrofen, Atrazine
(B) Atrazine, BHC, Pyrethrum
(C) Pyrethrum, EDB, Methyl bromide
(D) 2. 4-D, BHC, EDB
Answer:
2, 4-D, Nitrofen, Atrazine
Question: Which one of the following does not use plant diseases.
(A) Viruses
(B) Bacteria
(C) Fungi
(D) Protozoa
Answer:
Protozoa
Question: Which one of the following includes only macronutrients?
(A) C, N, Ca
(B) H, Fe, P
(C) O, K, Cl
(D) K, S, Zn
Answer:
C, N, Ca
Question: The unwanted wild plants growing along with the crop plants are called
(A)weeds
(B) seedlings
(C) minor crops
(D) grasses
Answer:
weeds
Question: Damp grains in storage gets heated due to
(A) infestation by insects
(B) decrease in humidity
(C) decrease in atmospheric pressure
(D) high moisture content and growth of moulds
Answer:
high moisture content and growth of moulds
Question: Green manuring refers to
(A) adding green leaves to the soil
(B) growing of young and green crops of leguminous plants along with non leguminous plants
(C) addition of decomposed organic matter to soil
(D) none
Answer:
growing of young and green crops of leguminous plants along with non leguminous plants
Question: Improved storage structure includes
(A) grain silos
(B) pusa bin
(C) pusa kothar
(D) all of these
Answer:
all of these
Question: Which one of the following does not cause plant diseases?
(A) Viruses
(B) Bacteria
(C) Protozoa
(D) Fungi
Answer:
Protozoa
Question: EDB is a very effective
(A) rodent bait
(B) spraying insecticide
(C) fumigant for killing insects
(D) preservative of food grains
Answer:
fumigant for killing insects
Question: Dalapon is used to kill
(A)weeds
(B) Insects
(C) pests
(D) rodents
Answer:
weeds
Question: Ditches made between the two rows of a crop are
(A) furrows
(B) canals
(C) lines
(D) none
Answer:
furrows
Question: Which one of the following is a weed?
(A)wheat
(B) Chenopodium
(C) maize
(D) rice
Answer:
Chenopodium
Question: Pullorum is caused due to –
(A) Pasturella
(B) Mycoplasma
(C) Salmonella
(D) Spirochaete
Answer:
Salmonella
Question: Murrah is a high- yeilding breed of
(A) cow
(B) hen
(C) buffalo
(D) sheep
Answer:
buffalo
Question: Catla and rhou are examples of
(A)marine fish
(B) freshwater fish
(C) brackish water
(D) none of these
Answer:
freshwater fish
Question: The production and managment of fish is called
(A) aquaculture
(B) breeding
(C) pisciculture
(D) insemination
Answer:
pisciculture
Question: White revolution is related to the increase in the production of
(A) egg
(B) milk
(C) meat
(D) wool
Answer:
milk
Question: Silver revolution is related to the increase in the production of
(A) egg
(B) milk
(C) meat
(D) grains
Answer:
egg
Question: The process of of cross- breeding two individuals of different varieties is
(A) artificial insemination
(B) feeding
(C) hybridization
(D) none of these
Answer:
hybridization
Question: Buffalo’s milk does not contain
(A) vitamin C
(B) vitamin E
(C) protein
(D) carbohydrate
Answer:
vitamin C
Question: One of the following is a disease of poultry:
(A) Anthrax
(B) Pebrine disease
(C) Ranikhet disease
(D) Foot and mouth disease
Answer:
Ranikhet disease
Question: Bombay duck is :
(A)Hilsa ilisha
(B)Harpodpn neherius
(C) Pediceps ruficolis
(D) Coreochromis mossambicus
Answer:
Harpodpn neherius
Question: Jaffrabadi is a breed of :
(A) Sheep
(B) Cattle
(C) Horse
(D) Buffalo
Answer:
Buffalo
Question: Pashmina is obtained from a variety of :
(A) Sheep
(B) Goat
(C) Yak
(D) Rabbit
Question: Which of the following is popularly called ‘Ship of the desert’
(A) Yak
(B) Camel
(C) Donkey
(D) Horse
Answer:
Camel
Question: Lohi is a breed of
(A)Goat
(B) Sheep
(C) Horse
(D) Buffalo
Answer:
Sheep
Question: Fish liver – oil is rich in vitamins
(A) A and B
(B) B and C
(C) A and E
(D) A and D
Answer:
A and D
Question: The young chicken raised specially for meat are called
(A)Hen
(B) Broilers
(C) Pullets
(D) Ducklings
Answer:
Broilers
Question: Ranikhet disease is associated with
(A) Fishes
(B) Hens
(C) Pigs
(D) Honeybees
Answer:
Hens
Question: Name of freshwater edible fish
(A)Hilsa
(B) Pomphret
(C) Calbasu
(D) Bombay duck
Answer:
Calbasu
Question: National Dairy Research Institute is situtated in
(A) Lucknow
(B) Patna
(C) karnal
(D) Ludhiana
Answer:
karnal

We hope the above Crop Production & Management Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


