Please refer to Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper Term 2 With Solutions Set A provided below. The Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared based on the latest pattern issued by CBSE. Students should practice these guess papers for class 10 social science to gain more practice and get better marks in examinations. The Term 2 Sample Papers for Social Science Standard 10 will help you to understand the type of questions which can be asked in upcoming examinations.
Term 2 Sample Paper for Class 10 Social Science With Solutions Set A
SECTION-A
1. What type of flag was designed during the ‘Swadeshi Movement’ in Bengal? Explain its main features.
Answer : During the Swadeshi movement in Bengal, a tricolour flag (red, green and yellow) was designed. It had eight lotuses representing eight provinces of British India, and a crescent moon, representing Hindus and Muslims.
2. What is the importance of “least cost” while planning to establish an industry?
Answer : Industrialists set up offices and factories for production in region where they can get cheap labour and other resources at low cost. This is done so that the cost of production is low and industrialists can earn greater profits. Hence, the key to decision of the factory location in the least cost.
3. What is multi-party system?
Answer : When several parties compete for power and more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power either on their own strength or in alliance with other; the system called multi-party system, e.g., in India and France there are more than two political parties.
4. How do banks acts as a mediator?
Answer : Banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrower). People need only some currency for their day to day needs, so the extra cash they deposit it with the banks by opening a bank account in their name. Banks accept the deposit and also pay an amount of interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe and its earns an amount as an interest.
And bank use the major portion of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.

5. Study the data related to foreign trade (value in crores of rupees) in India and answer the questions that follow:
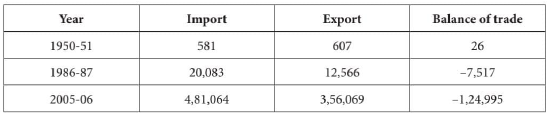
(i) What was the condition of our foreign trade in 1950-51?
Answer : The balance of trade was slightly favourable. The value of export exceeds the value of imports.
(ii) What is the ratio between import and export during the year 1986-87? Explain the term balance of trade.
Answer : Balance of trade means the difference between total value of exports and imports of a country. If there are more exports than imports it is favourable balance of trade; but if the imports are more than exports, then it is unfavourable balance of trade.
The ratio between the import and export trade in 1986-87 was 20 : 12.
SECTION- B
6. Examine any four conditions which should be taken care of by multinational companies to set up their production units.
OR
How money acts as a medium of exchange? Explain with example.
Answer : The MNCs must ensure that
(i) Cheap raw material is available.
(ii) Cheap yet skilled labour is available.
(iii) The overall production cost is low.
(iv) Availability oflarge consumer base.
OR
Money acts as a medium of exchange itself for goods and services. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want.
Thus, everyone prefers to receive payments in money and then exchange the money for things that they want.
For example : A shoemaker wants to sell shoes in the market and buy wheat. The shoemaker will first exchange shoes for money and then exchange the money for wheat. If the shoemaker had to directly exchange shoes for wheat without the use of money. He would have to look for a wheat growing farmer who not only wants to sell wheat but also wants to buy the shoe in exchange. Both the parties have to agree to sell and buy each others commodities. This is known as double coincidence of wants. While money eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants.
7. Why did political leaders differ sharply over the question of separate electorates?
Answer : Political leaders differed shortly over the question of separate electorates because of the following reasons :
(i) Scheduled caste leaders demanded a separate electorate that would choose Scheduled Caste members for legislative councils. They believed that political empowerment would resolve the problems of their social disabilities. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar clashed with Gandhiji at the Second Round Table Conference by demanding separate electorates for Scheduled Castes. But Gandhiji believed that separate electorates for Scheduled Castes would slow down their integration into society. Dr. Ambedkar, however, agreed to have joint electorates with the Hindus if the seats for Scheduled Castes were reserved in provincial and central legislative councils.
(ii) The Muslim leaders, like Muhammad Ali Jinnah and Muhammad Iqbal also demanded a separate electorate for the Muslims so that political rights and other interests of the Muslims could be protected. They were of the opinion that the majority of the people were the Hindus. If there prevailed the system of joint electorates, the Muslims would not be able to secure seats in the provincial and central legislative councils.
(iii) The Congress strongly opposed the British policy of Separate electorates. According to it, this provision would become an obstacle in the way of national movement for independence. The British wanted to sow the seeds of hatred in India in order to safeguard their tule in India.
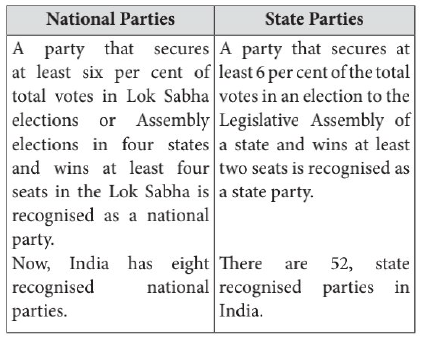
8. How are political parties recognised as regional and national parties in India? Explain.
Answer : Regional party or state party refers to a political party, which has its base in a particular region may be covering one or more states. They may have limited or pan-India aspirations and objectives. National party implies a political party that extends over the entire nation, in terms of representation and the area of influence. The national and the state parties are recognised by the Election Commission on the following criteria :
SECTION- C
9. Describe the importance of democratic government as an accountable and legitimate government.
OR
Describe any five characteristics of democracy.
Answer : Democratic government can be said to be accountable and legitimate government.
Accountable Government :
(i) When people choose their representatives, they are expected to be accountable. They can be replaced otherwise.
(ii) The citizens have the right and also the means to examine the process of decision making. This ensures accountability.
(iii) The government is expected to practice regular, free and fair elections and open discussions on important issues.
(iv) Democratic government can apparently be less efficient than a non-democratic government. This happens because a non-democratic government does not need to arrive at consensus among a diverse set of people. Democracy functions on the basis of deliberation and negotiation and hence decisions are often delayed. But this does not mean that a democratic government is less efficient.
Legitimate Government :
(i) A democratic government is people’s own government. That is why there is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world and there is the element of legitimacy attached to it.
(ii) People wish to be ruled by representatives elected by them. They also believe that democracy is suitable for their country. Democracy’s ability to generate support for itself is seen everywhere.
(iii) Though there are many reports of democracies ignoring the demands of people and there are routine tales of corruption but yet chances and hope of improvement exists in democratic setup.
OR
The characteristics of democracy are:
(i) Elected representatives rule the country.
(ii) Elections that are free and fair are held at regular periodicity.
(iii) Rights of the individual and citizens are protected and rule of law that prevails is equal for every one.
(iv) Independent judiciary functions without the intervention of the rulers. Opposition parties question the actions of the rulers and thus ensure good governance.
(v) Freedom of religion and culture is ensured.
10. Why banks lend to the poor women organised in SHGs?
OR
Analyse any five positive impact of globalisation on the lndian economy.
Answer : If the women are member of self help groups and the group is regular in savings, then it become eligible for availing loan from the bank because the group become responsible for the repayment of the loan. And in case of non-repayment of loan by any one member is followed up seriously by other member in the group. Because of this feature bank lend loan even to the poor women organised in SHGs.
OR
Positive impact of the globalisation on Indian economy:
(i) Availability of variety of products which has enabled the consumers to have greater choice and enjoy improved quality at lower price for several products.
(ii) This has led to better standards of living.
(iii) This has led to increase in foreign direct investment.
(iv) New jobs have been created in many sectors.
(v) Top Indian companies have benefited by investing in new technology and production methods. Some have made successful collaborations with foreign companies.
SECTION- D
11. Read the given text and answer the following questions :
India has one of the largest road networks in the world. In India, roadways have preceded railways. They still have an edge over railways in view of the ease with which they can be built and maintained. The growing importance of road transport vis-a-vis rail transport is rooted in the following reasons; (a) construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines, (b) roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography, (c) roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas, (d) road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances, (e) it also provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower, (j) road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
(i) How roadways have an edge over railways?
Answer : They can be easily built over various tracts of land, economically.
(ii) List two benefits of road transport.
Answer : hey provide last mile connectivity and they are economic in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
(iii) What is meant by feeder to other modes of transport?
Answer : Feeder means the link to other modes of transport. For example we go to the airports, railway stations or the sea ports by road.
12. Read the given text and answer the following questions :
Not all social groups were moved by the abstract concept of swaraj. One such group was the nation’s ‘untouchables’, who from around the 1930s had begun to call themselves dalit or oppressed. For long the Congress had ignored the dalits, for fear of offending the sanatanis, the conservative high-caste Hindus. But Mahatma Gandhi declared that swaraj would not come for a hundred years if untouchability was not eliminated. He called the
‘untouchables’ harijan, or the children of God, organised satyagraha to secure them entry into temples, and access to public wells, tanks, roads and schools. He himself cleaned toilets to dig11ijy the work of the bhangi (the sweepers), and persuaded upper castes to change their heart and give up ‘the sin of untouchability’. But Many dalit leaders were keen on a different political solution to the problems of the community. They began organising themselves, demanding reserved seats in educational institutions, and a separate electorate that would choose dalit members for legislative councils. Political empowerment, they believed, would resolve the problems of their social disabilities.
(i) What name Gandhiji gave to untouchables?
Answer : Gandhiji called the untouchables harijan or the children of God.
(ii) Why Congress had ignored the dalits?
Answer : Congress had ignored the dalits, for fear of offending the sanatanis, the conservative high-caste Hindus.
(iii) What did Gandhiji say about untouchables?
Answer : Gandhiji declared that swaraj would not come for a hundred, if untouchability was not eliminated, he organised satyagraha to secure their entry into temples, tanks, wells, etc. He himself cleaned toilets to dignify the work of the sweepers.
SECTION- E
13. (i) On the given outline Political Map of lndia, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(a) The city related to Jallianwalla Bagh incident.
(ii) On the same given map of lndia, locate the following :
(a) Mayurbhanj Iron Ore Mines
OR
Nammp Thermal Power Station
(b) Paradwip Port
Answer :


We hope you liked the above provided Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper Term 2 With Solutions Set A. Incase you want more sample papers please click on the links below.

