Please refer to Emerging Modes of Business Class 11 Business Studies notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Business Studies books for Class 11. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 11 Business Studies Emerging Modes of Business Notes and Questions
E-Business: E-Business may be defined as the conduct of industry, trade and commerce using the computer networks. Almost all types of business functions as well as managerial activities like production, inventory management, product development, accounting and finance, human resource management etc. can be carried out over computer networks.
E-Commerce: Commercial transactions conducted electronically on the internet is called ECommerce. It covers a firm’s interactions with its customers and suppliers over the internet. It is only a part of e-Business.
Scope of e-Business: Firm’s e-business transactions can be seen in the following four ways:
1. B2B Commerce: In this commercial transactions take place between different business organizations. It includes placing of purchase orders, invoices, quotations etc.
Business to Business(B2B) form major share of total e-commerce volume.
2. B2C Commerce: It means Business to Customers transactions. It include selling of goods, call centers, ATM facility….
3. Intra-B Commerce: Here the transactions take place within the firm. It includes use of computer networks in marketing, finance, production, purchase, human resource, Research and Development departments…. It also includes interaction of business with its employees (B2E) like salary payment, seeking suggestions from employees etc.
4. C2C Commerce: It means Customer to Customer. This type of commerce is best suited for dealing in goods for which there is no established market mechanism. The vast space of the internet ( eBay.com, olx.com, amazon.com, flipkart etc.) allows persons to globally search for potential buyers.

Benefits of e-Business:
1. Ease of formation – It is very easy to start due to less legal formalities and with a limited investment.
2. Convenience – Internet offers the convenience of 24 hours business.
3. Speed – Internet allows faster services.
4. Global reach – It provides a boundary less market.
5. Movement towards a paperless society – Use of internet has considerably reduced dependence on paperwork.
Limitations of e-Business:
1. Low personal touch – There is no face to face contact between the seller and buyer.
2. Incongruence between order and supply – Order taking is very fast, but the delivery of product takes time.
3. Need for technology – To access e-business, it requires familiarity with computer and internet. But it is not accessible for all people because of digital divide.
4. High risk – Difficulty in locating the persons and their places from which they are operating, problem of impersonation (someone may operate in your name), problem of leakage of confidential information such as credit card details, passwords etc. are the reasons for high risk.
5. People Resistance – Adjustment with new technology creates stress and a sense of insecurity to the employees.
6. Ethical fallouts – Information exchanged through internet may be stolen or misused by dishonest people for illegal activities.
Online transactions – Three stages are involved in online transactions:-
1. Pre purchase/sale stage – Advertising, collection of information etc.
2. Purchase/sale stage – Price negotiation, finalizing the deal and making payment.
3. Delivery stage – Dispatching goods to the buyers.
Procedure for online transaction
a. Registration – Before online shopping, one has to register with the online vendor by filling-up a registration form.
b. Placing an order – Here we can add the items in the shopping cart. Shopping cart is an online record of what you have picked up while browsing the online store.
c. Payment mechanism: Payment for the purchases through online shopping may be done in a number of ways such as-Cash on Delivery(CoD), cheque, net banking, credit/debit card, digital cash such as Paytm, Jio money, e-wallets etc.
Security and safety of e-Transactions
1. Transaction risks – In e-business, risk may arise for the seller or the buyer on account of default on order taking/giving, delivery as well as payment.
2. Data storage and transmission risk – Vital information may be stolen or modified to pursue some selfish motives or simply for fun. VIRUS – Vital Information Under
Siege (attack), Hacking, Brand hijacking etc. are some of risks in e-business.
A Virus is a program that attacks itself to computer system and destroys or corrupts the data. Installing and updating anti-virus programs is the solution.
Hacking refers to unauthorized access into website; hackers often destroy the data and information which causes huge loss to the business.
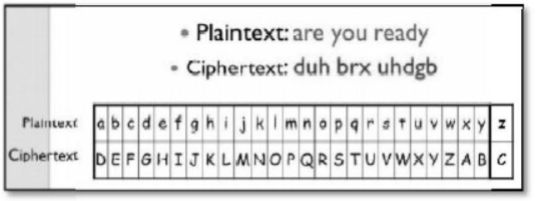
Data may be intercepted (interrupted) while in transmission. For this we can use cryptography. It is an act of protecting information by transforming it into an unreadable format called cipher text (secret language).
(Cryptography relates to the study of encryption. Encryption is translation of data into secret codes. Cipher text is encrypted text.)
3. Risk of threat to intellectual property and privacy – Once the information is published over Internet, it is difficult to protect it from being copied as it is an open space.
Resources required for successful e-business implementation:
a. Adequate computer with telecom network.
b. Technically qualified and trained work force.
c. Well developed websites.
d. Well developed telecommunication facilities.
e. A good system of making payments using credit instruments.
Outsourcing
It means source from outside. In other words outsourcing refers to hiring out non-core activities of business to third party specialists to take advantage of their experience, expertise and efficiency in performing such activities.
The term outsourcing is popularly known as BPO (Business Process Outsourcing and the idea behind this concept is that a business can concentrate in its core areas and leaving other activities as BPOs.
Eg: 1. Canteen in a business organization to a hotel.
2. Transportation of raw materials in a factory to a transport agency.
3. Selection of employees to a recruitment agency etc.
Features of Outsourcing
1. Contracting out – Non-core activities can be contracted out to outside agencies.
2. Non-core activities are outsourced – An organization should identify its core activities and non-core activities. Generally non-core activities are entrusted to BPOs on contractual basis.
3. Outsourcing through Captive Unit or Third Party –
a. Captive Unit – It is a part of BPO where an organization will use a wholly owned subsidiary instead of a third party in some other countries to minimize the cost and
for the use of resources offshore. Eg: General Electric Co. US started their own
subsidiary company in India for providing certain services to the parent company.
b. Third party – Here the process may be outsourced to a third party service provider who operates independently in the market.
Need/ Benefits/ Objectives of Outsourcing
1. Focusing attention – Outsourcing helps the business to focus on its core activities and contracting out the rest.
2. Quest for excellence – Outsourcing enables the business to pursue excellence in two ways. One, they excel themselves by focusing in core areas only. Two, they excel by availing non-core activities from specialists.
3. Cost reduction – BPOs helps to reduce the cost through specialization and division of labour. This happens because they provide the same service to a number of organizations. India is a preferred destination for BPO for various global organizations due to low manpower cost.
4. Growth through alliance – Through outsourcing, firm’s investment requirements are reduced in non-core areas, therefore they can expand rapidly.
5. Enhance economic development – Outsourcing stimulates entrepreneurship, employment and exports in the host countries which help the economy to develop.
Concerns over outsourcing
1. Confidentiality – If the outsourcing partner leaks out secret information to the competitors, it can harm the interest of the person who outsources it.
2. Sweat-shopping – A firm that outsources seeks to lower their costs. They will try to get maximum benefit from the low cost manpower of the host countries.
3. Ethical concerns – Generally BPOs works in developing or under developed countries, where they use child labour and wage discrimination for men and women etc. But it may not be allowed in the country of the person who outsourcing it.
4. Resentment in the home countries – Outsourcing results in loss of employment in home countries which may lead to opposition from the people and government. Eg:
When a US company starts a BPO in India, it will cause for unemployment in US.

We hope the above Emerging Modes of Business Class 11 Business Studies are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies


