Please refer to Natural Resources Class 9 Notes and Questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 9. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Natural Resources Class 9 Notes and Questions
1. The” Biosphere” is the life supporting zone of the earth with three sub-zones called as lithosphere (rock part), atmosphere (air part) and hydrosphere (water part). Breath of air
2. Composition of Air
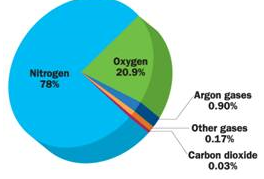
3. The interactions between different components of the Biosphereto maintain the balance between the biotic and a biotic component makes “Biogeochemical cycle”. Ex. Water Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle, Carbon cycle, Oxygen Cycle,
4. Role of atmosphere in climate control: atmosphere act as protective blanket for the earth. Since atmosphere is a bad conductor of heat, it keeps the average temperature of the earth constant. At night, it slows down the escape of heat into outer space.
5. The movement of air :the atmosphere gets heated from the solar radiation that is reflected back by the land or water bodies. As a result of heating, convection currents are set up in the air. Since land gets heated faster than water, the air over land gets heated faster than air above water bodies.
6. In coastal regions, during the day, the air above the land gets heated faster and starts rising. So a region of low pressure is created and air over sea moves into this area of low pressure. The movement of air from one region to the other region causes Wind.
7. During the day, the direction of wind would be from the sea to the land and at night, both land and sea starts to cool. Since water cools down slower than the land, the air above water would be warmer than air above land, thus the direction of wind would be from the land to the sea.
8. Air pollution: it is an undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics. It is caused due to an increase in the content of harmful substances (pollutant) such as oxides of nitrogen and sulphur, etc.
9. Harmful effect of air pollution :
• It affects the respiratory system causing breathing difficulties eg; bronchitis, asthma, lung cancer, tuberculosis, etc.
•Burning of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum releases oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. Inhalation of these gases is dangerous.
• Combustion of fossil fuel also increases the amount of suspended particles in air. The presence of high levels of all these pollutants, reduce visibility in cold weather where water also condenses out of air forming smog.
• Acid rain formed from the gases like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides present in polluted air. It causes damage to living and non- living thing.
3. The Water Cycle:
a)The process in which water evaporates and falls on the land as rain and later flows back into the sea via rivers is known as the “Water Cycle”.Water flows through rocks containing soluble minerals, some of them get dissolved in the water. Thus the rivers carry many nutrients from the land to sea and these are used by the marine organisms.
b)When the water vapors condense as water droplets and grow big and heavy, they fall down in the form of “rain”. It ranges from 5 cm to 200 cm of rain fall in a year in ourcountry. In large parts of India, rains are mostly brought by the south-west or north-east monsoons. Depressions in the Bay of Bengal may also cause rains in some areas.
c)Water is a wonder liquidbecause all cellular processes take place in a water medium; substances are transported in a dissolved form; terrestrial forms require fresh water to maintain the equilibrium of salts; major resource to determine the life on the earth.
d)The dissolved fertilizers (NPK fertilizers), pesticides (DDT), sewage (Disease causing Organisms), waste from factories (Mercury) and water released from the dams can affect the life forms on the earth. The dissolved Oxygen is being used by the animals and plants that live in water, would adversely affect the aquatic organisms. The change in temperature would be dangerous for the eggs and larvae of the various animals particularly susceptible to temperature changes. It leads to “water pollution”.
8. Nitrogen Cycle:
a) The nitrogen gas makes up 78% of our atmosphere. It is essential for the synthesis of proteins, DNA, RNA, urea, alkaloids and Vitamins.
b) The simple molecular nitrogen from the atmosphere is converted into more complex molecules in the living beings and back again to atmosphere is called “Nitrogen Cycle”.
i)Nitrogen fixation by Lightening: During lightning, the molecular nitrogen is converted into oxides of nitrogen and dissolves in water to give nitric and nitrous acids and fall on lands along with rains. These are then utilized by various life forms.
ii) Nitrogen fixation by Bacteria:The molecular nitrogen is converted into nitrates and nitrites, by free living bacteria or the bacteria present in the root nodules of legumes.
iii) The conversion of molecular nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites is called as” Nitrification”. Plants generally covert them into amino acids. The conversion of nitrates and nitrates into Ammonia is called as” Ammonification”. The conversion of Ammonia into molecular Nitrogen is called as” Denitrification”. Thereby nitrates and nitrites are converted into molecular or elemental nitrogen in the nature.
The Carbon cycle:
i) The Carbon dioxidegas makes up 0.039 % of our atmosphere. Carbon occurs in the elemental form as diamonds and graphite in earth. Carbon is essential for the synthesis of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids and Vitamins in living organisms.
ii) The Carbon dioxide Fixation:Green plants convert Carbon dioxide into glucose in the presence of sunlight through Photosynthesis. The glucose molecules are converted into other biologically important molecules. And many marine animals use carbonates dissolved in sea water to make shells, exoskeletons.
iii) The combustion: The Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is added by the process of combustion, where fuels are burnt to provide energy for various needs like heating, cooking, transportation, and industrial process.
iv) The Greenhouse Effect: The percentage of Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is said to have doubled since the industrial revolution when human beings stated burning fossil fuels on a very large scale. The Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. The increase in the Carbon dioxide content would cause more heat to be retained by the atmosphere and lead to Global Warming. It is called” Greenhouse Effect”.
6 .Oxygen Cycle:
i) The Oxygen gas makes up 21 % of our atmosphere. Oxygen is essential component of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acidsin living organisms.
ii) Oxygen from our atmosphere is used up in three processes, namely combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere in only one major process, that is, Photosynthesis, it is called as Oxygen Cycle.
iii) The air is heated faster than water; the air over land would also be heated faster than the air over water bodies. The movement of air from one region to the other creates winds, during the day the direction of the wind would be from the sea to land. At night, both land and sea start to cool.
iv) The oxides of nitrogen and sulphur gases dissolve in rain to gives rise to “Acid rains”. The smog is a visible indication of Air Pollution. The pollutantsbring respiratory, cardiac problems and The organisms called Lichens are found on the bark of trees, they are indicators of pollution free environment. Three atoms of Oxygen ( O3) is called as Ozone. The Ozone is poisonous but absorbs harmful radiations from the Sun. The Ozone layer around the earth, if, dwindles further may cause Health hazards including Cancers . Recently discovered the Ozone hole; in the region of Antarctica.
Natural Resources Class 9 Notes and Questions
Question. Name two kharif crops.
Ans : Paddy and soyabean.
Question. Name two rabi crops.
Ans : Wheat and gram.
Question. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Ans : Fertilisers are synthesized in factories from inorganic materials. On the other hand, manure is made from organic materials; through the process of decomposition. Excessive use of fertilisers is not good for soil and may lead to soil pollution. Use of manure is beneficial for soil.
Question. Name any three methods of irrigation and briefly describe them.
Ans : (a) Drip irrigation : In this kind of irrigation, water is supplied drop by drop near the roots of the crops or plants. They is generally used in the areas where there is a scarcity of water. However, it is very expensive.
(b) Sprinkler system : In this system, the water escapes from the revolving nozzles and is sprinkled like rain on the crops. This system is used for sandy soils and uneven land.
(c) Surface irrigation : Method to supply water to agricultural lands from well, river, dam, etc.
Question. What is mariculture?
Ans : The culture of marine fish in sea water is called mariculture.
Question. What are macro-nutrients?
Ans : The nutrients required by plants in larger quantity is called macro-nutrients. They are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulphur.
Question. State the meaning of capture fishing and culture fishing.
Ans : Capture fishing : It is done from natural resources. Culture fishing : It is done by fish farming.
Question. Name four marine fish varieties.
Ans : Pomphret, mackerel, tuna and sardines.
Question. From where do plants get nutrients?
Ans : Air, water and soil provides nutrients to plants.
Question. Differentiate between milch and draught animals.
Ans : Milk producing animals are called mulch animals. Animals used for farm labour are called draught animals.
Question. Why should weeds be constantly removed from cultivated fields?
Ans : Weeds take up nutrients and reduce the growth of the crop.
Question. What is meant by bee-keeping? Name : (a) the variety commonly used for commercial honey production. (b) the variety having high honey collection capacity.
State how pasturage is related to honey production.
Ans : Beekeeping is the practice of rearing bee for making honey (a) Indian bee (Apis ceranaindica), (b) The Italian (Apis mellifera) bees have high honey collectioncapacity. Pasturage is the availability of flowers to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. Pasturage is related to honey production because it determines the taste of honey and the quantity of honey.
Question. Why do we eat pea and groundnut?
Ans : Pea (matar) provides us protein whereas groundnut provide us necessary fats.
Question. Mention two examples of mixed cropping.
Ans : Some combinations of mixed cropping are : wheat and mustard, groundnut and sunflower.
Question. Write four methods of weed control.
Ans : Spraying weedicide, mechanical removal, sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation also help in weed-control.
Question. State one importance of photoperiod in agriculture.
Ans : Photoperiod in agriculture provide adequate light for flowering.
Question. Name one micronutrient and one macronutrient which plants take from the soil.
Ans : Macronutrients are : Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg) and Micronutrients are : Boron (B), Chlorine (Cl).
Question. Name the two vitamins which are added in the poultry feed.
Ans : Vitamins A and K.
Question. Organism which enriches the soil with nutrients is called biofertilizers.
(a) Write its advantage. (b) Give example.
Ans : (a) Biofertilizers are non-pollutant sources of plant nutrients. They are renewable.
(b) Example of biofertilizers are- Rhizobium, Blue green algae.
Question. A group of Science Club students made a compost pit in the school, they collected all bio-degradable waste from the school canteen and used it to prepare the compost.
(a) Name, two waste that can be used for the compost and two wastes obtained from canteen which cannot be used for the compost making.
(b) What is the other important component required for making the compost?
Ans : (a) Two waste used for compost are vegetable peels and fruit peels. Two waste materials that cannot be used as compost are polythene bags and plastic items.
(b) Bacteria and fungi present in soil are the other important component for making compost.
Question. From where do plants acquire the following nutrients?
(a) Nitrogen, (b) Hydrogen.
Ans :
(a) Nitrogen from soil,
(b) Hydrogen from waste.
Question. Name the cereals which provide us carbohydrate for energy requirement.
Ans : Cereals such as wheat, rice, maize, millets and sorghum provide us carbohydrate for energy requirement.
Question. Give technical term for milk producing females and farm labour animals.
Ans : Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals), while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals.
Question. List two desirable traits for fodder crops.
Ans : Tallness and profused branching are the desired characteristics for producing a higher yield of fodder crops.
Question. What are the major group of activities involved for improving of crop yields?
Ans :
(i) Crop variety improvement
(ii) Crop production improvement
(iii) Crop protection improvement
Question. Give brief sketch on advantages and disadvantages on manure and fertilizers.
Ans : Advantages of manure :
(i) It increases the number of friendly microbes.
(ii) It improves the texture of soil by adding organic matter (humus).
(iii) It increases soil fertility, water holding capacity and aeration.
(iv) It reduces soil erosion.
(v) It is cheap.
Disadvantages of manure :
(i) They have fewer amounts of nutrients as compared to fertilizers.
(ii) Manures are bulky and not easy to store and transport.
Fertilizers : These are commercially manufactured inorganic salts containing one or more essential plant nutrients like NPK, which are used to increase soil fertility.
Advantages of fertilizers :
(i) They are nutrient specific and required in small amounts.
(ii) They are water soluble and absorbed by the plant easily.
(iii) They are easy to store and transport. Disadvantages of fertilizers :
(i) Fertilizers can change the soil structure by killing the soil microbes.
(ii) Fertilizers can change the chemical composition of soil.
(iii) Accumulation of fertilizers in water bodies causes eutrophication.
Question. What are the main characters required in a crop during its improvement practices?
Ans :
The useful characters that are required in a crop during its improvement :
(i) Disease resistance
(ii) Response to fertilizer
(iii) Product quality
(iv) High yield
(iii) Intergeneric – between two different genera
Question. What are the main characters required in a crop during its improvement practices?
Ans : The useful characters that are required in a crop during its improvement :
(i) Disease resistance
(ii) Response to fertilizer
(iii) Product quality
(iv) High yield
Question. Give difference between apiculture and aquaculture.
Ans : Domestication of honeybees or production of honey and wax on commercial bases is called apiculture. Farming and management of fish and other aquatic animals and plants in water is called aquaculture.
Question. What are fertilizers? Excess use of fertilizers is not advisable, explain.
Ans : Fertilizers are commercially produced plant nutrients. They supply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. hey are used to ensure good vegetative growth, giving rise to healthy plants.
Excessive use of fertilizers are not advisable as:
(a) It leads to soil and water pollution.
(b) It can destroy the fertility of soil.
Question. Why there is necessity of animal husbandry?
Ans : To fulfil growing demand for milk, eggs and meat and providing self employment livestock production is needed.
Question. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage? Also mention any two preventive measures to control loss of grains during storage.
Ans : Factors responsible for losses are :
Biotic : Insects, rodents, fungi, mites and bacteria.
Abiotic : Inappropriate moisture and temperatures in the place of storage. Cleaning of the produce before storage, proper drying of the produce first in sunlight and then in shade, and fumigation are preventive measures to control loss of grains during storage.
Question. What are the various methods of irrigation in India?
Ans : Most of agriculture in India is rain-fed, several different kinds of irrigation system are adopted to supply water to agricultural lands. The resources are-wells, canals,rivers and tanks.
(i) Wells : Dug wells and tube wells. In dug wells water is collected from water— bearing strata.
(ii) Tubewells : Water from deeper strata.
(iii) Canals : Most extensive irrigation system. Canals receive water from reservoirs or rivers. The main canal is divided into branch canals having further distributaries to irrigate fields.
(iv) River lift system : Water is directly drawn from the river for supplementing irrigation in areas close to rivers.
(v) Tanks : These are small storage reservoirs, which intercept and store the run-off of smaller catchment areas.
Question. What are the factors for which variety improvement of crop is done?
Ans : (a) Higher yield : It increases production of crop.
(b) Biotic and abiotic resistance : Crop should be resistant to biotic factors like diseases, insects, pests and abiotic factors like drought, salinity, heat, etc.
(c) Change in maturity duration : Short-duration maturity allows farmer to grow more crops in a year with short duration maturity and reduces the crop production cost.
(d) Wider adaptability : Crop should be able to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
(e) Desirable agronomic characteristics : Crop should have tallness and dwarfness as per need. Dwarfness is required for cereals, so that few nutrients are consumed.
Question. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil,
(b) Sowing,
(c) Weeding,
(d) Threshing
Ans :
(a) Preparation of soil : Preparation of soil is the first step of farming. Soil is loosened and turned over. This helps in making the soil more airy so that roots can breathe in air. Moreover, loosening of soil also facilitates better penetration of roots into the soil. Seeds can be easily sown in loosened soil.
(b) Sowing : The method of putting the seeds into soil is called sowing. Traditionally, seed is sown manually by spreading the seeds by hands. This process is called broadcasting. Seed drills are used when sowing needs to be done on a large scale.
(c) Weeding : Removal of weeds is called weeding. Unwanted plants which grow along with the crop are called weeds. They compete for resources; like sunlight, water and air; with the main crop. So, it is necessary to remove weeds for proper growth ofcrops. Weeding is usually done manually by using hands and sickles. Sometimes weedicides are also sprayed.
(d) Threshing : Separation of grains from harvested stems is called threshing. For smaller quantity, threshing is done by hands. For somewhat bigger quantity, threshing is done using animal; especially bullocks. Animals are made to trample over the harvested stock which helps in separation of grains. Threshing machines are used for bigger quantities.
Question. What is the advantage of composite fish culture?
Ans : The composition of six species of fish in composite fish is highly advantageous because:
(i) These fishes do not compete for food among themselves
(ii) They have different food habit
(iii) Food in all parts of pond is utilized due to different food habits
Question. Why Apis mellifera is adopted for domestication to produce honey?
Ans : The Italian species of honey bee, i.e. Apis mellifera is adopted for its many good qualities. They :
(i) sting less
(ii) have good honey collection capacity
(iii) produce with less swarming
(iv) have ability to protect itself from enemy
(v) stay in beehives for a long time
Question. “Shorter the duration of the crop from sowing to harvesting, the more economical is the variety.” Give reason for this.
Ans : Farmers can grow more crops in a year due to short duration of crop growth, and reduce the cost of crop production.
Question. Name different types of crop production practices involved in India.
Ans : They are (a) no cost production, (b) low cost production and (c) high cost production.
Question. Name the nutrients that plant obtains from air and water.
Ans : Air – Carbon and oxygen
Water – Hydrogen and oxygen
Question. Name the products obtained from apiculture.
Ans : Honey and wax both are obtained from apiculture.
Question. What is meant by bee-keeping?
Ans : Rearing of bees for the production of honey on a large scale is called bee-rearing.
Question. Name two exotic breeds of cattle.
Ans : Jersey and Brown Swiss
Question. What are the practices used for dairy industry?
Ans : The practices used for dairy industry to get the optimum yield are :
(i) Shelter : The shelter should be clean, spacious and airy.
(ii) Feeding : Proper food at proper time is essential for dairy animals.
(iii) Rearing of animals : Providing them proper health care and protection from pathogens, diseases and proper vaccination.
(iv) Breeding : The crossing of different variety of milch animals to obtain a breed that can produce more yield of milk.
Question. Large amount of food grains get spoiled every year in India due to improper storage of food grains. How can this be avoided?
Ans : Food grains get spoiled by insects, fungi, rodents, bacteria, moisture at the place of storage. Storage losses can be reduced by taking some preventive and control measures.
(i) The seeds that are to be stored should be dry
(ii) The grains should be cleaned
(iii) The grains should be fumigated using chemicals that kills pest.
(iv) The storage houses should be waterproof.
(v) The grains should be stored in sealed gunny bags.
(vi) The bags should be kept few centimetres away from the wall.
(vii) The walls and the floor should be water-proof with no holes in it, to avoid rodents, pests.
Question. What are weeds? How can we control them? Give different methods of weed control.
Ans : Unwanted plants which grow along with crops are called weeds. Weeds compete with crops for natural resources; like sunlight, water and nutrients. Thus, weeds hamper the growth of crops. Weeds are usually removed manually by hands and by sickles. This process is called weeding. Sometimes, weedicides are also sprayed to kills weeds. Weeds can be controlled by different methods :
(a) Weedicides : These are the chemicals sprayed on the weeds to kill them. Excessive use is poisonous and causes environmental pollution.
(b) Mechanical removal : In this method weeds are uprooted by removing manually or by machines.
(c) Preventive methods : Proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation helps in weed control.
Question. Explain different types of fisheries.
Ans : The different types of fisheries are marine fisheries; inland fisheries, capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture.
(i) Marine fisheries : Marine fishes are caught using fishing nets.
(ii) Mariculture : Marine .fishes are cultured in seawater.
(iii) Inland fisheries : The fisheries done in freshwater resources like canals, ponds, reservoirs and rivers.
(iv) Capture fishing : It is done in sea-water, estuaries and lagoons.
(v) Aquaculture : Culture of fish done in different water bodies is called aquaculture.
Question. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Ans : Continuous plantation of crops in a field affects soil fertility. Plants utilize all the nutrients from soil which leads to depletion of nutrients in the soil. As a result, soil fertility reduces drastically.
Question. A group of gardening club students prepared a kitchen garden in the school campus and did organic farming to grow the vegetables. Then the students presented their group work in the assembly to spread the awareness and make students understand the importance of organic products.
(a) What is horticulture?
(b) What is green manure?
Ans : (a) Hotriculture is the commercial production of vegetables and fruits.
(b) The green plants like sun hemp are turned into the soil which enriches the soil with nitrogen and phosphorus and is called green manure.
Question. What are the three advantages of shorter duration of the crop in between sowing and harvesting?
Ans : Short durations allow farmers to grow multiple rounds of crops in a year. Short duration also reduces the cost of crop production. Uniform maturity makes the harvesting process easy and reduces losses during harvesting.
Question. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Ans : Cross breeding between a two good variety crops is called hybridization that also results in a new improved variety. Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic. This results in genetically modified crops.
Question. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Ans : During the storage of grains, various biotic factors such as insects, rodents, mites, fungi, bacteria, etc. and various abiotic factors such as inappropriate moisture, temperature, lack of sunlight, etc. are responsible for losses of grains. These factors act on stored grains and result in degradation, poor germ inability, discolouration, etc.
Question. List any six factors for which variety improvement in crops is done.
Ans :
(i) Higher yield,
(ii) Improved quality,
(iii) Biotic and abiotic resistance,
(iv) Change in maturity duration,
(v) Wider adaptability,
(vi) Desirable characteristics.
Question. Name two breeds of cows selected for long lactation period.
Ans : After giving the birth of a calf, a cow secretes milk. The duration of milk secretion of a cow that is the period of time till which the cow secretes milk is known as lactation period. Brown Swiss and jersey are selected for their long lactation period.
Question. Name two fresh initiatives taken to increase the water availability for agriculture.
Ans : Two new irrigation systems have been developed to save water and increase the availability of water to the crops. These are :
(1) Drip irrigation system : Here, water is supplied to the roots of the plants directly in a drop wise manner. This prevents unnecessary wastage of water.
(2) Sprinkler system : Here water is sprinkled over the crops like it happens in rain. So, water is absorbed by the soil in a better way.
Question. How do plants get nutrients?
Ans : Nutrients are supplied to plants by air, water and soil. Air supplies carbon and oxygen, hydrogen comes from water and soil supplies the other thirteen nutrients to plants.
Question. What are the new varieties obtained by cross breeding of Indian and exotic breeds of poultry?
Ans : The new variety/traits obtained by cross breeding of Indian and exotic breeds of poultry are :
(i) Number and quality of chicks
(ii) Dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production
(iii) Summer adaptation capacity/tolerance to high temperature
(iv) Low maintenance requirements
(v) Reduction in the size of the egg-laying bird with ability to utilise more fibrous and cheaper diet, formulated using agricultural by products.
Question. Distinguish between a mullet and a prawn.
Ans : Mullet is a type of fish while prawn is a crustacean. Both live in water and serve as a food supplement worldwide. Prawn belongs to group arthropoda whereas mullet belongs to group Pisces.
Question. What is composite fish culture system? Mention one merit and one demerit of this system.
Ans : The composite fish culture system is a technology to grow both local and imported fish species in the water in the paddy field. One problem with such composite fish culture is that many of these fish breed only during monsoon mixed with other species, one of the advantages is that fish do not compete for food.
Question. What are the different ways/methods of hybridisation?
Ans :
Hybridisation can be :
(i) Intervarietal – between different varieties of crops
(ii) Interspecific – between two species of same genus
(iii) Intergeneric – between two different genera
Question. What is organic farming?
Ans : Farming method in which no chemical fertilizers, pesticides or herbicides are used. Instead of using chemical, farmer uses all organic matter for growth of crops. Example : Manure, neem leaves as pesticides and for grain storage.
Question. Mention the components of food present in vegetable and fruits.
Ans : Vegetables, spices and fruits provide a range of vitamins and minerals in addition to small amounts of proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
Question. How does deficiency of nutrients affect the crop?
Ans : Physiological processes can be affected by deficiency of any nutrient in plants including reproduction, growth and susceptibility to diseases.
Question. What is Pisciculture?
Ans : The production and management of fish is called Pisciculture.
Question. What are the harmful effects of fertilizer?
Ans : Continuous use of fertilizer can cause of soil and water pollution and also destroy soil fertility.
Question. How does Bombay duck differ from common carp?
Ans : Bombay duck is a marine fish, while common carp is a freshwater fish.
Question. State the difference between compost and vermicompost.
Ans : The compost is obtained by decomposition of organic waste like animal excreta, plant waste, etc. naturally due to decomposition by bacteria. Vermi-compost : Red-worms are added to organic matter in the process of decomposition to obtain compost to fasten. This will fasten the process.
Question. Name any two weeds.
Ans : Parthenium and Xanthium.
Question. What causes disease in plants?
Ans : It is caused by pathogens such as bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Question. Name two Indian cattle.
Ans : Bos indicus – cows
Bos bubalis – buffaloes
Question. Name any two fodder crops.
Ans : Berseem and sudan grass are raised as food for the livestock, called fodder crops.
Question. What do you understand by photoperiod of sunlight?
Ans : Photoperiod are related to the duration of sunlight required for plant growth.
Question. Define hybridisation.
Ans : Hybridisation refers to crossing between genetically dissimilar plants, to obtain better variety of crops.
Question. What are genetically modified crops?
Ans : A gene with required characters can introduce into a crop for its improvement is called genetically modified crop.
Question. How does Bos indicus differ from Bos bubalis?
Ans : Bos indicus is a cow while Bos bubalis is a buffalo.
Question. Name two types of food required for milch animals.
Ans : Maintenance requirement – food required to keep animal healthy. Milk producing requirement – food required for increased lactation animal food includes roughage and concentrate also.
Question. What is apiculture?
Ans : Keeping bee for obtaining honey commercially is called apiculture.
Question. What are weeds? Give example.
Ans : Unwanted plants growing with main crops are called weeds. Example : Xanthium, Parthenium, Cyperinus Rotundus.
Question. In what way broilers, feed is different from layers?
Ans : Broilers, feed is protein rich with adequate fat. The level of vitamins A and K is kept high in the poultry feeds.
Question. Which one broilers or layers mature earlier?
Ans : Broilers have fast growth rate.
Question. What type of shelter is provided to broiler and layers?
Ans : Broilers do not require much space and lighting.
Question. State one demerit with composite fish culture system.
Ans : Fish breed only during monsoon and lack of availability of good quality seeds.
Question. Mention any two advantages of using Italian bee variety in honey production.
Ans : The Italian bees have high honey collection capacity. They sting somewhat less. They stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed very well.
Question. State the reason of introducing Italian bee variety in bee farms.
Ans : An Italian bee variety, A mellifera, has also been brought in to increase yield of honey.
Question. Which nutrients are supplied by cereals and pulses?
Ans : Carbohydrate is supplied by cereals and protein is supplied by pulses.
Question. Define animal husbandry.
Ans : Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals by humans for profit.
Question. Name two factors responsible for wastage of grains during storage.
Ans : Factors responsible for such losses are :
Biotic : insects, rodents, fungi, mites and bacteria,
Abiotic : inappropriate moisture and temperatures in the place of storage.
Question. (i) Name an exotic variety of honey bee grown in India.
(ii) What is called the rearing of fish on a large scale?
Ans :
(i) Apis cerana indica
(ii) Pisciculture
Question. Is breeding and rearing of Bombay duck part of poultry farming or a part of pisciculture?
Ans : It is a part of pisciculture as Bombay duck is fish not a duck.
Question. What is the tremendous increase in the production of eggs in India known as?
Ans : Golden revolution and Silver revolution.
Question. State the preventive and control measures used before grains are stored.
Ans :
(i) Cleaning of the grains.
(ii) Keep seeds in sunlight to provide moisture.
(iii) Using chemicals that kills pest.
Question. How do insect pests attack the plant and affect it?
Ans : Insect pests attack the plants and reduces yield in three ways :
(i) They cut the root, stem and leaf.
(ii) They suck the cell sap from various parts of the plant.
(iii) They bore into stem and fruits.
Question. Define manures. What are its three different kinds? State two limitations of manures.
Ans : Manure is an organic matter prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste. They are : Compost, vermi-composting and green manure.
Two limitations of manures are :
(i) Supplies small quantities of nutrients to the soil
(ii) Losses about half the available nitrogen
(iii) Releases greenhouse gases
Question. What is the advantage of crop rotation?
Ans : Rotation of crops helps in saving on nitrogenous fertilizers, because leguminous plants grown during the rotation of crops can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil with the help of itrogen fixing bacteria.
Question. What are the types of food requirements of dairy animals? Why external and internal parasites live on and in the cattle can be fatal.
Ans : Roughage and concentrates are the types of food requirements of dairy animals. The external parasites live on the skin and mainly cause skin diseases. The internal parasites like worms, affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage the liver.
Question. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
Ans : Sending crop to sugar factory ” Irrigation ” Harvesting ” Sowing ” Preparation of soil ” Ploughing the field ” Manuring Preparation of soil ” Ploughing the field ” Manuring
” Sowing ” Irrigation ” Harvesting ” Sending crop to sugar factory.
Question. What are manures? Give its classification.
Ans : Substance rich in organic matter and also supplies small quantities of nutrients to soil is called manure. Manure is classified based on the kind of biological material used to make it as :
(i) Compost, (ii) Vermi-compost, (iii) Green manure.
(i) Compost : The manure prepared by decomposing farm waste, livestock excreta, plant waste, etc. in a pit is known as compost.
(ii) Vermi-compost : When the above given matter is allowed to decompose in the pit along with some earthworms to fasten the process of decomposition is called vermi-composting.
(iii) Green manure : Some plants like sun-hemp are used to prepare manure by mulching them into oil by plough is known as green manure.
Question. What are the different patterns of cropping?
or
What are the different cropping systems?
Ans : Different systems of growing crop :
(a) Mixed cropping : Two or more crops grow simultaneously on the same piece of land, is called mixed cropping.
Example : Wheat + grain, wheat + mustard.
(ii) Inter-cropping : It is a method of growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. A few row of one crop alternate with a few rows of second crop.
Example : Soyabean + Maize or Bajra + Lobia.
(iii) Crop rotation : The growing of different crops on a piece of land in a succession is known as crop rotation.
Question. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Ans : The crop of wheat needs mild to moderate temperature and frost free days; along with irrigation but no water logging. Winters are suitable for growing wheat. In the kharif season; which coincides with the peak summer months in India, temperature is at its peak which is not suitable for wheat. Moreover, during rainy season lot of water accumulates in fields which would be harmful for wheat crop. Hence, if wheat is sown in the kharif season; the productivity would be minuscule and would not be profitable for the farmers.

We hope the above Natural Resources Class 9 Notes and Questions are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science


