Please refer to Class 12 Business Studies Sample Paper Term 2 With Solutions Set D provided below. The Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies have been prepared based on the latest pattern issued by CBSE. Students should practice these guess papers for class 12 Business Studies to gain more practice and get better marks in examinations. The Term 2 Sample Papers for Business Studies Standard 12 will help you to understand the type of questions which can be asked in upcoming examinations.
Term 2 Sample Paper for Class 12 Business Studies With Solutions Set D
Short Answer Type Questions – I
1. Identify and explain the function of management where ability of an organization to achieve its goal depends upon the quality of its human resources?
Answer. Staffing function of management.
Staffing has been described as the managerial function of filling and keeping filled the positions in the organization structure. Human resources are the most important asset of an organization. The ability of an organization to achieve its goal depends upon the quality of its human resources. Therefore, staffing is a very important managerial function. No organization can be successful unless it can fill and keep filled the various positions provided for in the organization structure with the right kind of people.
2. ISQAA SOLAR Limited is searching for options to raise ₹ 20,000 crores from the primary market for diversification and modernisation of existing projects. It hired the services of a renowned financial consultancy firm, DHAN LAXMI PVT. Ltd. to suggest options for the same. DHAN LAXMI PVT. LTD. suggested a list of options to the Board of Directors of the company. It was decided that for the immediate requirement of ₹ 1,500 crore , the company will give a privilege to existing shareholders to subscribe to a new issue of shares according to the terms and conditions of the company. ₹ 4,500 crore would be raised by allotment of securities to a consortium of financial institutions, instead of inviting subscription from the public by making a direct appeal to investors to raise capital. It was further decided to raise capital to the tune of ₹ 6,000 crore through an issuing house. All these options were accepted by the Board of Director. The Board further decided to raise ₹ 8,000 crore through the online system of the stock exchange by entering into an agreement with the exchange. Identify and explain the method of floatation of new issues in the primary market, not taken up by ISQAA SOLAR Ltd.
Answer. Offer through Prospectus: Offer through prospectus is the most popular method of raising funds by public companies in the primary market. This involves inviting subscription from the public through issue of prospectus. A prospectus makes a direct appeal to investors to raise capital, through an advertisement in newspapers and magazines. The issues may be underwritten and also are required to be listed on at least one stock exchange. The contents of the prospectus have to be in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act and SEBI disclosure and investor protection guidelines.
3. Explain briefly ‘transfers’ and ‘promotions’ as internal sources of recruitment.
Answer. (i) Transfers: Transfers involve shifting of an employee from one job to another, one department to another or from one shift to another, without a substantive change in the responsibilities and status of the employee. It may lead to changes in duties and responsibilities, working condition etc., but not necessarily salary. Transfer is a good source of filling the vacancies with employees from overstaffed departments. It is practically a horizontal movement of employees. Shortage of suitable personnel in one branch may be filled through transfer from another branch or department.
(ii) Promotions: Promotions involve shifting an employee to a higher position, carrying higher responsibilities, facilities, status and pay. This practice helps to improve the motivation and increases loyalty and satisfaction level of employees. It has a great psychological impact over the employees because a promotion at the higher level may lead to a chain of promotions at lower levels in the organization.
4. Sameer has set up an export house after completing his masters in fashion designing. As the quality of the garment depends on the quality of raw material used, he assures that the fabric meets the requirements by conducting a series of tests for the fabrics like shrinkage test, testing color fastness to washing, color fastness to light, color fastness to perspiration etc. through laboratory tests. Later on, at the production areas, fabric inspection is also conducted by stopping the production process. The tests help to detect the deviations and also take corrective action. Moreover, he ensures that complete training about production process is given to every worker at the time of joining his export house. In context of the above case:
(i) Identify the function of management being performed by Sameer by conducting tests to assure for the quality of the garments manufactured in his export house.
(ii) Briefly explain the term ‘deviations.’
Answer. (i) Controlling is the function of management being performed by Sameer by conducting tests to assure good quality of the garments manufactured in his export house.
(ii) The term ‘deviations’ refers to the difference between the actual performance and planned performance. If the actual performance is more than the planned performance, it may be said to be positive in nature or vice-versa.
Short Answer Type Questions – II
5. Bharat is the Managing Director of Liva Ltd. The company had established a good name for itself and had been doing well. It was known for timely completion of orders. The Production Manager, Ms. Rohini was efficiently handling the processing of order and had a team of twenty motivated employees working under her. Everything was going on well. Unfortunately, she met with an accident. Bharat knew that in the absence of Ms. Rohini, the company may not be able to meet the deadlines. He also knew that not meeting the deadlines may lead to customer dissatisfaction with the risk of loss of business and goodwill. So, he had a meeting with his employees in which accurate the speedy processing of orders was planned. Everybody agreed to work as team because the behavior of Bharat was positive towards the employees of the organization. Hence everyone put in extra time and efforts and the targets were met on time. Not only this, Bharat visited Ms. Rohini and advised her to take sufficient rest. Identify and explain the leadership style followed by Bharat.
Answer. Democratic style of leadership has been adopted by Bharat.
Democratic or Participative leader: A democratic leader will develop action plans and makes decisions in consultation with his subordinates. He will encourage them to participate in decision making. This kind of leadership style is more common now a days, since leaders also recognise that people perform best if they have set their own objectives. They also need to respect the other’s opinion and support subordinates to perform their duties and accomplish organizational objectives. They exercise more control by using forces within the group.
6. Describe briefly the first three needs in the Maslow’s hierarchy theory of motivation.
OR
Explain the various elements of directing function of management.
Answer. The first three needs that exist in a hierarchy within every human being as per Maslow are stated below:
(i) Basic Physiological Needs: These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and are linked to primary needs like hunger, thirst, shelter etc. These needs of employees may be fulfilled by providing basic salary and the necessary breaks to use the washroom and eat food.
(ii) Safety/Security Needs: These needs offer security and protection from physical and emotional harm. Job security and safe working conditions may be offered to the employees for the fulfillment of these needs.
(iii) Affiliation/Belonging Needs: These needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship. By encouraging cooperative teamwork and by being-an accessible and kind superior these needs of employees may be fulfilled.
OR
The various elements of directing function of management are discussed below:
(i) Motivation: Motivation means incitement or inducement to act or move. In the context of an organization, it means the process of making subordinates to act in a desired manner to achieve certain organizational goals. It is the process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goals. Motivation depends upon satisfying needs of people. Motivation can be either positive or negative. Positive motivation provides positive rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition etc., Negative motivation uses negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening etc. which also may induce a person to act in the desired way.
(ii) Leadership: Leadership is the process of influencing the behavior of people by making them strive voluntarily towards achievement of organizational goals. Leadership indicates the ability of an individual to maintain good interpersonal relations with followers and motivate them to contribute for achieving organizational objectives. Leadership tries to bring change in the behavior of others. Leadership is exercised to achieve common goals of the organization.
(iii) Communication: Communication is defined as a process of exchange of ideas, views, facts, feelings etc., between or among people to create common understanding. Communication can be formal and informal. Formal communication flows through official channels designed in the organization chart. This communication may take place between a superior and subordinate, a subordinate and superior or among same cadre employees or managers. Communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication is said to be informal communication. Informal system of communication is generally referred to as the ‘grapevine’ because it spreads throughout the organization with its branches going out in all directions in utter disregard to the levels of authority.
7. Explain the following statement; ‘Wealth Maximization’ is the primary objective of financial management.
Answer. Wealth Maximization is the primary objective of financial management means that maximizing the market value of investment in the shares of the company thereby increases the shareholder’s wealth. The financial decisions that a company undertakes have an impact on the market price of its equity shares.
Wealth maximization is possible only by the following methods :
(i) Ensuring availability of sufficient funds at all times and at a reasonable cost.
(ii) Ensuring effective utilisation of funds e.g., utilizing the idle funds.
(iii) Ensuring safety of funds by creating reserves for different purposes, reinvestment of profits, etc.
8. ‘Tosto’ is a company known for manufacturing good quality confectionery products. The automated system of production ensures uniformity in production and quality maintenance. The quality assurance team conducts stringent checks at all stages, records and analyses the deviations and takes the necessary corrective actions right from the procurement of raw material to its processing, production and packaging. The company has a well-equipped in-house quality inspection cell where confectionery products are tested on various parameters of quality by the team of experienced quality staff. In context of the above case:
Explain the statement, “records and analyses the deviations and takes the necessary corrective actions”.
Answer. The statement “records and analyses the deviations and takes the necessary corrective actions” refers to the following steps involved in the process of controlling:
(i) Comparing the actual performance with the standards: This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired results. Comparison becomes easier when standards are set in quantitative terms.
(ii) Analyzing deviations: Once the deviations are identified, it is important to analyze them through:
(a) Critical point control: All the deviations may not be significant. Moreover, it may not be either economical nor easy to monitor each and every activity in the organization. Therefore, every organization identifies and states its specific key result areas (KRAs) or critical points which require tight control as they are likely to have a significant effect on the working of the business. Any deviations on these points are attended to urgently by the management.
(b) Management by exception: Management by exception is the principle of management control which is based on the belief that if you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing. Therefore, only significant deviations which go beyond the permissible limits should be brought to the notice of the management.
(iii) Taking corrective action: The last step in controlling process involves taking corrective action whenever the deviation occurs beyond the permissible limits so that they do not reoccur in future. However, the standards may be revised if it is not possible to check deviations through corrective action.
Long Answer Type Questions
9. On Sonika’s birthday, her mother gave her a pair of gold earrings. After one month, Sonika observed that the earrings were losing their shine. She checked the mark on the earrings and found that it was not a proper Hallmark and her mother had been cheated by the shopkeeper. So, she filed a complaint in the District Commission which rejected it. Not satisfied by the decision of the District Commission, she was very much disturbed and she decided to appeal further. The consumer court was satisfied about genuineness of the complaint and issued necessary directions to the shopkeeper.
(i) Identify and explain the consumer rights that has been exercised by Sonika in the above situation.
(ii) Also, state any three directions that might have been issued by the court.
OR
‘Fashion Ltd.’ is engaged in the manufacturing of apparel. Over the years, it has become a popular brand due to its good product quality and exclusive designing. The company plans to open its own retail showrooms in metropolitan cities in India. In order to meet its financial needs, it has offered for subscription an IPO of ₹4 lakh equity shares in the price band of ₹430 – ₹445 each. As per the guidelines of SEBI, the company has provided a complete disclosure of the relevant details in its prospectus.
(i) Identify and explain the right of the consumer being fulfilled by the directives of SEBI in the above-mentioned case.
(ii) Briefly explain any three points highlighting the importance of consumer protection from the point of view of the businessmen.
Answer. (i) The consumer rights that has been exercised by Sonika in the given situation are as follows:
(a) Right to be Heard: The consumer has a right to file a complaint and to be heard in case of dissatisfaction with a good or a service. It is because of this reason that many enlightened business firms have set up their own consumer service and grievance cells. Many consumer organizations are also working towards this direction and helping consumers in redressal of their grievances.
(b) Right to seek Redressal: The consumer has a right to get relief in case the product or service falls short of his expectations. The Consumer Protection Act provides a number of reliefs to the consumers including replacement of the product, removal of defect in the product, compensation paid for any loss or injury suffered by the consumer, etc.
(ii) Directions that might have been issued by the court are as follows:
(a) Removal of defects from the goods;
(b) Replacement of the goods;
(c) Refund of the price paid;
(d) Removal of defects or deficiencies in the services;
(e) Award of compensation for the loss or injury suffered;
(f) Discontinue and not to repeat unfair trade practice or restrictive trade practice;
(g) To withdraw hazardous goods from being offered for sale;
(h) To cease manufacture of hazardous goods and resist from offering services which are hazardous in nature;
(i) If the loss or injury has been suffered by a large number of consumers who are not identifiable conveniently, to pay such sum (not less than 25% of the value of such defective goods or services provided) which shall be determined by the Commission;
(j) To issue corrective advertisement to neutralize the effect of misleading advertisement;
(k) To provide adequate costs to parties.
OR
(i) The Right to information is being fulfilled by the directives of SEBI. According to the Right to information, the consumer has the right to get complete information about the product that he or she may propose to buy. Moreover, as per law, it is mandatory for the marketers to provide complete information about the product or service to buyers.
(ii) The importance of consumer protection from businessmen’s point of view is outlined below:
(a) Long-term Interest of Business: Enlightened businesses realize that it is in their longterm interest to satisfy their customers. Satisfied customers not only lead to repeat sales but also provide good feedback to prospective customers and thus, help in increasing the customer-base of business. Thus, business firms should aim at long-term profit
maximization through customer satisfaction.
(b) Business uses Society’s Resources: Business organizations use resources which belong to the society. They, thus, have a responsibility to supply such products and render such services which are in public interest and would not impair public confidence in them.
(c) Social Responsibility: A business has social responsibilities towards various interest groups. Business organizations make money by selling goods and providing services to consumers. Thus, consumers form an important group among the many stakeholders of business and like other stakeholders, their interest has to be well taken care of.
(d) Moral Justification: It is the moral duty of any business to take care of consumer’s interest and avoid any form of their exploitation. Thus, a business must avoid unscrupulous, exploitative and unfair trade practices like defective and unsafe products, adulteration, false and misleading advertising, hoarding, black marketing etc.
(e) Government Intervention: A business engaging in any form of exploitative trade practices would invite government intervention or action. This can impair and tarnish the image of the company. Thus, it is advisable that business organizations voluntarily resort to such practices where the customers’ needs and interests will well be taken care of.
10. Explain the various money market instruments.
Answer. The various money market instruments are discussed below:
(i) Treasury Bill: A Treasury bill is basically an instrument of short-term borrowing by the Government of India maturing in less than one year. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds issued by the Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short-term requirement of funds. Treasury bills are issued in the form of a promissory note. They are highly liquid and have assured yield and negligible risk of default. They are issued at a price which is lower than their face value and repaid at par. Treasury bills are available for a minimum amount of ₹25,000 and in multiples thereof.
(ii) Commercial Paper: Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period. It is issued by large and creditworthy companies to raise short-term funds at lower rates of interest than market rates. It usually has a maturity period of 15 days to one year. The issuance of commercial paper is an alternative to bank borrowing for large companies that are generally considered to be financially strong. It is sold at a discount and redeemed at par. The original purpose of commercial paper was to provide short-terms funds for seasonal and working capital needs.
(iii) Call Money: Call money is short term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of one day to fifteen days, used for inter-bank transactions. Call money is a method by which banks borrow from each other to be able to maintain the cash reserve ratio. The interest rate paid on call money loans is known as the call rate. It is a highly volatile rate that varies from day-to-day and sometimes even from hour-to-hour.
(iv) Certificate of Deposit: Certificates of deposit (CD) are unsecured, negotiable, shortterm instruments in bearer form, issued by commercial banks and development financial institutions. They can be issued to individuals, corporations and companies during periods of tight liquidity when the deposit growth of banks is slow but the demand for credit is high. They help to mobilise a large amount of money for short periods.
(v) Commercial Bill: A commercial bill is a bill of exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. It is a short-term, negotiable, self-liquidating instrument which is used to finance the credit sales of firms. When goods are sold on credit, the buyer becomes liable to make payment on a specific date in future. The seller could wait till the specified date or make use of a bill of exchange. The seller (drawer) of the goods draws the bill and the buyer (drawee) accepts it. On being accepted, the bill becomes a marketable instrument and is called a trade bill. These bills can be discounted with a bank if the seller needs funds before the bill matures. When a trade bill is accepted by a commercial bank it is known as a commercial bill.
11. Satnam Ltd. are the manufactures of ‘Gents Designer Suits’ with their own trade mark. During the year 2013-14, the company employed 30 senior technicians to work on machines imported from America for manufacturing ‘Gents Designer Suits’. The technicians were employed on probation of one year. They were put on their respective jobs after one months on the job training. Because of the faulty selection process, the technicians could not perform well. Ten of them left the job on their own and 12 had to be removed by the company during the probation period. Now the company is in the process of selecting new technicians. Advice the company about the types of selection tests that may be used for selecting the desired technicians.
Answer. Important Tests Used for Selection of Employees:
(i) Intelligence Tests: This is one of the important psychological tests used to measure the level of intelligence quotient of an individual. It is an indicator of a person’s mental ability or the ability to make decisions and judgments.
(ii) Aptitude Test: It is a measure of individuals potential for learning new skills. It indicates the person’s capacity to develop. Such tests are good indices of a person’s future success score.
(iii) Personality Tests: Personality tests provide clues to a person’s emotions, her reactions, maturity and value system etc. These tests probe the overall personality. Hence, these are difficult to design and implement.
(iv) Trade Test: These tests measure the existing skills of the individual. They measure the level of knowledge and proficiency in the area of professions or technical training. The difference between aptitude test and trade test is that the former measures the potential to acquire skills and the later the actual skills possessed.
(v) Interest Tests: Every individual has fascination for some job than the other. Interest tests are used to know the pattern of interests or involvement of a person.
12. Miracle Ltd. deals in the sale of stationery and office furniture. They source the finished products from reputed brands who give them four to six months credit. Because of increase in the demand for electronic items, they are planning to sell these items also. For this, they have decided to join hands with a Japanese electronic goods manufacturer, to open sales outlets throughout India. Explain any five factors affecting the working capital requirements of Miracle Ltd.
OR
Alpha Enterprises is a company manufacturing water geyser. The company has a functional structure with four main functions department i.e Production, Marketing, Finance and Human Resource. The company has a share capital of ₹ 10,00,000 divided into shares of ₹ 100 each. For expansion purpose, the company requires additional funds of ₹ 5,00,000. The management is considering the following alternatives for raising funds:
Alternative 1: Issue of 10,000 Equity shares of ₹ 100 each
Alternative 2: Issue of 10% Debentures of ₹ 5,00,000
The company’s present Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) is ₹ 2,00,000 p.a. Assuming that the rate of Return of Investment remains the same after expansion, which alternative should be used by the company in order to maximise the returns to the equity shareholders. The Tax rate is 50%. Show the working.
Answer. Factors affecting the working capital requirements of Miracle Ltd. are discussed below:
(i) Nature of Business: The basic nature of a business influences the amount of working capital required. A trading organization usually needs a smaller amount of working capital compared to a manufacturing organization. This is because there is usually no processing. Therefore, there is no distinction between raw materials and finished goods. Sales can be affected immediately upon the receipt of materials, sometimes even before that. In a manufacturing business, however, raw material needs to be converted into finished goods before any sales become possible. Other factors remaining the same, a trading business requires less working capital. Similarly, service industries which usually do not have to maintain inventory require less working capital.
(ii) Scale of Operations: For organizations which operate on a higher scale of operation, the quantum of inventory and debtors required is generally high. Such organizations, therefore, require large amount of working capital as compared to the organizsations which operate on a lower scale.
(iii) Business Cycle: Different phases of business cycles affect the requirement of working capital by a firm. In case of a boom, the sales as well as production are likely to be larger and, therefore, larger amount of working capital is required. As against this, the requirement for working capital will be lower during the period of depression as the sales as well as production will be small.
(iv) Seasonal Factors: Most business have some seasonality in their operations. In peak season, because of higher level of activity, larger amount of working capital is required. As against this, the level of activity as well as the requirement for working capital will be lower during the lean season.
(v) Production Cycle: Production cycle is the time span between the receipt of raw material and their conversion into finished goods. Some businesses have a longer production cycle while some have a shorter one. Duration and the length of production cycle, affects the amount of funds required for raw materials and expenses. Consequently, working capital requirement is higher in firms with longer processing cycle and lower in firms with shorter processing cycle.
(vi) Credit Allowed: Different firms allow different credit terms to their customers. These depend upon the level of competition that a firm faces as well as the credit worthiness of their clientele. A liberal credit policy results in higher number of debtors, increasing the requirement of working capital.
(vii) Credit Availed: Just as a firm allows credit to its customers it also may get credit from its suppliers. To the extent it avails the credit on purchases, the working capital requirement is reduced.
(viii) Operating Efficiency: Firms manage their operations with varied degrees of efficiency. For example, a firm managing its raw materials efficiently may be able to manage with a smaller balance. This is reflected in a higher inventory turnover ratio. Similarly, a better debtor’s turnover ratio may be achieved reducing the amount tied up in receivables. Better sales effort may reduce the average time for which finished goods inventory is held. Such efficiencies may reduce the level of raw materials, finished goods and debtors resulting in lower requirement of working capital.
(ix) Availability of Raw Material: If the raw materials and other required materials are available freely and continuously, lower stock levels may suffice. If, however, raw materials do not have a record of un-interrupted availability, higher stock levels may be required. In addition, the time lag between the placement of order and the actual receipt of the materials (also called lead time) is also relevant. Larger the lead time, larger the quantity of material to be stored and larger shall be the amount of working capital required.
(x) Growth Prospects: If the growth potential of a concern is perceived to be higher, it will require larger amount of working capital so that it is able to meet higher production and sales target whenever required.
(xi) Level of Competition: Higher level of competitiveness may necessitate larger stocks of finished goods to meet urgent orders from customers. This increases the working capital requirement. Competition may also force the firm to extend liberal credit terms discussed earlier.
(xii) Inflation: With rising prices, larger amounts are required even to maintain a constant volume of production and sales. The working capital requirement of a business thus, become higher with higher rate of inflation.
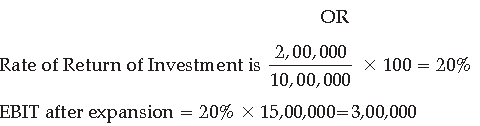

The company should use Plan 2 in order to increase the return to the equity shareholders.