Please refer to Food Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Food Notes and Questions
FOOD
* Food is one of the most basic requirements of life.
* Food is made up of several kinds of energy – rich substance called nutrients. There are five types of nutrients – carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
Functions of food:
* Food provides energy.
* Food helps in growth and development.
* Food helps in the replacement of wom out tissue, repair of demaged cells and healing of wounds.
* Food protects the body against disease.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR):
The smallest amount of energy that body needs to keep itself alive is called basal metabolic rate (BMR).
BALANCED DIET
* A balanced diet is one which provides proper amount and proportin of fats, carbohydrate, proteins, vitamins and minerals, needed for the growth and maintanance of the body, A balanced diet should have three main qualities:
1. It should be rich in essential nutrients like mineralas and vitamins.
2. It should provide the exact amount of raw materials needed for growth, development, repair and replacement of body tissue.
3. It should provide the right amount of energy required by the body.
CLASSIFICATION OF FOOD
* Food can be classfied under three different catagories on the basis of Its functions :
(i) Energy giving food : Carbohydrates and fats. Eg. cereals, sugars, oils, etc.
(ii) Body building food : Proteins, minerals and facts. e.g. pulses, beans, milk, fish, etc.
(iii) Protective food : Vitamins & minerals. eg. vegetables, fruits, milk, etc.
BASIC CONSTITUENTS OF FOOD
(a) CARBOHYDRATES : Carbohydrates are organic compounds, hydrogen and oxygen.
* They are the main source of energy in our body.
* One gram of carbohydrates yields about 4 kilocalories of heat energy.
* A major portions of our food consist of carbohydrates, e.g., rice, chapatis.
* It excess amount of carbohydrates are prevent in the body, they are converted into fats and stored under the skin and around various organs of the body.
Some examples of carbohydrates :
* Celluslose : It is the chief constituent of plant cell wall.
* Starch : It is main stored food of plants.
* Glycogen : It is main stored food of animals.
(i) Sources of carbohydrates : The carbohydrates in our food are obtained mainly from the plant sources like wheat, rice, maize, potato etc.
KNOWLEDGE BOOSTER
Sugarcane store carbohydrates in the form of sucrose.
(ii) Biological significance of carbohydrates :
* Carbohydrates serve as an important stuructural material in some animals and in all plants, where they constitute the cellulose framework e.g. cellulose framwork e.g. cellulose in plants.
* Carbohydrates are used as respiratory fuel in animal cells.
* Some carbohydrates have highly specific functions e.g. ribose and deoxyribose in the nuceloprotein of the cells, the lectose of milk.
* Starch and sugars are the two carbodydrates which provide most of the energy to our body.
(b) Fats : Fats are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
* They have lower oxygen content tghan carbohydrates.
* They are very important sources of energy.
* One gram of fat yields 9 kilocalories of energy.
* A layer of fat molecule consists of three molecules of fatty are insoluble in water butt soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether, benzene etc,.
(i) Source of fats : Fats are supplied to our body by different foods like butter, ghee, cheese, groundnut etc. All the cooking cells (like ground – nut oil coconut (oil) provide us fats.
(ii) Biological significance of fats :
* Fat deposits under the skin to protect various tissues.
* It provides a steady source of energy.
* Fats also help in forming of cell membrance and other organelies.
* They help in transportation of fat – soluble vitamins in our body.
* Fat is deposited in more amount in person those require more energy like growing children and sportsmen etc.
(c) PROTEINS : The name protein was coined by Berzelius in 1838.
Chemically proteins are polymers of molecular units called as amino acids. The amino acids are linked together by a peptide bonds. There are about 20 amino acids that take part in the formation of proteins. The 20 amino acids are further divided into two groups :
• Essential amino acids: They are 10 in number. They are not synthesized in a human body and are obtained from food so they are called as essential amino acids. e.g., Methionine, Leucine and tryptophan.
Non -essential amino acids: They are also 10 in number. They are synthesized in a human body & are thus termed as non -essential amino acids. e,g. , Alanine, Asparagine, Aspartic acid and cystine .
(i) Sources of proteins: Pulses, peas, beans, nuts, cheese, milk are the important sources of proteins.
(ii) Biological significance of proteins:
They act as a structural components of cell. They are essential for growth and repair of the body.
They help to catalyze various reactions occurring in our body.
They play important roles as hormones, antibodies, etc.
All the enzymes are made up of proteins.
Haemoglobin , the respiratory pigment of animals is a conjugated protein composed of globin and haem(pigment).
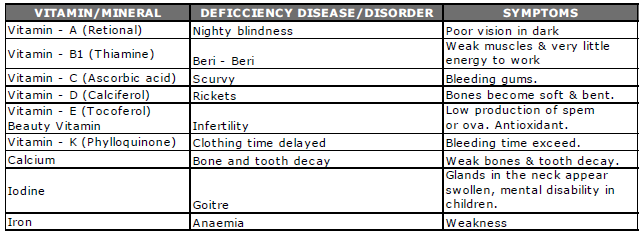
(d) VITAMINS: Vitamins are organic compounds esse ntial for the growth of the body. They are required by the body in very small quantities. Vitamins are classified into two types.
(A) Fat soluble Vitamins A, D, E, K.
(B) Water soluble Vitamins Band C.
(i) Source of Vitamin : These are obtained from fruits, cod liver etc.
(ii) Biological significance of Vitamin: They keep the body healthy and prevent it from diseases. If the diet does not contain the required amount of vitamins, it results in vitamin deficiency diseases.
(e) MINERALS: Human body requires about fifteen different kinds of minerals. Calcium and phosphorus are needed for the growth of bones and teeth. Iron is needed for the formation of haemoglobin in blood .
Iodine , sodium, potassium and zinc are necessary for a good healthy body.
(i) Source of minerals: Meat, eggs, milk, green vegetables and fruits are rich in minerals.
(ii) Biological significance of minerals ; Minerals are required by the body in trace amounts and are essential for growth, repair and replacement processes. They form a major part of many body chemicals and tissues .
(f) ROUGHAGE: Cellulose forms the fibre content in food and that fibre content is called roughage . Roughage keeps the digestive system in good working condition.
(i) Source of Roughage: It is a plant fibre found in vegetables, fruits, peas, beans, maize and in the barn which surrounds wheat grains.
(ii) Biological significance of Roughage :
It absorbs water and poisonous waste from food during digestion.
Food without roughage forms hard dry lumps of waste which get stuck in the gut causing constipation.
(g) WATER: The human body contains 70 % of water. It has no food value but it is still one of the essential components of living matter.
(i) Biological significance of Water : Water performs the following functions in our body :
It transports food materials within the body.
It helps in the formation of urine and faeces.
It regulates the body temperature.
It is an essential part of blood and digestive juices.
TEST FOR CARBOHYDRATES, FATS & PROTEINS
(a) Test for carbohydrates : Take few drops of iodine solution & add it in to boiled rice or potato. The formation of blue-black colour confirms the presence of starch (carbohydrate).
(b) Test for fats: When ghee I butter rubbed on wh ite paper, that portion of paper turns translucent indicating the presence of fats.
(c) Test for proteins: Take the few drops of egg albumin in a test tube and add a few drops of concentrated nitric acid to it.
The white colour of the albumin changes to yellow. Now, pour the acid out of the test tube but keep the white of the egg in the test tube . Add a few drops of ammonium hydroxide to it. The colour changes to violet which shows the presence of proteins.
PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT
* Crop: When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop.
* India is a vast country. The climatic conditions like temperature. humidity and rainfall vary from one region to another. D fferent types of crops require different climatic conditions like: Rainy season (Kharif crop) and Winter season (Rabi crop).

* Basic practiCes of crop production : Cultivation of crops involves several activities under taken by a farmers over period of time.
* practices these activities are listed below :
(i) Preparation of soil
(ii) Sowing
(iii) Adding manure and ferti/izers
(iv) Irrigation
(v ) Protecting from weeds
(vi) Harvesting
(vii) Storage
(a) Preparation of 8011 :
The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop.
* One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to tum the soil and loosen it.
* This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil.
* The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil.
* Various processes are included under preparation of soli these are as follows
(i) Ploughing or Tilling: The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
* This is done by using a plough. Ploughs are made of wooo or Iron.
* The ploughed field may na, _ big pieces of soil called crumbs.

Significance of ploughing :
• This practice loosens the soil.
• The soil is overturned and properly aerated.
• This allows the roots to penetrate deeper easily.
(II) Levelling: This Is the agricultural process to make the soil in level for sowing the seeds. This is done by Leveller which is made of wood or iron. It is a flat 1.8 -2 In long wooden plank with a log to pul weight on it.
Significance of levelling : This practice smoothens the soil surface.
(b) Agricultural Implements : The tools which are used in cultivation of plants are known as agricultural implements. Some of these tools are used manually whereas others are used with the help of some animals like bullocks and camels. Nowadays tractors and combine harvesters are helping the farmers in their work. A list of commonly used agricultural implements along with their uses are given below.

• Maintenance and Care of Agricultural Implements The ti p of the plough shou ld be sharpened at regular intervals for easy penetration into the soil. Tools should not be kept in the open during rains , otherwise they will rust. Tools of iron can be rubbed with a piece of brick to clean them from rust. Occasional servicing of tractors and combines is ad visable. Sprayers should be washed with water thoroughly before and after each spraying.
(c) Sowing : Sowing is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality seeds are selected.
Good quality seeds should be clean, healthy and good variety.
• Selection of seeds : Good quality seeds are heavier than damaged seeds. Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. So they float on water. Seeds should be high yielding varieties, free from insects and pests.
• Sowing the seeds: It is done by broadcaster and seed drill . Broadcasting is the random sowing of seeds manually. In seed drill method seeds are sown uniformally at proper distances and depths.


* It ensures that seeds get coverd by the soil after sowing.
* This prevents demage caused by birds.
* Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
Transplantation : The process in which seeds are sown in nurseries and seedlings are transferred to the main field e.g. Paddy.
• The uncultivated fields are known as fallow.
• Precautions during sowing :
(i) Spacing should be proper.
(ii) Seeds should be treated with funglcldes.
(iii) Depth should be proper.
(d) Adding Ma nures and Fertilizers :
(i) Manure: A manure is a mixture of various decomposed organic sUbstances like dead leaves, city garbage, agricultural wastes, animal dung, crop residue etc. through the action of microbes.
• Manure increases the fertility and productivity of crops.
• As it contains plenty of organic compounds and almost all the essential elements (inorganic nutrients) required by the plants.
Advantages of manures :
The organic manure Is considered better than fertilizers. This is because,
(i) it costs less.
(ii) it increases organic matter in soil.
(iii) it reduces soil erosion.
(iv) it enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
(v) it increases the number of friendly microbes.
(vi) it makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
(vii) it improves the texture of the soil.
• Disadvantages of manures :
(i) Manures are bulky and not easy to be absorbed.
(ii) They have low amount of nutrients.
(ii) Fertilizers : These are commercially manufactured inorganic salts or an organic compound containing one or more essential plant nutrients like Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium which are used for increasing soil fertillity.
• Fertilizers usually contain higher amount of nutrients than manures hence requ ired in small quantities.(On ly urea is an organic compound)
Advantages of fertilizers:
(A) They are nutrient specific.
(B) They are required in small quantities.
(C) They are water soluble so can be applied to absorb by the plants easily.
Disadvantages offertilizers :
(A) They cause water pollution .
(B) Fertilizers can change the chemical composition of soil.
(C) They can cause eutrophication in near by water bodies.

(e) Irrigation:
Process of supplying water to crop plants growing in the fields by means of canals, reservoir, wells ,tube-wells etc. is known as irrigation.
• Purpose of Irrigation: In agriculture irrigation fulfills the following requirements and goals of crop plants:
• Irrigation supplies two essential macronutrientshydrogen and oxygen to the crop plants.
• It provides moisture to the soil , which helps in the germination of seeds.
• It helps in growth and elongation of the roots of crop plants .
• It helps in the absorption of nutrients by the roots of crop plants from the soil.
• It helps in increasing the number of aerial branches called tillers in the crop plants so as to get good crop yield.
COMMON DISEASES OF CROPS
Crop plants can be destroyed by a variety of disease causing organisms. The crop diseases can be divided into four major categories :
(i) Seed borne diseases: Caused by fungi generally and spread through seeds. e.g. Ergot of bajra.
(ii) Soil borne diseases: Spread through soil. e.g. Smut of bajra.
(iii) Air borne diseases: Spread through air. e.g. Rust 01 wheat.
(iv) Water borne diseases : Spread through water. e.g. Bacterial blight of rice.
• Sustainable Agriculture : We know hat agriculture is as old as human civilization. In earlier time human needs were limited so nature was not adversely affected by exploitation of natural resources. With increase of human population, the basic needs of food, cloth and shelter continue to increase. With rapid development natural resources are over exploited, because of consumerism and unplanned use of natural resources. The soil has become barren. As a result the natural resources are getting depleted at much faster rate. SustaInable agriculture means such agriculture practices that can continue for very long time without damaging the natural resources. Its aim is that human requ’,rements snoulCl be lumnecl but not at the cost of environment. For sustainable agriculture, practices of mixed farming, mixed cropping and crop rotation are used.
GREEN REVOLUTION
• It was started in 1960s due to increase in demand of food .
• The use of agricultural practices by Indian farmers over last 40 years led to the “Green Revolution”.
• This was in true sense wheat revolution because it’s main aim was to increase production of wheat by using various modern agricultural practices.
ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
Science which deals with the scientific management of animals including their feeding, breeding, weeding & heeding (disease control) is called as Animal husbandry.
Some Important Terminologies
• A Balanced diet : When diet supplies all the nutrients In the right quantity according to the requirement of the body, it is called a balanced diet
• Basal metabolic rate (BMR): The smallest amount of energy that body needs to keep alive is called basal metabolic rate.
Olympiad Problems NCERT Class 7 Food
Question. Examine the following statements.
(A) Iron, necessary for the human body, is abundantly found in green vegetables.
(B) Zinc is one of the essential trace elements required for human body.
(C) Fats and minerals are not the essential nutrients for a balanced diet of humans.
(D) The foods that generate energy In the body after complete oxidation are in the form
of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Which one of the following alternatives is wrong?
(A) A (B) B
(C) C (D) D
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following statements is wrong?
(A) Quinine an antimalarial drug is obtained from the plant cinchona.
(B) Pulses are rich sources of starch and minerals.
(C) Sunflower is a good source of vegetable oil.
(D) Green vegetables are good sources of vitamins and minerals.
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following food will provide the nutrient for the growth of tissue in human body
(A) Cheese
(B) Fruit
(C) Sweets
(D) Vegetables
Answer
D
Question. Anaemia disease is due to Deficiency of which substance ?
(A) Iron
(B) Vitamin A
(C) Fat
(D) Protein
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following will provide maximum roughage in your diet?
(A) Egg
(B) Tomato
(C) Cabbage
(D) Rice
Answer
C
Question. Calciferol is the name of
(A) Vitamin A
(B) Vitamin B
(C) Vitamin D
(D) Vitamin E
Answer
D
Question. Ascorbic acid is also called as :
(A) Vit 0
(B) Vit K
(C) Vit E
(D) Vit C
Answer
D
Question. Which vitamin is obtained from an orange?
(A) Vitamin -A
(B) Vitamin -B
(C) Vitamin -C
(D) Vitamin -D
Answer
C
Question. Which components of diet should be given more to children ?
(A) Carbohydrates
(B) Mineral -salt
(C) Fats
(D) Protein
Answer
D
Question. Low production of sperms or ova (infertility) is due to the defiCiency of
(A) Vitamin-A
(B) Vitamin· C
(C) Vitamin -E
(D) Vitamin· K
Answer
E
Question. Iodine solution is used for
(A) Testing for fat
(B) Testing for carbohydrate
(C) Testing for protein
(D) Testing for vitamin
Answer
B
Question. Which form carbohydrate are present in Cane Sugar·
(A) Maltose
(B) Fructose
(C) Sucrose
(D) Glucose
Answer
C
Question. In a cell highest quantity of constituents is
(A) Lipid
(B) Water
(C) Amino acid
(D) Nucleic acid
Answer
B
Question. Vitamin A deficiency in humans lead to:
(A) Night blindness
(B) Beri beri
(C) Rickets
(D) Scurvy
Answer
A

We hope the above Food Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


