Please refer to Transportation Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Transportation Notes and Questions
Plants & animals both required food for; air & water for the maintenance & breeding of a cell. Each has to be supplied to the cell of the body in a right quantity .
The transport of material in plants is carried out by the vascular tissue.
Vascular Tissue :
There are 2 types of vascular tissues found in plants
* Xylem : Xylem transport water & nutrient upwards from the roots to the leave. Evaporation of water from the leaves during transpiration produces a pulling force causing water to move up
* Phloem : It carry the food prepared by the leaves during photosynthesis downward to all parts of the plants.
Transportation of water, minerals & food :
* The roots have root hairs which increase the surface area of the root for absorption of water & minerals dissolved in water. The root hair come in contact with water present between soil particles.

Traspiration pulls :
* The water move from the root hair to the xylem in the root. The absorbed water then moves up the stem through the xylem by the force developed in the leaves by the transpiration, called transpiration pull.
Ascent of sap :
* The fluid containing water & dissolved nutrient is called sap. The movement of sap through the xylem is called ascent of sap
Translocation :
* The food is transported from the leaves to other parts of the plant, called translocation.
EXCRETION IN PLANT
* Plants have no special organs for excretion. The excess amount of CO2 & water removed out through stomata also from the outer surface of stem, leave, fruit etc.
* Some waste products are colleced in vacuoles in the leaves & bark of trees & excrete them by shedding the leaves & barks
* Some waste products which are harmless, stored inside the plant body. Rubber raphides are examples of such products.
TRANSPIRATION
The process of loss of water in the form of vapours through the aerial parts of the plant is called transpiration.

TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS
In higher animals, digested food, gases & waste material are carried by blood. Blood flows through a network of tubes, which are called blood vessles & form a system known as circulatory system.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
It consist of heart, blood vessels & the blood.
Heart :
* It is a muscular organ, which pumps blood around the blood vessels.
* It has four chambers viz left auricle, left ventricle, right auricle and right ventricle.
* Ventricles are the two lower chambers. The left ventricle receives blood from the left auricle and pumps up into aorta. Aorta is the largest artery in the body.
* The right ventricle receives blood from the right auricle and pumps it through pulmonary trunk of the lungs.
* The four chamber open and close about 100000 times a day.
* Heartbeat that we can hear is due to contraction and relaxation of heart muscles or cardiac muscles. Heart in a healthy body beats around 72 times in a minute.
* Contraction is held in auricles and relaxation is done in ventricles.
* Contraction of cardiac muscles is called systole and relaxation of cardiac muscle is called diastole.
* During diastole, heart receives blood and during systole, ventricles contract to pump blood into blood vessels.
* Sound of heartbeat is called ‘Lub-dub’ sound. ‘Lub’ is due to contraction of ventricles and ‘dub’ is due to closer of auricle valves.
* The heartbeat is measured by an instrument called ‘stethoscope’. A device makes the sound of heartbeat large. Noting of pulse rate is noting the number of times heart beats in a minute.
Blood vessels :
* These are blood-filled tubes.
* Arteries, veins and capillaries called blood vessels.

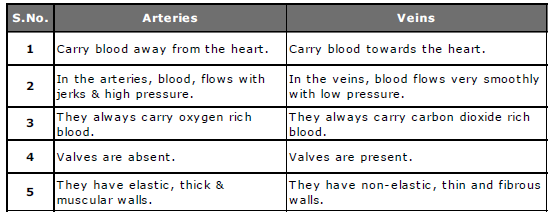
Arteries :
* Arteries are thick walled blood vessels, making up the arterial system and carrying blood away from the heart.
* Smaller arteries are called arterioles.
* Arterioles are branched off from arteries.
* Except in the pulmonary arteries, the blood contains oxygen.
* In all arteries, blood carries dissolved food and waste, brought into the heart by veins and is then transferred to arteries.
* Arteries carry the food to the cells and waste to the kidneys.
Veins :
* Veins are wide, thick walled, blood vessels.
* Veins make the venous system and carries blood back to the heart.
* Small veins are called venules.
* Veins contain valves to stop blood flowing backwards due to gravity and are formed of merging venules
* The blood in the veins leading from the digestive system and liver also carries dissolved food. This is transferred to the arteries in the heart.
Capillaries :
* Narrow, thin walled blood vessels branching off arterioles to form a complex network is called capillaries.
* Dissolved food and oxygen pass out through the walls of capillaries to the body cells and carbon dioxide and waste pass in
* The capillaries of the digestive organs and liver also pick up food
* Finally, capillaries join up to form small veins called venules
Blood :
* It is a connective tissue in fluid form
* An adult human has around 5.5 litres of blood
* A red fluid flows in the body
* It supplies food and oxygen to every body cell
* It removes wastes from the cells
* It regulates body temperature
* It protects against infection
CONSTITUENT OF BLOOD
RBC (Red Blood Corpuscles) :
* This is also called erythrocytes.
* RBC is a red disc shaped cells with no nuclei.
* They are made in the bone marrow and contain haemoglobin (an iron compound that gives blood a dark red colour).
* RBC combines with oxygen to form oxy-haemoglobin and the blood becomes bright red.
* The red cells pass the oxygen to the body cells by the process of diffusion and then returns to the – lungs with haemoglobin.
WBC (White Blood Corpuscles) :
* This is also called leucocytes.
* WBC is large, opaque blood cells, which helps in body defence.
* WBC makes antibodies. Antibodies produce antigens, which combat against any bacterial or viral infection. Antigens are mostly protein.
Plasma :
* It is a pale liquid with 90% water in it.
* Plasma contains the blood cells.
* Plasma carries dissolved food for the body cells, waste matter, and carbon dioxide secreted by them.
Platelets :
* It is also called thrombocytes.
* It is a very small, disc shaped bodies with no nuclei.
* It is made in the bone marrow.
* They gather particularly in an injured area, where they are important in clotting the blood.
REMOVAL OF WASTE
The process of removing waste from the body is called excretion Several organs of body is involved in the process of excretion –
* The waste generated in the process of digestion is expelled from the large intestine through anus.
* Carbon dioxide produced in the process of respiration is expelled from the lungs through the nostrils.
EXCRETION IN HUMANS
Chemical waste like urea are excreted by urinary system & skin.The excretory system in human beings consists of the following organs:
– A pair of kidneys
– A pair of ureters
– The urinary bladder
– Urethra
Urinary system or Excretory system :

* Kidneys :
In our body there is a pair of kidneys located in the abdomen, one each on either side of the vertebral column. Each kidney is brick red in colour and bean-shaped. It weighs about 150 g and is about 12 cm in length, 6 cm in width and 3 cm in thickness
* Uterers :
The ureters are two thin-walled, urine carrying ducts. A ureter originates from each kidney and is about 30 cm in length. The ureters run downward and open into the urinary bladder
* Urinary Bladder :
It is a bag-like structure in which urine is stored. Its size and position varies with the amount of urine it contains.
* Urethra :
The urethra is the duct which finally discharges urine from the body
Function of Kidney
* They filter wastes from the blood
* They help in the formation of urine
* They help in eliminating harmful substances from the body.
* They maintain the water and mineral balance in the body.
Skin :

* Skin is the outer body covering of human body. It is made up of several tissue layers cushioned by fats underneath.
* Skin has many functions. Skin provides stimulation, protects against infection, prevents from drying out, regulates body temperature, stores fat, makes vitamin D, and above all excretes waste such as sweat.
Olympiad Problems NCERT Class 7 Transportation
Question. The process by which a plant loses water through the stomata is called –
(A) Excretion
(B) Transpiration
(C) Respiration
(D) Sweating
Answer
B
Question. Urea is a waste produced in the process of the breaking down of –
(A) Protein
(B) Fats
(C) Carbohydrate
(D) Sugar
Answer
A
Question. The smallest functional unit of kidney is –
(A) Nephron
(B) Capillary
(C) Urethra
(D) Ureter
Answer
A
Question. Which component of blood helps in clotting ?
(A) RBC
(B) WBC
(C) Platelets
(D) Plasma
Answer
C
Question. The opening of urinary bladder is known as –
(A) Nephron
(B) Urethra
(C) Ureter
(D) Nephridia
Answer
B
Question. The cause of wilting of plant is –
(A) More absorption
(B) More transpiration
(C) Low respiration
(D) None
Answer
B
Question. Blood from the lungs enter the heart through the –
(A) Pulmonary artery
(B) Arota
(C) Pulmonary vein
(D) Venacava
Answer
C
Question. Pumping station of blood is –
(A) Heart
(B) Auricle
(C) Blood vessel
(D) Ventricle
Answer
A
Question. Bean shaped excretory organ of human is –
(A) Kidney
(B) Urethra
(C) Ureter
(D) Urinary bladder
Answer
A
Question. It transport the water & minerals from root to leaves in plants –
(A) Xylem
(B) Cambium
(C) Phloem
(D) Stomata
Answer
A
Question. In plants excess amount of carbon dioxide ascaps through the –
(A) Stomata
(B) Phloem
(C) Xylem
(D) Cambium
Answer
A
MCQs for NCERT Class 7 Science Transportation
Question. Water will be absorbed by root hairs when
(A) concentration of solutes in the cell sap is high
(B) plant is rapidly respiring
(C) they are separated from soil by a permeable membrane
(D) concentration of salts in the soil is high
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is connected with transport of water in plants?
(A) Phloem
(B) Xylem
(C) Epidermis
(D) Cambium
Answer
B
Question. The transpiration in plants will be lowest
(A) when there is high humidity in the atmosphere
(B) there is excess of water in the cell
(C) environmental conditions are very dry
(D) high wind velocity
Answer
A
Question. Rate of transpiration in a dorsi ventral leaf is
(A) greater at the upper surface
(B) greater at the lower surface
(C) equal at both the surfaces
(D) none of the above
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following processes keeps plant cool?
(A) Transpiration
(B) Guttation
(C) Photosynthesis
(D) Translocation
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is the most common type of transpiration?
(A) Stomatal
(B) Lenticular
(C) Foliar
(D) Cuticular
Answer
A
Question. The process of the escape of liquid from the tip of uninjured leaf or through hydathodes is called
(A) transpiration
(B) guttation
(C) evapo-transpiration
(D) evaporation
Answer
B
Question. Pressure exerted in the tracheary elements of a xylem as a result of metabolic activity of roots which forces the water into xylem vessel and upwards into the stem for a certain height is
(A) osmotic pressure
(B) root pressure
(C) atmospheric pressure
(D) turgor pressure
Answer
B
Question. Both erythrocytes and leucocytes are formed in the –
(A) bone marrow
(B) thymus
(C) arterial walls
(D) lymph nodes
Answer
A
Question. Indicate correct statement for man?
(A) Arteries always carry oxygenated blood while veins always carry deoxygenated blood
(B) Arteries are provided with valves while veins are devoid of valves
(C) Arteries always carry blood away from the heart, while veins always carry blood towards the heart
(D) Venous blood is returned to left auricle
Answer
C
Question. The smallest blood vessel in the body is
(A) capillary
(B) artery
(C) vena cava
(D) vein
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following has no muscular walls?
(A) Artery
(B) Arteriole
(C) Capillary
(D) Vein
Answer
C
Question. The exchange of materials between blood and intestitial fluid occurs only at the
(A) veins
(B) capillaries
(C) arteries
(D) arterioles
Answer
B
Question. The cells constituting walls of the blood capillaries are known as
(A) parietal cells
(B) haemocytes
(C) oxyntic cells
(D) endothelial cells
Answer
D
Question. About how much blood is in the circulatory system of an average person?
(A) 1 litre
(B) 2 litres
(C) 5 litres
(D) 10 litres
Answer
C
Question. Iron in haemoglobin exists as
(A) unionsed iron atom
(B) ferric ions only
(C) ferrous ions only
(D) ferric or ferrous ions depending upon the oxygenated state
Answer
C
Question. The advantage of RBC’s being biconcave is that
(A) to increase surface area
(B) they can be packed up like coins
(C) they can fit into capillaries
(D) none of the above
Answer
A
Question. Which blood constituent makes up more of the volume of blood?
(A) Red blood cells
(B) Plasma
(C) Blood proteins
(D) White blood cells
Answer
B
Question. The tricuspid valve occurs between the
(A) right auricle and right ventricle
(B) pulmonary aorta
(C) cortico-systemic aorta and left ventricle
(D) left ventricle
Answer
A
Question. In the heart of man the bicuspid valve is situated between
(A) right ventricle and pulmonary aorta
(B) left auricle and left ventricle
(C) right auricle and right ventricle
(D) postcaval and auricle
Answer
B
Question. Systole causes
(A) entry of blood into lungs
(B) entry of blood into heart
(C) exit of blood from heart
(D) exit of blood from ventricles
Answer
D
Question. Pulse beat is measured from
(A) artery
(B) nerve
(C) capillary
(D) vein
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is called pace maker of the heart?
(A) SA node
(B) A V node
(C) Chordae tendinae
(D) A V septum
Answer
A
Question. The universal donor has ………………… blood group
(A) A
(B) B
(C) AB
(D) O
Answer
D
Question. Blood cells that help to stop bleeding in human beings are
(A) red blood cells
(B) white blood cells
(C) blood platelets
(D) haemoglobin
Answer
C

We hope the above Transportation Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


