Please refer to Nutrition In Plants Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Nutrition In Plants Notes and Questions
Plants play role of producers in nature. are producers, which produce food for all living organic. They
utilize sun’s radiant energy & convert into chemical energy. In this way, they also plays role of
converter. Plants use sunlight in photosynthesis. During photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight CO2
& H2O convert in to carbohydrate & O2 molecules.
MECHANISM OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS

• Steps of photosynthesis :
• Chlorophyll traps the sunlight.
• CO2 & water molecule used as raw material.
• Now the chlorophyll convert the raw material into carbohydrate.
• Oxygen is generated as a by product in this process.
REQUIREMENT OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Green plants need the following things to prepare their own food :
• Carbon Dioxide : Plants take up carbon dioxide from the atmospheric air through stomata present on
the undersurface of the leaves. Guard cells around stomata regulate their opening and closing.
• Chlorophyll : It is the green pigment presents in the leaf. The green colour of leaves is due to the
presence of chlorophyll. It is usually present in special cell organelle called chloroplast. Chlorophyll
captures solar energy during photosynthesis.
• Sunlight : Sunlight comes from the sun. It is essential as it provides the energy required for the reaction.
• Water and Minerals : Roots of the plants absorb water along with minerals from the soil and transport
them to the leaves for photosynthesis.

• Importance of photosynthesis :
• It is primary source of food production for all other living organisms.
• It maintain balance oxygen & CO2 in the atmosphere.

NUTRITION IN NON GREEN PLANTS
Non green plants like bacteria & fungi do not contain chlorophyll. So they cannot prepare their food
by photosynthesis. These types of plants are heterotrophic plants.

(1) Parasites : Plants which depends on other living organism for their nutritional requirement known as
parasitic plants. Dodder (Amarbel) is a plant parasite which produces special sucking roots called
haustoria. For absorption of food from the host plant.
(2) Saprophytes : Plants which depends on dead organic matter for their nutrition, known as saprophytic
plants. For example – Bacteria & fungi.
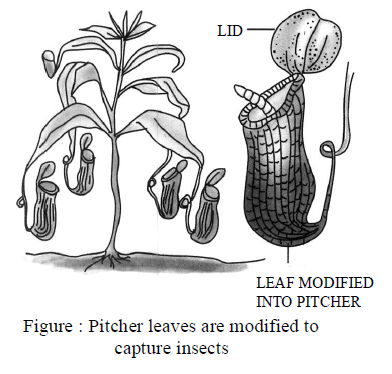
(3) Carnivorous & insectivorous plants : Some plants also take food just like animals. Their food
consists of small insects. For example – Pitcher plants.
In a pitcher plant leaf is modified into a pitcher like structure when any insects sits on it, the lid is
closed & the insect is trapped in pitcher. It is then digested by the secretion of enzymes.
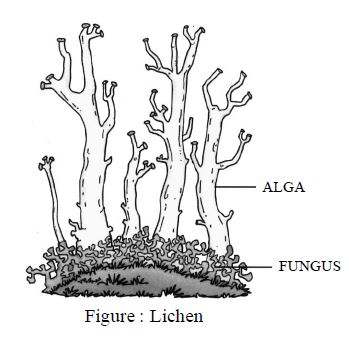
(4) Symbiosis : It is a partnership between two organisms in which both partner get benefited from each
other.
For example : Lichen.
Lichen is a combination of an alga & a fungus. In which, the fungus provides water & minerals to the
alga whereas the alga supplies organic food to fungus.
HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION IN ANIMAL
Animals and non-green plants like fungi, etc. cannot manufacture their own food. For their food, they
depend upon green plants, directly or indirectly. Therefore, they are called heterotopous and their
mode of nutrition is known as heterotrophic nutrition.
All animals are divided into three categories on the basis of their eating habits :
• Herbivorous Animals : Animals which feed directly on plants are called herbivorous animals or herbivores.
Examples are cow, buffalo, goat, etc.
• Carnivorous Animals : Animals which eat the flesh of other animals are called carnivorous animals or
carnivores. Examples are lion, tiger, etc.
• Omnivorous Animals : Animals which eat both plants and flesh of other animals are called omnivorous
animals or omnivorous. Examples are human beings, pig, crow, cockroach, etc.
Olympiad Problems NCERT Class 7 Nutrition In Plants
Question: The plant that feeds & traps on insects is –
(A) Drosera (
B) Sunflower
(C) Cuscuta
(D) Mango
Answer:
Drosera
Question: The green pigment in the leaves is called –
(A) Chlorophyll
(B) Anthocyanin
(C) Chloroplast
(D) None
Answer:
Chlorophyll
Question: Which one of the following is a parasite ?
(A) Mushroom
(B) Fungi
(C) Dodder
(D) Pitcher’s plant
Answer:
Dodder
Question: Rhizobium is a good example of –
(A) insectivorous
(B) symbiosis
(C) parasitic
(D) none of these
Answer:
symbiosis
Question: Cuscuta is an example of –
(A) autotroph
(B) parasite
(C) saprophyte
(D) host
Answer:
parasite
Question: Autotrophic nutrition found only in –
(A) plants
(B) animals
(C) both
(D) none
Answer:
plants
Question: The plant that feeds and traps on insects is –
(A) venus-fly trap
(B) cuscuta
(C) sunflower
(D) none of these
Answer:
venus-fly trap
Question: Association of two different organisms in which
both are benefited is called –
(A) symbiosis
(B) nutrition
(C) saprophytic
(D) parasitic
Answer:
symbiosis
Question: CO2 & O2 balance in atmosphere is due to –
(A) Photorespiration
(B) Photosynthesis
(C) Respiration
(D) Leaf anatomy
Answer:
Photosynthesis
MCQs for NCERT Class 7 Science Nutrition In Plants
Question: Raw materials for photosynthesis :
(A) Carbon dioxide
(B) Water
(C) Sunlight
(D) All of them
Answer:
All of them
Question: An example of an autotrophic plant is ……..
(A) Mushrooom
(B) Mould
(C) Dodder
(D) Neem
Answer:
Neem
Question: An example of a saprophytic plant is ……
(A) Dodder
(B) Monotropa
(C) Mushroom
(D) All of them
Answer:
Mushroom
Question: The life processes that provide energy are
(A) nutrition
(B) respiration
(C) both nutrition and respiration
(D) response to stimuli
Answer:
both nutrition and respiration
Question: Which of these is not necessary for photosynthesis?
(A) carbon dioxide
(B) chlorophyll
(C) light
(D) nitrogen
Answer:
nitrogen
Question: Of the following identify the carnivorous plant
(A) Pitcher plant
(B) Venus fly trap
(C) Both of them
(D) None of them
Answer:
Both of them
Question: CO2 and O2 balance in atmosphere is due to
(A) photorespiration
(B) photosynthesis
(C) respiration
(D) leaf anatomy
Answer:
photosynthesis
Question: During photosynthesis the oxygen in glucose comes from
(A) water
(B) carbon dioxide
(C) both from water and carbon dioxide
(D) oxygen in air
Answer:
water
Question: The source of O2 liberated in photosynthesis is
(A) photosynthetic enzyme
(B) carbohydrate present in leaf
(C) water
(D) carbon dioxide
Answer:
water
Question: Grana refers to
(A) glucolysis of glucose
(B) by-product of photosynthesis
(C) stacks of thylakoids
(D) stacks of quantasomes
answer:
stacks of thylakoids
Question: Which of the following wavelength of light is absorbed maximum for photosynthesis?
(A) Red light
(B) Blue light
(C) Green light
(D) Yellow light
Answer:
Blue light
Question: Which of the following is the least effective in photosynthesis?
(A) Red light
(B) Blue light
(C) Green light
(D) Violet
Answer:
Green light
Question: The assimilatory power in photosynthesis is
(A) ATP
(B) NADPH
(C) ATP and NADPH2
(D) ATP, NADPH and CO2
Answer:
ATP and NADPH2
Question: A specific function of light energy in the process of photosynthesis is to
(A) activate chlorophyll
(B) split water
(C) synthesis glucose
(D) reduce CO2
Answer:
activate chlorophyll
Question: ATP formation during photosynthesis is known as
(A) phosphorylation
(B) photophosphorylation
(C) oxidative phosphorylation
(D) substrate level phosphorylation
Answer:
photophosphorylation
Question: Dark reaction in photosynthesis is called so because
(A) it does not require light energy
(B) cannot occur during daytime
(C) occurs more rapidly at night
(D) it can also occur in darkness
Answer:
it does not require light energy
Question: Dark reaction of photosynthesis occurs in the
(A) stroma of the chloroplast outside the lamellae
(B) space between the two membranes of the chloroplast
(C) membranes of the stroma lamellae
(D) thylakoid membrane of the grana
Answer:
stroma of the chloroplast outside the lamellae
Question: Holophytic nutrition means-
(A) autotrophism
(B) heterotrophism
(C) symbiotism
(D) parasitism
Answer:
autotrophism
Question: Autotrophic nutrition occurs in
(A) Fungi
(B) Plants
(C) Some protists and prokaryotes
(D) Both B and C
Answer:
Both B and C
Question: Mushroom, Rhizopus and Yeast are
(A) Chemosynthetic
(B) Parasitic
(C) Holozoic
(D) Saprophytic
Answer:
Saprophytic
Question: Chlorophyll is present
(A) in the grana of chloroplast
(B) on the surface of chloroplast
(C) in the stroma of chloroplast
(D) none of these
Answer:
in the grana of chloroplast
Question: Chlorophyll cannot absorb one of the following
(A) red light
(B) blue light
(C) blue and red light
(D) green light
Answer:
green light
Question: The oxygen in photosynthesis is released from-
(A) CO2
(B) H2O
(C) Carbohydrate
(D) Chlorophyll
Answer:
H2O
Question: Dark reaction of photosynthesis occurs in
(A) Grana
(B) Stroma
(C) Matrix
(D) Cytoplasm
Answer:
Stroma
Question: Photosynthesis proceeds in sequence of –
(A) Dark phase and light phase
(B) Light phase alone
(C) Light phase and dark phase
(D) Dark phase alone
Answer:
Light phase and dark phase
Question: In bacterial photosynthesis, the hydrogen donor is –
(A) H2O
(B) H2SO4
(C) NH3
(D) H2S
Answer:
H2S
Question: Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in –
(A) grana
(B) pyrenoid
(C) stroma
(D) none of these
Answer:
grana
Question: Which of the following is the best equation representing photosynthesis?

Answer:

Question: In which part of chloroplast light reaction of photosynthesis occurs?
(A) Grana
(B) Stroma
(C) Matrix
(D) All the above
Answer:
Grana
Question: The raw materials for photosynthesis are –
(A) CO2 & O2
(B) sunlight and CO2
(C) water and chlorophyll
(D) CO2 and water
Answer:
CO2 and water

We hope the above Nutrition In Plants Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


